Data replication plays a crucial role in modern data management. It ensures that your data remains available and reliable, even during unexpected disruptions. By replicating data across multiple systems, you enhance your business's ability to make informed decisions quickly. This process supports real-time analytics, allowing you to gain immediate insights from your data. Tools like FineDataLink and FineBI facilitate seamless data replication, improving analytics capabilities and ensuring business continuity. With these tools, you can maintain high data availability and enhance your organization's overall performance.
What is Data Replication?
Definition and Explanation of Data Replication
Data replication involves creating and storing multiple copies of data across different locations or servers. data replication involves creating This process ensures that your data remains consistent and up-to-date, which is crucial for high availability, disaster recovery, and load balancing in distributed systems. By replicating data, you can improve data availability and accessibility across a network. This means that even if one server fails, you still have access to your data from another location.
Basic concept of data replication
At its core, data replication is about copying data from one location to another. data replication is about copying This ensures that organizations maintain up-to-date copies of their data. You can think of it as having a backup plan for your data. If one system goes down, another can take over without any loss of information. This is particularly important for businesses that rely on real-time data processing and need to ensure that their operations run smoothly without interruptions.
Key components involved in data replication
Several key components play a role in data replication. First, you have the source data, which is the original data that needs to be copied. Then, there are the target locations where the data will be replicated. These could be other servers or databases. The replication process itself involves transferring data from the source to the target locations. Tools like FineDataLink facilitate this process by providing real-time data synchronization capabilities, ensuring minimal latency and efficient data transfer.
Historical Context of Data Replication
Understanding the historical context of data replication helps you appreciate how far this technology has come. Over the years, advancements in real-time replication technologies have significantly improved the speed and efficiency of data replication processes.
Evolution of data replication technologies
In the early days, data replication was a manual process, often involving physical copies of data being transported from one location to another. As technology advanced, automated systems were developed to handle data replication more efficiently. Today, with the rise of distributed databases and real-time data processing, data replication has become an essential part of data management strategies. Tools like FineBI have emerged, offering enhanced data analysis through replication, supporting real-time data integration.
Milestones in data replication development
Several milestones mark the development of data replication technologies. The introduction of networked databases allowed for more seamless data replication across multiple locations. The development of cloud computing further revolutionized data replication by enabling data to be stored and accessed from anywhere in the world. More recently, the focus has shifted towards real-time data replication, allowing businesses to make informed decisions quickly. This evolution has been driven by the need for high availability and reliability, especially in the event of hardware failures or other disruptions.
Benefits of Data Replication
Data replication offers numerous advantages that enhance the efficiency and reliability of your data management systems. By understanding these benefits, you can make informed decisions about implementing data replication strategies in your organization.
Data Availability
Ensuring data is accessible at all times
Data replication ensures that your data remains accessible, even during unexpected disruptions. By maintaining multiple copies of your data across different locations, you can access your information whenever needed. This continuous availability is crucial for businesses that rely on real-time data processing and need to ensure smooth operations.
Reducing downtime and service interruptions
Downtime can significantly impact your business operations. With data replication, you minimize service interruptions by having backup copies ready to take over if one system fails. This redundancy reduces the risk of data unavailability and helps maintain seamless service delivery.
Data Reliability
Enhancing data integrity and consistency
Data replication enhances the integrity and consistency of your data. By synchronizing data across multiple systems, you ensure that all copies remain up-to-date and accurate. This consistency is vital for making reliable business decisions based on current information.
Protecting against data loss
Data loss can have severe consequences for any organization. Data replication acts as a safeguard, protecting your data from loss due to hardware failures, system breaches, or other unforeseen events. By having multiple copies stored in different locations, you reduce the risk of losing critical information.
Disaster Recovery
Role of replication in disaster recovery plans
Data replication plays a crucial role in disaster recovery plans. In the event of a catastrophe, such as a system breach or hardware failure, you can recover data from backup locations. This capability ensures business continuity and minimizes the impact of disasters on your operations.
Case studies of successful disaster recovery using replication
Case Study 1: Financial Institution
A leading financial institution implemented data replication to enhance its disaster recovery strategy. By using FineDataLink, they achieved real-time data synchronization across multiple servers. This setup allowed them to recover quickly from a hardware failure, ensuring uninterrupted service to their clients.
Case Study 2: Healthcare Provider
A healthcare provider faced a system breach that threatened patient data. With data replication in place, they restored data from a secure backup location. This swift recovery protected sensitive information and maintained trust with their patients.
These case studies highlight the effectiveness of data replication in disaster recovery scenarios. By leveraging tools like FineDataLink and FineBI, organizations can enhance their resilience and ensure data availability, reliability, and security.
Types of Data Replication
Data replication can be implemented in various ways, each with its own set of processes and benefits. Understanding these types helps you choose the best method for your organization's needs.
Synchronous Replication
Definition and process
Synchronous replication involves copying data simultaneously to multiple locations. This ensures that all copies remain consistent in real-time. When you write data to the primary location, it immediately replicates to the secondary location. This process guarantees that both locations have identical data at any given moment.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- Real-time consistency: You achieve up-to-the-moment data accuracy, which is crucial for applications requiring immediate data availability.
- Data integrity: Ensures that all copies of data are consistent, reducing the risk of discrepancies.
Disadvantages:
- Performance impact: The need for immediate data writing can slow down system performance, especially over long distances.
- Higher resource consumption: Requires more bandwidth and processing power to maintain real-time synchronization.
Asynchronous Replication
Definition and process
Asynchronous replication first writes data to the primary location and then replicates it to the secondary location at scheduled intervals. This method does not require immediate consistency, allowing for more flexibility in data transfer timing.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- Efficiency: Faster and more efficient for long-distance replication, as it does not require immediate data writing.
- Reduced performance impact: Less strain on system resources compared to synchronous replication.
Disadvantages:
- Potential data lag: There may be a delay between updates, leading to temporary inconsistencies between data copies.
- Risk of data loss: In the event of a failure before replication occurs, some data might be lost.
Near-Synchronous Replication
Definition and process
Near-synchronous replication strikes a balance between synchronous and asynchronous methods. It aims to minimize the delay in data replication while avoiding the performance drawbacks of full synchronous replication. Data is replicated almost immediately after being written to the primary location, but with slight delays to optimize performance.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- Balanced performance: Offers a compromise between real-time consistency and system efficiency.
- Improved data accuracy: Reduces the risk of significant data discrepancies while maintaining better performance than synchronous replication.
Disadvantages:
- Complex setup: Requires careful configuration to achieve the desired balance between speed and consistency.
- Slight data lag: Although minimized, there is still a potential for minor delays in data replication.
Understanding these types of data replication allows you to select the most suitable approach for your organization's specific needs. Tools like FineDataLink and FineBI can facilitate these processes, ensuring efficient data management and enhancing your business's overall performance.
Use Cases of Data Replication
Data replication serves as a cornerstone in various operational strategies, ensuring that your business remains resilient and efficient. Let's explore some practical applications where data replication proves invaluable.
Business Continuity
Importance in maintaining operations
In today's fast-paced business environment, maintaining uninterrupted operations is crucial. Data replication ensures that your systems remain operational even during unexpected disruptions. By having multiple copies of your data, you can quickly switch to a backup system if the primary one fails. This redundancy minimizes downtime and keeps your business running smoothly.
Examples of business continuity through replication
Consider a scenario where a retail company experiences a server failure during peak shopping hours. With data replication in place, the company can seamlessly transition to a backup server, ensuring that customers continue to shop without interruption. Another example involves a financial institution that uses data replication to maintain real-time transaction processing, even during system maintenance or upgrades.
Load Balancing
How replication aids in load distribution
Data replication plays a vital role in load balancing by distributing data across multiple servers. This distribution ensures that no single server becomes overwhelmed with requests, enhancing the overall performance and responsiveness of your systems. By replicating data, you can efficiently manage high volumes of traffic and maintain optimal service levels.
Real-world examples of load balancing
A popular streaming service uses data replication to distribute content across various servers worldwide. This strategy ensures that users experience minimal buffering and fast load times, regardless of their location. Similarly, an e-commerce platform employs data replication to handle increased traffic during sales events, ensuring a smooth shopping experience for customers.
Data Migration
Role of replication in data migration strategies
Data migration involves transferring data from one system to another, often as part of an upgrade or consolidation effort. Data replication facilitates this process by ensuring that data remains consistent and accessible throughout the migration. By replicating data, you can minimize downtime and reduce the risk of data loss during the transition.
Successful data migration case studies
Case Study: Tech Company
A leading tech company successfully migrated its data to a new cloud-based system using data replication. By employing FineDataLink, they ensured real-time synchronization between the old and new systems, minimizing downtime and maintaining data integrity. This seamless transition allowed the company to enhance its data analytics capabilities with FineBI, providing deeper insights into customer behavior.
Case Study: Healthcare Organization
A healthcare organization faced the challenge of migrating patient records to a new electronic health record system. Through data replication, they maintained access to critical patient information throughout the migration process. This approach ensured that healthcare providers could continue delivering quality care without disruption.
These examples highlight the versatility and effectiveness of data replication in various scenarios. By leveraging tools like FineDataLink and FineBI, you can enhance your organization's resilience, efficiency, and data management capabilities.
Challenges in Data Replication
Data replication offers numerous benefits, but it also presents several challenges that you must address to ensure effective implementation. Understanding these challenges helps you develop strategies to overcome them and maximize the advantages of data replication.
Data Consistency Issues
Maintaining data consistency across multiple locations is a significant challenge in data replication. When you replicate data, ensuring that all copies remain identical and up-to-date is crucial for maintaining data integrity.
Common consistency challenges
- Latency: Delays in data transfer can lead to inconsistencies between data copies.
- Conflicts: Simultaneous updates to the same data in different locations can result in conflicts.
- Network Failures: Interruptions in network connectivity can cause discrepancies in data synchronization.
Solutions to maintain consistency
- Conflict Resolution Mechanisms: Implement automated systems to detect and resolve conflicts.
- Regular Audits: Conduct frequent checks to ensure data consistency across all locations.
- Advanced Tools: Use tools like FineDataLink to facilitate real-time data synchronization, minimizing latency and ensuring consistent data replication.
Network Bandwidth Constraints
Network bandwidth plays a critical role in data replication. Limited bandwidth can hinder the replication process, affecting data availability and performance.
Impact of bandwidth on replication
- Slower Data Transfer: Insufficient bandwidth can slow down the replication process, leading to delays in data availability.
- Increased Latency: High latency can result from limited bandwidth, affecting real-time data access.
- Potential Data Loss: Inadequate bandwidth may cause data packets to drop, leading to incomplete data replication.
Strategies to optimize bandwidth usage
- Data Compression: Compress data before transmission to reduce the amount of bandwidth required.
- Prioritize Critical Data: Focus on replicating essential data first to ensure availability during bandwidth constraints.
- Scheduled Replication: Perform data replication during off-peak hours to minimize the impact on network resources.
Cost Considerations
Implementing data replication involves financial implications that you need to consider. Balancing the costs with the benefits is essential for making informed decisions.
Financial implications of implementing replication
- Infrastructure Costs: Setting up and maintaining the necessary hardware and software for data replication can be expensive.
- Operational Expenses: Ongoing costs include network bandwidth, storage, and personnel for managing replication processes.
- Licensing Fees: Some replication tools, like FineBI, may require licensing fees, adding to the overall cost.
Cost-benefit analysis
- Evaluate ROI: Assess the return on investment by comparing the costs of data replication with the benefits, such as improved data availability and disaster recovery.
- Scalability: Consider the scalability of your replication solution to ensure it meets future needs without incurring excessive costs.
- Leverage Efficient Tools: Utilize cost-effective tools like FineDataLink to streamline data replication processes and reduce expenses.
By addressing these challenges, you can enhance the effectiveness of your data replication strategy, ensuring that your organization benefits from improved data availability, reliability, and performance.
Best Practices for Implementing Data Replication
Implementing data replication effectively requires careful planning and execution. By following best practices, you can ensure that your data remains secure, consistent, and readily available.
Planning and Strategy
Importance of a well-defined replication strategy
A well-defined replication strategy forms the backbone of successful data management. It ensures that your data remains accessible and reliable, even during unexpected disruptions. According to industry findings, 82% of companies experience at least one unplanned outage annually. A robust replication strategy can prevent costly outages by maintaining data integrity and business continuity.
Steps to develop an effective plan
- Assess Your Needs: Identify the critical data that requires replication. Consider factors like data volume, frequency of updates, and business requirements.
- Choose the Right Tools: Select tools like FineDataLink and FineBI that offer real-time synchronization and advanced data management capabilities.
- Define Replication Goals: Set clear objectives for your replication strategy. Determine the desired level of data availability, consistency, and recovery time.
- Develop a Schedule: Establish a replication schedule that aligns with your business operations. Consider peak usage times and network bandwidth constraints.
- Test and Validate: Regularly test your replication processes to ensure they meet your objectives. Validate data consistency and recovery capabilities.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Tools and techniques for monitoring replication
Effective monitoring is crucial for maintaining the integrity of your replicated data. Utilize monitoring tools that provide real-time insights into replication processes. These tools can alert you to potential issues, such as data inconsistencies or network failures, allowing for prompt resolution.
- Automated Alerts: Set up automated alerts to notify you of any anomalies in the replication process.
- Performance Dashboards: Use dashboards to visualize replication metrics and identify trends or bottlenecks.
Regular maintenance practices
Regular maintenance ensures that your replication systems remain efficient and reliable. Implement the following practices:
- Routine Audits: Conduct regular audits to verify data consistency across all locations.
- System Updates: Keep your replication tools and infrastructure updated to leverage the latest features and security enhancements.
- Capacity Planning: Monitor storage and network capacity to accommodate growing data volumes.
Security Measures
Ensuring data security during replication
Data security is paramount during replication. Protect your data from unauthorized access and potential breaches by implementing robust security measures.
- Encryption: Encrypt data during transmission and storage to safeguard sensitive information.
- Access Controls: Implement strict access controls to limit data access to authorized personnel only.
Implementing encryption and access controls
Encryption and access controls are essential components of a secure replication strategy. They ensure that your data remains confidential and protected from cyber threats.
- Data Encryption: Use strong encryption protocols to secure data in transit and at rest.
- Role-Based Access: Assign access permissions based on user roles and responsibilities, minimizing the risk of unauthorized data access.
By adhering to these best practices, you can enhance the effectiveness of your data replication strategy. Tools like FineDataLink and FineBI can facilitate seamless replication, ensuring that your organization benefits from improved data availability, reliability, and security.
Role of FanRuan in Data Replication
FanRuan plays a pivotal role in the realm of data replication, offering innovative solutions that enhance data management and analytics. Through its products, FineDataLink and FineBI, FanRuan empowers businesses to achieve seamless data integration and analysis.
FineDataLink's Contribution
Real-time data synchronization capabilities
FineDataLink excels in providing real-time data synchronization. This capability ensures that your data remains consistent and up-to-date across multiple systems. By minimizing latency, FineDataLink enhances system performance and provides a seamless user experience. You can rely on this tool to maintain high data availability, even during unexpected disruptions.
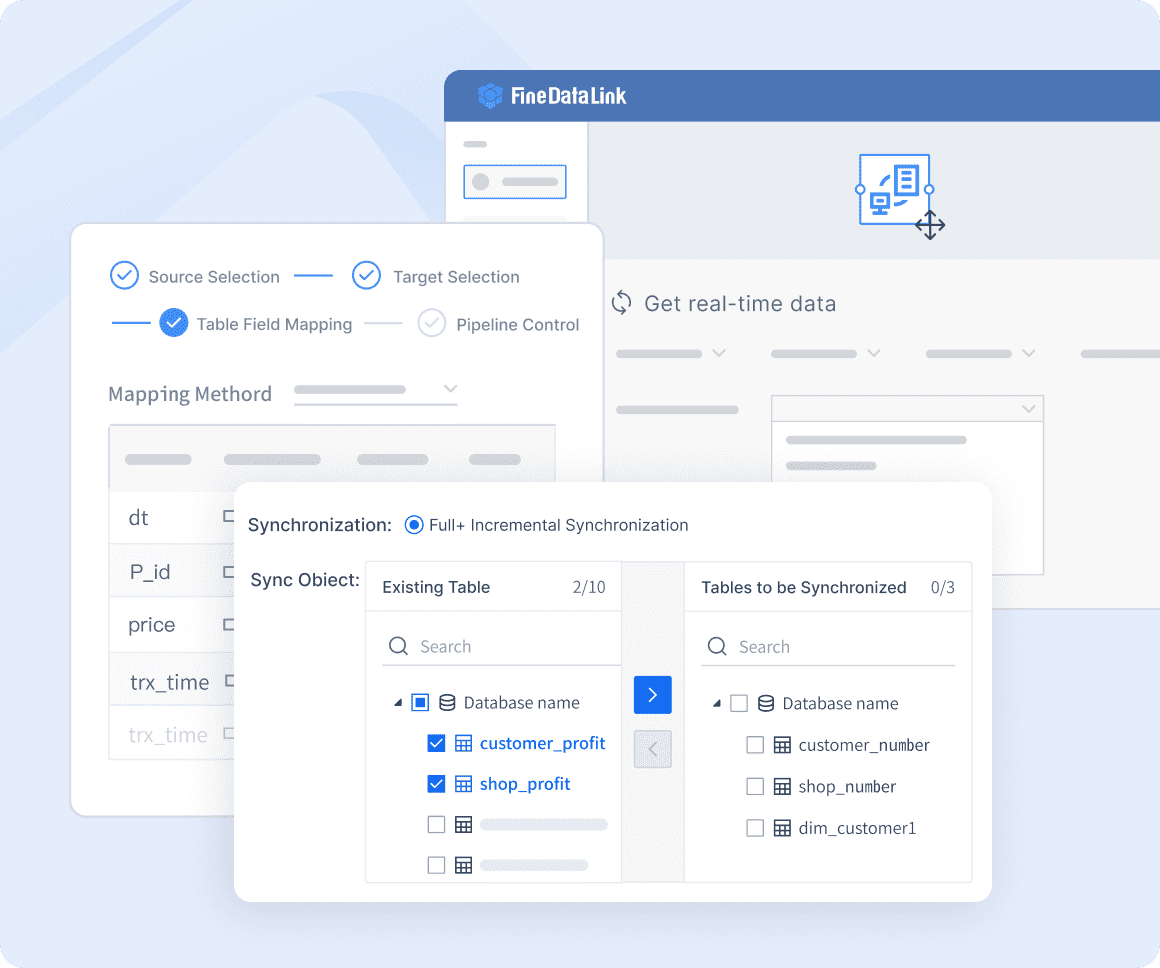
Advanced ETL & ELT data development
With advanced ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) capabilities, FineDataLink simplifies complex data integration tasks. Its low-code platform allows you to automate data pipelines, reducing the burden of manual processes. This efficiency enables you to focus more on deriving valuable insights from your data, rather than maintaining infrastructure.
FineBI's Role
Enhancing data analysis through replication
FineBI transforms raw data into actionable insights through its robust data analysis features. By leveraging data replication, FineBI ensures that your analytics are based on the most current data available. This real-time analysis capability boosts decision-making efficiency, allowing you to respond promptly to changing business conditions.
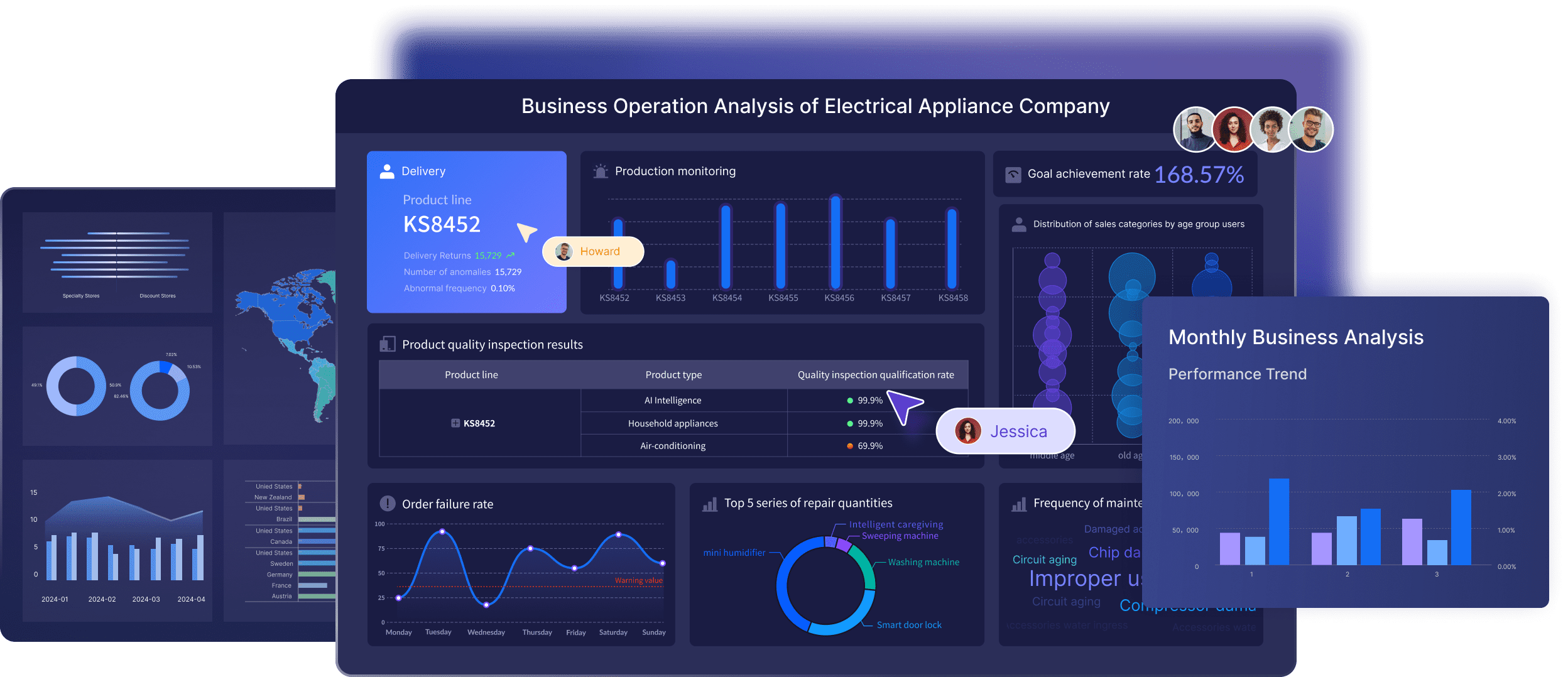
Supporting real-time data integration
FineBI supports real-time data integration, enabling you to connect and analyze data from various sources seamlessly. This integration facilitates comprehensive reporting and analytics, providing a holistic view of your business operations. With FineBI, you can track key performance indicators, identify trends, and predict future outcomes with confidence.

FanRuan's solutions, FineDataLink and FineBI, exemplify the power of data replication in modern data management. By integrating these tools into your operations, you can enhance data availability, reliability, and analytical capabilities, driving long-term success and growth.
Future Trends in Data Replication

Data replication continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and industry demands. As you explore future trends, you'll discover innovations that promise to reshape data management.
Emerging Technologies
Innovations in replication technology
New technologies are transforming how you approach data replication. Innovations like blockchain and edge computing offer exciting possibilities. Blockchain ensures secure and tamper-proof data replication, enhancing trust and transparency. Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and improving real-time data access. These technologies empower you to replicate data more efficiently and securely.
Potential impact on data management
These innovations significantly impact data management. Blockchain's decentralized nature enhances data integrity, making it ideal for industries requiring high security. Edge computing reduces the load on central servers, improving system performance. By adopting these technologies, you can achieve greater data availability and reliability, aligning with the insights of Jeffrey Richman, a renowned expert in data replication strategies. He emphasizes that "availability, scalability, and data integrity are what they are all about, plain and simple!"
Industry Predictions
Expert insights on the future of replication
Industry experts foresee a future where data replication becomes even more integral to business operations. As data volumes grow, the need for efficient replication solutions intensifies. Experts predict that automation and artificial intelligence will play pivotal roles in streamlining replication processes. These technologies will enable you to manage data more effectively, ensuring seamless integration across platforms.
Anticipated challenges and opportunities
While opportunities abound, challenges persist. Managing data consistency across diverse environments remains a hurdle. However, advancements in AI-driven conflict resolution offer promising solutions. By leveraging these tools, you can overcome consistency issues and optimize replication strategies. The future holds immense potential for those who embrace these innovations, allowing you to stay ahead in the ever-evolving landscape of data management.
Data replication stands as a cornerstone in modern data management, ensuring that your data remains accurate, accessible, and available. This process is vital for maintaining service continuity and enhancing decision-making capabilities. As technology evolves, the role of data replication will continue to grow, offering even more robust solutions for disaster recovery and system resilience. You are encouraged to explore and apply data replication strategies like those offered by FineDataLink and FineBI. These tools can significantly improve your organization's performance and ensure that your data remains secure and reliable.
FAQ
Data replication involves copying data from one location to another, ensuring that identical copies exist across multiple systems. This process enhances data availability and reliability, allowing you to access critical information even if one system fails.
Data replication plays a crucial role in maintaining business continuity. By having multiple copies of your data, you can ensure that operations continue smoothly during unexpected disruptions. It also supports real-time analytics, enabling you to make informed decisions quickly.
Synchronous Replication: Data is copied simultaneously to multiple locations, ensuring real-time consistency.
Asynchronous Replication: Data is first written to the primary location and then replicated to secondary locations at scheduled intervals.
Near-Synchronous Replication: This method balances the need for real-time consistency with system efficiency, replicating data almost immediately after it's written.
FineDataLink provides real-time data synchronization capabilities, ensuring that your data remains consistent and up-to-date across multiple systems. Its advanced ETL and ELT features simplify complex data integration tasks, allowing you to focus on deriving valuable insights from your data.
FineBI leverages data replication to transform raw data into actionable insights. By ensuring that your analytics are based on the most current data available, FineBI boosts decision-making efficiency and supports real-time data integration.
Data Consistency Issues: Ensuring that all copies remain identical and up-to-date can be challenging.
Network Bandwidth Constraints: Limited bandwidth can hinder the replication process, affecting data availability.
Cost Considerations: Implementing data replication involves financial implications, including infrastructure and operational expenses.
Use conflict resolution mechanisms and regular audits to maintain data consistency.
Optimize bandwidth usage through data compression and scheduled replication.
Conduct a cost-benefit analysis to evaluate the return on investment and leverage efficient tools like FineDataLink.
Continue Reading About Data Replication
2025 Best Data Integration Solutions and Selection Guide
Explore top data integration solutions for 2025, enhancing data management and operational efficiency with leading platforms like Fivetran and Talend.
Howard
Dec 19, 2024
2025's Best Data Validation Tools: Top 7 Picks
Explore the top 7 data validation tools of 2025, featuring key features, benefits, user experiences, and pricing to ensure accurate and reliable data.
Howard
Aug 09, 2024
2025 Data Pipeline Examples: Learn & Master with Ease!
Unlock 2025’s Data Pipeline Examples! Discover how they automate data flow, boost quality, and deliver real-time insights for smarter business decisions.
Howard
Feb 24, 2025
Best Data Integration Platforms to Use in 2025
Explore the best data integration platforms for 2025, including cloud-based, on-premises, and hybrid solutions. Learn about key features, benefits, and top players.
Howard
Jun 20, 2024
Best Data Integration Vendors for Seamless Workflows
Discover the top 20 data integration vendors of 2025 for seamless workflows. Compare tools like Talend, AWS Glue, and Fivetran to optimize your data processes.
Howard
Jan 22, 2025
Best Data Management Tools of 2025
Explore the best data management tools of 2025, including FineDataLink, Talend, and Snowflake. Learn about their features, pros, cons, and ideal use cases.
Howard
Aug 04, 2024