Histograms are essential tools in data analysis, offering a visual representation of the frequency distribution of data. They enable you to identify patterns and trends, such as determining the most frequent age group among customers or evaluating student performance in Malaysia's schools. For instance, financial analysts in Malaysia utilize histograms to evaluate market risks, while healthcare professionals depend on them to monitor patient recovery times.
If you're wondering how to make histogram in Excel, the process is simple and versatile. Excel provides multiple options, including built-in chart tools, the Data Analysis ToolPak, and formulas, to create clear and impactful visualizations. Each approach allows you to analyze your data effectively and gain valuable insights in Malaysia.
Before creating a histogram in Excel, you need to prepare your data properly. This step ensures that your chart accurately represents the data distribution. Follow these tips to prepare your data:
For example, if you are analyzing quarterly revenue trends across banking segments, sorting the data and defining bins can help uncover insights about revenue distributions, outliers, and variability. Investment bankers often use these insights to make informed decisions and provide strategic advice.
Excel's built-in histogram chart feature simplifies the process of creating a histogram. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you:
This step-by-step process is straightforward and user-friendly, making it ideal for beginners in Malaysia. Whether you are working on a basic histogram or a more complex dataset, Excel's built-in tools provide a seamless experience.
Customizing bins and chart design enhances the clarity and interpretability of your histogram. Here’s how you can do it:
Customizing your histogram allows you to tailor it to your specific needs in Malaysia. For instance, adjusting bin limits can highlight outliers, while using overlapping histograms enables comparative analysis between datasets. These features make Excel's built-in histogram chart a powerful tool for data visualization.

The Data Analysis ToolPak is a powerful Excel add-in that simplifies statistical and engineering analysis. It includes tools for regression, descriptive statistics, and histograms, making it an excellent choice for creating a histogram in Excel. Follow this tutorial to enable the ToolPak, set up your data, and generate a histogram chart.
To access the Data Analysis ToolPak, you need to enable it first. This process is straightforward and ensures you can use its advanced features for creating a histogram.
Tip: The ToolPak provides 19 functional tools for statistical analysis, making it a valuable resource for data-driven tasks.
Here’s how to enable the ToolPak:
Once enabled, the ToolPak appears under the Data tab, ready for use. Its accessibility and user-friendly interface make it ideal for analyzing frequency distribution and other statistical data.
Before creating a histogram, you need to prepare your data and define bin ranges. Proper preparation ensures accurate results and a clear visualization of your data distribution.
Follow these steps to prepare your data:
For example, if you are analyzing sales data, bins can represent revenue intervals such as $0-$500, $501-$1000, and so on. This setup allows you to visualize trends and identify outliers in your dataset.
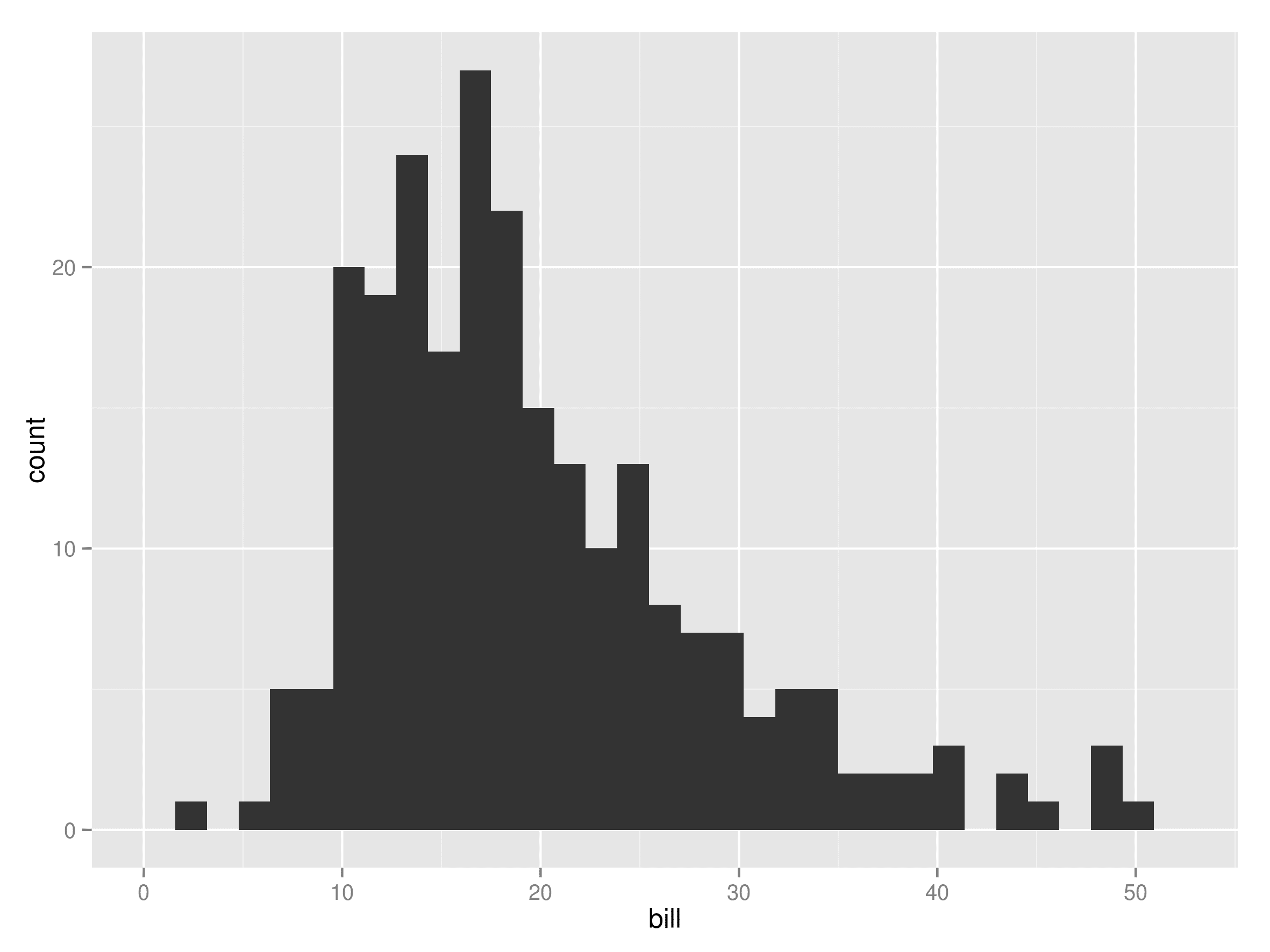
Once your data and bins are ready, you can use the ToolPak to create a histogram chart. The process is simple and produces both a frequency table and a histogram chart for analysis.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | A histogram displays the frequency distribution of numerical data, dividing it into 'bins' and showing the frequency in each bin. |
| Examples in HR | 1. Performance Review Scores: Visualize employee performance levels. 2. Salary Distribution: Analyze salary fairness. 3. Applicant Ages: Assess age distribution of job applicants. |
| Steps to Create in Excel | 1. Select 'Data Analysis'. 2. Choose 'Histogram'. 3. Enter Input Range. 4. Define bin range or let Excel create it. 5. Specify output location. Excel generates a frequency table and Histogram chart. |
After generating the histogram, interpret the results by analyzing the frequency distribution. For instance, in HR analytics, you can use histograms to evaluate salary fairness or identify age trends among job applicants. This visualization helps you make informed decisions based on data patterns.
By using the Data Analysis ToolPak, you can create a histogram in Excel efficiently and gain deeper insights into your data. Whether you are working with sales figures, employee performance metrics, or customer demographics, this tool simplifies the process and enhances your analysis.

Proper preparation of data and bins is essential when creating a histogram. Start by analyzing the distribution of your data. This helps you understand its range and variability. Next, choose a binning method that aligns with your analysis goals in Malaysia. Common methodologies include Sturges’ Rule, Scott’s Method, and the Freedman-Diaconis Rule. These methods provide guidelines for determining bin width and the number of bins based on your dataset.
| Methodology | Description |
|---|---|
| Sturges’ Rule | Provides a guideline for determining the number of bins based on sample size. |
| Scott’s Method | Suggests bin width based on the standard deviation of the data. |
| Freedman-Diaconis Rule | Uses the interquartile range to determine bin width, suitable for non-normally distributed data. |
Follow these best practices to prepare your data effectively:
By preparing your data and bins carefully, you ensure that your histogram chart accurately represents the frequency distribution of your data.
The FREQUENCY formula in Excel calculates how often values occur within specified intervals. To use this formula, organize your data into a single column and define your bins in another column. Then, follow these steps:
For example, if you are analyzing sales data, bins could represent revenue intervals such as $0-$500, $501-$1000, and so on. The FREQUENCY formula groups the data into these intervals, providing a clear view of the frequency distribution.
Once you have calculated the frequency distribution, you can convert the results into a histogram chart. Follow these steps:
To enhance your chart, consider these tips:
This tutorial simplifies the process of creating a histogram in Excel using the FREQUENCY formula. By following these steps, you can visualize your data effectively and gain valuable insights into its distribution in Malaysia.
When you make a histogram in Excel, you rely on its built-in tools or formulas. These options are effective for basic visualizations. However, FineReport offers advanced features that take your data visualization in Malaysia to the next level.
| Feature | Excel | FineReport |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | User-friendly for basic charts. | Drag-and-drop interface for quick customization. |
| Customization | Limited design options for bins and styles. | Extensive customization for colors, styles, and interactivity. |
| Data Integration | Works well with Excel files and basic sources. | Connects to 100+ data sources, including databases and APIs. |
| Real-Time Updates | Requires manual updates. | Supports real-time data synchronization. |
| Advanced Visuals | Basic chart styles. | Over 70 chart styles, including interactive options. |
FineReport excels in customization and real-time data integration. It allows you to create visually stunning and interactive histograms. If you need advanced features, FineReport is a better choice for professional data visualization.

FineReport provides unmatched customization options for histograms. You can adjust every detail to suit your needs in Malaysia. For example, you can modify bin widths, colors, and labels with just a few clicks. The software also supports interactive features like drill-downs, which let you explore data in greater detail.
FineReport’s ability to connect to multiple data sources enhances its flexibility. You can integrate data from databases, APIs, or spreadsheets. This feature ensures your histogram reflects the most up-to-date information. Additionally, FineReport offers over 70 chart styles, allowing you to choose the perfect design for your analysis.
Another standout feature is its real-time data synchronization. Unlike a histogram in Excel, which requires manual updates, FineReport automatically refreshes your data. This capability is especially useful for monitoring dynamic datasets, such as sales trends or production metrics.
By using FineReport, you can create professional-grade histograms that go beyond Excel’s capabilities. Its advanced features make it an excellent tool for businesses and analysts in Malaysia who need detailed and interactive visualizations.
Choosing the right bin sizes is crucial for creating an accurate histogram in Excel. Incorrect binning can distort the frequency distribution, leading to misinterpretation of data. For example, bins that are too large merge distinct data groups, hiding important details. On the other hand, bins that are too small clutter the chart, making random noise appear as significant trends.
Binning is a foundational step in histogram creation. Properly sized bins reveal patterns like central tendencies and outliers, helping you make informed decisions. Poorly sized bins obscure these patterns, which can result in flawed strategies. For instance, a retail manager might misinterpret sales data due to incorrect binning, leading to poor stock decisions.
To avoid these mistakes, ensure your bins are equal in size and align with the range of your data. Unequal bin sizes complicate interpretation because the area of the bars no longer represents frequency accurately. Always use continuous numeric data for histograms. If your data is categorical, opt for a bar chart instead.
Preparing your data correctly prevents errors and ensures your histogram accurately represents the frequency distribution. Follow these guidelines to avoid common pitfalls:
For example, if you’re analyzing sales trends, clean your dataset by removing duplicates and irrelevant entries. Define bins that align with your analysis goals in Malaysia, such as revenue intervals. Proper preparation ensures your histogram highlights meaningful insights without distortion.
Excel users often encounter errors when creating histograms. These issues can disrupt your workflow and lead to inaccurate results. Here’s a quick reference table for common errors and their descriptions:
| Error Code | Description |
|---|---|
| #DIV/0! | Division by zero error. |
| #N/A | Value not available. |
| #VALUE! | Wrong type of argument or operand. |
| #REF! | Reference to a non-existent cell. |
| #NAME? | Unrecognized name in formula. |
| #NUM! | Problem with a number in a formula. |
| #NULL! | Intersection of two areas that don’t intersect. |
To resolve these errors, double-check your formulas and ensure your data ranges are correctly defined. For example, if you encounter a #DIV/0! error, verify that no division by zero occurs in your calculations. Addressing these issues promptly ensures your histogram in Excel remains accurate and reliable.
Creating histograms in Excel offers flexibility and accessibility. You can use the built-in chart for quick visualizations, the Data Analysis ToolPak for statistical insights, or the FREQUENCY formula for detailed customization. Each method serves different needs in Malaysia, making them valuable tools for data analysis.
Experiment with these approaches to find the best fit for your data. For advanced customization, FineReport provides unmatched features like real-time updates and interactive designs. Its capabilities elevate your visualizations, helping you uncover deeper insights in Malaysia. FanRuan’s solutions empower you to transform data into actionable intelligence, enhancing decision-making and business growth in Malaysia.
Click the banner below to try FineReport for free and empower your enterprise to transform data into productivity!

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles

Self-Service Analytics Defined and Why You Need It
Self-service analytics lets you analyze data without IT help, empowering faster, data-driven decisions and boosting agility for your business.
Lewis
Jan 04, 2026

Best Self-Service Tools for Analytics You Should Know
See which self-service tools for analytics let business users access data, build dashboards, and make decisions faster—no IT help needed.
Lewis
Dec 29, 2025

Understanding Predictive Analytics Services in 2026
Predictive analytics services use data and AI to forecast trends, helping businesses make informed decisions, reduce risks, and improve efficiency in 2026.
Lewis
Dec 30, 2025