

Financial Data Management involves using specialized software and algorithms to track financial information within organizations. Businesses today rely heavily on accurate data for decision-making. Effective management of financial data ensures consistency, accuracy, and reliability. Poor quality data can lead to increased costs and poor decisions. Proper Financial Data Management transforms disparate information into a strategic advantage. Every business benefits from managing financial data effectively.
Understanding Financial Data Management
Key Components of Financial Data Management
Data Collection
Financial data management begins with data collection. Organizations gather financial data from various sources, including transactions, invoices, and receipts. Automated systems streamline this process, reducing manual errors. Accurate data collection forms the foundation for reliable financial analysis.
Data Storage
Data storage is crucial for maintaining financial records. Modern applications use cloud solutions to store vast amounts of data securely. Cloud storage offers scalability and accessibility, ensuring data remains available for analysis. Legacy systems often lack these capabilities, leading to fragmented data storage.
Data Analysis
Data analysis transforms raw data into actionable insights. Financial data management employs advanced algorithms and software to analyze data trends. Predictive analytics helps organizations forecast future financial performance. This proactive approach enables better decision-making and risk management.
Types of Financial Data
Transactional Data
Transactional data includes all financial transactions within an organization. This data captures sales, purchases, and payments. Accurate transactional data is essential for financial reporting and auditing. Financial data management ensures this data remains consistent and reliable.
Historical Data
Historical data provides a record of past financial activities. Organizations use historical data to identify trends and patterns over time. Analyzing historical data helps in making informed business decisions. Effective financial data management maintains the integrity of this data for long-term analysis.
Market Data
Market data encompasses information about financial markets. This includes stock prices, interest rates, and economic indicators. Organizations rely on market data to make investment decisions. Financial data management integrates market data with internal financial information for comprehensive analysis.
Importance of Financial Data Management
Enhancing Decision-Making
Real-time Data Access
Real-time data access plays a crucial role in Financial Data Management. Organizations can make informed decisions by accessing up-to-date financial information. This immediate availability of data helps in tracking financial performance and identifying trends. Real-time data access reduces the risk of outdated or incorrect information influencing decisions.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics transforms how organizations approach decision-making. Financial Data Management uses advanced algorithms to analyze historical data and predict future outcomes. This proactive approach allows businesses to anticipate market trends and adjust strategies accordingly. Predictive analytics supports better risk management and enhances overall financial planning.
Regulatory Compliance
Financial Reporting Standards
Adhering to financial reporting standards is essential for any organization. Financial Data Management ensures that all financial records comply with established guidelines. Accurate and consistent data is necessary for producing reliable financial statements. Compliance with reporting standards helps maintain transparency and trust with stakeholders.
Data Privacy Laws
Data privacy laws protect sensitive financial information from unauthorized access. Financial Data Management includes measures to safeguard data integrity and confidentiality. Organizations must comply with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA to avoid legal penalties. Ensuring data privacy builds customer trust and enhances the organization's reputation.
Challenges in Financial Data Management
Data Quality Issues
Inaccurate Data
Inaccurate data poses a significant challenge in Financial Data Management. Errors in data entry, outdated information, and discrepancies can lead to incorrect financial reporting. Financial institutions must ensure data accuracy to comply with strict regulations. Dirty data makes it difficult to meet reporting requirements, potentially leading to hefty fines. Effective Financial Data Management requires regular audits and validation processes to maintain data integrity.
Incomplete Data
Incomplete data also hampers Financial Data Management. Missing information can skew analysis and lead to poor decision-making. Financial institutions need comprehensive data to generate accurate financial statements and forecasts. Data gaps can result from manual entry errors or system limitations. Implementing robust data collection methods and automated systems can help mitigate this issue. Ensuring completeness in financial data is crucial for reliable analysis and reporting.
Data Security Concerns
Cyber Threats
Cyber threats represent a major concern in Financial Data Management. Hackers target financial institutions to steal sensitive information. Cyber attacks can compromise data integrity and lead to significant financial losses. Financial institutions must implement strong cybersecurity measures to protect their data. Regular security assessments and updates are essential to defend against evolving threats. Financial Data Management must prioritize data security to safeguard valuable information.
Data Breaches
Data breaches pose a severe risk to Financial Data Management. Unauthorized access to financial data can result in identity theft and financial fraud. Data breaches damage an organization's reputation and erode customer trust. Financial institutions must comply with data privacy laws to protect sensitive information. Measures such as encryption, access controls, and monitoring systems can help prevent breaches. Ensuring data security is vital for maintaining customer confidence and regulatory compliance.
Best Practices for Effective Financial Data Management
Implementing Robust Data Governance
Data Policies
Organizations must establish clear data policies to ensure effective Financial Data Management. These policies define how financial data should be collected, stored, and analyzed. A strong data governance framework ensures data quality and accessibility. Regular audits and data validation processes maintain the accuracy and consistency of data. Data policies also help in complying with regulatory requirements.
Data Stewardship
Data stewardship involves assigning specific roles and responsibilities for managing financial data. The people responsible for data within an organization need to be clearly identified. These individuals must possess the necessary knowledge and skills to manage data effectively. Data stewards ensure that data policies are followed throughout the process chain. This role is crucial for maintaining data integrity and security.
Leveraging Technology
Financial Management Software
Financial management software plays a vital role in Financial Data Management. These tools automate data collection, storage, and analysis processes. Automation reduces manual errors and enhances data accuracy. Financial management software provides real-time data access, enabling better decision-making. Organizations can use these tools to generate accurate financial reports and forecasts.
Cloud Solutions
Cloud solutions offer scalable and secure storage options for financial data. Cloud storage ensures that data remains accessible and available for analysis. Organizations can leverage cloud solutions to integrate various data sources seamlessly. This integration helps in creating a comprehensive view of financial performance. Cloud solutions also provide advanced security features to protect sensitive financial information.
Practical Applications and Benefits of Financial Data Management
Case Studies of Financial Data Management
Successful Implementation Examples
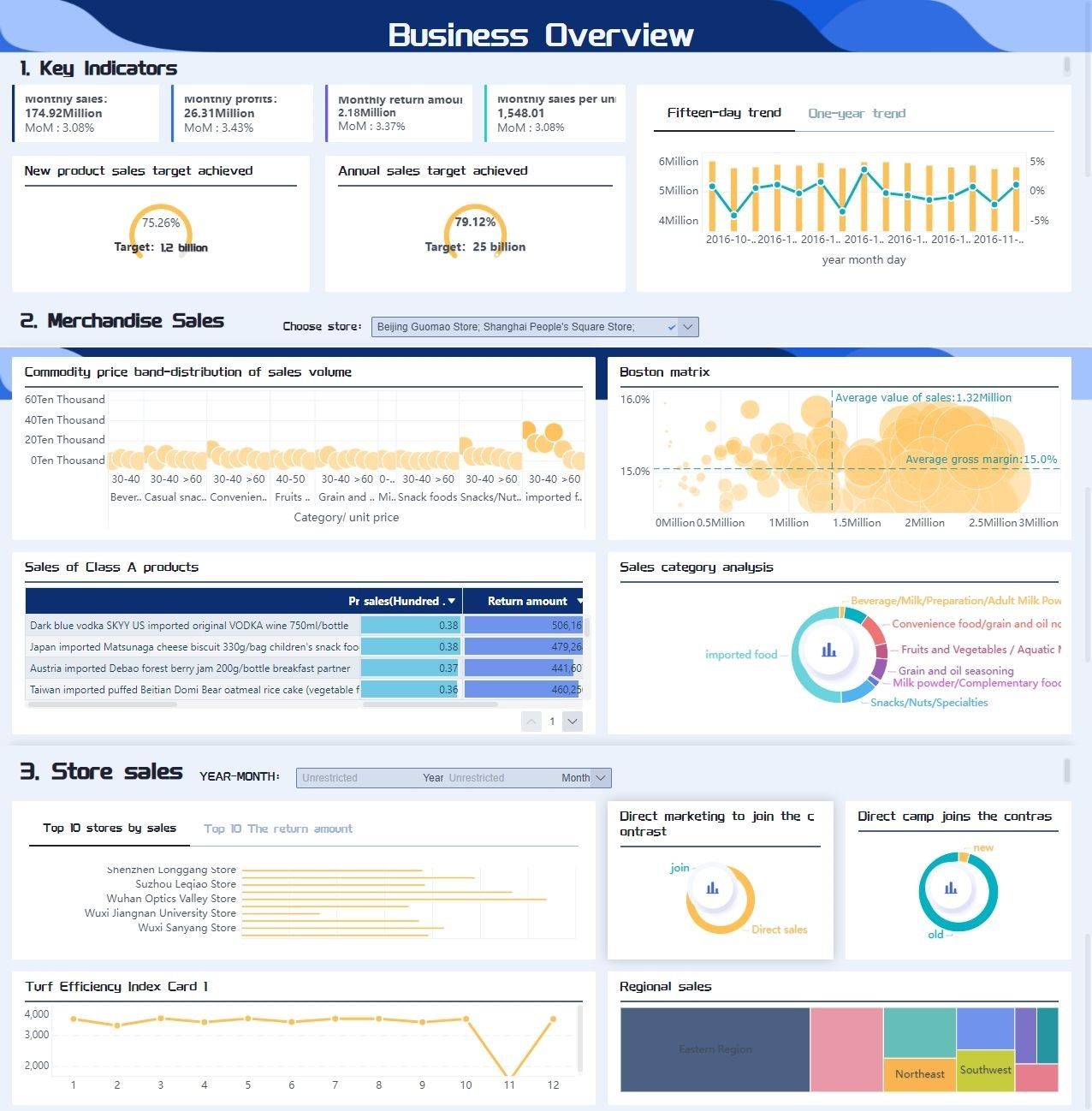
Case Study 1: Retail Sector
A leading retail company implemented advanced financial data management solutions. The company integrated artificial intelligence and machine learning into its financial systems. This integration enabled the company to perform predictive analytics. The company could forecast sales trends and optimize inventory levels. As a result, the company improved operational efficiency and reduced costs.
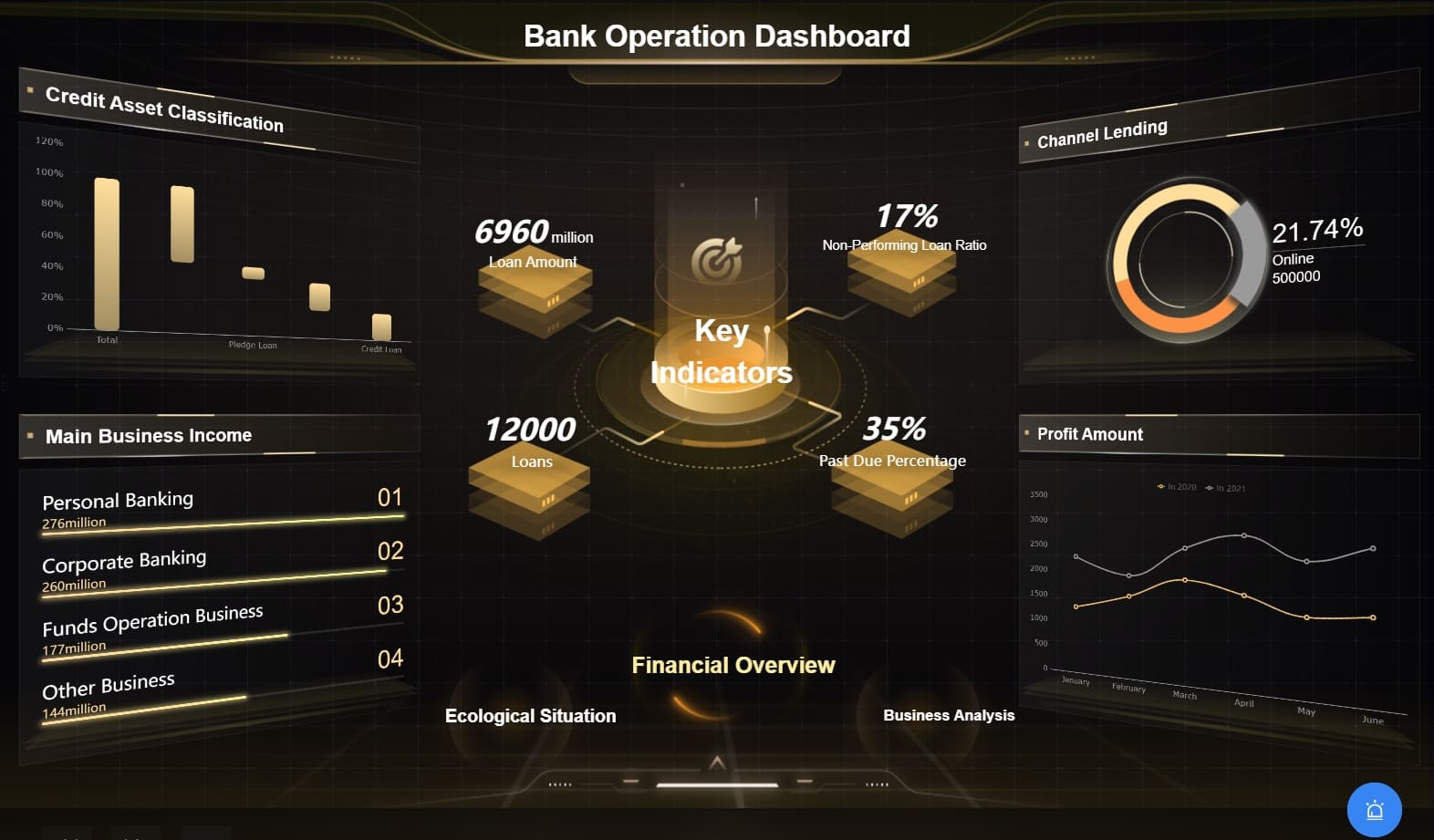
Case Study 2: Banking Industry
A major bank faced challenges with data silos and fragmented information. The bank adopted a comprehensive financial data management platform. This platform consolidated all financial data into a single, accessible system. The bank utilized data visualization tools to gain insights into customer behavior. The bank enhanced its decision-making process and improved customer satisfaction.
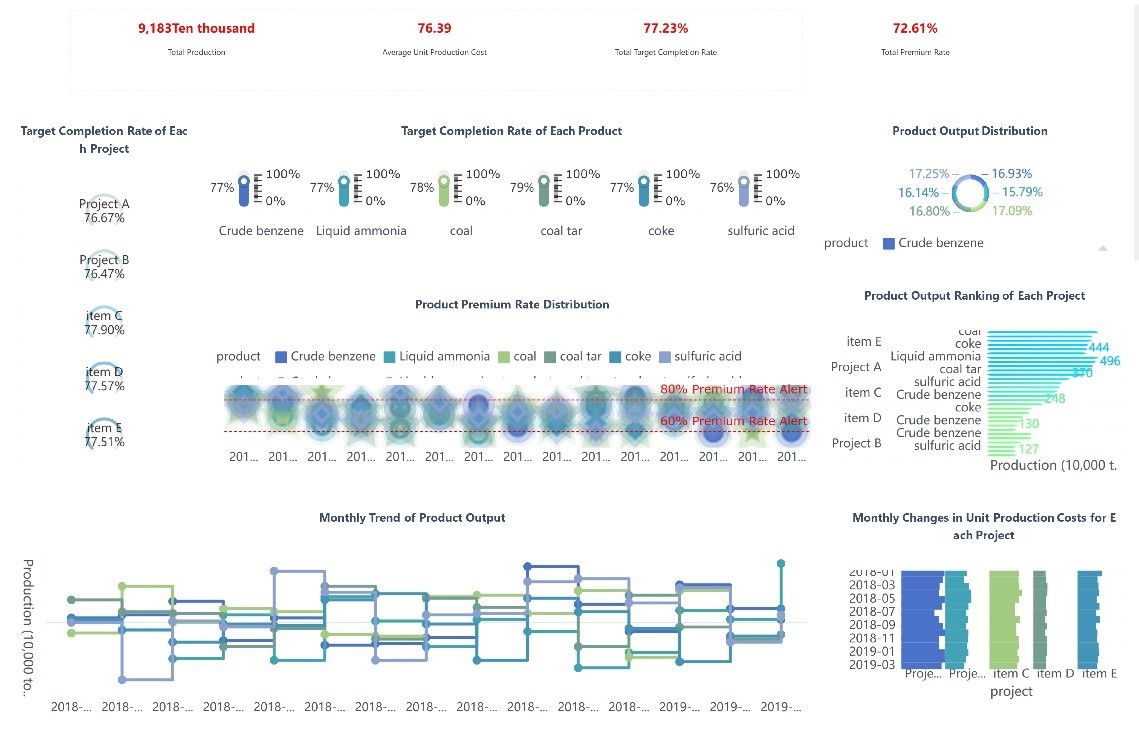
Case Study 3: Manufacturing Sector
A manufacturing firm struggled with inaccurate and incomplete financial data. The firm implemented robust data governance policies and automated data collection processes. The firm ensured data accuracy and completeness through regular audits. The firm leveraged cloud solutions for secure and scalable data storage. These measures led to better financial reporting and compliance with regulatory standards.
Benefits to Businesses
Improved Efficiency
Effective financial data management streamlines data collection, storage, and analysis. Automated systems reduce manual errors and enhance data accuracy. Organizations can access real-time financial information, enabling quick decision-making. Improved efficiency leads to better resource allocation and increased productivity.
Cost Savings
Organizations can achieve significant cost savings through proper financial data management. Accurate data reduces the risk of financial errors and fraud. Predictive analytics helps organizations anticipate market trends and adjust strategies. Organizations can optimize their operations and reduce unnecessary expenses. Cost savings contribute to overall financial stability and growth.
Financial Data Management plays a crucial role in modern business. Effective management ensures accurate and reliable financial information. This leads to better decision-making and regulatory compliance. The future of Financial Data Management looks promising with advancements in technology. Organizations should adopt best practices and leverage tools like financial management software and cloud solutions. These measures will enhance efficiency and security, transforming financial data into a strategic asset.
FAQ
Financial Data Management involves using specialized software and algorithms to track financial information within organizations. It ensures consistency, accuracy, and reliability of financial data.
Effective financial data management enhances decision-making, ensures regulatory compliance, and improves operational efficiency. It transforms disparate information into a strategic advantage.
Organizations can implement robust data governance policies, leverage technology such as financial management software and cloud solutions, and ensure data accuracy through regular audits.
Common challenges include data quality issues, such as inaccurate and incomplete data, and data security concerns, such as cyber threats and data breaches.
Businesses gain improved efficiency, cost savings, better decision-making, and enhanced compliance with regulatory standards.
Continue Reading About Financial Data Management
Location Data Management: Key Techniques and Tools
Explore location data management. Learn more about key techniques and essential tools for location data management.
Howard
Jul 15, 2024
10 Game-Changing Project Management Reporting Types!
Unlock project success with 10 must-know reporting types! Track progress, manage risks, and stay on budget like a pro.
Lewis
Mar 03, 2025
Essential Guide to Supplier Data Management Best Practices
Master supplier data management with best practices to enhance relationships, boost efficiency, and secure data using advanced tools like FineDataLink.
Howard
Nov 04, 2024
How Data Management Consultants Boost Operational Efficiency
Boost operational efficiency with data management consultants. Enhance decision-making, streamline processes, and achieve cost savings with expert strategies.
Howard
Nov 29, 2024
Best Data Management Tools of 2025
Explore the best data management tools of 2025, including FineDataLink, Talend, and Snowflake. Learn about their features, pros, cons, and ideal use cases.
Howard
Aug 04, 2024
How to Set Up a Comprehensive Data Analysis Framework
Master data analysis with a comprehensive framework. Learn to set objectives, manage data, and visualize insights for strategic decision-making.
Lewis
Oct 30, 2024


