

You need a simple way to know what a company is worth. Enterprise value helps you find this answer. It shows the value of a business to everyone who invests, not just shareholders. The table below explains how experts describe it:
| Definition | Description |
|---|---|
| Enterprise Value | A capital structure-neutral metric that measures the value of a company's operations to all stakeholders, including equity and debt capital providers. |
| Calculation | Calculated by taking the equity value of a company and adding non-equity claims such as net debt, preferred stock, and minority interest. |
Enterprise value counts debt and cash, so you see the true size of a company. Market capitalization only looks at shares and misses other key things. This makes enterprise value very helpful when you study companies for mergers or buyouts.
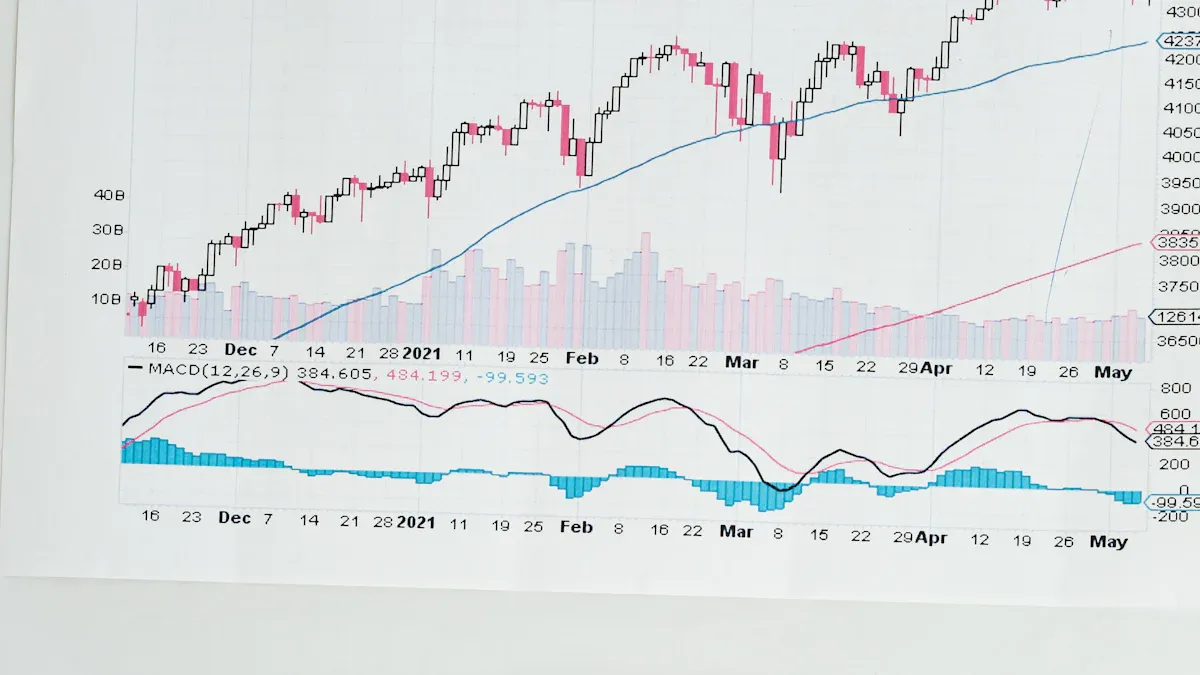
To put enterprise value into context, you can explore it visually through an interactive enterprise business analysis dashboard above. Please click to engage.
Built with FineBI, this dashboard lets you click through metrics, compare company performance, and understand how changes in debt, equity, and cash flow affect enterprise value in real time.
You may ask what enterprise value means. Enterprise value shows the whole worth of a company. It is not just what shareholders own. If you want to buy a business, you need to know the total cost. This includes debts and cash. Enterprise value gives you this answer.
Enterprise value has a few main parts. These are:
First, you start with market capitalization. This is the share price times the number of shares. Next, you add total debt, preferred stock, and minority interest. Last, you subtract cash and cash equivalents. This shows you what it takes to own the company.
Note: Market capitalization only shows the value of shares. It does not count debt or cash. Enterprise value includes everything. This gives you a better view.
Here is a table that explains how top textbooks show the calculation:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Capitalization | Price per share times total shares. |
| Total Debt | All short-term and long-term debt added together. |
| Cash on Hand | Cash, cash equivalents, and payments for goods or services sold. |
| Enterprise Value Formula | Enterprise Value = Market Capitalization + Net Debt - Cash and Cash Equivalents. |
| Example Calculation | If a company has a 2,000 short-term debt, 6,000 cash, the enterprise value is $14,000. |
Financial experts use enterprise value to find a company's total worth. This is important when companies are bought or sold. They take out cash because it is not used in daily business. This way, you see the real value of the company, including all assets and debts.
Enterprise value is important because it shows the full worth of a company. If you only look at market capitalization, you may miss key facts. Enterprise value helps you make smarter choices, especially in big deals.
Here are some reasons why enterprise value matters:
When companies merge or get bought, enterprise value is very important. You need to check both enterprise and equity values to set the right price. This helps everyone make smart choices. Enterprise value also helps you see if a deal is fair for both sides.
Some people make mistakes with enterprise value. Here are common errors:
Tip: Always use enterprise value with other financial tools. This helps you avoid mistakes and get the best results.
Enterprise value is a key metric for company valuation. It helps you see the big picture, compare companies fairly, and make better choices in business deals.

If you want to know a company’s worth, enterprise value helps. You use a simple formula to figure it out:
EV = Market Capitalization + Debt + Minority Interest + Preferred Shares - Cash and Cash Equivalents
This formula adds up all the important parts. You count the market value of shares, all debts, minority interests, and preferred shares. Then you take away cash and cash equivalents. Cash is subtracted because it is not used in daily business.
Here is a table that explains each part:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Capitalization | The total market value of a company's outstanding shares. |
| Total Debt | The sum of all short-term and long-term debt. |
| Cash | Liquid assets available to the company. |
| Minority Interest | The portion of a subsidiary owned by other entities. |
| Preferred Shares | Shares that have preferential rights over common shares. |
Each part changes the enterprise value. If you add more debt, enterprise value gets bigger. If you add more cash, enterprise value gets smaller.
Here are two examples:
Debt, equity, and cash are important for enterprise value. Debt is added because you must pay it if you buy the company. Equity is added because it is the value of shares. Cash is subtracted because it is not needed for daily work.
Think about buying a house. The total price is like enterprise value. The down payment is equity. The loan is debt. If the house has cash inside, you subtract that from the price. This shows the real cost.
If debt goes up, enterprise value goes up. If cash goes up, enterprise value goes down. You should watch these changes when you compare companies or think about buying one.
Enterprise value shows the real cost to own a company. You get the full picture by looking at debt, equity, and cash together.
FineBI makes enterprise value analysis easy to do. The interface is simple to use. You do not need special tech skills. You can link many data sources together. This brings all your financial data into one place. It helps you see the whole company’s value.
Here is how FineBI helps with enterprise value and other financial numbers:
| Feature Description | Contribution to Analysis |
|---|---|
| User-friendly interface for data visualization | You can make dashboards quickly and focus on enterprise value. |
| Integration of various data sources | It combines data from different places for a full company view. |
| Collaborative features | You can share ideas and work with others on valuation. |
| Adaptive layouts and theme customization | You can show your findings in ways everyone understands. |
FineBI works with real-time data. You can connect to live databases and see new updates right away. Your enterprise value numbers are always current. You can drag and drop to make charts and dashboards. Leaders use cockpit dashboards to watch key numbers for valuation.
| Feature Description | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Self-service query service platform | Connects to live data for up-to-date valuation. |
| High efficiency in data processing | Handles lots of data, so results are trustworthy. |
| Custom drag-and-drop analysis | You can make charts for enterprise value without coding. |
| Management cockpit dashboard | Shows important numbers for quick choices. |
FanRuan gives strong tools for finance and business intelligence. You can use these tools to make company valuation better. FanRuan offers data analysis, reports, and ways to link data. These features help you gather and study all the data for good valuation.

You can make dashboards that show key financial numbers. This makes it easier to explain enterprise value to others. FanRuan’s tools let you look deeply at your company’s finances. You can use them for mergers, buyouts, and financial reports. This helps you make smart choices with solid data.
FanRuan’s business intelligence tools help you find trends and spot risks. You can share what you learn with your team. This makes the valuation process faster and more dependable. With FanRuan, you get everything you need for enterprise value analysis and company valuation.
When you look at companies, you often see market value in news. Market value means the price of all shares added together. You find it by multiplying share price by total shares. People use market value because it is fast and simple.
Enterprise value gives you more details. It adds debt and takes away cash from market value. This shows what you pay to own the whole company. You see the real market value, not just shares.
Here is a table that shows the main differences:
| Metric | Market Value (Market Cap) | Enterprise Value |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total value of a company's shares | Market value plus debt minus cash |
| Calculation | Share Price × Total Shares | Market value + Total Debt - Cash |
| Usage | Quick size comparison | True market value for deals and analysis |
| Sensitivity | Changes with stock price | More stable, includes all financial parts |
| Best for | Comparing similar companies | Mergers, acquisitions, and valuation ratios |
Use market value for quick checks. Use enterprise value for the full story, especially in big deals.
Tip: Always look at both market value and enterprise value. This helps you know if a company is really worth its price.
You can use other market value metrics to study companies. These help you learn how a business does and if it is a good buy.
Here is a table to help you see the differences:
| Metric | Description | Key Difference |
|---|---|---|
| Enterprise Value | Market value plus debt minus cash | Shows total market value, not just shares |
| P/E Ratio | Market value divided by earnings per share | Focuses on equity, can miss debt and cash |
| EV/EBITDA | Market value compared to core earnings | Ignores capital structure, fair for all companies |
Use market value metrics together. This gives you a clear view of a company’s health and true value.
Enterprise value helps you see what it really costs to buy a company. It works best when companies merge or get bought. This metric shows the real price because it counts debt and cash. You can use it to compare different offers to buy a company. It is also helpful for stock-based deals and picking the best offer.
Here are some times when enterprise value is useful:
Enterprise value gives you more details than just looking at financial reports. It helps you know the real cost, not just the share price.
But enterprise value has some limits. The table below lists the main ones:
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| Off-balance sheet items | Enterprise value does not count things like leases or hidden debts, so it may miss some costs. |
| Sensitivity to interest rates | If interest rates change, debt costs change, so enterprise value can go up or down. |
| Comparability | It is hard to compare with other numbers that only look at shares or book value. |
You should always read the financial statements closely. This helps you find important details you might miss.
When you use enterprise value, there are some things you must check. These steps help you avoid mistakes and get good results.
You should also watch out for these mistakes:
Tip: Enterprise value is a great tool, but you should use it with other numbers and always check the full financial statements to get the best view.
Knowing about enterprise value helps you find out what a business is really worth. When you use tools like FanRuan and FineBI, you get some good things:
If you use enterprise value with other numbers, you will understand how a company is doing.
FanRuan
https://www.fanruan.com/en/blogFanRuan provides powerful BI solutions across industries with FineReport for flexible reporting, FineBI for self-service analysis, and FineDataLink for data integration. Our all-in-one platform empowers organizations to transform raw data into actionable insights that drive business growth.
Enterprise value tells you how much a company is worth. Market capitalization only looks at the value of shares. Enterprise value adds debt and takes away cash. This gives you a fuller view of the company.
Cash is not used in the company’s daily work. Taking away cash shows the real cost to buy the company. You want to know what it really costs to own everything.
Enterprise value works for most companies. It is best for companies with debt and cash. For banks or financial firms, you might need other ways because their balance sheets are special.
FineBI lets you bring data from different places together. You can make dashboards to watch enterprise value. You see new numbers right away. You can share what you find with your team and make better choices.

