Plantation management means organizing, monitoring, and improving every part of a plantation’s operation. Today, you see its value rise as plantations drive economic growth, support communities, and restore environments in Malaysia. Many plantations in Malaysia now boost income, secure food, and even promote gender equality.
Digital transformation changes how you manage a plantation in Malaysia. Using data-driven tools like FanRuan and FineReport, you can increase crop yields by up to 30% and save water. AI, sensors, and dashboards help you make better decisions, reduce waste, and protect the environment.
When you look at plantation management, you see a system that focuses on organizing and improving every part of a plantation. Plantation management covers planning, monitoring, and making decisions for large areas of land. You often find this approach in commercial agriculture, where the goal is to maximize output and profit. Unlike other agricultural systems, plantation management usually means growing a single crop over a large area. This method relies on advanced technology, hired labor, and external inputs like fertilizers and pesticides.
You can see the difference between plantation management and other systems by looking at the financial risks and scale. Farmers in plantation or mono-cropping systems often face higher debts and more financial pressure than those in mixed or diversified farms.
| Statistic Description | Plantation/Mono-cropping System (Scale Economies) | Other Agricultural Systems (Scope Economies) |
|---|---|---|
| Average farmer debt in Punjab | 42,000 INR | 20,000 INR (National average) |
| Percentage of financially unviable farmers in Balasore, Odisha | ~50% | N/A |
| Percentage of farmers making losses across six major crops in Balasore | ~30% | N/A |
These numbers show that plantation management, with its focus on scale, brings unique challenges compared to other types of agriculture.
Plantation farming stands out as a key part of commercial agriculture. You usually see plantation farming on large estates or farms, where one main crop covers most of the land. This system is common in crops like oil palm, tea, coffee, and rubber. The characteristics of plantation farming include large land areas, single-crop focus, and a strong link to global markets. You often find plantation farming in tropical regions, where the climate supports year-round growth in Malaysia.
The characteristics of plantation farming also include the use of modern machinery and a workforce that manages planting, harvesting, and processing. Plantation farming supports both domestic needs and export markets, making it a major player in commercial agriculture.
| Location | Plantation/Farm Name | Land Area (hectares) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ghana | Norpalm oil palm plantation | 4,500 | Former state-owned, partially privatised, produces palm oil for domestic and export markets. |
| Kenya | Kisima farm | 6,000 | Fourth-generation family estate, processes flour and canola oil, expanded into floriculture. |
| Zambia | Zambeef Chiawa estate | 10,000 | Produces wheat, maize, soybean mainly for domestic market, no on-farm processing. |
| Ghana | Mango farmers (medium-scale) | 5,000 | Medium-scale sector with export accreditation to EU market. |
| Zambia | Commercial farm blocks (Mkushi) | 176,000 | State-designed commercial farm blocks with medium- to large-scale farms. |
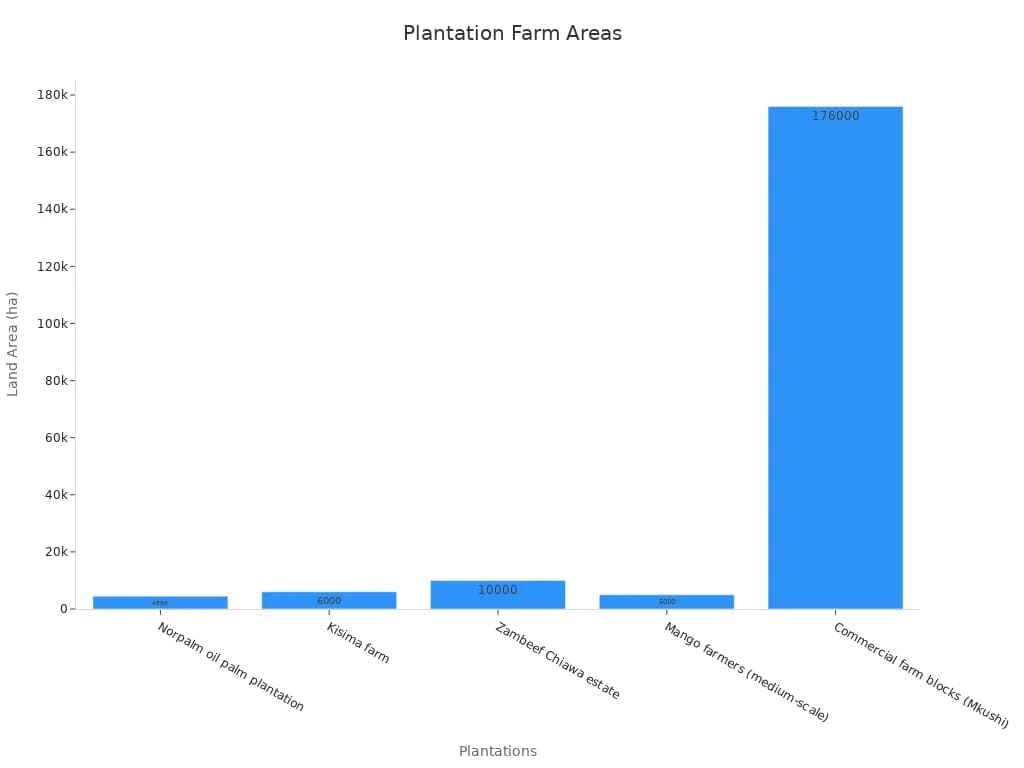
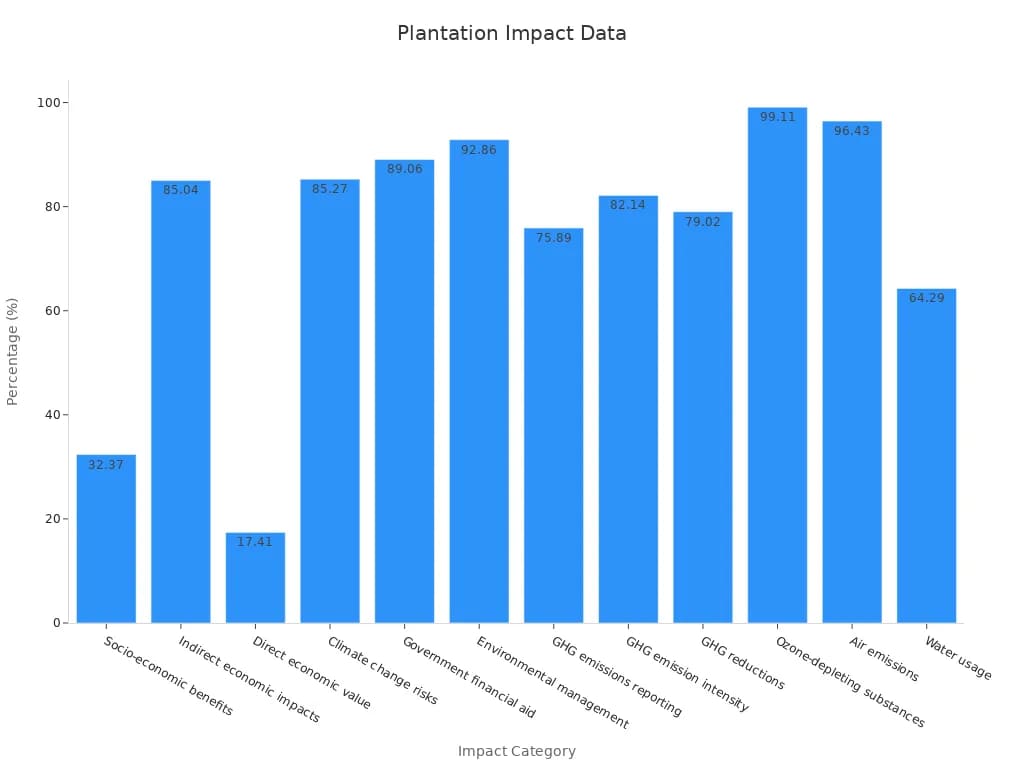
You can see from the chart that plantation farming often involves thousands of hectares. This scale is much larger than most traditional farms. Plantation farming shapes the landscape of commercial agriculture and plays a big role in food supply and trade in Malaysia.
You play a vital role in plantation farming by making smart choices at every stage. Planning starts with selecting the right land and crop. You look at soil quality, rainfall, and climate. Crop selection matters because it affects yield and profit. Many growers now use improved seeds and clones. For example, research shows that using selected eucalypt clones can boost productivity from 5-6 m³/ha/year to 20-25 m³/ha/year. This means you get more from each hectare.
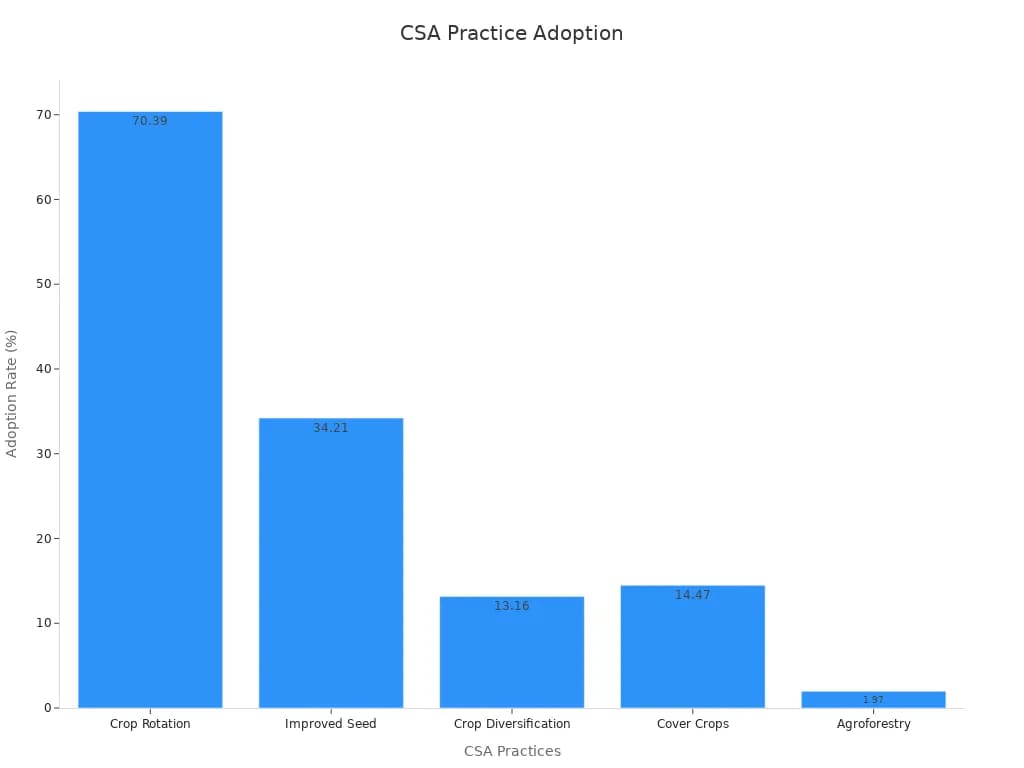
Labor management is another key part of plantation farming. You organize teams for planting, weeding, and harvesting. Automation and training help reduce costs and improve results. Sustainability is now a top priority. You follow agro-management practices like crop rotation and cover cropping. These steps protect the soil and keep pests away. In Senegal, 70% of farmers use crop rotation, and 34% use improved seeds. These trends show that more people adopt multiple practices together.
Note: Barriers like lack of knowledge (29.6%) and financial limits (22.4%) can slow adoption. You can overcome these by joining training programs and seeking support.
Here is a table showing how different practices and trends support better plantation farming:
| Practice or Trend | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Seeds | Use of high-yield clones | 4x increase in productivity |
| Crop Rotation | Alternating crops each season | Better soil and pest control |
| Automation | Machines for planting and harvesting | 12% labor cost reduction |
| Sustainability Certification | Meeting environmental standards | 95% compliance rate |
You can transform plantation farming by using digital tools. FineReport, from FanRuan, helps you collect and analyze data from every part of your plantation in Malaysia. You track yield per hectare, monitor water and energy use, and check compliance with sustainability standards. Real-time dashboards show you where to act fast. For example, you might see a 15% increase in yield after using better planning and reforestation.

You also measure your impact on the community. Plantation farming can create jobs and improve local infrastructure in Malaysia. FineReport lets you track these changes with metrics like the Community Development Impact Score. You can see a 20% boost in consumer trust when you share transparent data.
Here is a table of key metrics you can monitor with digital tools:
| Metric | Benchmark | Example Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Yield per Hectare | 8-10 tonnes/ha | 15% increase with better practices |
| Cost Efficiency Ratio | 0.75 | 10-15% cost savings |
| Community Impact Score | 85/100 | 25% better infrastructure |
| Resource Use | Energy and water per hectare | 10% energy cost reduction |
You use these insights to make better decisions. Plantation tree crop management becomes easier and more effective in Malaysia. By combining research, technology, and agro-management practices, you help your plantation thrive and support sustainability.
You see plantation farming shape economies and communities around the world. When you manage a plantation well, you create jobs for people in Malaysia. Workers find steady employment in planting, harvesting, and processing. This helps families earn income and improves living standards. Plantation farming often leads to better roads, schools, and health centers because companies invest in local infrastructure. You notice that communities grow stronger when plantations support education and healthcare.
Plantation farming also drives economic growth. Many countries rely on crops like oil palm, tea, and coffee for export income. These crops bring in foreign currency and help balance national budgets. When you use modern management tools, you can track how much your plantation contributes to the local economy. FineReport lets you monitor job creation, wages, and community projects. You see the real impact of your work in numbers and stories in Malaysia.
Social responsibility matters in plantation management. You have the power to promote gender equality by hiring women and supporting their advancement. Some plantations offer training programs that help workers learn new skills. This builds a more skilled workforce and opens up new opportunities. When you focus on fair wages and safe working conditions, you set a standard for others in Malaysia to follow.
Plantation farming does more than grow crops. It builds communities, supports families, and drives progress.

You play a key role in protecting the environment through sustainable plantation farming. The choices you make affect soil, water, and air quality. When you use best management practices in Malaysia, you help restore land and increase biodiversity. For example, intercropping grain and beans can boost yields by over 70% compared to growing just one crop. Farmers who use intercropping also earn at least 25% more profit. Crop rotation with cereal-legume systems increases yields by at least 36%. Maize yields rise 1.3 times after legumes instead of maize. In Ghana, soil and water conservation technologies have raised rice yields by about 24% and net returns by 16%.
You also help fight climate change. Sustainable plantation farming captures carbon in the soil and plants. The table below shows how different farming systems sequester carbon each year:
| Farming System Category | Carbon Sequestered per Hectare (t C/ha/yr) | Total Carbon Sequestered (Mt C/yr) | Carbon Sequestered per Household (t C/yr) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smallholder irrigated | 0.15 | 0.011 | 0.06 |
| Wetland rice | 0.34 | 2.53 | 0.29 |
| Smallholder rainfed humid | 0.46 | 0.34 | 0.20 |
| Smallholder rainfed highland | 0.36 | 0.23 | 0.56 |
| Smallholder rainfed dry/cold | 0.26 | 0.20 | 0.32 |
| Dualistic mixed | 0.32 | 8.03 | 14.95 |
| Coastal artisanal | 0.20 | 0.032 | 0.15 |
| Urban-based and kitchen garden | 0.24 | 0.015 | 0.07 |
| Total | 0.35 | 11.38 | 0.91 |
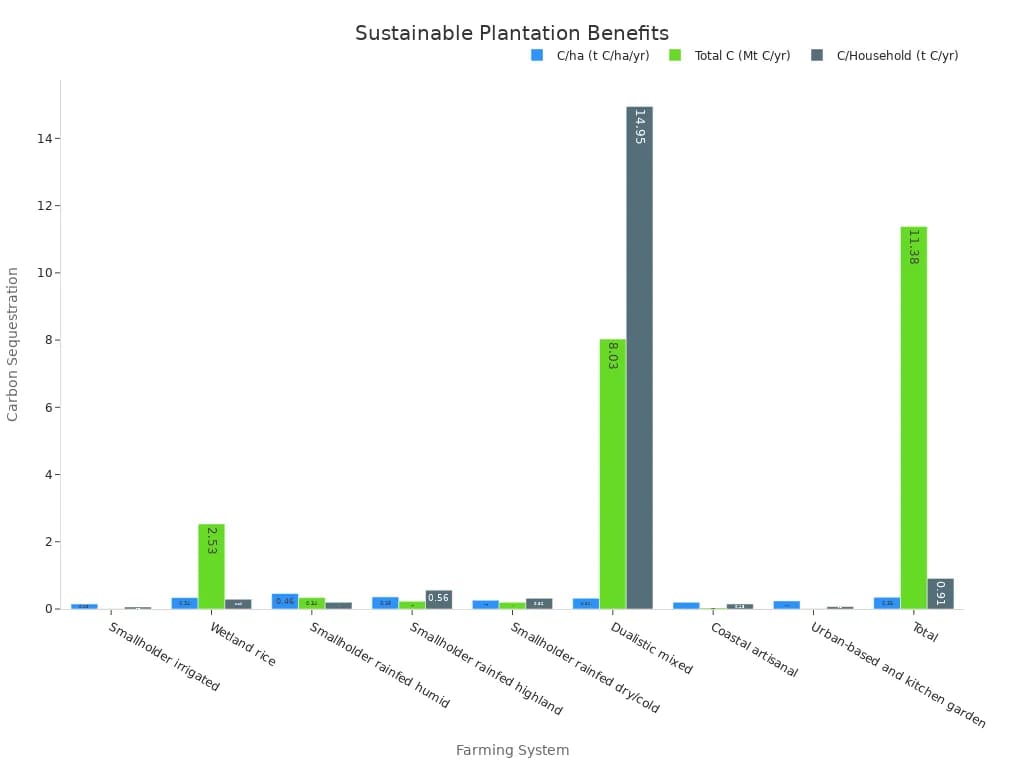
You see that sustainable plantation farming systems sequester an average of 0.35 tons of carbon per hectare each year. Across 37 million hectares, this adds up to about 11.4 million tons of carbon captured annually. This reduces the environmental impact of agriculture and helps slow climate change.
You can also reduce chemical use by adopting new techniques. In China, agricultural subsidies have helped rice farmers cut fertilizer use. Every time subsidies doubled, fertilizer use dropped by 3.4%. This happened because farmers used better methods and expanded their planting area. When you use less fertilizer, you protect water sources and reduce pollution.
Modern plantation management tools like FineReport help you track your environmental impact. You can monitor water and energy use, soil health, and biodiversity. FineReport gives you real-time dashboards to see where you can improve. You make decisions that support the sustainability of a crop and protect the environment for future generations.
Sustainable plantation farming proves that you can increase yields, protect the environment, and support communities at the same time.
You see that environmental sustainability does not mean lower productivity. Research shows that farms with high ground vegetation cover do not lose yields. When you keep the soil healthy and reduce chemical inputs, you support biodiversity and ecosystem functions. Plantation farming, when managed well, becomes a force for good in the world.
When you manage a plantation well, you unlock many advantages. Plantation farming increases productivity by using modern tools and data-driven decisions. You can boost yields and reduce waste by applying resources exactly where they are needed. For example, large-scale field experiments from the Data-Intensive Farm Management Project show that using precision agriculture helps you make better choices for your fields. You see higher crop yields, less waste, and healthier crops.
You also save money by using fertilizers and water more efficiently. Plantation farming lets you plan labor and equipment schedules, which reduces downtime and costs. When you use digital tools like FineReport, you track every part of your plantation in real time. This helps you spot problems early and act fast. You also support the environment by reducing chemical use and protecting soil health.
Plantation farming can bring financial stability, better community development, and stronger resilience against risks. Studies in Akure, Nigeria, show that farmers who see the benefits—like higher income and better environmental services—are more likely to adopt new practices. Your decisions help balance economic growth with environmental care.
You also face real challenges in plantation management. Market volatility can cause crop prices to swing by over 30% each year. This makes your income uncertain and affects how much food people can afford. Climate change brings unpredictable weather, droughts, and floods, which can lower your yields. Over one-third of the world’s soils suffer from degradation, making it harder to grow healthy crops.
Pests and diseases spread quickly in monoculture systems, which are common in plantation farming. You must stay alert and use smart management to protect your crops. Sometimes, you struggle with access to credit, land security, or technical knowledge. These barriers can slow down your progress.
You see these challenges in real life. For example, rubber plantation smallholders in Southeast Asia face global price swings and long waiting periods before trees mature. In Africa, some plantations failed because of poor market demand and low yields.
When you use tools like FineReport, you can monitor risks, track market trends, and make informed decisions. This helps you adapt quickly and keep your plantation strong. Research shows that even with these challenges, you can achieve win-win outcomes by matching inputs to crop needs and using sustainable practices. Plantation farming, when managed well, balances productivity, profit, and ecological health.
A modern plantation management dashboard gives you a clear view of your operations. You can track energy use, emissions, and the status of each plantation block in real time. Digital dashboards help you make better decisions and improve efficiency across your entire plantation.
You can monitor power use across your plantation with advanced sensors and cloud-based systems. Wireless sensor networks (WSN) send data to the cloud, which reduces the energy used by each sensor and extends their life. These systems let you see how much power each device or area uses. You can spot problems early and adjust your energy plan.
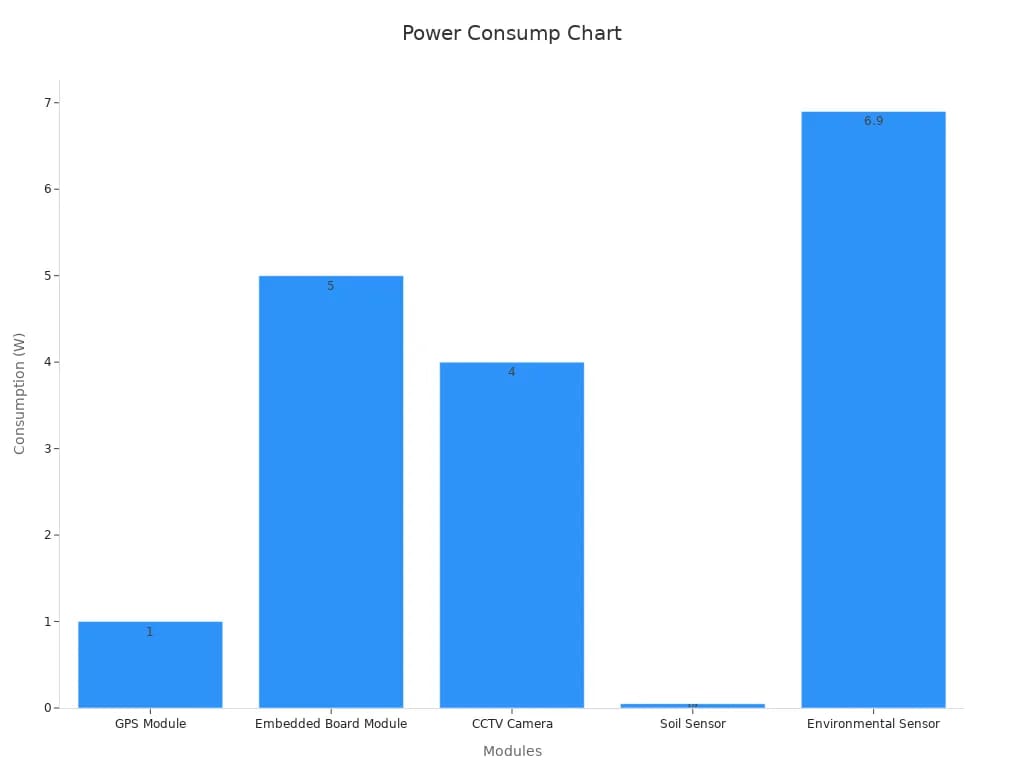
Here is a table showing the power consumption of different modules in a typical monitoring system:
| Module | Voltage | Current | Power Consumption |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Module | 5 V DC | 0.2 A | 1 W |
| Embedded Board Module | 9 V DC | 0.5 A | 5 W |
| CCTV Camera | 9 V DC | 0.4 A | 4 W |
| Soil Sensor | 5 V DC | 0.01 A | 0.05 W |
| Environmental Sensor | 3 V DC | 2.3 A | 6.9 W |
| Total | 12 V DC | 1.4 A | 16.95 W |
Solar panels can power these systems, making them sustainable. AI can also help by adjusting lighting and climate controls, which can cut energy use by up to 15%. You get real-time alerts if something uses too much power.
You can track greenhouse gas emissions from your plantation in Malaysia using digital dashboards. These tools show you how much carbon dioxide your fields release each month. For example, new plantations may release more CO2 than mature ones. Over time, you can see if your efforts to reduce emissions are working.
You can compare emissions from different soil types. Plantations on peat soil can emit three times more CO2 than those on mineral soils. By monitoring these numbers, you can target areas for improvement and adopt greener practices.
| Statistical Evidence | Description | Statistical Result |
|---|---|---|
| Mean annual net emission (NEE) | Average yearly CO2 emission | 17.9 ± 1.3 Mg CO2-C ha−1 year−1 (65.6 ± 4.8 Mg CO2 ha−1 year−1) |
| Net annual emission from peat plantation | Peat vs mineral soils | 36.4 Mg CO2 ha−1 year−1 on peat, three times higher than mineral soils |
You can use your dashboard to manage each block of your plantation in Malaysia. The dashboard shows you the status of every field, including crop health, soil moisture, and yield. You can see which blocks need more water or fertilizer. This helps you use resources wisely and avoid waste.
Digital dashboards make a big difference. Farms using dashboards have reduced irrigation by up to 59% and fertilizer use by over 30% in some crops. Here is a table comparing farms with and without digital dashboards:
| Crop Type | Farms Using Dashboard | Farms Not Using Dashboard | Reduction in Irrigation | Reduction in Fertilizer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olive | 5 | 5 | 59% | 31.4% |
| Potato | 4 | 4 | 27% | Decrease in 3 of 4 types |
With a plantation management dashboard, you can make smarter choices, save money, and protect the environment of Malaysia.
Plantation management shapes the future of agriculture. You can boost productivity, protect the environment, and support communities in Malaysia with smart decisions.
You have the power to make a difference with every choice you make.
Click the banner below to experience FineReport for free and empower your enterprise to convert data into productivity!

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles
What is a data management platform in 2025
A data management platform in 2025 centralizes, organizes, and activates business data, enabling smarter decisions and real-time insights across industries.
Howard
Dec 22, 2025

Top 10 Database Management Tools for 2025
See the top 10 database management tools for 2025, comparing features, security, and scalability to help you choose the right solution for your business.
Howard
Dec 17, 2025

Best Data Lake Vendors For Enterprise Needs
Compare top data lake vendors for enterprise needs. See which platforms offer the best scalability, integration, and security for your business.
Howard
Dec 07, 2025