Data preservation ensures that your data remains accessible and intact over time. In today's digital age, its importance has skyrocketed. With 75% of organizations experiencing ransomware attacks and 68% of breaches involving human error, safeguarding data is crucial. Data preservation not only protects against these threats but also supports compliance and operational continuity. Tools like FineDataLink and FineBI play a pivotal role in this process by offering real-time data synchronization and insightful analysis. This blog aims to shed light on why preserving data is essential for your organization.
Understanding Data Preservation
Definition and Scope of Data Preservation
What is Data Preservation?
Data preservation involves maintaining and safeguarding your data for long-term access. This practice ensures that your data remains usable and intact for future needs. You might think of it as a digital time capsule, keeping your information safe and accessible over the years. The goal is to protect data integrity and usability, allowing you to retrieve and use it whenever necessary.
Scope of Data Preservation
The scope of data preservation extends beyond just storing data. It encompasses a series of managed activities designed to ensure continued stability and access to your data. This includes implementing measures to avoid data corruption and unauthorized modification. You need to consider various factors such as data format, storage medium, and access protocols. By doing so, you ensure that your data remains reliable and accessible, even decades after its creation.
Historical Context of Data Preservation
Evolution of Data Preservation
Data preservation has evolved significantly over the years. In the early days, Fritz Pfleumer invented magnetic tape, which allowed data to be stored magnetically. This invention became widely used for data storage and backup systems. As technology advanced, so did the methods of preserving data. Today, digital archives and storage capacities have grown tremendously. For instance, LTO-9 tape can store 24 TB natively, enabling larger digital archives to preserve human knowledge and experience.
Key Milestones in Data Preservation
Several key milestones have marked the journey of data preservation. The invention of magnetic tape was a significant breakthrough, providing a reliable method for data storage. Over time, the development of effective data preservation processes has become crucial. These processes involve a well-defined, defensible, and balanced approach, including legal hold, collection, forensics, and evidence management. Each milestone has contributed to the robust data preservation practices we rely on today.
Importance of Data Preservation
Data preservation plays a crucial role in various aspects of modern life. It ensures that your data remains accessible and intact over time, supporting legal, business, and cultural needs.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Data Preservation in Legal Contexts
In legal contexts, data preservation is essential. You must maintain and safeguard electronically stored information (ESI) for potential discovery during litigation. This process involves keeping data intact to prevent it from being destroyed, deleted, or altered. By preserving data, you ensure that potential evidence remains available for legal proceedings. This practice helps uphold justice by providing accurate and reliable information.
Regulatory Requirements
Compliance with data protection laws and regulations is a fundamental responsibility. Laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) protect individuals' data rights. You must adhere to these regulations to avoid legal penalties and maintain trust with stakeholders. Data preservation supports compliance by ensuring that data remains secure and accessible, meeting legal obligations and protecting individuals' privacy.
Business and Operational Continuity
Role in Business Operations
Data preservation is vital for business operations. It ensures that your organization can access critical information when needed. By maintaining data integrity, you support decision-making processes and operational efficiency. Data preservation helps you avoid disruptions caused by data loss or corruption, allowing your business to function smoothly.
Impact on Business Continuity
Preserving data impacts business continuity significantly. In the event of a disaster or system failure, you need access to reliable data to resume operations quickly. Data preservation provides a safety net, ensuring that your business can recover and continue serving customers. By safeguarding data, you protect your organization's reputation and financial stability.
Cultural and Historical Significance
Preserving Cultural Heritage
Data preservation holds cultural significance by safeguarding valuable information for future generations. You play a role in preserving cultural heritage by maintaining access to historical documents, artworks, and other cultural artifacts. This practice ensures that future generations can learn from and appreciate the past.
Historical Data Preservation
Historical data preservation involves maintaining records and data for research and documentation purposes. By preserving historical data, you contribute to the understanding of past events and trends. This practice supports academic research and helps society learn from history, shaping a better future.
Methods of Data Preservation

In today's digital landscape, preserving data is crucial for ensuring its longevity and accessibility. You can employ various methods to achieve effective data preservation. These methods encompass both digital and physical techniques, each offering unique benefits.
Digital Preservation Techniques
Digital preservation involves strategies that maintain the integrity and accessibility of electronic data over time. Here are some key techniques: digital preservation techniques
Data Backup Strategies
Data backup serves as a fundamental component of digital preservation. By regularly creating copies of your data, you safeguard against potential loss due to hardware failures, cyberattacks, or accidental deletions. Implementing a robust backup strategy involves:
- Regular Backups: Schedule frequent backups to ensure that you capture the most recent data changes.
- Multiple Locations: Store backups in different physical or cloud locations to protect against localized disasters.
- Automated Systems: Use automated backup systems to minimize human error and ensure consistency.
These strategies help maintain data integrity and provide a safety net in case of data loss.
Use of Cloud Storage
Cloud storage offers a modern solution for data preservation. By leveraging cloud services, you can store vast amounts of data securely and access it from anywhere. Key advantages include:
- Scalability: Easily adjust storage capacity based on your needs without investing in physical infrastructure.
- Redundancy: Benefit from built-in redundancy features that cloud providers offer, ensuring data availability even if one server fails.
- Accessibility: Access your data from any device with an internet connection, facilitating collaboration and remote work.
Cloud storage not only enhances data preservation but also streamlines data management processes.
Physical Preservation Methods
While digital methods are essential, physical preservation remains relevant for certain types of data. These methods focus on maintaining tangible records and converting them into digital formats.
Archiving Physical Records
Archiving involves organizing and storing physical documents in a way that ensures their longevity. To effectively archive physical records, consider:
- Controlled Environment: Store documents in a climate-controlled environment to prevent deterioration.
- Proper Labeling: Use clear labeling and indexing systems to facilitate easy retrieval.
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic audits to assess the condition of archived materials and address any preservation needs.
Archiving physical records preserves valuable information and supports legal and historical documentation.
Conversion to Digital Formats
Converting physical records into digital formats enhances accessibility and preservation. This process involves:
- Scanning and Digitization: Use high-quality scanners to create digital copies of physical documents.
- Metadata Creation: Add descriptive metadata to digital files to improve searchability and context.
- Secure Storage: Store digital files in secure databases or cloud storage solutions to protect against data loss.
By digitizing physical records, you ensure their preservation and make them easily accessible for future use.
Challenges in Data Preservation
Data preservation presents several challenges that you must navigate to ensure the longevity and accessibility of your data. These challenges often stem from technological limitations and financial constraints.
Technological Challenges
Obsolescence of Technology
Technology evolves rapidly, and this can pose a significant challenge for data preservation. You may find that the hardware or software used to store data becomes obsolete over time. For instance, older storage media like floppy disks or magnetic tapes may no longer be supported by modern systems. To combat this, you should regularly update your storage solutions and migrate data to current formats. This proactive approach helps maintain access to your data as technology advances.
Data Format Challenges
Data formats also change, which can affect your ability to access preserved data. Some formats may become outdated, making it difficult to retrieve or use the data stored in them. You should adopt widely accepted and open formats for data storage. This strategy ensures compatibility with future technologies and reduces the risk of data becoming inaccessible. Regularly reviewing and updating data formats can help you avoid these challenges.
Data formats also change, which can affect your ability to access preserved data. Some formats may become outdated, making it difficult to retrieve or use the data stored in them. You should adopt widely accepted and open formats for data storage. This strategy ensures compatibility with future technologies and reduces the risk of data becoming inaccessible. Regularly reviewing and updating data formats can help you avoid these challenges.
Financial and Resource Constraints
Cost of Data Preservation
Preserving data can be costly. You need to invest in storage solutions, backup systems, and regular maintenance. Cloud storage offers a scalable option, but pricing varies based on factors like storage capacity and additional services. You should carefully evaluate your needs and choose a cost-effective solution that balances budget constraints with data preservation requirements. By doing so, you can manage expenses while ensuring data security.
Resource Allocation
Effective data preservation requires adequate resources, including personnel and technology. You may face challenges in allocating these resources, especially if your organization has limited budgets or competing priorities. Prioritizing data preservation in your resource planning can help address this issue. You should allocate sufficient resources to maintain and update data storage systems, ensuring that your data remains accessible and secure over time.
Best Practices for Data Preservation
To ensure your data remains accessible and intact over time, you should adopt best practices for data preservation. These practices help maintain data integrity and usability, allowing you to retrieve and use your data whenever necessary.
Developing a Data Preservation Plan
Creating a comprehensive data preservation plan is essential for safeguarding your data. This plan outlines the strategies and actions you will take to preserve your data effectively.
Key Components of a Preservation Plan
- Data Assessment: Identify the types of data you need to preserve and their importance. This helps prioritize resources and efforts.
- Durable Formats: Store your data in formats that are less likely to become obsolete. This ensures long-term accessibility.
- Multiple Locations: Secure your data in various locations to protect against loss from localized disasters.
- Encryption: Use encryption to safeguard your data from unauthorized access.
- Regular Backups: Schedule frequent backups to capture the most recent data changes and prevent data loss.
- Data Repositories: Utilize data repositories for long-term preservation, ensuring data remains accessible over time.
Implementation Strategies
- In-Place Preservation: Preserve data in its original location to prevent accidental deletion. This strategy maintains data integrity and ensures easy access.
- Release Holds: Avoid indefinite data preservation by releasing holds when they are no longer necessary. This allows you to resume normal operations and manage data efficiently.
- Scheduled Data Destruction: Implement a schedule for data destruction to manage storage space and reduce costs. This practice ensures that only relevant data is preserved.
Regular Audits and Updates
Conducting regular audits and updates is crucial for maintaining the effectiveness of your data preservation efforts.
Importance of Regular Audits
Regular audits help you assess the condition of your preserved data and identify any potential issues. By conducting audits, you can:
- Ensure data integrity and accuracy.
- Verify compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
- Identify outdated formats or storage solutions that need updating.
Updating Preservation Methods
As technology evolves, you must update your preservation methods to keep pace. Consider the following strategies:
- Migrate Data: Regularly migrate data to current formats and storage solutions to maintain accessibility.
- Review Formats: Adopt widely accepted and open formats to ensure compatibility with future technologies.
- Enhance Security: Update encryption and security measures to protect against emerging threats.
By following these best practices, you can effectively preserve your data and ensure its long-term accessibility and usability.
Role of FanRuan in Data Preservation
In the realm of data preservation, FanRuan stands out with its innovative tools designed to maintain data integrity and accessibility. By leveraging advanced technologies, FanRuan ensures that your data remains secure and usable over time.
FineDataLink for Data Integration
FineDataLink plays a pivotal role in data integration, offering solutions that enhance data preservation efforts.
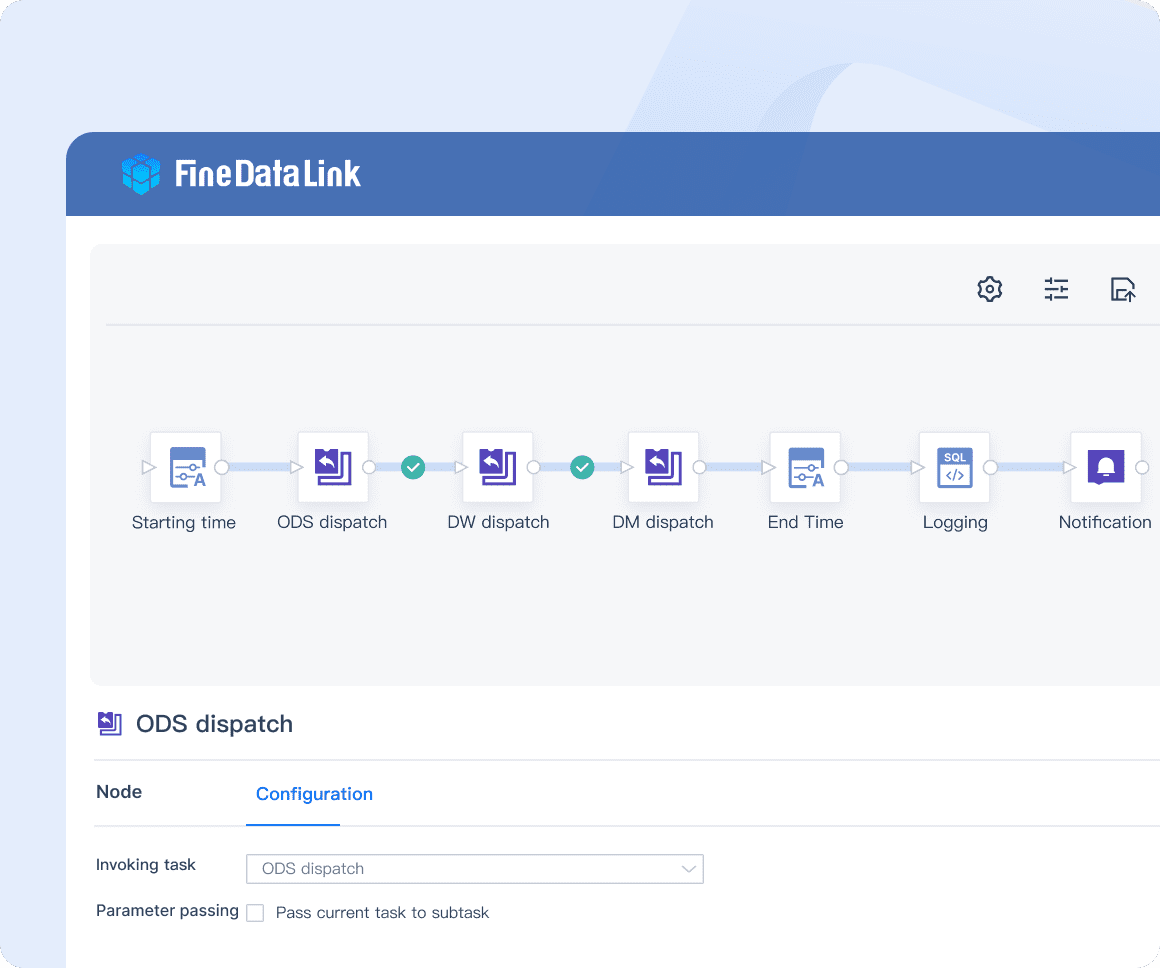
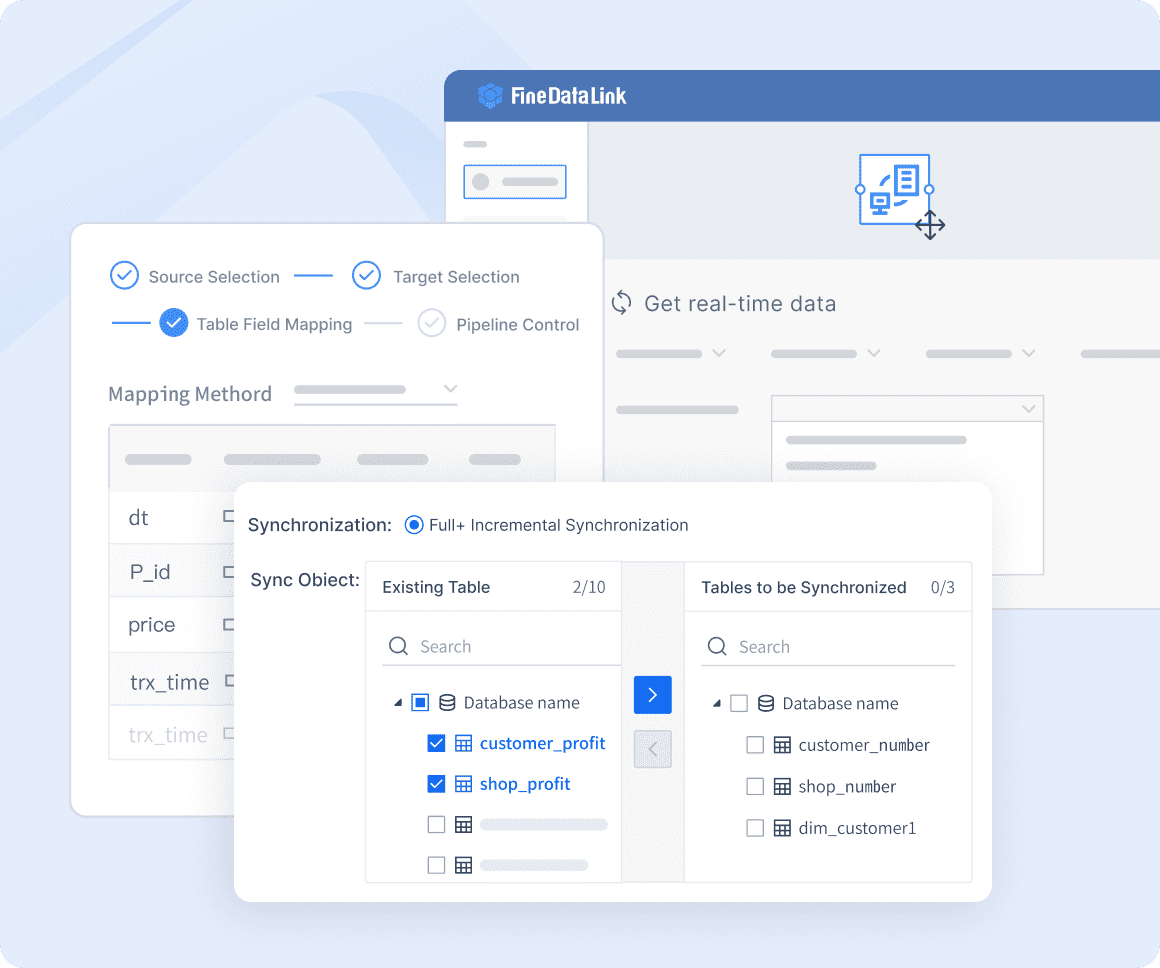
Real-time Data Synchronization
With FineDataLink, you achieve real-time data synchronization. This feature ensures that your data is consistently updated across multiple systems. By minimizing latency, you reduce the risk of data loss or inconsistencies. Real-time synchronization keeps your data current and reliable, which is crucial for effective data management.
ETL/ELT Capabilities
FineDataLink also excels in ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) capabilities. These processes allow you to efficiently transform and load data into data warehouses. By doing so, you support long-term data storage and accessibility. FineDataLink simplifies complex data integration tasks, making it easier for you to manage and preserve your data.
FineBI for Data Analysis
FineBI complements data preservation by transforming raw data into actionable insights.
Transforming Data into Insights
FineBI empowers you to analyze and visualize data effectively. By connecting to various data sources, FineBI enables you to create insightful visualizations. These visualizations help you track key performance indicators (KPIs) and identify trends. By transforming data into insights, FineBI enhances your understanding of data, supporting informed decision-making.
Supporting Decision-Making
FineBI supports decision-making by providing real-time data analysis. With its high-performance computing engine, FineBI processes large datasets quickly. This capability allows you to conduct analysis instantly after data updates. By offering timely insights, FineBI helps you make informed decisions, which is essential for dynamic business environments.
Future of Data Preservation

The future of data preservation promises exciting advancements and challenges. As technology evolves, new methods and tools will emerge to ensure data remains accessible and secure.
Emerging Technologies
Role of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming data preservation. These technologies automate data management tasks, making it easier for you to maintain data integrity. AI can predict potential data loss scenarios and suggest preventive measures. ML algorithms analyze data patterns, helping you identify anomalies and ensure data accuracy. By leveraging AI and ML, you enhance your ability to preserve data effectively.
Blockchain in Data Preservation
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized approach to data preservation. It provides a secure and transparent way to store data, ensuring its authenticity. Each data entry in a blockchain is immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or deleted. This feature makes blockchain an ideal solution for preserving sensitive information. By adopting blockchain, you can enhance data security and trustworthiness.
Trends and Predictions
Future Trends in Data Preservation
Several trends are shaping the future of data preservation. The increasing volume of data requires scalable storage solutions. Cloud storage continues to grow in popularity due to its flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, the rise of remote work necessitates robust data preservation strategies to ensure accessibility from anywhere. You must stay informed about these trends to adapt your data preservation practices accordingly.
Predictions for the Next Decade
In the next decade, data preservation will become more integrated with everyday business operations. You will likely see a shift towards more automated and intelligent systems that require minimal human intervention. The focus will be on enhancing data accessibility while maintaining security. As data ethics gain importance, you will need to ensure compliance with evolving regulations. By preparing for these changes, you can position yourself to effectively manage and preserve data in the future.
Actionable Data Preservation Steps for Organizations
Implementing Data Preservation Strategies
To effectively preserve your organization's data, you must implement robust strategies. These strategies ensure that your data remains secure and accessible over time.
Steps to Begin Data Preservation
- Assess Your Data Needs: Identify the types of data you need to preserve. Determine their importance and prioritize them accordingly. This step helps you allocate resources efficiently.
- Develop a Preservation Plan: Create a comprehensive plan that outlines your data preservation goals and methods. Include details on storage solutions, backup schedules, and security measures.
- Choose the Right Tools: Select tools and technologies that align with your preservation needs. Consider solutions like FineDataLink for real-time data synchronization and FineBI for insightful data analysis.
- Implement Storage Solutions: Use a combination of cloud and physical storage to safeguard your data. Ensure that your storage solutions are scalable and secure.
- Regularly Backup Data: Schedule frequent backups to capture the latest data changes. Store backups in multiple locations to protect against data loss from localized disasters.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Continuously monitor your data preservation efforts. Evaluate the effectiveness of your strategies and make necessary adjustments to improve data security and accessibility.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Monitoring and evaluation play a crucial role in maintaining effective data preservation. Regularly review your data preservation processes to ensure they meet your organization's needs. Conduct audits to verify data integrity and compliance with legal requirements. By doing so, you can identify potential issues and address them promptly, ensuring your data remains reliable and accessible.
Educating Stakeholders
Educating stakeholders about data preservation is essential for fostering a culture of data security and responsibility within your organization.
Importance of Stakeholder Education
Educating stakeholders ensures that everyone understands the significance of data preservation. It empowers them to take proactive steps in safeguarding data. By raising awareness, you reduce the risk of data breaches and enhance overall data security.
Methods to Educate and Engage
- Workshops and Training Sessions: Organize workshops and training sessions to educate stakeholders about data preservation practices. Provide hands-on experience with tools and technologies used in data preservation.
- Informative Materials: Distribute informative materials such as brochures, guides, and videos. These resources help stakeholders understand data preservation concepts and best practices.
- Regular Updates: Keep stakeholders informed about updates in data preservation strategies and technologies. Share success stories and case studies to demonstrate the impact of effective data preservation.
- Engagement Activities: Encourage stakeholder engagement through interactive activities. Use quizzes, discussions, and feedback sessions to reinforce learning and gather insights.
By implementing these methods, you create an informed and engaged workforce that actively contributes to data preservation efforts.
Data preservation is crucial for maintaining the integrity and accessibility of your information. You must prioritize it to protect against data loss and ensure compliance with regulations. By adopting best practices, you safeguard your data for future use. Consider implementing strategies like regular backups and using secure storage solutions. Educate your team on the importance of data preservation to foster a culture of responsibility. Your commitment to these practices will enhance data security and support long-term success.
FAQ
Data preservation involves maintaining access to your data over time. It ensures that your information remains usable and intact for future needs. Think of it as a digital time capsule, safeguarding your data for years to come.
Data preservation is crucial for several reasons. It supports research, historical documentation, legal purposes, and compliance with regulations. By preserving data, you ensure that valuable information remains available for future use.
In legal contexts, data preservation ensures that electronically stored information (ESI) remains intact for potential discovery during litigation. Compliance with data protection laws, like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), requires you to maintain secure and accessible data.
Effective data preservation involves both digital and physical techniques. Digital methods include data backup strategies and cloud storage. Physical methods involve archiving records and converting them to digital formats. Each method offers unique benefits for maintaining data integrity.
Organizations often encounter technological and financial challenges. Rapid technological changes can render storage media obsolete. Financial constraints may limit resources for effective data preservation. Addressing these challenges requires strategic planning and resource allocation.
A comprehensive data preservation plan includes assessing your data needs, choosing durable formats, securing data in multiple locations, and scheduling regular backups. Implementing encryption and utilizing data repositories also enhance data security and accessibility.
Educating stakeholders about data preservation fosters a culture of data security and responsibility. Workshops, training sessions, and informative materials help stakeholders understand best practices and contribute to data preservation efforts.
Continue Reading About Data Preservation
2025 Best Data Integration Solutions and Selection Guide
Explore top data integration solutions for 2025, enhancing data management and operational efficiency with leading platforms like Fivetran and Talend.
Howard
Dec 19, 2024
2025's Best Data Validation Tools: Top 7 Picks
Explore the top 7 data validation tools of 2025, featuring key features, benefits, user experiences, and pricing to ensure accurate and reliable data.
Howard
Aug 09, 2024
Best Data Integration Vendors for Seamless Workflows
Discover the top 20 data integration vendors of 2025 for seamless workflows. Compare tools like Talend, AWS Glue, and Fivetran to optimize your data processes.
Howard
Jan 22, 2025
Best Data Integration Platforms to Use in 2025
Explore the best data integration platforms for 2025, including cloud-based, on-premises, and hybrid solutions. Learn about key features, benefits, and top players.
Howard
Jun 20, 2024
Customer Data Integration: A Comprehensive Guide
Master customer data integration to enhance business operations by combining data from multiple sources for a comprehensive customer view.
Howard
Sep 07, 2024
Data Analysis vs Data Analytics: What’s the Real Difference?
Data Analysis vs Data Analytics: What’s the Difference? Discover How One Interprets History While the Other Shapes Tomorrow. Explore Here!
Lewis
Mar 10, 2025