Pie charts offer a powerful way to translate data into a digestible visual representation. However, not all charts tell the right story. By using a pie chart generator, you can craft customized visualizations that align with your data's narrative in Malaysia. Thoughtful design choices, such as selecting appropriate colors or deciding to add a legend, can significantly improve clarity. This approach enables enhanced narrative building, turning your chart into a more effective visual tool. When done correctly, these adjustments unlock better insights and improve decision-making.
A pie chart is a circular graphic that divides a circle into sectors, each representing a proportion of the whole. The size of each sector corresponds to the data value it represents. This makes pie charts an intuitive way to visualize parts of a whole. For example, if you want to show how different departments contribute to a company’s revenue in Malaysia, a pie chart can clearly display each department’s share. According to Wikipedia, the arc length of each slice is proportional to the quantity it represents, making it a straightforward tool for effective visualization.
Tip: Use pie charts when you need to compare proportions or percentages within a dataset. They work best with small datasets for clarity.
Pie charts are widely used across industries to simplify complex data. They help you identify trends, compare proportions, and make informed decisions in Malaysia. Here are some practical applications:
| Industry | Use Case Description | Source Link |
|---|---|---|
| Finance | Illustrates invoice distribution across different payment periods for financial planning. | Harvest Financial and Invoicing Insights dashboard |
| Sales | Displays product categories by payment terms to understand product proportions. | Shopify Sales dashboard |
| Support | Assesses team workload by ticket status for resource allocation. | Support ticket status pie chart |
| Healthcare | Visualizes patient-reported pain levels for insights in healthcare settings. | Patient Health Monitoring dashboard |
| Government | Presents accidents by vehicle type for traffic safety analysis. | Motor Vehicle Accident Analysis dashboard |
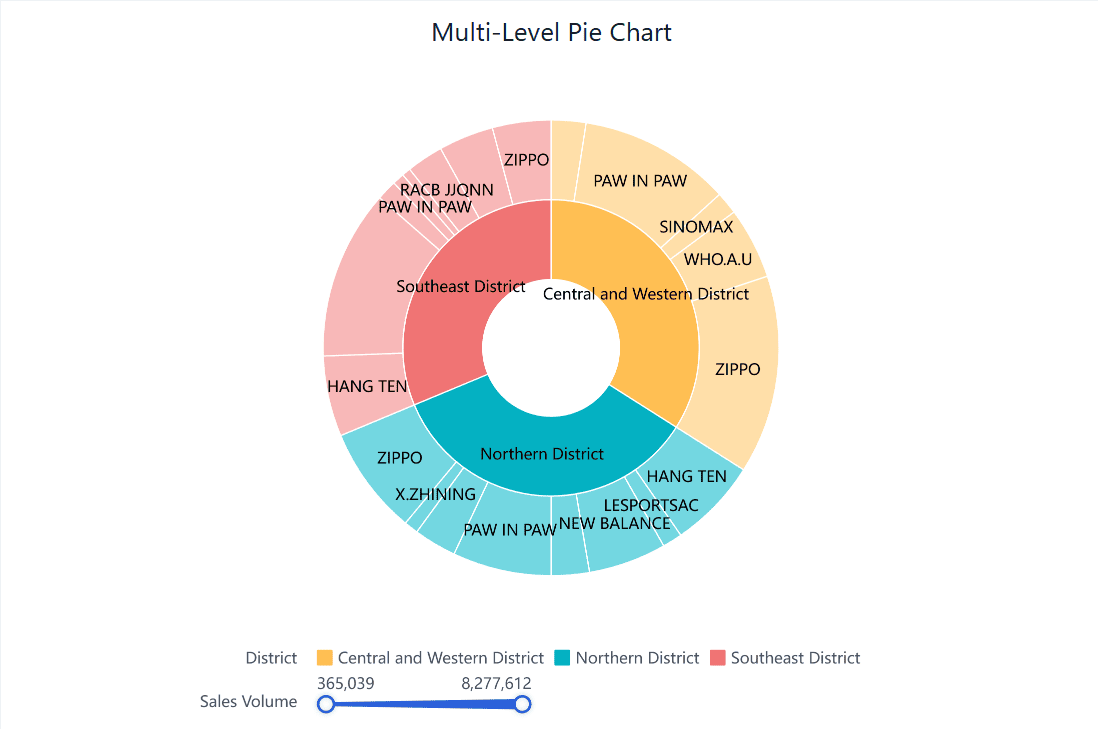
A multi-level pie chart, also known as a sunburst chart, displays hierarchical data. Each level represents a category, and the inner circles show higher-level categories. This type of chart is ideal for visualizing data with multiple layers, such as organizational structures or product categories.
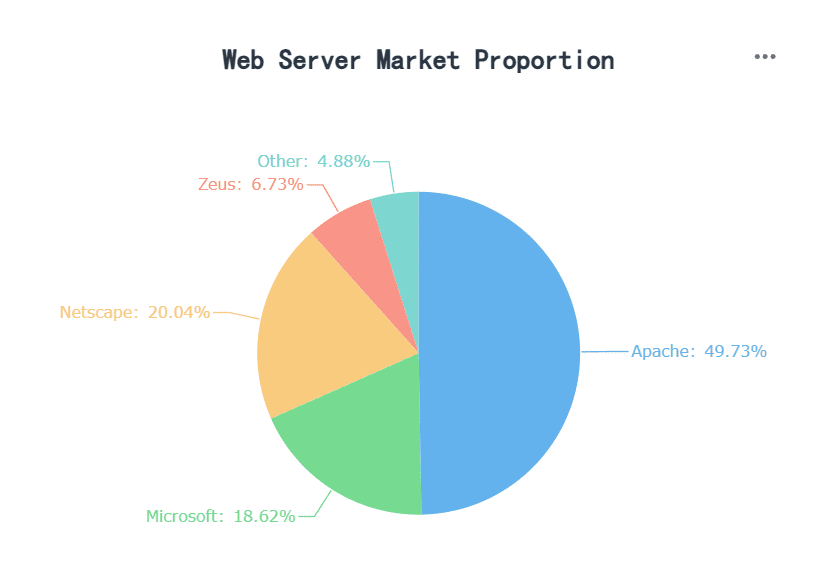
The standard pie chart is the most common type. It provides a basic representation of proportions, making it easy to understand. This chart works best for small datasets with clear distinctions between categories.
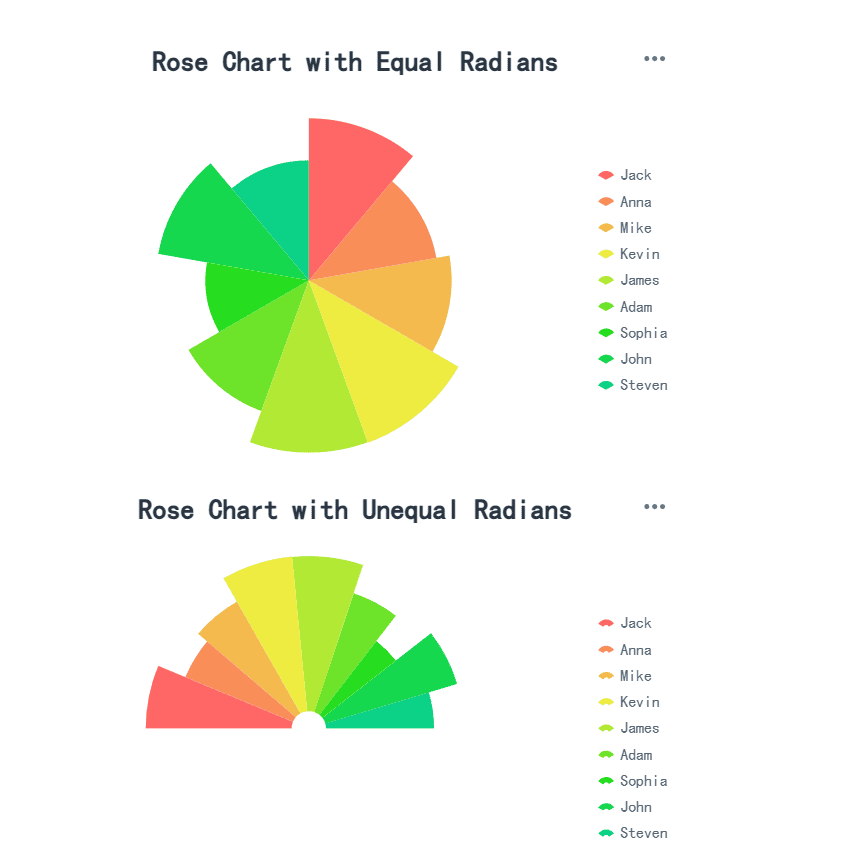
A rose chart, also called a polar area chart, uses sectors to represent data, but the radius of each sector varies based on the value. This type of chart adds a unique visual element, making it suitable for presentations where you want to engage your audience in Malaysia.
Note: While 3D pie charts and donut charts add visual depth, they may distort data perception. Use them cautiously to maintain accuracy.
Selecting appropriate colors plays a crucial role in creating effective visualizations. Colors help distinguish between categories in pie charts, making it easier for your audience in Malaysia to interpret the data. To achieve this, consider the following principles:
Different color schemes, such as complementary or analogous palettes, can enhance your chart's appeal in Malaysia. However, avoid overloading the chart with too many colors, as this can overwhelm the viewer. By focusing on clarity and accessibility, you can create a pie chart that communicates your data effectively.
Tip: Stick to a maximum of five to six colors for better readability and to maintain a clean design.
The order of slices in a pie chart significantly affects how your audience in Malaysia interprets the data. Sorting slices by size, from largest to smallest, helps highlight the most important categories. This arrangement draws attention to key insights and ensures a logical flow.
When slices are of similar size, grouping related categories together can improve comprehension. For instance, placing slices representing similar departments or regions next to each other creates a cohesive narrative.
Additionally, avoid cluttering the chart with too many small slices. If you have several minor categories, consider merging them into an "Other" category. This simplifies the visualization and prevents your audience in Malaysia from getting lost in the details.
| Insight | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Importance of Size | The size of pie chart segments must be distinct to effectively convey differences in data. |
| Accuracy of Data | Inaccurate data leads to misleading visualizations; pie charts should total 100% for meaningful representation. |
By organizing slices thoughtfully, you can guide your audience in Malaysia through the data and ensure they grasp the key takeaways.
Annotations provide additional context, making your pie chart more informative. Adding clear and concise labels directly to each slice ensures your audience in Malaysia understands the data without needing to refer to a legend. This approach improves clarity and reduces cognitive load.
For example, label values directly on the chart to show exact percentages or numerical values. This eliminates guesswork and enhances the chart's accuracy. You can also include brief notes or callouts to highlight significant trends or anomalies.
Annotations are particularly useful when presenting complex data. For instance, if your chart shows revenue distribution across multiple regions, a note explaining why one region outperforms others can add valuable context.
Note: Avoid overcrowding the chart with excessive text. Keep annotations concise and relevant to maintain a clean visualization design.
By incorporating annotations strategically, you can transform your pie chart into a powerful storytelling tool in Malaysia. This aligns with visualization best practices, ensuring your audience in Malaysia gains meaningful insights from your data.
When working with pie charts, simplicity often leads to better insights. Too many categories can overwhelm your audience in Malaysia and make the chart difficult to interpret. Instead of displaying every small data point, you can merge smaller categories into a single "Others" slice. This approach reduces clutter and highlights the most significant segments of your data.
Experts recommend limiting the number of categories in a pie chart to five. This ensures that each slice remains distinct and easy to compare. For example, if your chart represents sales by product category and several items contribute less than 2% each, grouping them under "Others" creates a cleaner visualization. This method not only improves readability but also directs attention to the key data points.
Tip: Use descriptive labels for the "Others" category. For instance, "Miscellaneous Expenses" or "Other Regions" provides more context than a generic label.
Merging smaller categories also helps maintain proportional accuracy. When too many small slices are included, the visual impact of larger slices diminishes. By consolidating minor segments, you allow the chart to emphasize the most critical data. This practice is particularly useful in presentations or reports where clarity and focus are essential.
Additionally, combining smaller categories can enhance storytelling. A pie chart with fewer, well-defined slices communicates a clear narrative. For instance, in a chart showing customer demographics, merging less-represented age groups into "Other Age Groups" simplifies the message while retaining its meaning. This approach ensures your audience in Malaysia grasps the main insights without getting lost in unnecessary details.
Remember, the goal of a pie chart is to make data accessible and engaging. By merging smaller categories, you create a visualization that is not only easier to read but also more impactful in Malaysia. This small adjustment can transform a cluttered chart into a powerful tool for decision-making.
Overloading a pie chart with too many slices can confuse your audience in Malaysia. When there are excessive categories, the chart becomes cluttered, making it difficult to distinguish between slices. This diminishes its ability to communicate meaningful insights. For example, if you include numerous small slices, viewers may struggle to interpret the data accurately.
To avoid this, limit the number of slices to five or seven. Combine smaller categories into an "Other" slice to simplify the visualization. This approach ensures that the chart remains clear and focused on the most significant data points.
Tip: Avoid using pie charts for datasets with many small differences. Instead, consider alternative visualizations like bar charts for better clarity.
| Common Pitfalls in Pie Charts | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Using too many categories or small slices | Leads to overcrowding and confusion, making it hard to distinguish between different sections. |
| Misleading visuals | Incorrectly sized slices can give a false impression of the data, especially with similar colors. |
| Lack of context | Without clear labels or explanations, viewers struggle to understand what each slice represents. |
Adding 3D effects to pie charts may seem visually appealing, but it often distorts data perception. The perspective created by 3D designs can make slices closer to the viewer appear larger than those further away. This misrepresentation skews the audience's understanding of the data.
Stick to a flat, 2D design for accuracy. A 2D pie chart ensures that the proportions of each slice remain true to the data. Avoid unnecessary dimensions that could mislead your audience in Malaysia.
| Evidence Description | Effect on Data Perception |
|---|---|
| 3D pie charts use perspective to create a visual effect. | This can lead to misinterpretation of the relative sizes of the slices. |
| Slices closer to the viewer appear larger than those further away. | This perspective distortion makes it harder for readers to accurately judge the relative sizes of the slices. |
| The use of unnecessary dimensions is discouraged in charts. | 3D pie charts are particularly difficult to interpret compared to 2D charts. |
Note: While 3D effects may look engaging, they compromise the integrity of your data visualization.
Accuracy is the foundation of effective pie chart design. Start by ensuring your data is clean and well-organized. Pie charts work best with categorical data where categories do not overlap. Limit the number of slices to maintain clarity and use logical ordering, such as descending size.
Follow these best practices to ensure data integrity:
Compliance with these standards not only enhances the chart's readability but also ensures ethical data representation. Accurate pie charts build trust and help your audience in Malaysia make informed decisions.
Tip: Always double-check that the total of your slices equals 100%. This ensures the chart reflects the data accurately.
Color contrast plays a vital role in making pie charts easy to read and interpret. When you use contrasting colors effectively, you help your audience in Malaysia distinguish between different slices at a glance. Poor contrast, on the other hand, can make your chart confusing and reduce its impact.
To ensure your pie chart is visually clear, follow these best practices:
Tip: Use a neutral background to make the colors in your pie chart pop. A white or light gray background enhances contrast and improves readability.
Color contrast also affects how your audience in Malaysia perceives the importance of each slice. Bright, bold colors like red or orange can draw attention to key data points. Subtle hues like pastel blue can be used for less critical categories. By strategically selecting colors, you can guide your audience’s focus and emphasize the most important insights.
Remember, the goal of pie charts is to communicate data effectively. Proper color contrast ensures your chart is not only visually appealing but also functional. This small design choice can make a big difference in how your audience in Malaysia understands your data.
Interactivity transforms static pie charts into dynamic tools for exploration. With FineBI, you can add features that allow users to engage directly with the data. This approach not only enhances user experience but also simplifies complex data interpretation.
Here are some interactive features you can implement:
These features make your pie charts more than just visual aids. They become tools for discovery, helping users uncover insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Tip: Start with simple interactive elements like drill-downs and legends. Gradually add more advanced features as needed.
Accessibility ensures that everyone, including individuals with disabilities, can benefit from your visualizations. FineBI supports features that make pie charts compliant with accessibility standards like Section 508 and the European Accessibility Act.
To create accessible pie charts, follow these best practices:
Compliance with accessibility standards not only meets legal requirements but also broadens your audience in Malaysia. Accessible pie charts demonstrate inclusivity and ensure that your data reaches everyone effectively.
Note: Test your charts with accessibility tools to identify and fix potential issues before sharing them.
Dynamic data updates turn pie charts into powerful tools for real-time decision-making. FineBI enables your charts to adjust automatically as data changes, ensuring they always display the most current information.
Here’s how dynamic updates enhance your pie charts:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Automatic Adjustment | Pie charts adjust slice sizes and labels dynamically when data changes. |
For example, in a sales dashboard, a pie chart showing revenue by product category can update instantly as new sales data comes in. This allows you to monitor trends and respond quickly to changes.
Dynamic updates also improve collaboration. Teams can view the same up-to-date chart, ensuring everyone works with consistent information. This fosters better communication and more informed decision-making.
Tip: Use dynamic updates for dashboards that require frequent monitoring, such as sales performance or customer feedback.
Customizing pie charts to reflect your brand in Malaysia identity can elevate your data visualizations. With FanRuan's FineBI, you can seamlessly integrate branding elements into your pie chart designs. This not only enhances the visual appeal but also reinforces your organization's identity in every presentation or report.
Branding in data visualization goes beyond aesthetics. It creates a cohesive experience for your audience in Malaysia. When your pie charts align with your brand's colors, fonts, and style, they become instantly recognizable. This consistency builds trust and professionalism. For example, a sales report featuring branded pie charts can leave a lasting impression on stakeholders, making your data more memorable.
FineBI offers several tools to help you customize pie charts with your branding. Here’s how you can achieve this:
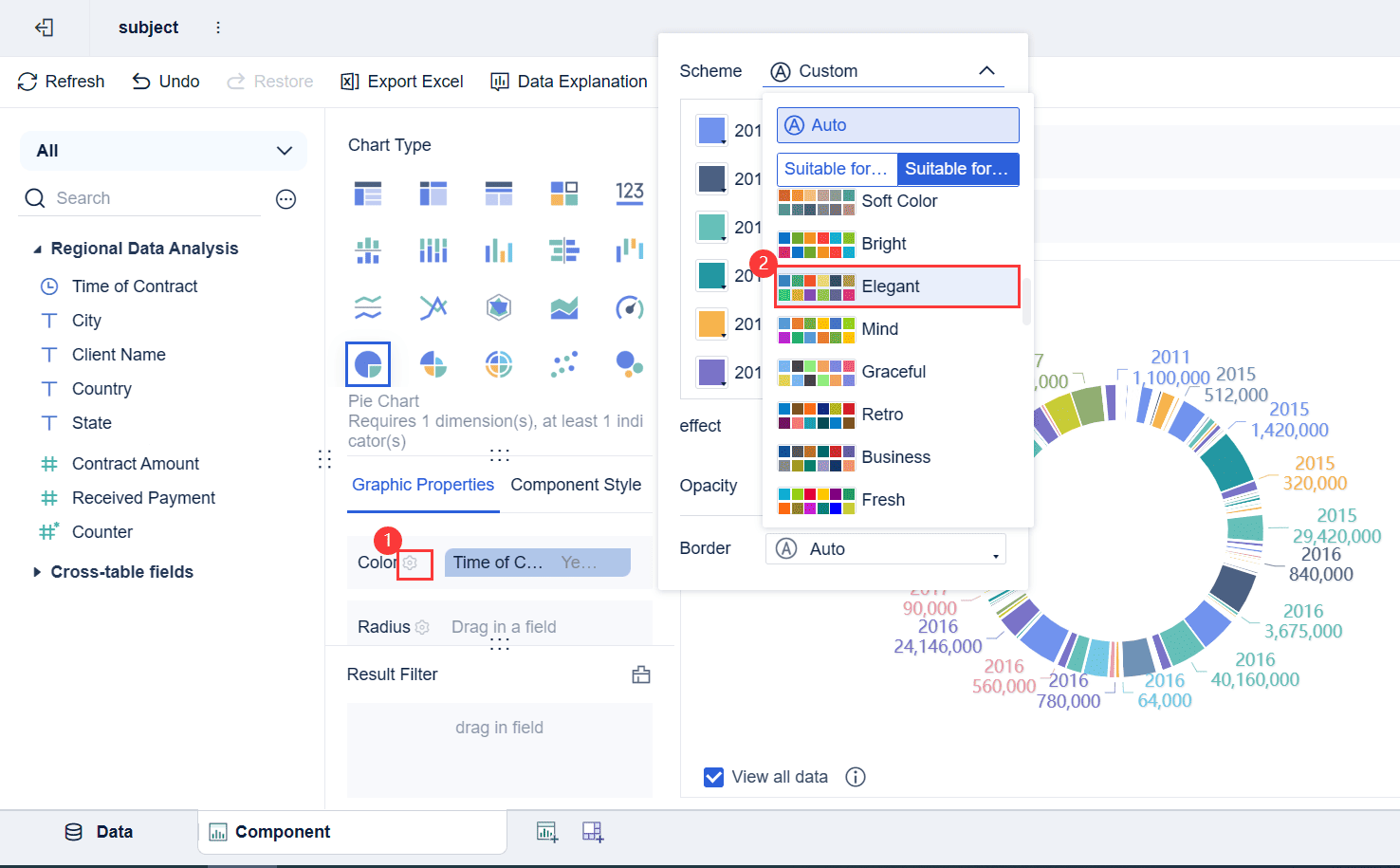
Incorporating branding into your pie charts offers several advantages:
By using FineBI, you can transform your pie charts into powerful tools that not only communicate data but also strengthen your brand in Malaysia. This customization ensures that every chart you create aligns with your organization's values and vision.
Tip: Start by defining your brand's visual guidelines, including colors, fonts, and logo placement. Use these guidelines to customize your pie charts in FineBI for a consistent and impactful presentation.
Simplifying your pie chart by limiting the number of categories improves clarity and focus. Research by Spence and Lewandowsky highlights that pie charts work best when they display a small number of categories with significant size differences. For example, a chart with five slices is easier to interpret than one with ten. Edward Tufte, a data visualization expert, also supports this approach, noting that fewer categories make proportions more perceptible.
| Source | Findings |
|---|---|
| Spence and Lewandowsky | Pie charts are effective with few categories and clear size differences. |
| Edward Tufte | Advocates limiting slices for better clarity and ease of understanding. |
When dealing with many small categories, group them into an "Other" slice. This keeps the chart clean and ensures the most critical data stands out. For instance, instead of showing ten product categories, combine those contributing less than 5% into a single slice labeled "Other Products." This approach simplifies the visualization while maintaining its accuracy.
Tip: Always ensure your pie chart totals 100% to maintain data integrity and reliability.
Donut charts offer a modern twist on traditional pie charts. By removing the center, they shift the focus from angles to arc lengths, making comparisons more intuitive. This design also creates space for additional information, such as a total value or a key metric, in the center.
For example, a donut chart showing sales by region could display the total revenue in the middle. This enhances the chart's storytelling potential while maintaining its visual appeal. Donut charts are particularly effective when you want to emphasize the overall contribution of a category, especially if it represents around 25% or 50% of the total.
Note: Avoid using donut charts if the data includes too many small segments. In such cases, consider alternatives like bar charts for better clarity.
FineBI takes pie chart customization to the next level, allowing you to create tailored visualizations that align with your data narrative. With its user-friendly interface, you can easily adjust colors, labels, and legends to match your brand or audience preferences in Malaysia.
Here’s how FineBI enhances your pie chart design:
For example, a sales dashboard created with FineBI can feature a pie chart that updates automatically as new sales data comes in. The legend can highlight key categories, such as "Top Products," making it easier for stakeholders to focus on critical insights.
Tip: Use FineBI’s templates to save time while ensuring your pie charts look professional and polished.
Mastering pie chart customization unlocks the full potential of your data. By following best practices, you can create visuals that are both accurate and impactful. For example, always choose the right chart type, maintain simplicity, and use colors intentionally to guide focus.
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Choose the right chart type | Selecting the appropriate chart is essential to convey the correct message. |
| Maintain visual simplicity | Simplify visuals by highlighting essential data points, avoiding unnecessary elements. |
| Focus on accuracy | Ensuring accuracy in data visuals is vital to prevent misleading representations. |
| Use color intentionally | Colors can enhance understanding when used purposefully, guiding the viewer's focus. |
FineBI makes this process seamless. Its advanced features allow you to customize charts effortlessly while ensuring clarity and precision. Thoughtful design transforms your data into actionable insights, empowering better decisions. Start applying these techniques today to elevate your visual storytelling!
Click the banner below to try FineBI for free and empower your enterprise to transform data into productivity!
How to make a pie of pie chart or bar of pie chart?

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles

Self-Service Analytics Defined and Why You Need It
Self-service analytics lets you analyze data without IT help, empowering faster, data-driven decisions and boosting agility for your business.
Lewis
Jan 04, 2026

Best Self-Service Tools for Analytics You Should Know
See which self-service tools for analytics let business users access data, build dashboards, and make decisions faster—no IT help needed.
Lewis
Dec 29, 2025

Understanding Predictive Analytics Services in 2026
Predictive analytics services use data and AI to forecast trends, helping businesses make informed decisions, reduce risks, and improve efficiency in 2026.
Lewis
Dec 30, 2025