Data ownership refers to the responsibility and control over data within an organization. You must understand its importance because it ensures data accuracy, reliability, and security. By prioritizing data ownership, you can achieve higher-quality data, allocate more time for impactful tasks, and foster better collaboration across teams. This concept plays a crucial role in data governance, providing accountability and controlled access to data. In various sectors, tools like FineDataLink, FineReport, and FineBI empower organizations to manage data effectively, ensuring that you derive maximum value from your data assets.
Defining Data Ownership
Legal Aspects of Data Ownership
Understanding the legal aspects of data ownership is crucial for ensuring compliance and protecting your rights. Laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) define specific guidelines and restrictions regarding data ownership rights. These laws emphasize the importance of consent, access, erasure, and withdrawal. By adhering to these regulations, you can ensure the safety and protection of data as a valuable asset.
Rights and Responsibilities
As a data owner, you hold certain rights and responsibilities. You have the authority to control who accesses your data and how it is used. This control empowers you to make informed decisions about your data. However, with these rights come responsibilities. You must ensure that your data is accurate, secure, and used ethically. This balance between rights and responsibilities fosters transparency and privacy rights.
Ownership vs. Custodianship
Data ownership and custodianship are often confused, but they have distinct roles. As a data owner, you possess the legal rights to your data. You decide how it is used and who can access it. In contrast, a data custodian manages and safeguards the data on your behalf. Understanding this distinction helps you maintain control over your data while ensuring its security and integrity.
Technical Aspects of Data Ownership
The technical aspects of data ownership focus on how you access and control your data. These aspects are essential for maintaining data integrity and ensuring that you can use your data effectively.
Data Access and Control
Data access and control are fundamental components of data ownership. You need to have the ability to access your data whenever necessary. This access allows you to make timely decisions and respond to changes in your environment. Control over your data ensures that only authorized individuals can view or modify it. By maintaining strict access controls, you can protect your data from unauthorized use or breaches.
Data Portability
Data portability is another critical aspect of data ownership. It refers to your ability to transfer your data from one system to another without losing its integrity. This capability is vital for ensuring that you can use your data across different platforms and applications. By prioritizing data portability, you can enhance your data's usability and maximize its value.
Historical Context of Data Ownership
Evolution of Data Ownership
Pre-digital Era
In the pre-digital era, data ownership was a straightforward concept. You could easily identify who owned physical records like books, ledgers, and documents. These tangible items were stored in libraries, offices, or homes. The owner had complete control over access and usage. This period emphasized the importance of safeguarding physical data from theft or damage.
Digital Transformation
The digital transformation revolutionized data ownership. With the advent of computers and the internet, data became intangible. You now store information in digital formats, making it easier to share and access. This shift introduced new challenges in defining ownership. As data moved online, questions arose about who truly owns digital information. The transformation also brought about the need for new laws and regulations to protect digital data.
Key Milestones of Data Ownership
Legislation and Policies
Legislation and policies have played a crucial role in shaping data ownership. Laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) have set clear guidelines on data rights and responsibilities. These regulations emphasize the importance of consent and transparency. They ensure that you, as a data owner, have control over your personal information. Such policies have unified different understandings of data ownership, calling for various modes to control data usage.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements have significantly impacted data ownership. New and advanced machines have entered the scene, changing how you manage and control data. Innovations like cloud computing and blockchain technology offer new ways to store and secure data. These technologies provide you with more control and flexibility over your data. However, they also raise questions about compatibility with existing legal frameworks. As technology evolves, so does the debate on how best to protect and manage data ownership.
Practical Implications of Data Ownership

Business Operations
Data ownership plays a pivotal role in shaping business operations. By understanding and leveraging your data, you can drive significant improvements in decision-making and gain a competitive edge.
Data-driven Decision Making
Data-driven decision-making empowers you to make informed choices based on accurate and reliable data. When you own your data, you have the authority to analyze it and extract valuable insights. This process allows you to identify trends, forecast outcomes, and make strategic decisions that align with your business goals. For instance, by analyzing customer data, you can tailor marketing strategies to target specific demographics, ultimately increasing sales and customer satisfaction.
Competitive Advantage
Owning your data provides a competitive advantage in the marketplace. With exclusive access to your data, you can develop unique products or services that set you apart from competitors. Additionally, data ownership enables you to protect proprietary information, ensuring that your innovations remain confidential. By safeguarding your data, you maintain control over your intellectual property and prevent unauthorized use by competitors.
Consumer Privacy
Data ownership also has significant implications for consumer privacy. As a data owner, you have the responsibility to protect consumer information and ensure transparency in data usage.
Data Protection
Data protection is a critical aspect of data ownership. You must implement robust security measures to safeguard consumer data from breaches and unauthorized access. This responsibility includes encrypting sensitive information, regularly updating security protocols, and conducting audits to identify vulnerabilities. By prioritizing data protection, you build trust with consumers and demonstrate your commitment to their privacy.
Consent and Transparency
Consent and transparency are essential components of ethical data ownership. You must obtain explicit consent from consumers before collecting or using their data. This process involves clearly communicating how you will use their information and providing options for them to opt-out if desired. Transparency in data practices fosters trust and ensures that consumers feel confident in sharing their information with you. By adhering to these principles, you uphold consumer rights and promote ethical data management practices.
Regulatory Aspects of Data Ownership
Understanding the regulatory aspects of data ownership is crucial for ensuring compliance and protecting your rights. Various global and industry-specific regulations govern how you manage and protect data. These regulations provide a framework for data governance, ensuring that you handle data responsibly and ethically.
Global Regulations
GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive data protection law that applies to all organizations operating within the European Union (EU) and those handling the data of EU citizens. GDPR defines clear guidelines on data ownership rights and responsibilities. It emphasizes the importance of consent, access, erasure, and withdrawal of data. By adhering to GDPR, you ensure that your data practices align with international standards, protecting both your organization and your customers.
GDPR requires you to implement robust data protection measures, such as encrypting sensitive information and conducting regular audits. These measures help safeguard data from breaches and unauthorized access, building trust with your customers and demonstrating your commitment to their privacy.
CCPA
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is another significant regulation that impacts data ownership. It focuses on protecting personal information and online data of California residents. CCPA requires you to maintain a secure data inventory, respond to consumer requests, and disclose a data privacy policy. By complying with CCPA, you ensure that your data practices are transparent and that consumers have control over their personal information.
CCPA emphasizes the importance of obtaining explicit consent from consumers before collecting or using their data. This regulation fosters transparency and ensures that consumers feel confident in sharing their information with you. By adhering to CCPA, you uphold consumer rights and promote ethical data management practices.
Industry-specific Regulations
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, data ownership is governed by specific regulations that prioritize patient privacy and data security. Laws like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) set strict guidelines on how you handle patient data. These regulations require you to implement robust security measures, such as encrypting sensitive information and conducting regular audits, to protect patient data from breaches and unauthorized access.
By complying with healthcare regulations, you ensure that your data practices align with industry standards, protecting both your organization and your patients. These regulations also emphasize the importance of obtaining explicit consent from patients before collecting or using their data, fostering transparency and trust.
Finance
In the finance industry, data ownership is governed by regulations that prioritize data security and consumer protection. Laws like the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) set strict guidelines on how you handle financial data. These regulations require you to implement robust security measures, such as encrypting sensitive information and conducting regular audits, to protect financial data from breaches and unauthorized access.
By complying with finance regulations, you ensure that your data practices align with industry standards, protecting both your organization and your customers. These regulations also emphasize the importance of obtaining explicit consent from consumers before collecting or using their data, fostering transparency and trust.
Importance of Data Ownership
Understanding data ownership is crucial for maintaining control over your data and ensuring its security and ethical use. By recognizing the importance of data ownership, you can protect your data from breaches, manage risks effectively, and uphold ethical standards in data management.
Security Concerns
Data ownership plays a vital role in addressing security concerns. When you own your data, you have the authority to implement measures that protect it from unauthorized access and breaches.
Data Breaches
Data breaches pose a significant threat to your data's security. As a data owner, you must take proactive steps to prevent breaches. Implementing strong security protocols, such as encryption and regular audits, helps safeguard your data. By doing so, you protect sensitive information and maintain the trust of your stakeholders.
Risk Management
Effective risk management is essential for data ownership. You need to identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them. This involves assessing vulnerabilities, implementing security measures, and regularly reviewing your data protection practices. By managing risks effectively, you ensure the integrity and reliability of your data.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are integral to data ownership. You have a responsibility to use your data ethically and ensure that it aligns with legal and moral standards.
Data Ethics
Data ethics involves understanding the value of your data and using it responsibly. You must consider the impact of your data practices on individuals and society. This includes respecting privacy rights, obtaining consent, and being transparent about data usage. By adhering to data ethics, you promote trust and accountability in your data management practices.
Fair Use
Fair use is a key aspect of ethical data ownership. You must ensure that your data usage complies with legal and ethical guidelines. This involves using data for its intended purpose and avoiding misuse or exploitation. By practicing fair use, you uphold the rights of individuals and contribute to a fair and just data ecosystem.
Challenges in Data Ownership

Data ownership presents several challenges that you must navigate to ensure effective data management. These challenges can impact your ability to maintain control over your data and protect it from misuse.
Data Misuse
Data misuse occurs when individuals or entities use data in ways that violate ethical standards or legal guidelines. This misuse can compromise the integrity of your data and lead to significant consequences.
Unauthorized Access
Unauthorized access happens when individuals gain entry to your data without permission. This breach can result in the exposure of sensitive information, leading to privacy violations and potential financial losses. You must implement strong security measures to prevent unauthorized access. Regular audits and encryption can help safeguard your data and maintain its confidentiality.
Data Manipulation
Data manipulation involves altering data to misrepresent information or achieve unauthorized outcomes. This manipulation can undermine the accuracy and reliability of your data, affecting decision-making processes. To combat data manipulation, you should establish strict data governance policies and conduct regular checks to ensure data integrity.
Ownership Disputes
Ownership disputes arise when multiple parties claim rights to the same data. These disputes can lead to conflicts and hinder your ability to manage data effectively.
Intellectual Property
Intellectual property disputes occur when parties disagree over the ownership of data-related innovations or creations. These disputes can result in legal battles and loss of control over valuable data assets. To avoid such conflicts, you should clearly define ownership rights and responsibilities in contracts and agreements.
Shared Data
Shared data ownership presents challenges in tracking and managing data rights. When multiple parties own data, it becomes difficult to determine who has control and authority over its use. You must establish clear guidelines for shared data ownership to ensure that all parties understand their rights and responsibilities. This clarity helps prevent conflicts and promotes collaborative data management.
By addressing these challenges, you can enhance your data management practices and protect your data from misuse and disputes.
Future Directions in Data Ownership
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies are reshaping the landscape of data ownership. They offer new opportunities and challenges for managing and securing data.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology revolutionizes data ownership by enhancing the efficiency, security, and privacy of data transactions. It creates a decentralized environment where you can securely trade data without relying on centralized authorities. This decentralization ensures that your data remains tamper-proof and transparent. However, blockchain also presents challenges, such as ambiguous data ownership and data integrity issues. You must navigate these challenges to fully leverage blockchain's potential in data management.
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming how you manage and analyze data. These technologies enable you to process vast amounts of data quickly and accurately. By using AI and ML, you can gain deeper insights into your data, identify patterns, and make informed decisions. However, the integration of AI and ML raises questions about data privacy and ownership. You need to ensure that your data practices align with ethical standards and protect individual rights.
Evolving Regulations
As technology evolves, so do the regulations governing data ownership. Staying informed about these changes is crucial for ensuring compliance and protecting your rights.
Anticipated Changes
Regulatory bodies worldwide are continuously updating data protection laws to address emerging challenges. You can expect new regulations that focus on enhancing data privacy and security. These changes may include stricter guidelines on data consent, access, and usage. By staying informed about anticipated changes, you can adapt your data practices to meet evolving legal requirements.
Global Harmonization
Global harmonization of data governance regulations aims to create a unified framework for data governance. This harmonization ensures that you can manage and protect data consistently across different jurisdictions. By aligning your data practices with global standards, you can facilitate cross-border data flows and enhance international collaboration. However, achieving global harmonization requires overcoming differences in legal systems and cultural perspectives on data ownership. You must engage in ongoing dialogue and cooperation to achieve this goal.
FanRuan's Role in Data Ownership
FanRuan plays a pivotal role in enhancing data ownership through its innovative products. By leveraging tools like FineDataLink, FineReport, and FineBI, you can effectively manage and utilize your data assets. These products empower you to integrate, visualize, and analyze data, ensuring that you derive maximum value from your data ownership.
FineDataLink and Data Integration
FineDataLink serves as a comprehensive data integration platform. It simplifies complex data tasks, allowing you to synchronize and transform data seamlessly.
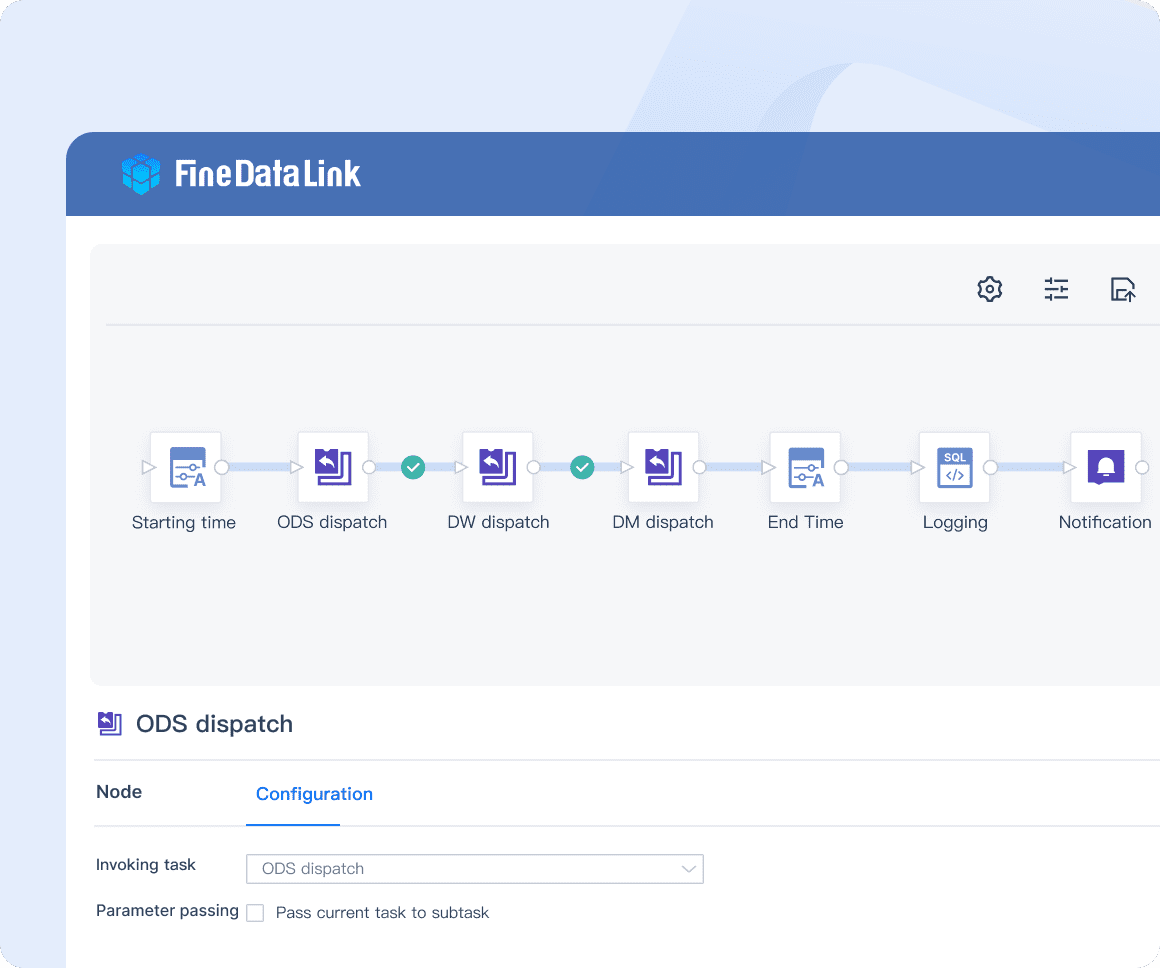
Real-time Data Synchronization
With FineDataLink, you can achieve real-time data synchronization. This feature ensures that your data remains up-to-date across various systems. By synchronizing data in real-time, you can make timely decisions and respond swiftly to changes in your environment. This capability is crucial for maintaining data accuracy and reliability.
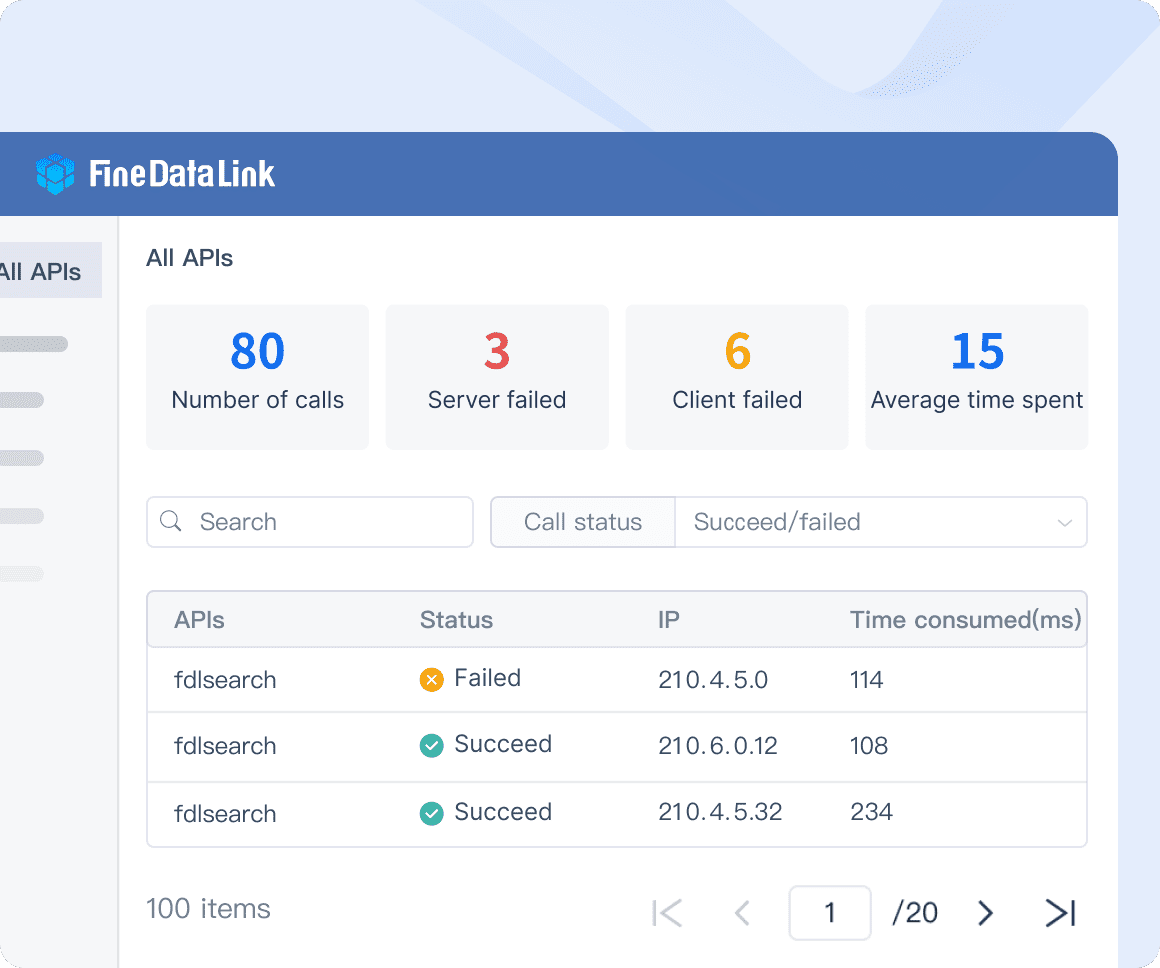
ETL/ELT Capabilities
FineDataLink also offers robust ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) capabilities. These features enable you to process large volumes of data efficiently. By utilizing ETL/ELT, you can transform raw data into actionable insights, enhancing your ability to make informed decisions. This process streamlines data management and improves overall operational efficiency.
FineReport and Data Reporting
FineReport is designed to enhance your data reporting capabilities. It allows you to create dynamic reports and dashboards, providing you with deeper insights into your data.
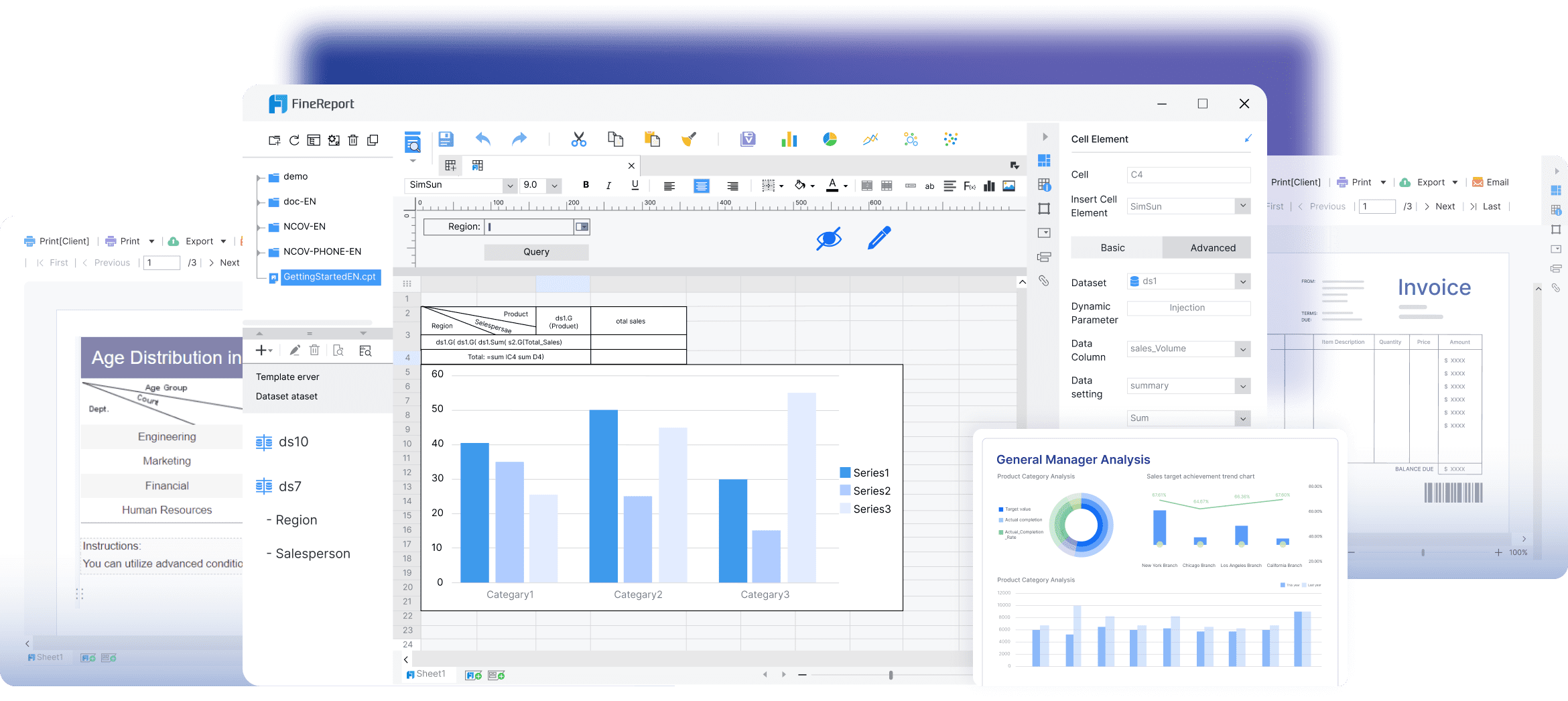
Data Visualization
Data visualization is a key feature of FineReport. It enables you to present data in a visually appealing and understandable format. By using diverse visualization types, you can uncover patterns and trends that might not be apparent in raw data. This feature helps you communicate complex information effectively, facilitating better decision-making.
Interactive Analysis
FineReport also supports interactive analysis. This feature allows you to engage with your data dynamically. You can explore different scenarios, drill down into details, and gain a comprehensive understanding of your data. Interactive analysis empowers you to identify opportunities and challenges, enabling you to make strategic decisions that drive growth.
Understanding data ownership is crucial for ensuring accountability and control over your information. It plays a vital role in data governance, helping you manage and secure your data assets effectively. Staying informed about data ownership allows you to navigate ownership rules and responsibilities, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. By applying best practices in data management, you can enhance data accuracy, reliability, and security. Embrace data ownership to establish trust and transparency within your organization, fostering a responsible data ecosystem that mitigates risks and safeguards valuable information.
FAQ
Data ownership refers to the legal rights and control over a particular set of data. It determines who has the authority to access, modify, share, and make decisions about the data. As a data owner, you hold the responsibility for ensuring the data's accuracy, security, and ethical use.
Data ownership is crucial because it ensures that you have control over your valuable data assets. This control allows you to drive strategic decisions, maintain data privacy and security, comply with regulations, and protect intellectual property. Proper data ownership helps you manage data effectively, avoid legal issues, and leverage data for competitive advantage.
Data ownership significantly impacts data integration processes. When different departments or systems own data, it often leads to data silos, making it challenging to access and integrate data from various sources. This fragmentation can complicate the process of transforming and synchronizing data, especially when dealing with diverse data formats. Effective data integration solutions must address these challenges by providing robust features for real-time synchronization and extensive connectivity options.
Organizations face several challenges regarding data ownership, including dealing with data silos, managing complex data formats, handling manual and time-consuming processes, lacking automation in data integration workflows, ensuring scalability and performance, integrating real-time data updates, and facing limited connectivity options to different data sources and systems.
Organizations can establish clear data ownership by implementing a robust data governance framework. This involves defining roles and responsibilities for data management, ensuring that data stewards and data governance teams are in place to oversee data quality and compliance. Clear policies and procedures should outline who is responsible for different data assets, how data should be handled, and the processes for data access and usage.
Data governance plays a crucial role in data ownership by establishing policies, procedures, and standards to ensure data is managed effectively and responsibly. It defines who within an organization has the authority and control over data assets, ensuring accountability and proper stewardship. This includes setting guidelines for data quality, security, privacy, and compliance, which helps in maintaining the integrity and reliability of data.
Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) define specific guidelines and restrictions regarding data ownership rights. These laws emphasize the importance of consent, access, erasure, and withdrawal. By adhering to these regulations, you can ensure the safety and protection of data as a valuable asset. They also influence global trends towards greater accountability in protecting consumer data.
Ethical considerations in data ownership involve understanding the value of your data and using it responsibly. You must consider the impact of your data practices on individuals and society. This includes respecting privacy rights, obtaining consent, and being transparent about data usage. By adhering to data ethics, you promote trust and accountability in your data management practices.
Continue Reading About Data Ownership
15 Best Software Reporting Tools for 2025
Explore the top 15 software reporting tools for 2025. Compare features, pricing, and usability to find the best fit for your business needs.
Lewis
Oct 08, 2024
2025's Best Data Validation Tools: Top 7 Picks
Explore the top 7 data validation tools of 2025, featuring key features, benefits, user experiences, and pricing to ensure accurate and reliable data.
Howard
Aug 09, 2024
2025 Data Pipeline Examples: Learn & Master with Ease!
Unlock 2025’s Data Pipeline Examples! Discover how they automate data flow, boost quality, and deliver real-time insights for smarter business decisions.
Howard
Feb 24, 2025
2025 Best Data Integration Solutions and Selection Guide
Explore top data integration solutions for 2025, enhancing data management and operational efficiency with leading platforms like Fivetran and Talend.
Howard
Dec 19, 2024
Best Data Integration Platforms to Use in 2025
Explore the best data integration platforms for 2025, including cloud-based, on-premises, and hybrid solutions. Learn about key features, benefits, and top players.
Howard
Jun 20, 2024
Best Data Integration Vendors for Seamless Workflows
Discover the top 20 data integration vendors of 2025 for seamless workflows. Compare tools like Talend, AWS Glue, and Fivetran to optimize your data processes.
Howard
Jan 22, 2025