Data duplication, a prevalent issue in organizations, refers to the existence of identical data copies across systems. This redundancy leads to wasted storage space and increased costs. For instance, some companies find that up to 80% of their corporate data is duplicated. Addressing this issue is crucial for business intelligence, as duplicate data can result in inaccurate reports and poor decision-making. Tools like FineDataLink and FineBI play a vital role in managing data duplication, enhancing data quality, and ensuring efficient data utilization.
What is Data Duplication?
Definition and Explanation of Data Duplication
Data duplication refers to the presence of identical data entries across various systems or databases. This phenomenon often arises from inconsistent data collection and entry processes. When organizations fail to establish uniform procedures for data handling, duplicate records proliferate. These duplicates can lead to inaccurate reports and analytics, steering businesses in the wrong direction.
Characteristics of Data Duplication
Data duplication exhibits several distinct characteristics:
- Redundancy: Multiple copies of the same data exist, consuming unnecessary storage space.
- Inaccuracy: Duplicate data can skew insights, leading to poor decision-making.
- Cost Implications: Storing redundant data increases cloud storage costs and affects backup speed.
Common Sources of Data Duplication
Several factors contribute to data duplication:
- Human Error: Mistakes during manual data entry often result in duplicate records.
- Data Integration Issues: Inadequate integration between systems can lead to redundant data entries.
- Improper Data Gathering Techniques: Flawed methods of collecting data, such as online scraping, can introduce duplicates.
Types of Data Duplication
Understanding the types of data duplication helps in addressing the issue effectively.
Intentional vs. Unintentional Duplication
- Intentional Duplication: Sometimes, organizations deliberately create duplicate data for backup or redundancy purposes. While this can enhance data security, it also increases storage costs.
- Unintentional Duplication: This occurs due to errors or oversight, often leading to inefficiencies and inaccuracies in data analysis.
Internal vs. External Duplication
- Internal Duplication: This type of duplication happens within an organization. It often results from inconsistent data management practices across departments.
- External Duplication: Occurs when data from external sources, such as third-party vendors, gets duplicated within the organization's systems.
By recognizing these types and sources of data duplication, organizations can implement strategies to mitigate their impact, thereby improving data quality and reducing unnecessary costs.
Causes of Data Duplication
Data duplication often arises from various sources, leading to inefficiencies and inaccuracies in business operations. Understanding these causes is crucial for organizations aiming to maintain data integrity and optimize their business intelligence efforts.
Data Entry Errors
Data entry errors represent a significant source of data duplication. These errors can occur due to human mistakes or systematic issues during data collection.
Human Errors in Data Entry
Human errors frequently lead to duplicate data entries. Employees may inadvertently enter the same information multiple times, especially when dealing with large volumes of data. This repetition results in redundant records that clutter databases and skew analytics. Training employees on accurate data entry practices can help mitigate this issue.
Systematic Errors in Data Collection
Systematic errors in data collection processes also contribute to data duplication. Automated systems may malfunction, causing repeated entries of the same data. For instance, a glitch in a data import script might duplicate records during each run. Regular system audits and maintenance can prevent such errors, ensuring data accuracy.
System Integration Issues
System integration challenges often result in data duplication, particularly when merging data from different sources.
Inconsistent data formats across systems can lead to duplication. When systems fail to recognize identical data due to format discrepancies, they may treat them as separate entries. For example, one system might store dates as "MM/DD/YYYY," while another uses "DD-MM-YYYY." This inconsistency can create duplicate records. Standardizing data formats across systems can alleviate this problem.
Lack of Standardization
A lack of standardization in data management practices exacerbates data duplication. Without uniform procedures for data handling, different departments might store the same data in varied ways. This inconsistency leads to multiple versions of the same data, complicating data analysis. Implementing standardized data management protocols can reduce duplication and enhance data quality.
By addressing these causes of data duplication, organizations can improve their data management practices, leading to more accurate insights and better decision-making.
Impact of Data Duplication on Business Intelligence

Data duplication significantly affects business intelligence by compromising data quality and inflating storage costs. Organizations must understand these impacts to maintain efficient operations and accurate insights.
Data Quality Issues
Data quality forms the backbone of effective business intelligence. When data duplication occurs, it introduces several challenges that can undermine this foundation.
Inaccurate Reporting
Duplicate data often leads to inaccurate reporting. When multiple copies of the same data exist, reports may reflect inflated figures or incorrect metrics. For instance, sales data duplicated across systems might result in overstated revenue figures. This inaccuracy can mislead stakeholders, causing them to make decisions based on flawed information. Ensuring data accuracy requires vigilant monitoring and deduplication efforts.
Misleading Insights
Misleading insights arise when duplicate data skews analysis results. Analysts rely on clean, accurate data to derive meaningful insights. However, when data duplication occurs, it can distort trends and patterns. For example, customer behavior analysis might show false trends due to repeated entries of the same customer data. This distortion can lead businesses to implement ineffective strategies. By eliminating duplicates, organizations can ensure their insights remain reliable and actionable.
Increased Storage Costs
Data duplication not only affects data quality but also imposes financial burdens on organizations through increased storage costs.
Redundant Data Storage
Storing duplicate data consumes valuable storage space. As data volumes grow, so do the costs associated with maintaining redundant copies. Organizations may find themselves investing in additional storage infrastructure to accommodate unnecessary data. This investment diverts resources from other critical areas, impacting overall efficiency. Implementing data deduplication techniques can help reduce storage needs and associated costs.
Inefficient Resource Utilization
Inefficient resource utilization results from managing and maintaining duplicate data. IT teams spend considerable time and effort handling redundant data, which could be better spent on optimizing systems and processes. Additionally, duplicate data increases backup times and network traffic, further straining resources. By addressing data duplication, organizations can streamline operations and allocate resources more effectively.
Role of FanRuan in Managing Data Duplication
FanRuan plays a pivotal role in addressing data duplication challenges through its innovative solutions. By leveraging advanced tools like FineDataLink and FineBI, organizations can enhance data integration and analysis, ensuring efficient data management and utilization.
FineDataLink for Data Integration
FineDataLink serves as a comprehensive platform for seamless data integration. It simplifies complex data tasks, making it an essential tool for businesses aiming to manage data duplication effectively.
Real-Time Data Synchronization
Real-time data synchronization stands as a core feature of Real-time data synchronization. This capability ensures that data remains consistent across various systems, reducing the likelihood of duplicate entries. By synchronizing data in real-time, organizations can maintain data integrity and accuracy, which are crucial for reliable business intelligence.
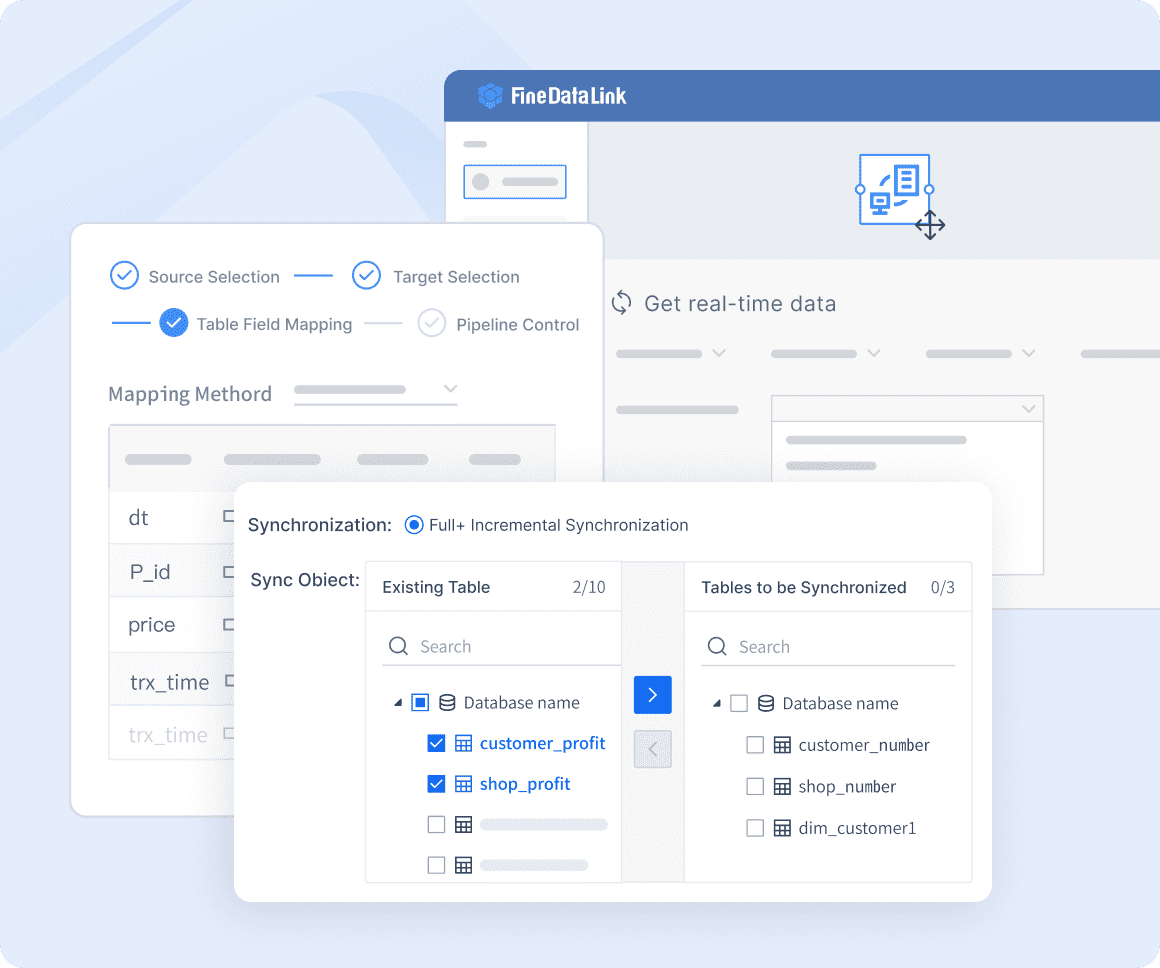
ETL/ELT Capabilities
FineDataLink also offers robust ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) capabilities. These functions allow for efficient data processing and transformation, enabling organizations to streamline their data workflows. By utilizing these capabilities, businesses can identify and eliminate duplicate data, optimizing storage and reducing costs.
FineBI for Enhanced Data Analysis
FineBI empowers organizations to perform advanced data analysis, transforming raw data into actionable insights. Its features facilitate better decision-making by providing clear and accurate visualizations.
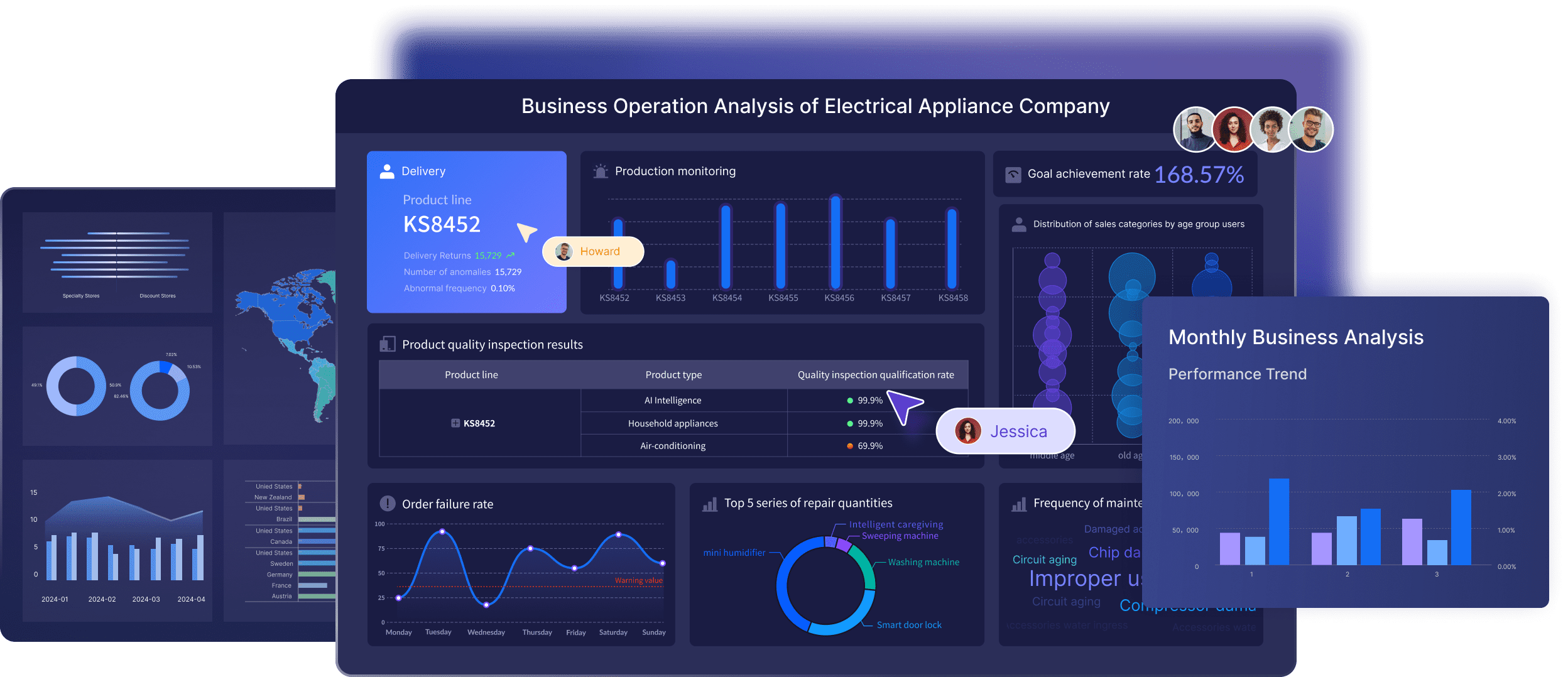
Data Visualization
Data visualization is a key component of FineBI. It allows users to create insightful visual representations of data, making it easier to identify patterns and trends. By visualizing data effectively, organizations can detect anomalies and duplicates, ensuring that their analyses are based on accurate information.
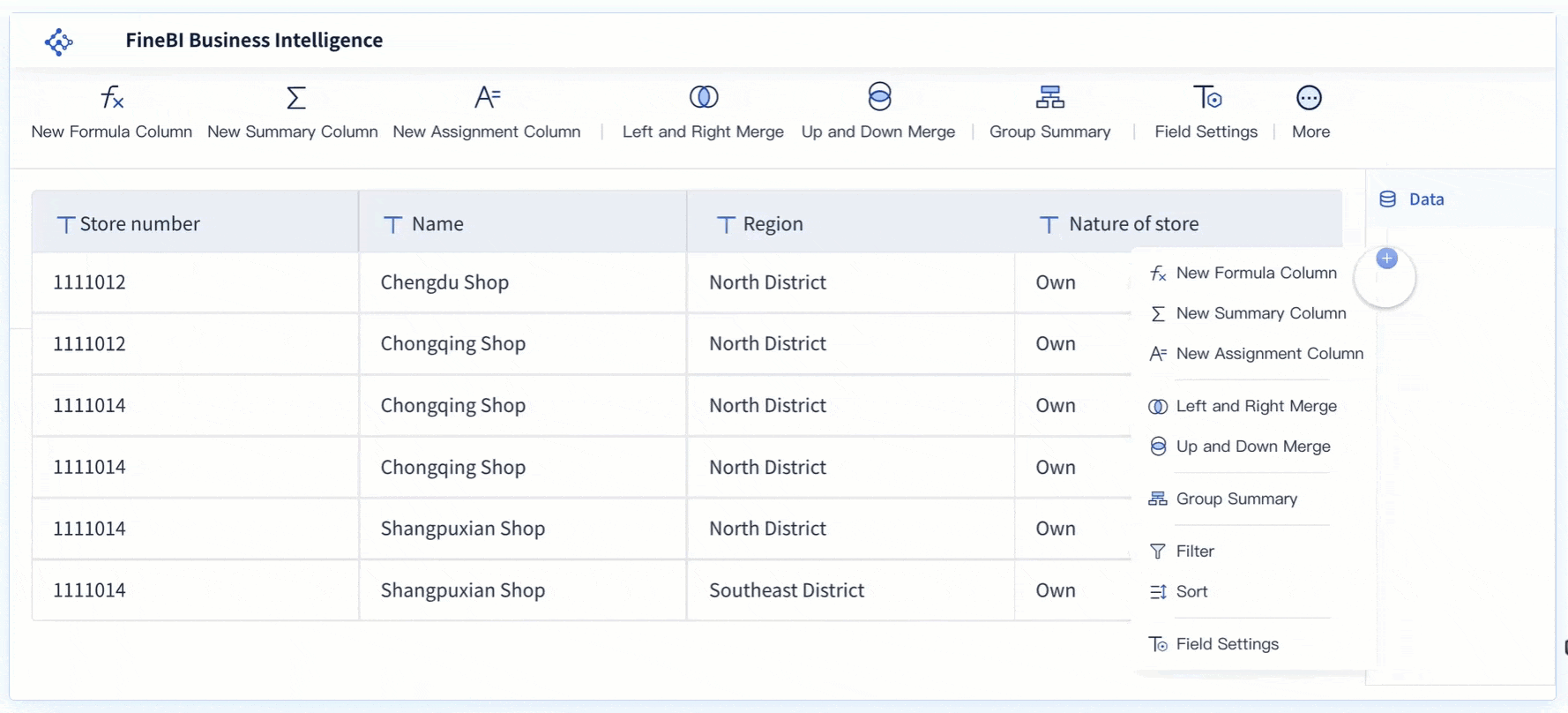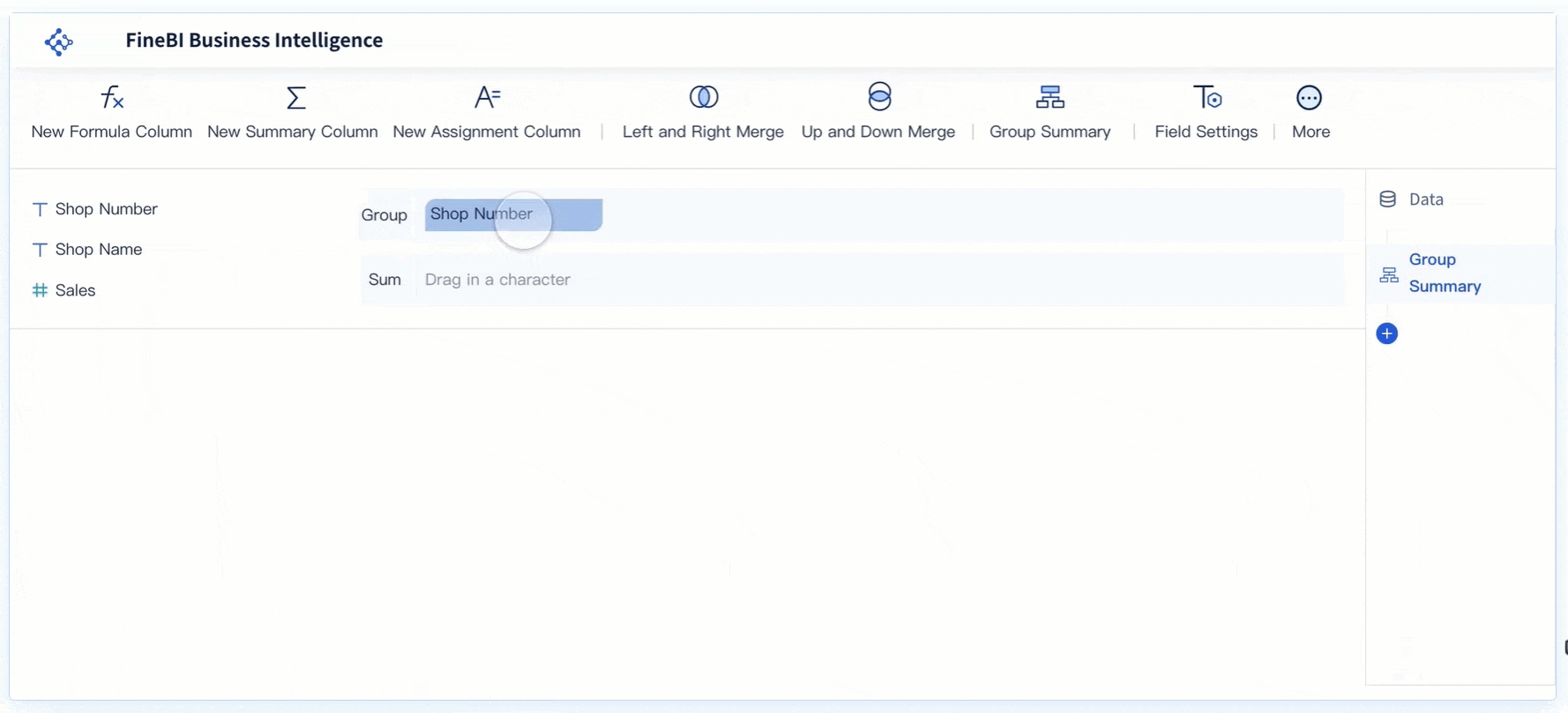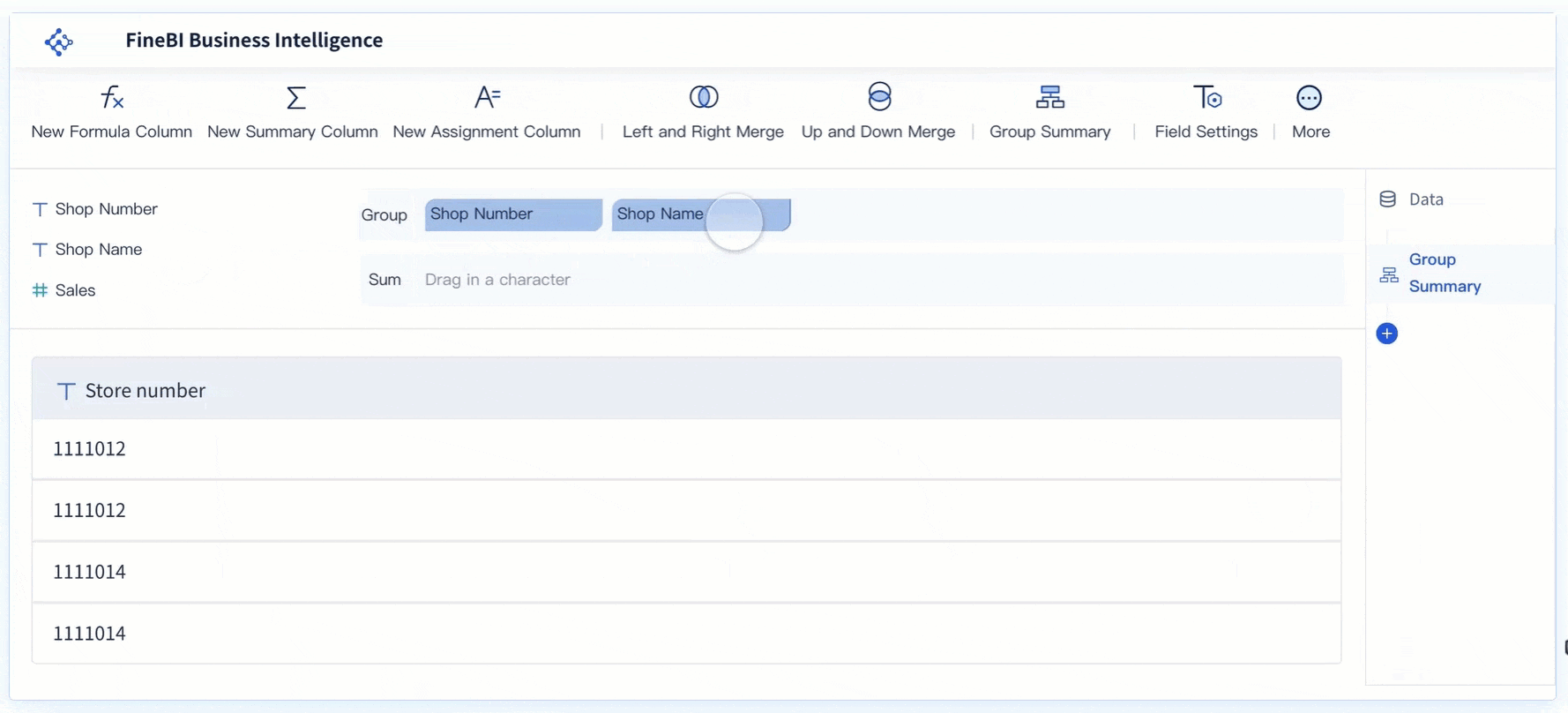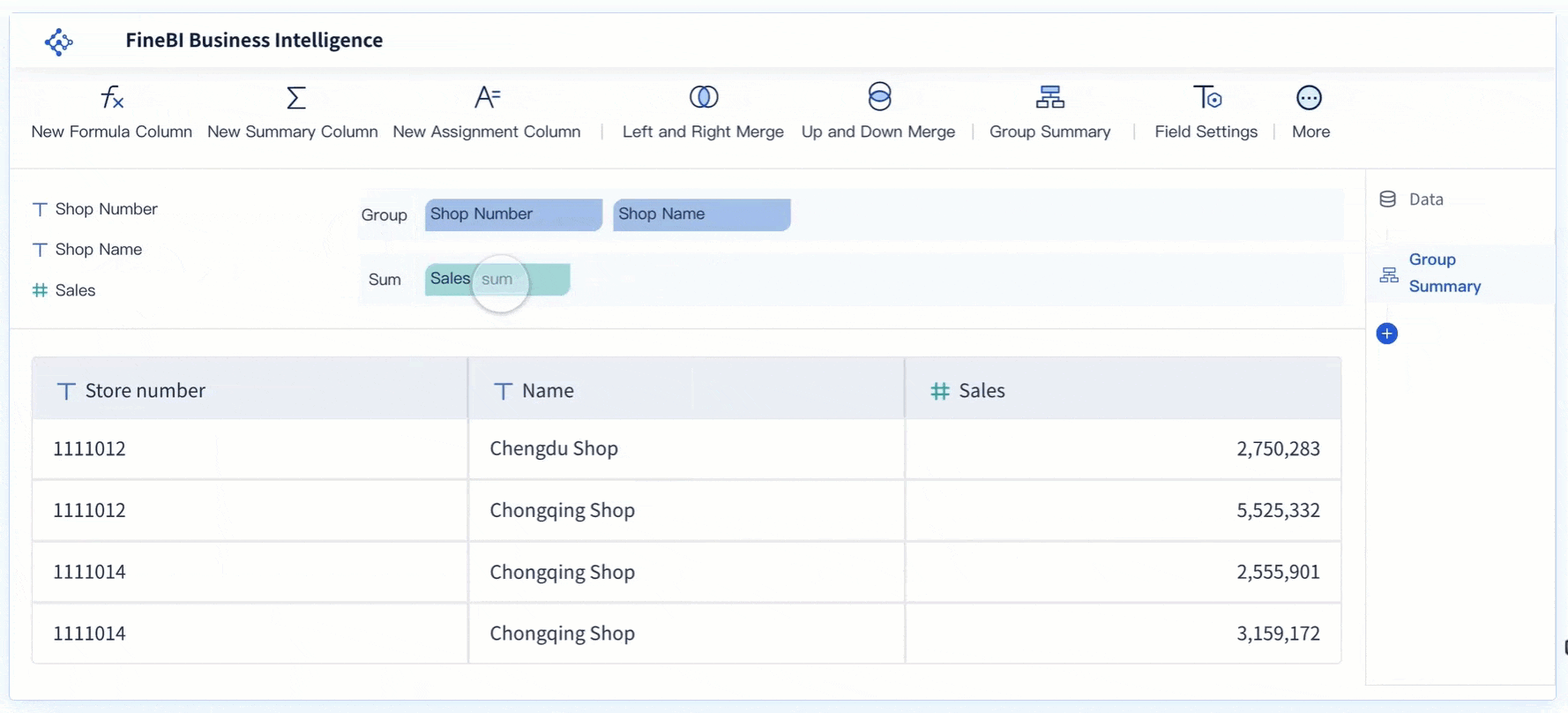
Real-Time Analysis
Real-time analysis capabilities in FineBI enable users to conduct immediate data assessments. This feature ensures that decision-makers have access to the most current data, free from duplication errors. By providing real-time insights, FineBI helps organizations respond swiftly to changing business conditions, enhancing their strategic agility.
Comparing Data Duplication with Related Concepts
Data Deduplication vs. Data Compression
Definitions and Differences
Data deduplication and data compression both aim to optimize storage, but they operate differently. Data deduplication identifies and removes duplicate copies of data, storing only one instance of repetitive blocks. This process significantly reduces storage space requirements by eliminating redundancy. In contrast, data compression reduces the size of data files by encoding information more efficiently, without necessarily removing duplicates.
"Data deduplication is a procedure that assists in lowering storage costs and optimizing free space on the volume."
While deduplication focuses on eliminating redundant data, compression focuses on reducing the overall size of data files. Both techniques enhance storage efficiency, but deduplication specifically targets duplicate data.
Use Cases and Applications
Data deduplication proves essential in environments with high data redundancy, such as backup systems and cloud storage. It helps reduce storage costs and improves version control by maintaining only unique data instances. Organizations use deduplication to manage large volumes of data efficiently, saving resources like storage space and compute power.
Data compression finds application in scenarios where bandwidth and storage are limited. It is commonly used for transmitting data over networks and storing media files. Compression allows for faster data transfer and reduced storage needs, making it ideal for applications requiring quick access to large datasets.
Data Deduplication vs. Data Encryption
Security vs. Efficiency
Data deduplication and data encryption serve different purposes. Deduplication focuses on efficiency by reducing storage space through the elimination of redundant data. It optimizes data management and lowers storage costs. Encryption, on the other hand, prioritizes security by converting data into a coded format, protecting it from unauthorized access.
"Deduplication involves identifying and eliminating redundancy by saving only one instance of repetitive blocks."
While deduplication enhances storage efficiency, encryption ensures data confidentiality and integrity. Organizations often balance these techniques to achieve both secure and efficient data management.
Complementary Techniques
Data deduplication and encryption can complement each other in data management strategies. By deduplicating data before encryption, organizations can reduce the amount of data that needs to be encrypted, saving processing time and resources. This approach maintains data security while optimizing storage efficiency.
Strategies to Manage Data Duplication
Organizations must adopt effective strategies to manage data duplication, ensuring data integrity and optimizing storage. These strategies involve data cleaning techniques and implementing robust data governance practices.
Data Cleaning Techniques
Data cleaning techniques play a crucial role in eliminating duplicate records and enhancing data quality. Two primary methods include data scrubbing and data normalization.
Data Scrubbing
Data scrubbing involves identifying and correcting errors in datasets. This process removes duplicate entries and ensures data accuracy. Organizations often rely on user feedback and advanced technologies like AI and ML to spot and resolve duplicate records. These technologies can automate the scrubbing process, making it more efficient and less prone to human error.
Data Normalization
Data normalization standardizes data formats across systems. This technique reduces redundancy by organizing data into a consistent structure. By normalizing data, organizations can prevent duplication caused by inconsistent data entry. This approach not only improves data quality but also facilitates easier data integration and analysis.
Implementing Data Governance
Implementing data governance is essential for managing data duplication effectively. It involves establishing data standards and conducting regular data audits.
Establishing Data Standards
Establishing data standards ensures uniformity in data handling across an organization. These standards define how data should be entered, stored, and maintained. By adhering to these guidelines, organizations can minimize the risk of data duplication. Consistent data management practices lead to improved data quality and reduced storage costs.
Regular Data Audits
Regular data audits help identify and eliminate duplicate records. These audits involve reviewing datasets to ensure compliance with established data standards. By conducting audits frequently, organizations can maintain data integrity and quickly comply with data regulations. This proactive approach prevents the accumulation of duplicate data, optimizing storage utilization and enhancing data management efficiency.
Benefits of Reducing Data Duplication
Reducing data duplication offers numerous advantages that enhance both data quality and cost efficiency. By addressing this issue, organizations can streamline their operations and improve decision-making processes.
Enhanced Data Quality
Improving data quality stands as a primary benefit of reducing data duplication. When organizations eliminate duplicate records, they achieve: Improving data quality
Improved Accuracy
Accurate data forms the foundation of effective business operations. Duplicate data often leads to discrepancies, such as multiple departments updating the same customer record, which can cause confusion. By removing duplicates, organizations ensure that their data remains accurate and reliable. This accuracy supports better decision-making and enhances overall operational efficiency.
Reliable Business Insights
Reliable insights depend on clean and accurate data. Data duplication can skew analytics, leading to misleading conclusions. By eliminating duplicates, businesses can trust their data-driven insights, resulting in more informed strategies and decisions. This reliability fosters confidence among stakeholders and supports long-term success.
Cost Efficiency
Reducing data duplication also contributes significantly to cost efficiency. Organizations can optimize their resources and reduce expenses by addressing this issue.
Reduced Storage Needs
Duplicate data consumes unnecessary storage space, leading to increased costs. By eliminating redundant data, organizations can reduce the amount of storage required. This reduction not only lowers storage costs but also delays the need for additional hardware investments. For businesses with large volumes of data stored in the cloud, deduplication can result in substantial cost savings.
Optimized Resource Allocation
Efficient resource allocation becomes possible when data duplication is minimized. IT teams spend less time managing redundant data, allowing them to focus on more critical tasks. Additionally, reducing duplicate data decreases backup times and network traffic, further optimizing resource utilization. This optimization leads to improved productivity and streamlined operations across the organization.
By focusing on reducing data duplication, organizations can enhance data quality and achieve cost efficiency, ultimately supporting better business outcomes.
Challenges in Addressing Data Duplication
Organizations face numerous challenges when addressing data duplication. These challenges can be categorized into technical and organizational aspects, each presenting unique obstacles that require strategic solutions.
Technical Challenges
Complexity of Data Systems
Modern organizations often operate complex data systems. These systems consist of multiple databases and applications, each with its own data management protocols. This complexity makes it difficult to identify and eliminate duplicate data. Oracle, a leader in data management, highlights that duplicate data creates additional burdens across hardware and bandwidth. These burdens lead to increased costs and inefficiencies. Simplifying data systems and implementing centralized data management can help mitigate these challenges.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Legacy systems pose another significant challenge. Many organizations still rely on outdated systems that lack the capability to detect and manage duplicate data effectively. Integrating these systems with modern data management solutions can be difficult. The lack of compatibility often results in data silos, where duplicate data proliferates unchecked. Organizations must invest in upgrading or replacing legacy systems to ensure seamless data integration and deduplication.
Organizational Challenges
Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is a common organizational challenge. Employees may hesitate to adopt new data management practices, fearing disruption to established workflows. This resistance can hinder efforts to address data duplication. To overcome this, organizations should focus on change management strategies. Educating employees about the benefits of reducing duplicate data, such as improved data quality and cost savings, can foster acceptance and cooperation.
Lack of Awareness
A lack of awareness about the impact of data duplication further complicates efforts to address it. Many organizations underestimate the extent of duplicate data and its consequences. Oracle emphasizes that duplicate data compromises data quality, leading to inaccurate reports and analytics. Raising awareness through training and communication can help organizations recognize the importance of tackling data duplication. By understanding its impact, they can prioritize initiatives to improve data management practices.
Practical Applications and Real-Life Examples

Industry-Specific Applications
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, data deduplication plays a crucial role in managing patient records. Hospitals often deal with vast amounts of data, including medical histories, test results, and billing information. By implementing deduplication techniques, healthcare providers can ensure that patient records remain accurate and up-to-date. This accuracy is vital for delivering quality care and making informed medical decisions.
Retail
Retail businesses benefit from data deduplication by optimizing their inventory management systems. Duplicate data entries can lead to discrepancies in stock levels, affecting sales and customer satisfaction. By eliminating redundant data, retailers can maintain accurate inventory records, streamline operations, and improve customer service. This approach also reduces storage costs, allowing retailers to invest in other areas of their business.
Retail dashboard created by FineReport
Managing data duplication is crucial for maintaining data accuracy and optimizing business intelligence. By implementing effective data management strategies, organizations can enhance decision-making and foster a collaborative environment. Proactive measures, such as utilizing AI and machine learning, minimize redundant records, leading to improved operational efficiency. Organizations should adopt best practices for data quality and efficiency, ensuring that their data remains reliable and actionable. This approach not only saves resources but also reduces costs, ultimately supporting better business outcomes.
FAQ
Data duplication occurs when identical copies of data exist within a system or across multiple systems. This redundancy often results from inconsistent data entry practices, integration issues, or human errors. It can lead to increased storage costs and inaccurate data analysis.
Data duplication negatively impacts business intelligence by skewing reports and analytics. Duplicate data can lead to misleading insights, causing businesses to make decisions based on incorrect information. It also increases storage costs and complicates data management.
Several factors contribute to data duplication:
Human Errors: Mistakes during manual data entry often result in duplicate records.
System Integration Issues: Inadequate integration between systems can lead to redundant data entries.
Inconsistent Data Formats: Different formats across systems can create duplicates when data is merged.
Organizations can manage data duplication through several strategies:
Data Cleaning: Techniques like data scrubbing and normalization help eliminate duplicates.
Data Governance: Establishing data standards and conducting regular audits ensure consistent data management.
Advanced Tools: Utilizing platforms like FineDataLink and FineBI can streamline data integration and analysis, reducing duplication.
FineDataLink prevents data duplication by enabling real-time data synchronization across systems. Its ETL/ELT capabilities streamline data processing, ensuring consistent and accurate data integration. This reduces the likelihood of duplicate entries and enhances data quality.
Yes, data deduplication and encryption can complement each other. Deduplicating data before encryption reduces the amount of data that needs encrypting, saving processing time and resources. This approach maintains data security while optimizing storage efficiency.
Reducing data duplication enhances data quality and cost efficiency. It ensures accurate and reliable business insights, supporting better decision-making. Additionally, it lowers storage costs and optimizes resource allocation, improving overall operational efficiency.
Continue Reading About Data Duplication
2025 Best Data Integration Solutions and Selection Guide
Explore top data integration solutions for 2025, enhancing data management and operational efficiency with leading platforms like Fivetran and Talend.
Howard
Dec 19, 2024
2025's Best Data Validation Tools: Top 7 Picks
Explore the top 7 data validation tools of 2025, featuring key features, benefits, user experiences, and pricing to ensure accurate and reliable data.
Howard
Aug 09, 2024
Best Data Integration Platforms to Use in 2025
Explore the best data integration platforms for 2025, including cloud-based, on-premises, and hybrid solutions. Learn about key features, benefits, and top players.
Howard
Jun 20, 2024
Best Data Management Tools of 2025
Explore the best data management tools of 2025, including FineDataLink, Talend, and Snowflake. Learn about their features, pros, cons, and ideal use cases.
Howard
Aug 04, 2024
Data Pipeline Automation: Strategies for Success
Understand definition and key components of data pipeline automation. Explore the essential strategies for successful data pipeline automation.
Howard
Jul 18, 2024
Designing Data Pipeline Architecture: A Step-by-Step Guide
Learn how to design data pipeline architecture for seamless data flow, ensuring efficient processing and analytics for informed business decisions.
Howard
Nov 06, 2024