You rely on an annual report to see clear, honest business information about an organisation. This report gives you a snapshot of how the organisation performed over the past year. When you read an annual report, you gain insight into the company’s finances, goals, and challenges. Organisations use annual reports to build accountability with you and other stakeholders. Transparency in these reports can impact real-world outcomes, such as the cost of debt. For example, recent studies show that when regulators review annual reports and ask for more detail, organisations often face higher debt costs. This process improves transparency and helps everyone understand the true state of the business.
You can think of an annual report as a comprehensive financial document that tells the story of an organisation’s year. This report gives you a clear look at how the organisation performed, what it achieved, and where it faced challenges. Most annual reports include audited financial statements, business highlights, and commentary from management. These details help you understand not just the numbers, but also the strategies and goals behind them.
Public companies must prepare and share an annual report every year. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and SEBI require these reports to ensure transparency and reliability. Private companies often produce annual reports as well, especially if they want to build trust with investors or secure financing. The format of an annual report follows established principles. You will usually find sections like corporate information, financial highlights, a letter from the CEO, management discussion and analysis (MD&A), financial statements, notes, and an auditor’s report. These sections follow generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), which means you can compare reports from different organisations with confidence.
Annual reports stand out as the most credible source of information for investors, shareholders, and other stakeholders. They include details you cannot find anywhere else, such as business achievements and management’s own explanations.
The core of every annual report is the set of financial statements. These statements include:
Independent auditors review these statements to make sure they are accurate and follow accounting standards. This process adds another layer of trust to the report.
You rely on annual report to make informed decisions about an organisation. These reports give you a transparent view of how a company manages its money, sets goals, and measures success. When you read an annual report, you see not just the numbers, but also the story behind them. This transparency builds accountability and trust between the organisation and its stakeholders.
A study of listed companies found that the timing and quality of annual report publication depend on factors like company size and retained earnings. This shows that organisations see timely disclosure as a critical part of communication with stakeholders. Private companies also benefit from filing annual reports on time. Doing so can improve access to financing and help keep business operations running smoothly.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Transparency | Annual reports provide detailed financial and operational data, helping you make informed choices. |
| Accountability | Reporting on goals and results shows the organisation takes your interests seriously. |
| Financial Statements | Income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement reveal financial health. |
| Management Analysis | Leaders explain results and future plans, giving you context for the numbers. |
| Corporate Governance | Details on board members and ethics ensure responsible operation. |
| Stakeholder Use | Investors and supporters use reports for analysis, evaluation, and planning. |
You can trust annual reports because they go through strict audit and assurance processes. Full audits cover most activities and provide reasonable assurance that the information is accurate. This level of verification increases your confidence in the report.
Annual reports are not just a regulatory requirement. They are a vital communication tool. They help you, as an investor, employee, or partner, understand the true state of an organisation. When you read an annual report, you gain the knowledge you need to make smart decisions and support organisations that align with your values.
When you open an annual report, you see a clear structure that helps you find important information quickly. Most reports follow a similar format, making it easier for you to compare different companies. Here are the typical components you will find:
Investors and analysts pay special attention to the management discussion and analysis, financial statements, and risk factors. These sections help you understand the company’s financial position, performance drivers, and potential challenges.
Financial statements form the heart of every annual report. You use these documents to assess the company’s financial position and track its progress over time. The main financial statements include:
You rely on these financial statements to evaluate financial highlights, liquidity, and profitability. Research shows that clear and easy-to-read financial statements often link to better financial performance. When companies make their financial document simple and transparent, you can trust the numbers and make smarter decisions.
The management discussion and analysis section gives you context for the numbers in the financial statements. Company leaders explain what drove the results, how they handled challenges, and what they plan for the future. This section helps you see beyond the numbers and understand the company’s strategy. Market analysts often focus on this part because it reveals management’s thinking and future plans.
FineReport from FanRuan helps you create annual reports that are clear, accurate, and visually engaging. You can integrate data from many sources, automate financial reporting, and design custom dashboards. FineReport makes it easy to present financial highlights and financial statements in a way that everyone can understand. With its drag-and-drop interface, you save time and reduce errors. You also gain tools to visualize the company’s financial position and performance, making your annual report more useful for all stakeholders.
Annual reports serve many people inside and outside an organisation. You can use these reports to make decisions, track progress, and understand how a company operates. Let’s look at the main groups who benefit from annual reports.
You, as an investor or shareholder, depend on annual reports to judge the financial health of an organisation. These reports give you access to key data like Return on Assets (ROA) and Return on Equity (ROE). With this information, you can measure how well a company uses its resources and whether new strategies, such as adopting new technology, improve results. Research shows that annual reports help you make informed investment choices by providing clear, verifiable numbers. When you see strong performance in these reports, you gain confidence in your investment decisions.
Tip: FineReport from FanRuan helps you visualize financial data, making it easier to spot trends and compare companies.

If you work in management or as an employee, you use annual reports to set goals and track progress. These reports include important Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as gross profit margin, net profit margin, and efficiency ratios. You can use these KPIs to understand how your department is doing and where you need to improve. Regular updates from annual reports help you stay focused on your targets and adjust your plans as needed.
FineReport makes it simple to share dashboards and reports across departments. You can tailor information for different teams, helping everyone stay informed and motivated.
Regulators and the public rely on annual reports to check if an organisation follows the rules and operates responsibly. Studies show that annual reports are the most trusted source for corporate transparency. Regulators use the information to monitor companies and make decisions about oversight. The public, including customers and community members, can see how a company handles risks, ethics, and social responsibility.
Note: FanRuan solutions help organisations create clear, accurate reports that meet regulatory standards and build public trust.
Annual reports connect you to the real story of an organisation. Whether you invest, manage, or simply want to know more, these reports give you the facts you need.
When you fail to file an annual report, you expose your company to serious risks. These risks affect your legal standing, finances, and daily operations. Many companies underestimate the impact of missing a filing deadline, but the consequences can be severe and long-lasting.
You face immediate legal trouble if you do not file your annual report on time. Most states impose late penalties right away. Continued failure can lead to the loss of your company’s good standing or even the right to do business. When this happens, the state may consider your business nonexistent. You lose the protection of limited liability, which means your personal assets could be at risk in lawsuits. Regulatory agencies, such as the SEC, can also impose fines and sanctions. In some cases, investors may sue if they suffer losses due to your late or missing disclosures. A study in Georgia found that about 30% of companies miss the nine-month deadline, with many facing enforcement actions as a result.
Missing a filing deadline does not just bring penalties. It can damage your reputation and erode trust with investors and regulators.
Failing to file your annual report can hurt your finances in several ways:
Severe cases can lead to lawsuits, executive firings, or even bankruptcy.
Operational problems often follow legal and financial trouble. You may lose the right to operate in your state. This can force you to stop business activities until you resolve the issue. Vendors and customers may hesitate to work with you if your company loses good standing. You might also lose the ability to bid on contracts, as many organizations require up-to-date filings. If you stop doing business in a state but do not file the proper withdrawal paperwork, you still face penalties for missing reports.
Staying current with your annual report keeps your business running smoothly and protects your reputation.
When you look at business reports, you may notice several types that seem similar. Each serves a different purpose and follows its own rules. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right report for your needs.
You often see both an annual report and a 10-K from public companies. Both cover a full year, but they are not the same. The annual report gives you a broad overview. It uses visuals, stories, and highlights to help you understand the company’s journey. You find messages from the CEO, colorful charts, and summaries of achievements. The 10-K, on the other hand, is a formal filing required by the SEC. It contains detailed financial data, risk factors, and management’s discussion in a strict format.
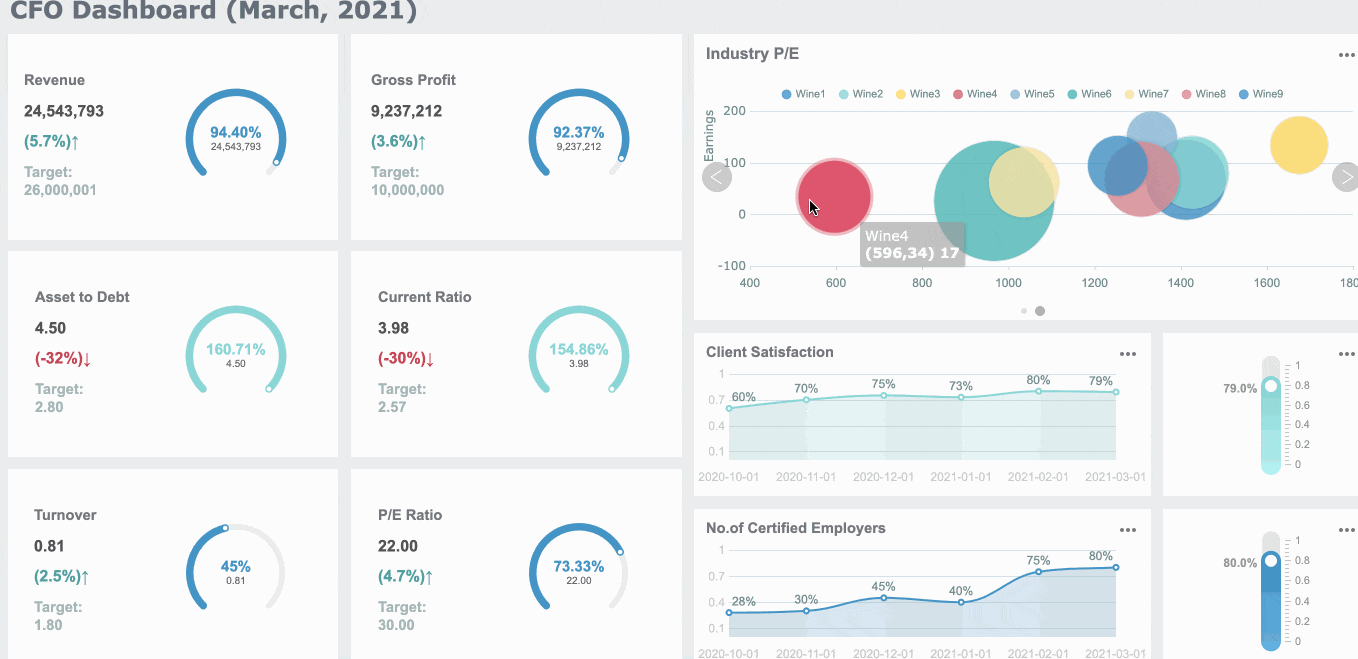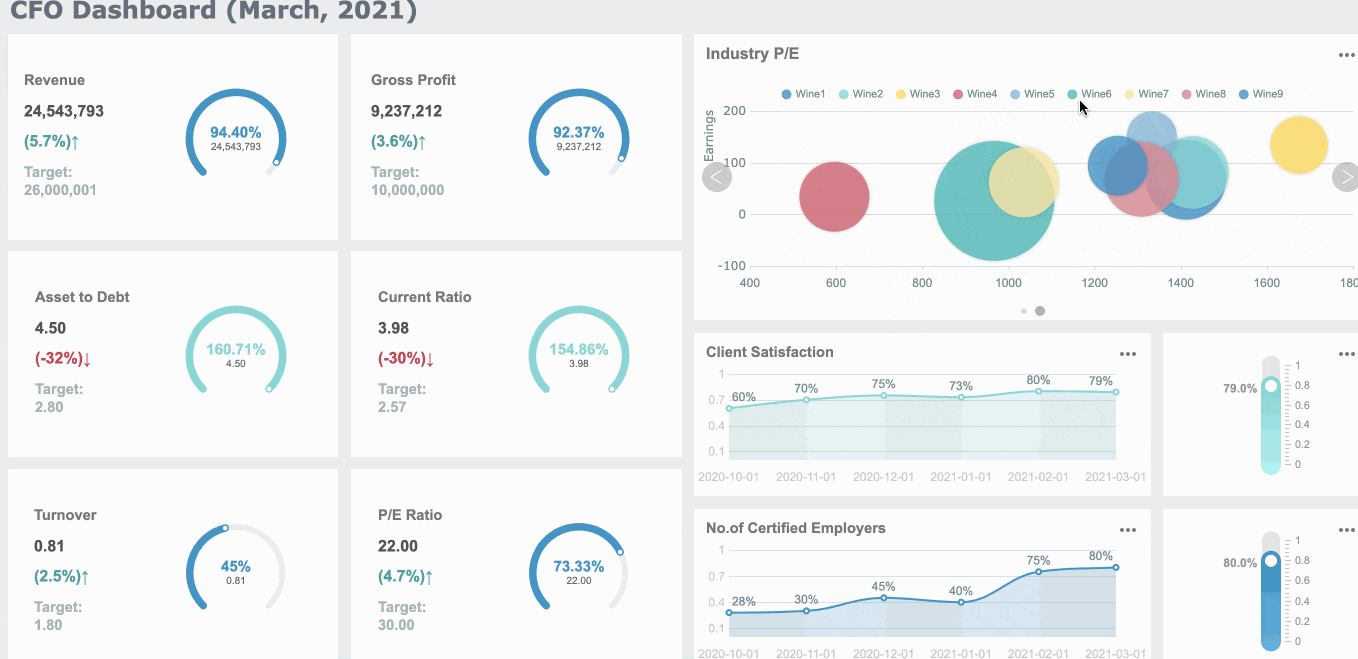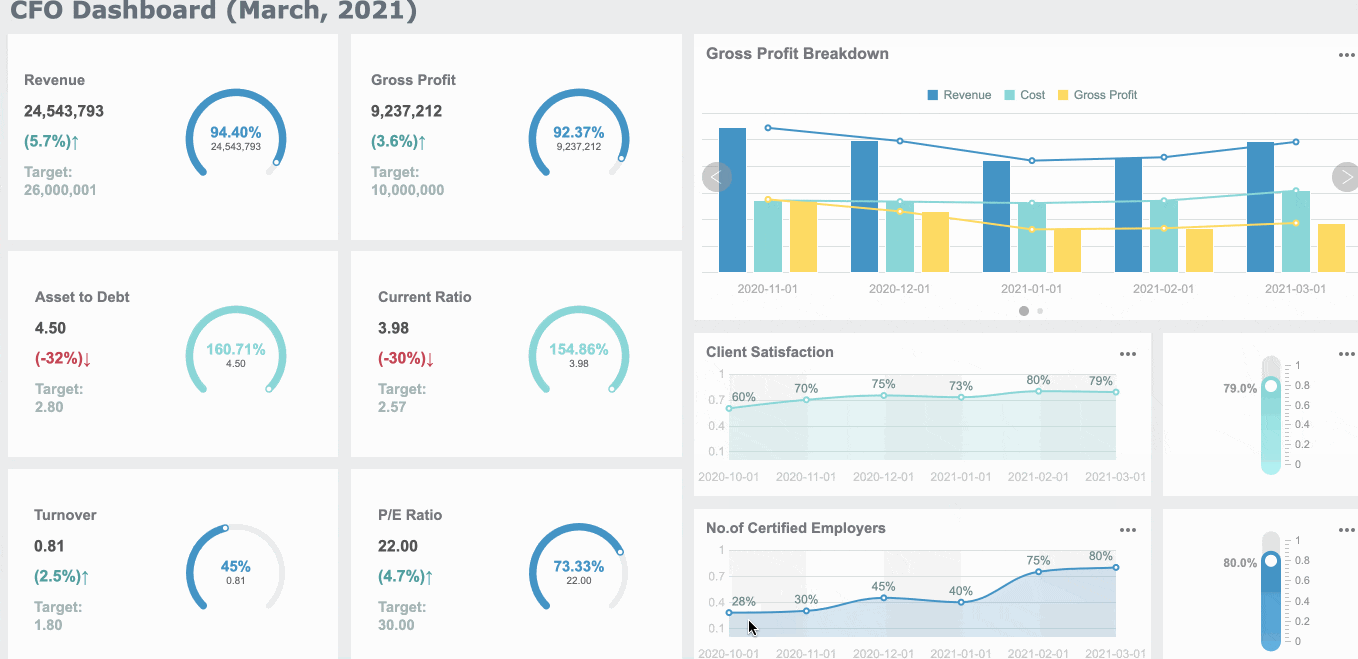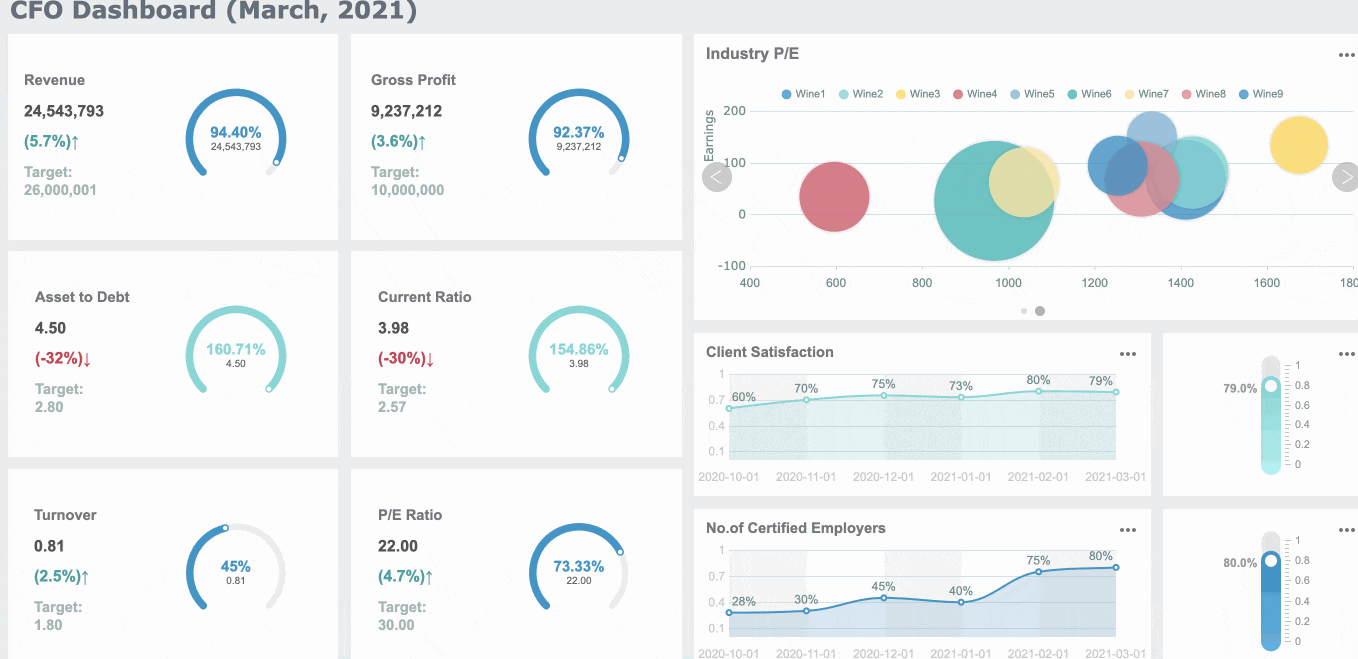
Here is a table to help you compare:
| Filing Type | Frequency | Audit Status | Key KPIs Included | Presentation Style | Regulatory Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Report | Yearly | Audited | Balance sheet, income statement, cash flow, year-over-year comparison | Visual, narrative, includes CEO letter and graphics | For shareholders, less strict, includes auditor’s report |
| 10-K | Yearly | Audited | Earnings per share, detailed financials, risk factors, non-GAAP measures | Detailed, follows SEC rules, five sections | SEC filing, strict, includes MD&A and auditor’s certification |
The 10-K focuses on numbers and compliance. It requires management to explain changes in sales, profits, and liquidity with clear data. The annual report tells the company’s story and builds trust with investors.
You also see interim reports, such as the 10-Q, during the year. These come out every quarter. Interim reports give you updates on recent performance. They are less detailed and usually unaudited. You use them to track short-term trends and spot changes early.
FineReport supports all these report types. You can create detailed annual reports, 10-Ks, and interim updates using one platform. FineReport helps you present data clearly, whether you need a visual summary or a detailed regulatory filing.
You gain real insight into a company’s strategy and performance when you use well-prepared reports. Strong board oversight and clear reporting practices help you see the full picture, reducing information gaps and supporting better decisions. FineReport from FanRuan-en gives you the tools to create accurate, easy-to-read reports that build trust and support growth. Use these reports to guide your choices and strengthen your connection with stakeholders.
Click the banner below to experience FineReport for free and empower your enterprise to convert data into productivity!

작성자
Seongbin
FanRuan에서 재직하는 고급 데이터 분석가
관련 기사

보고서 자동화 프로그램으로 공무원 업무 혁신하기
보고서 자동화 프로그램으로 공무원 업무 효율 30% 향상, 오류 감소, 맞춤형 보고서 제작까지 혁신적 행정 환경을 실현합니다.
Seongbin
2025년 12월 15일
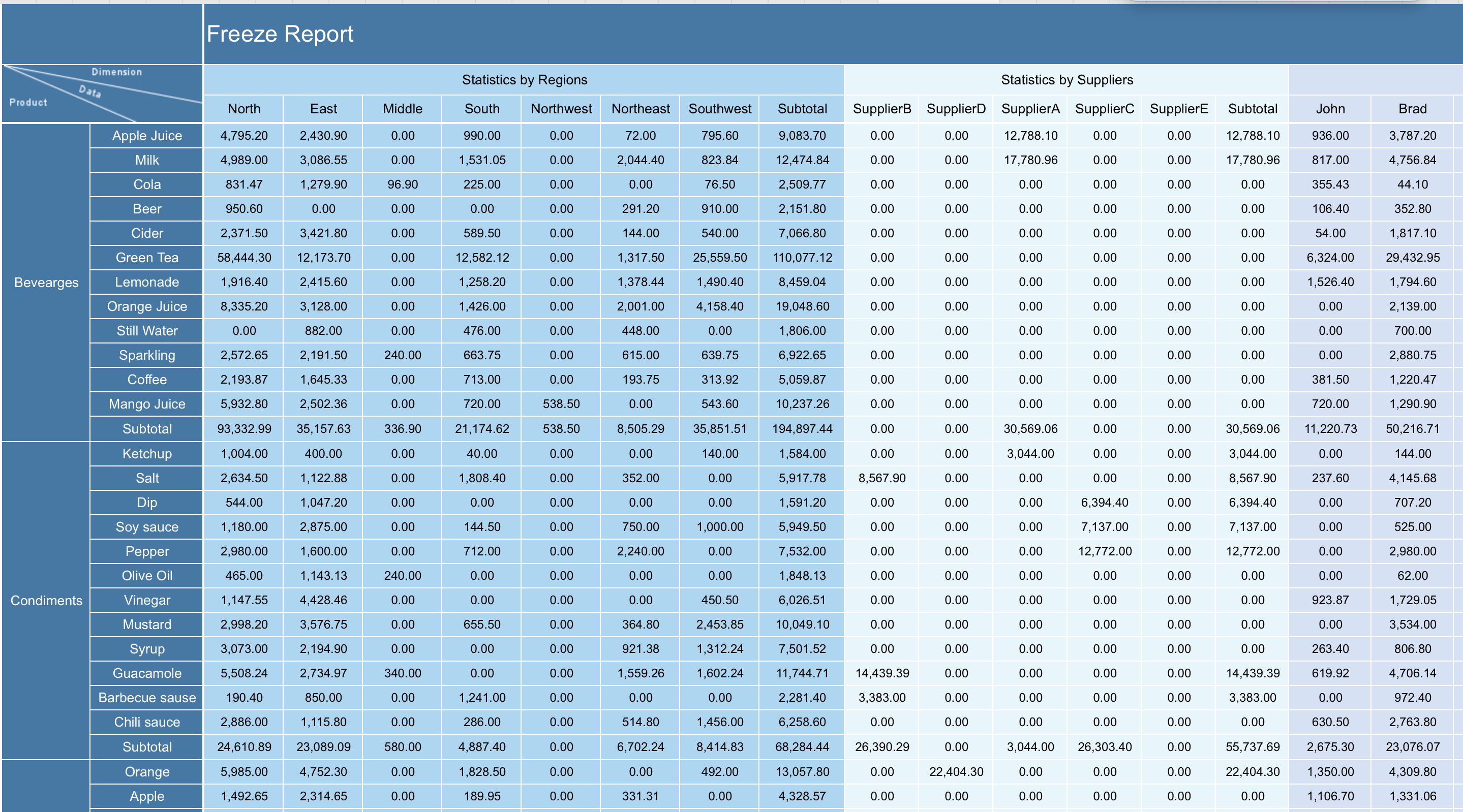
2026년 최신 표 만드는 사이트 비교
2026년 표 만드는 사이트 비교! 주요 기능, AI 자동 표 생성, 협업, 가격, 모바일 지원 등 목적별 추천과 선택 기준을 한눈에 확인하세요.
Seongbin
2025년 12월 04일

손익계산서 쉽게 작성하는 방법
손익계산서 작성 시 수익·비용 분류, 항목 누락 방지, 자동화 팁 등 실무에 바로 적용할 수 있는 쉬운 작성 방법을 안내합니다.
Seongbin
2025년 11월 17일