In today's digital age, data movement plays a pivotal role in how you interact with technology. It involves transferring data between various systems, ensuring that the right information reaches the right place at the right time. This process is essential for businesses and individuals alike. For businesses, understanding data movement can lead to improved decision-making and operational efficiency. As more companies embrace the Internet of Things (IoT), the demand for effective data movement continues to grow, projected to reach $10.98 billion by 2025. By grasping its significance, you can harness data's full potential.
Understanding Data Movement
Definition and Scope of Data Movement
What is Data Movement?
Data movement refers to the process of transferring data from one location to another. This can involve moving data between different databases, servers, applications, or even across cloud platforms. You might think of it as the digital equivalent of transporting goods from one warehouse to another. The goal is to ensure that data reaches its intended destination accurately and efficiently. This process is crucial for maintaining data integrity and accessibility, which are vital for effective decision-making and operations.
Scope of Data Movement in IT
In the realm of Information Technology (IT), data movement encompasses a wide range of activities. It includes data integration, replication, and transformation. These activities ensure that data is available where and when you need it. For instance, businesses often use data movement to synchronize information across various systems, enabling seamless operations. As technology evolves, the scope of data movement continues to expand, incorporating new methods and tools to handle increasing data volumes.
Historical Context of Data Movement
Evolution of Data Movement
The journey of data movement has seen significant milestones. One of the earliest advancements was the development of magnetic tape by Fritz Pfleumer. This innovation revolutionized data storage efficiency, laying the groundwork for modern data storage technologies. Later, E. F. Codd introduced relational databases, transforming how businesses organized and managed data. These databases became the standard, allowing for more structured and efficient data movement.
Key Milestones in Data Movement Technology
Several key events have shaped the landscape of data movement. Dr. Joseph Carl Robnett Licklider envisioned a network of computers, pioneering the concept of cloud computing. This idea eventually led to the development of cloud storage technology, which plays a crucial role in today's data movement strategies. Another pivotal moment was Tim Berners-Lee's creation of the World Wide Web. This innovation transformed the internet, making it accessible to everyone and enabling global information sharing. These milestones highlight the dynamic nature of data movement and its impact on technology and society.
Importance of Data Movement
Business Implications of Data Movement
Impact on Business Operations
Data movement significantly impacts business operations. By transferring data efficiently, you ensure that information flows seamlessly across various departments. This process optimizes system performance and enhances data availability. For example, when you consolidate data from multiple sources, you break down data silos. This consolidation allows for smoother operations and better resource allocation. Data movement also plays a crucial role in data archiving and database replication, ensuring that your business maintains data integrity and accessibility.
Role in Decision Making
In decision-making, data movement proves invaluable. By moving data to dedicated systems for processing and analysis, you empower decision-makers with timely and accurate information. This process involves data extraction, transformation, and loading, which enables comprehensive data analysis. As a result, you can make informed decisions that drive business growth and efficiency. Data movement also supports data warehousing, providing a centralized location for data analysis. This centralization enhances your ability to analyze trends and make strategic decisions.
Technological Significance of Data Movement
Enhancing Data Accessibility
Data movement enhances data accessibility by ensuring that data reaches the right systems at the right time. This accessibility is vital for businesses that rely on real-time data to operate efficiently. By transferring data between systems, you improve data synchronization and availability. This process involves using technologies like cloud data warehousing and hybrid data movement. These technologies distribute data across storage tiers, optimizing storage utilization and ensuring that data is readily accessible when needed.
Supporting Data Analytics
Supporting data analytics is another critical aspect of data movement. By moving data to systems designed for analysis, you facilitate timely data processing. This support is essential for businesses that rely on data-driven insights to stay competitive. Data movement enables you to integrate data from various sources, providing a comprehensive view of your business operations. This integration allows for more accurate data analysis, helping you identify trends and make informed decisions. Additionally, data movement optimizes system performance, ensuring that your analytics tools operate efficiently.
Technologies Involved in Data Movement

Data Transfer Protocols
Data transfer protocols form the backbone of data movement. They define the rules for transferring data between systems, ensuring that data reaches its destination securely and efficiently.
Common Protocols Used
Several protocols facilitate data movement. File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is one of the oldest and most widely used. It allows you to transfer files over a network. Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) enhances FTP by adding a layer of security, encrypting data during transit to prevent unauthorized access. Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and its secure version, HTTPS, are essential for transferring data over the web. These protocols ensure that data moves seamlessly between web servers and clients. Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) handles email data movement, ensuring that messages reach their intended recipients.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Each protocol offers unique advantages. FTP is simple and efficient for large file transfers. SFTP provides enhanced security, making it ideal for sensitive data. HTTP and HTTPS are crucial for web-based data movement, offering compatibility with most web applications. However, these protocols also have drawbacks. FTP lacks encryption, posing security risks. SFTP, while secure, can be slower due to encryption overhead. HTTP is not inherently secure, requiring HTTPS for safe data movement. Understanding these pros and cons helps you choose the right protocol for your needs.
Data Movement Tools
Data movement tools streamline the process of transferring data between systems. They save you time and resources by automating data movement tasks.
Popular Tools and Software
Several tools facilitate data movement. Apache NiFi offers a user-friendly interface for designing data flows, making it easy to manage data movement. Talend provides a comprehensive suite of tools for data integration and movement, supporting various data sources and formats. Informatica PowerCenter is another popular choice, known for its robust data movement capabilities and scalability. These tools help you automate data movement, ensuring that data reaches its destination accurately and efficiently.
Criteria for Choosing Tools
When selecting data movement tools, consider several factors. Compatibility with your existing systems is crucial. Ensure that the tool supports the data sources and formats you use. Scalability is another important consideration. Choose a tool that can handle your current data volume and scale as your needs grow. Security is paramount, especially when moving sensitive data. Look for tools that offer robust encryption and access controls. Finally, consider the tool's ease of use. A user-friendly interface can save you time and reduce the learning curve.
Data movement plays a vital role in modern IT environments. By understanding the technologies involved, you can ensure that your data moves efficiently and securely, supporting your business operations and decision-making processes.
Strategies for Effective Data Movement
Planning and Execution of Data Movement
Steps in Planning Data Movement
To ensure successful data movement, you must start with a solid plan. Here are some steps to guide you:
- Identify Data Sources and Destinations: Determine where your data currently resides and where it needs to go. This step helps you understand the scope of the data movement process.
- Assess Data Volume and Velocity: Evaluate the amount of data you need to move and how quickly it needs to be transferred. This assessment will influence your choice of tools and protocols.
- Select Appropriate Tools and Protocols: Choose the right tools and protocols based on your data volume, velocity, and security requirements. Consider factors like compatibility, scalability, and ease of use.
- Develop a Timeline: Create a timeline for the data movement process. Include milestones and deadlines to keep the project on track.
- Test the Process: Before executing the full data movement, conduct a test run. This step helps you identify potential issues and make necessary adjustments.
Execution Best Practices
Executing data movement requires careful attention to detail. Follow these best practices to ensure a smooth process:
- Monitor Data Transfer: Keep an eye on the data transfer process to ensure everything is moving as planned. Use monitoring tools to track progress and identify any bottlenecks.
- Validate Data Integrity: After the data transfer, verify that the data has arrived intact and unaltered. Use checksums or hash functions to confirm data integrity.
- Document the Process: Maintain detailed records of the data movement process. Documentation helps you track changes and provides a reference for future projects.
Security Considerations of Data Movement
Ensuring Data Security
Data security is paramount during data movement. Here are some strategies to protect your data:
- Encrypt Data in Transit: Use encryption protocols to secure data as it moves between systems. This step prevents unauthorized access and ensures data confidentiality.
- Implement Access Controls: Restrict access to data movement tools and systems. Only authorized personnel should have the ability to initiate or modify data transfers.
- Regularly Update Security Measures: Keep your security protocols and tools up to date. Regular updates help protect against new threats and vulnerabilities.
Compliance with Regulations
Compliance with data regulations is crucial to avoid legal and reputational risks. Consider the following:
"Failure to comply with data regulations can lead to severe penalties, both financially and reputationally." - Data Compliance Regulations
- Understand Relevant Regulations: Familiarize yourself with data protection laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. These laws provide a blueprint for your security policies.
- Integrate Compliance into Data Pipelines: Ensure that your data movement processes align with regulatory requirements. Incorporate data governance and security measures to safeguard data and maintain compliance.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Perform audits to verify compliance with data regulations. Regular audits help identify areas for improvement and ensure ongoing adherence to legal standards.
By following these strategies, you can effectively manage data movement while ensuring security and compliance.
Challenges in Data Movement
Technical Challenges in Data Movement
Bandwidth Limitations
Bandwidth limitations can significantly hinder data movement. When you transfer large volumes of data, limited bandwidth can slow down the process. This delay affects the efficiency of data operations. To overcome this challenge, consider optimizing your data transfer methods. Compressing data before transfer can reduce the load on your network. Additionally, scheduling data transfers during off-peak hours can help manage bandwidth usage more effectively.
Data Integrity Issues
Ensuring data integrity during movement is crucial. You must maintain the accuracy and completeness of data as it moves between systems. Data cleansing and validation are essential steps in this process. They help identify and correct errors before data transfer. According to a study on Data Integrity and Security in Data Movement, focusing on these aspects ensures that the data remains reliable and useful for business operations. Regular checks and validations can prevent data corruption and loss, safeguarding the integrity of your data.
Organizational Challenges in Data Movement
Resistance to Change
Organizational resistance to change poses a significant challenge in data movement. Employees may hesitate to adopt new technologies or processes. This resistance can slow down the implementation of effective data movement strategies. To address this, you should focus on change management. Educate your team about the benefits of data movement and provide training to ease the transition. Encouraging open communication and addressing concerns can also help reduce resistance.
Resource Allocation
Allocating resources effectively is another organizational challenge. Data movement projects require time, personnel, and financial investment. You need to ensure that these resources are available and used efficiently. Prioritizing data movement initiatives and aligning them with business goals can help optimize resource allocation. By doing so, you can ensure that your data movement efforts support your organization's overall objectives and drive growth.
Practical Examples of Data Movement

Case Studies of Data Movement
Successful Implementations
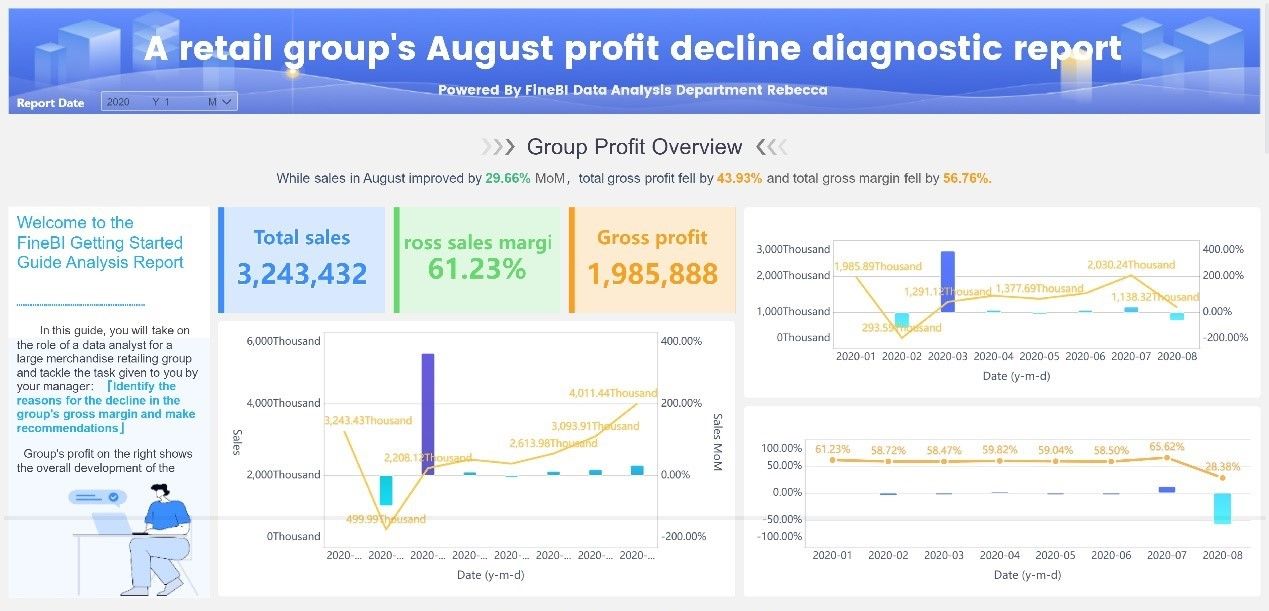
Case Study: Retail Giant's Data Integration
A leading retail company successfully implemented a data movement strategy to integrate data from various sources. They used advanced data movement tools to consolidate customer data, sales figures, and inventory levels. This integration allowed them to gain a comprehensive view of their operations. As a result, they improved inventory management and enhanced customer service. The company reported a 20% increase in sales due to better-targeted marketing campaigns.
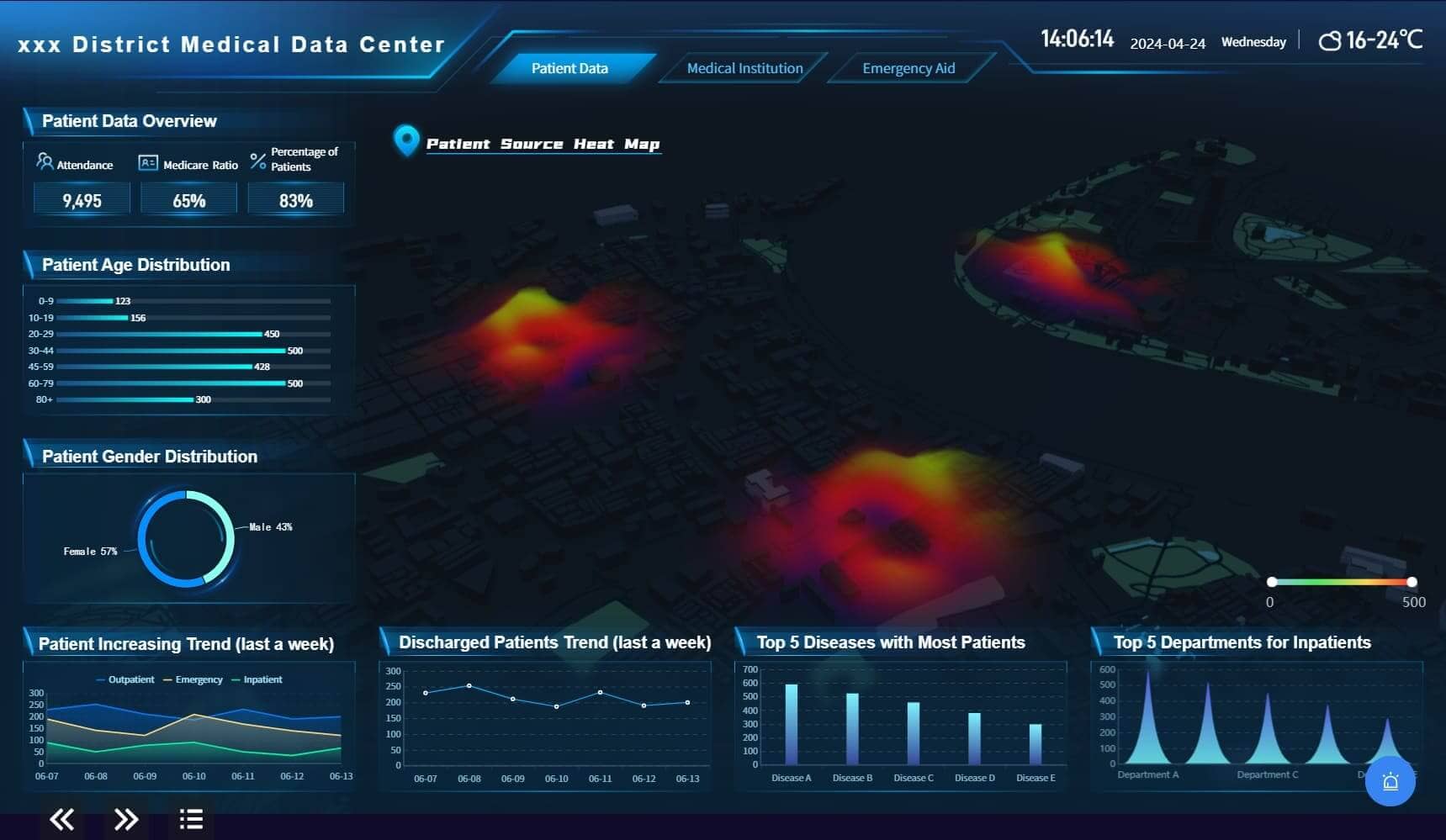
Case Study: Healthcare Provider's Data Synchronization
A major healthcare provider implemented a secure data movement solution to synchronize patient records across multiple facilities. By using encryption protocols, they ensured the confidentiality of sensitive patient information. This synchronization enabled healthcare professionals to access up-to-date patient data, leading to timely and accurate diagnoses. The provider noted a significant improvement in patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
Lessons Learned
- Data Security is Paramount: Always prioritize data security during movement. Use encryption and access controls to protect sensitive information.
- Integration Enhances Decision-Making: Integrating data from various sources provides a holistic view of operations. This integration supports informed decision-making and strategic planning.
- Choose the Right Tools: Selecting appropriate data movement tools is crucial. Ensure compatibility with existing systems and scalability for future growth.
Industry Applications of Data Movement
Data Movement in Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, data movement plays a critical role. It supports timely patient care decisions, comprehensive research analyses, and personalized medicine. By transferring patient data securely, healthcare providers can ensure high-quality care and increase operational efficiency. For example, when patient records are synchronized across facilities, healthcare professionals can access the latest information, leading to better treatment outcomes.
Data Movement in Finance
The finance industry relies heavily on data movement to maintain accurate and up-to-date records. Financial institutions use data movement to transfer transaction data, customer information, and market trends between systems. This process ensures data availability and reliability, which are essential for making informed investment decisions. By implementing robust data movement strategies, financial organizations can enhance their analytical capabilities and improve customer service.
Future Trends in Data Movement
Emerging Technologies of Data Movement
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming data movement. These technologies automate tasks like data cleansing and transformation, making data processes more efficient. You can use AI-powered tools to identify patterns and anomalies in data, ensuring accuracy and reliability. This automation reduces manual effort and speeds up data migration, allowing you to focus on strategic decision-making. As AI and ML continue to evolve, they will play an even more significant role in optimizing data movement.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers flexibility and scalability for data movement. By leveraging cloud platforms, you can migrate data seamlessly between on-premises servers and cloud environments. This flexibility allows you to scale your data operations according to your needs, ensuring that you can handle increasing data volumes. Cloud computing also enhances data availability and synchronization, enabling real-time access to information. As more organizations adopt cloud solutions, the importance of cloud computing in data movement will continue to grow.
Predictions and Innovations of Data Movement
Future Challenges
Data movement faces several challenges in the future. Bandwidth limitations and data integrity issues remain significant obstacles. As data volumes increase, you must find ways to optimize data transfer methods. Compressing data and scheduling transfers during off-peak hours can help manage bandwidth usage. Ensuring data integrity will require robust validation and cleansing processes. You must also address security concerns, as data breaches and unauthorized access pose ongoing threats.
Opportunities for Growth
Cloud computing will provide scalable solutions for data migration, enabling you to adapt to changing business needs.
By staying informed about these trends and innovations, you can harness the full potential of data movement and position your organization for success.
Data movement is crucial in today's digital landscape. It enables you to extract value from data, providing a competitive edge. By implementing effective data movement strategies, you ensure seamless data consolidation and transformation. This accessibility supports real-time decision-making, enhancing your organization's efficiency. Consider how data movement can benefit your context. As technology evolves, the potential for data movement grows. Stay informed about emerging trends and innovations. Embrace these changes to harness the full potential of your data, driving growth and success in your endeavors.
FAQ
Data movement involves transferring data from one location to another. This process ensures that data reaches its intended destination accurately and efficiently. You might think of it as moving goods from one warehouse to another, but in a digital context.
Data movement plays a crucial role in maintaining data integrity and accessibility. It supports business operations by ensuring that the right information is available at the right time. This availability enhances decision-making and operational efficiency.
Several methods facilitate data movement:
Data Integration: Combines data from different sources into a unified view.
Replication: Copies data from one location to another to ensure consistency.
Change Data Capture: Identifies and captures changes made to data.
Stream Processing: Processes data in real-time as it flows through systems.
Data transfer protocols define rules for transferring data between systems. They ensure secure and efficient data movement. Common protocols include:
FTP (File Transfer Protocol): Transfers files over a network.
SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol): Adds security to FTP by encrypting data.
HTTP/HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol/Secure): Transfers data over the web.
Several tools streamline data movement:
Apache NiFi: Manages data flows with a user-friendly interface.
Talend: Offers a suite of tools for data integration and movement.
Informatica PowerCenter: Known for robust data movement capabilities.
To protect your data:
Encrypt Data: Use encryption protocols to secure data in transit.
Implement Access Controls: Restrict access to data movement tools.
Regularly Update Security Measures: Keep protocols and tools up to date.
You may encounter:
Bandwidth Limitations: Can slow down data transfer.
Data Integrity Issues: Ensuring data accuracy during movement.
Organizational Resistance: Hesitation to adopt new technologies.
Emerging technologies like AI and cloud computing enhance data movement:
AI and Machine Learning: Automate data processes, improving efficiency.
Cloud Computing: Offers flexibility and scalability for data migration.
Continue Reading About Data Movement
How to Build a Python Data Pipeline: Steps and Key Points
Explore how to build a Python Data Pipeline by effective tools and libraries. Learn more about the steps and key points.
Howard
Jul 17, 2024
2025's Best Data Validation Tools: Top 7 Picks
Explore the top 7 data validation tools of 2025, featuring key features, benefits, user experiences, and pricing to ensure accurate and reliable data.
Howard
Aug 09, 2024
2025 Best Data Integration Solutions and Selection Guide
Explore top data integration solutions for 2025, enhancing data management and operational efficiency with leading platforms like Fivetran and Talend.
Howard
Dec 19, 2024
Best Data Management Tools of 2025
Explore the best data management tools of 2025, including FineDataLink, Talend, and Snowflake. Learn about their features, pros, cons, and ideal use cases.
Howard
Aug 04, 2024
Best Data Integration Vendors for Seamless Workflows
Discover the top 20 data integration vendors of 2025 for seamless workflows. Compare tools like Talend, AWS Glue, and Fivetran to optimize your data processes.
Howard
Jan 22, 2025
Covers Dashboard: Find Your Perfect Match
Choose the perfect covers dashboard to protect and style your car, enhancing its interior and resale value with the right material and fit.
Lewis
Nov 05, 2024