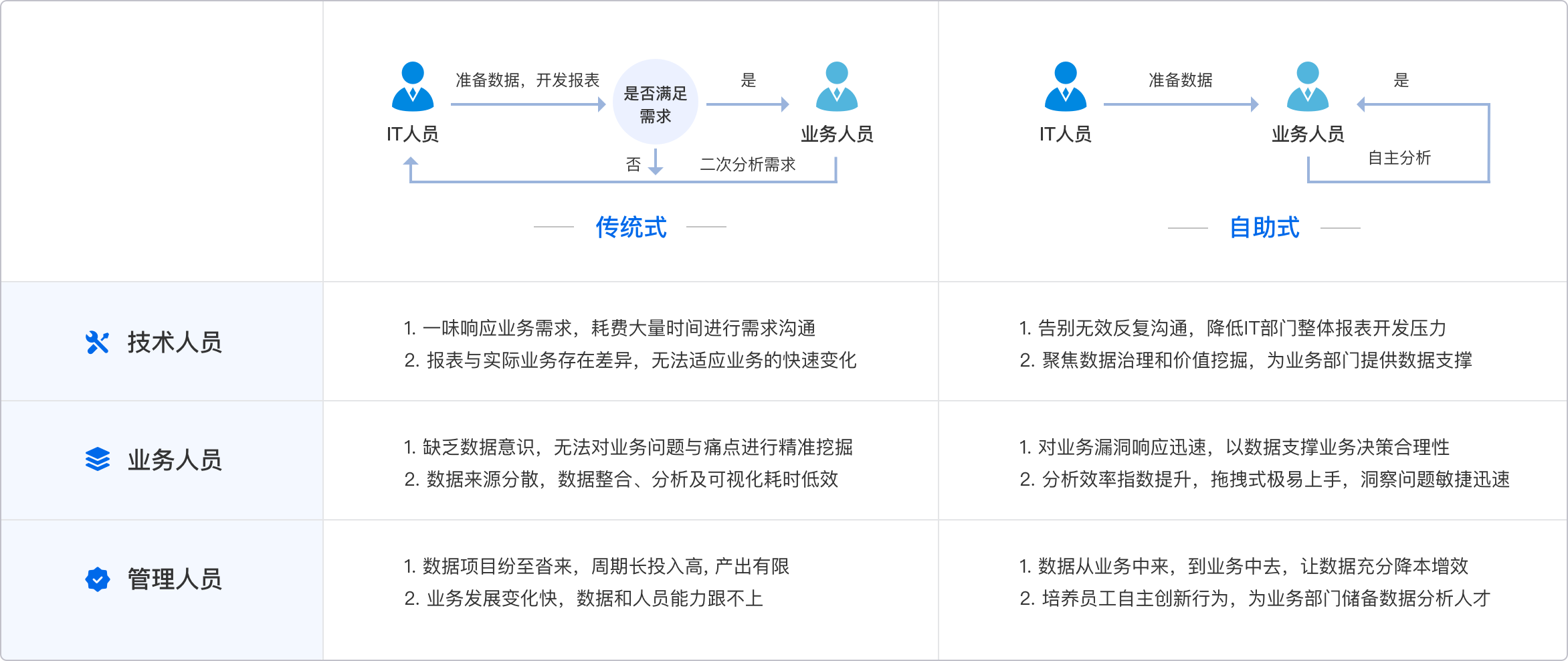
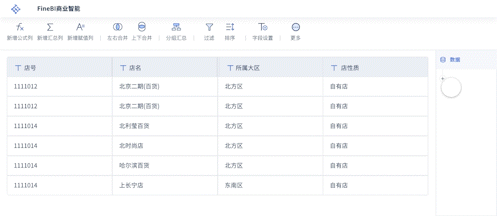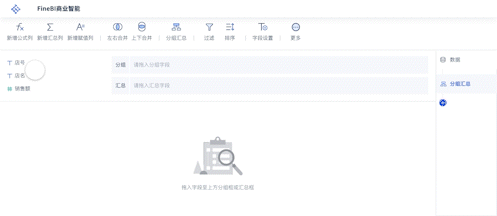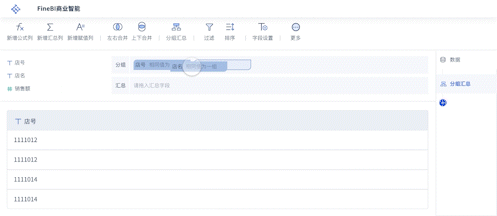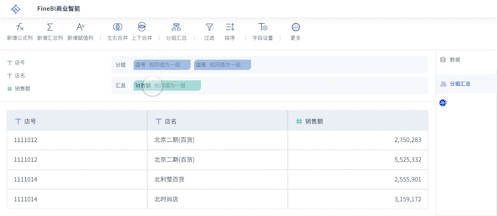
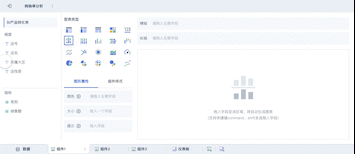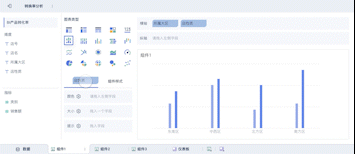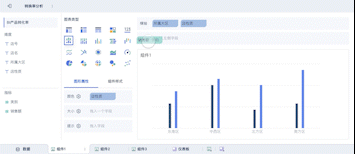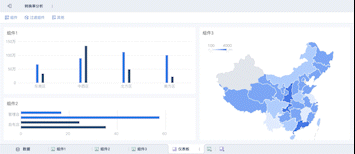
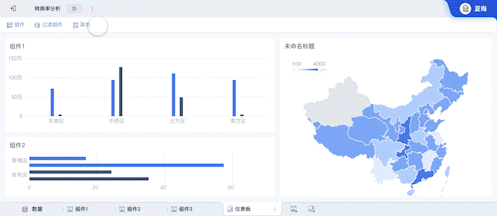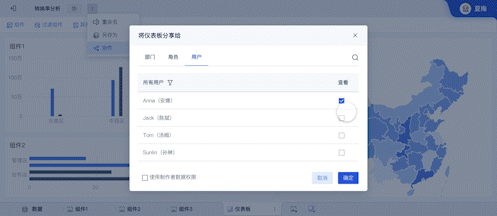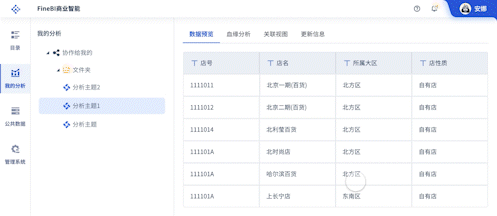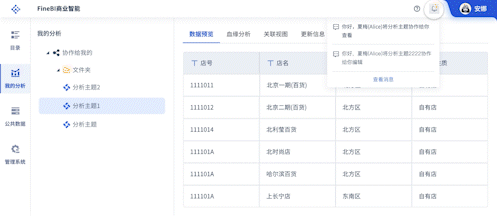
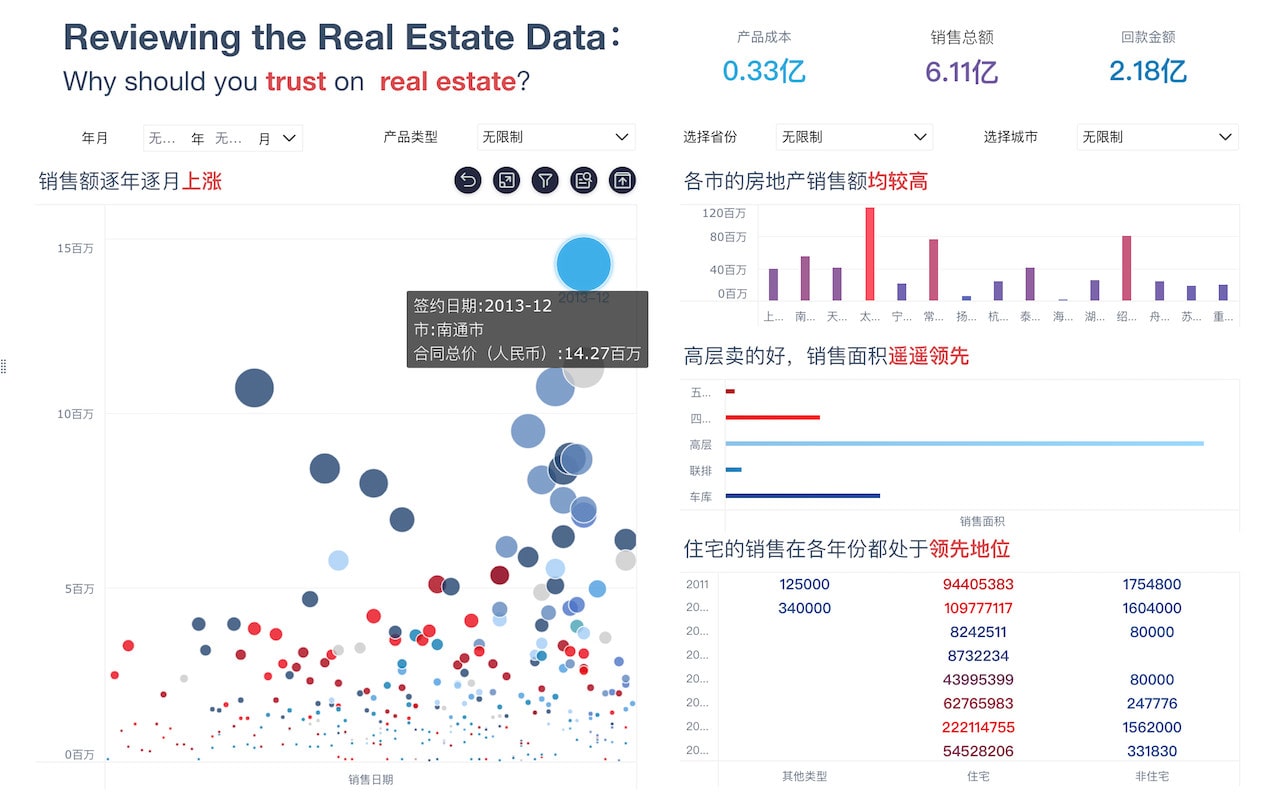
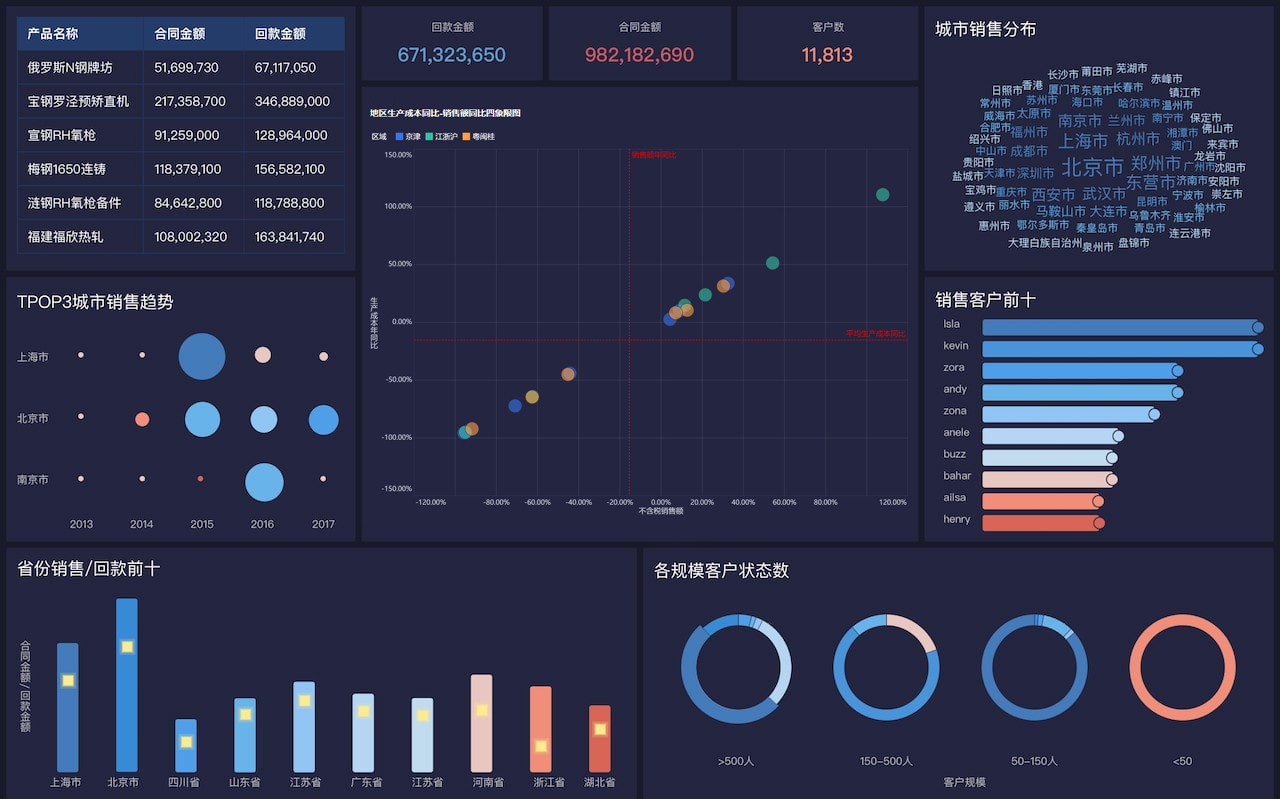
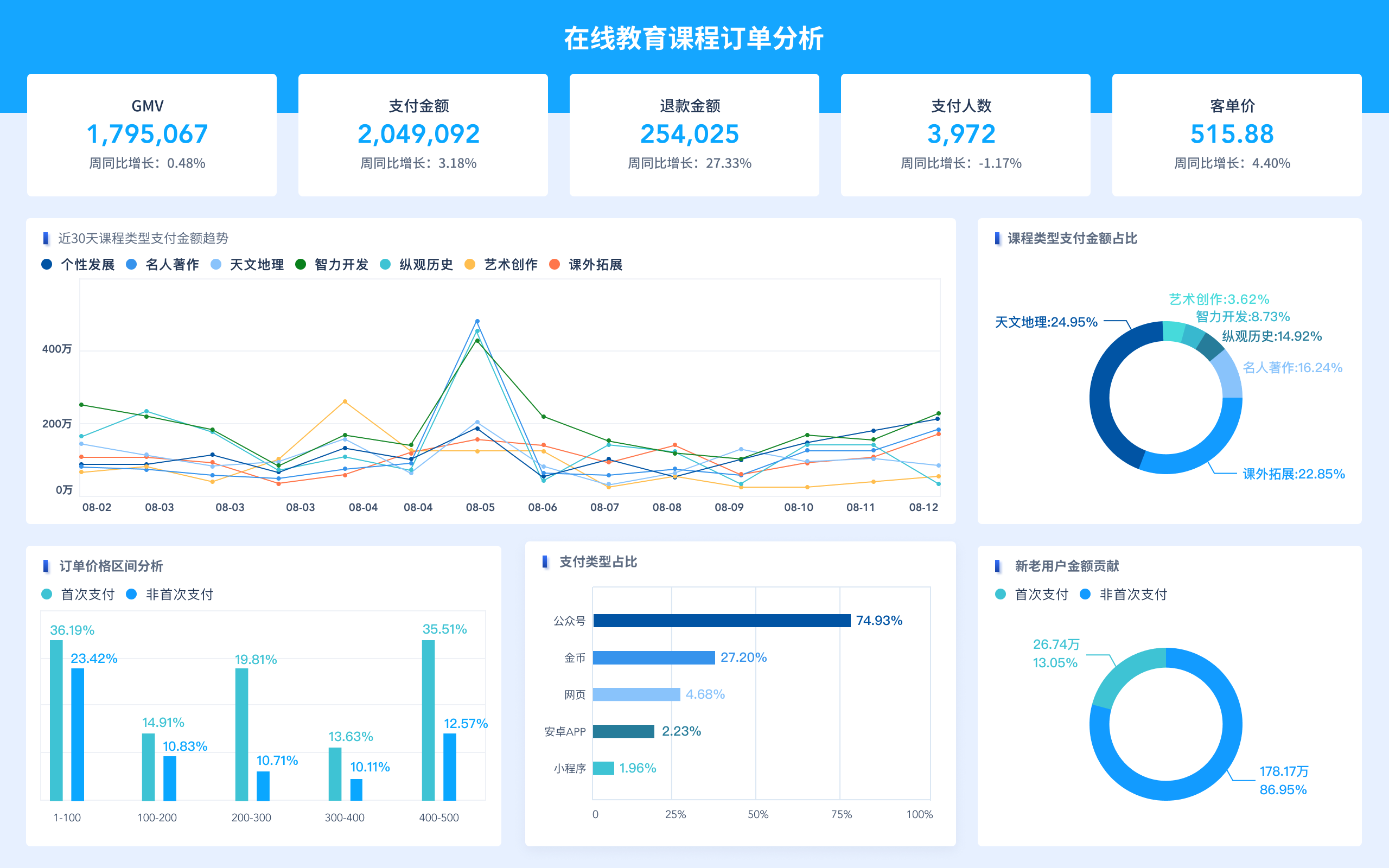
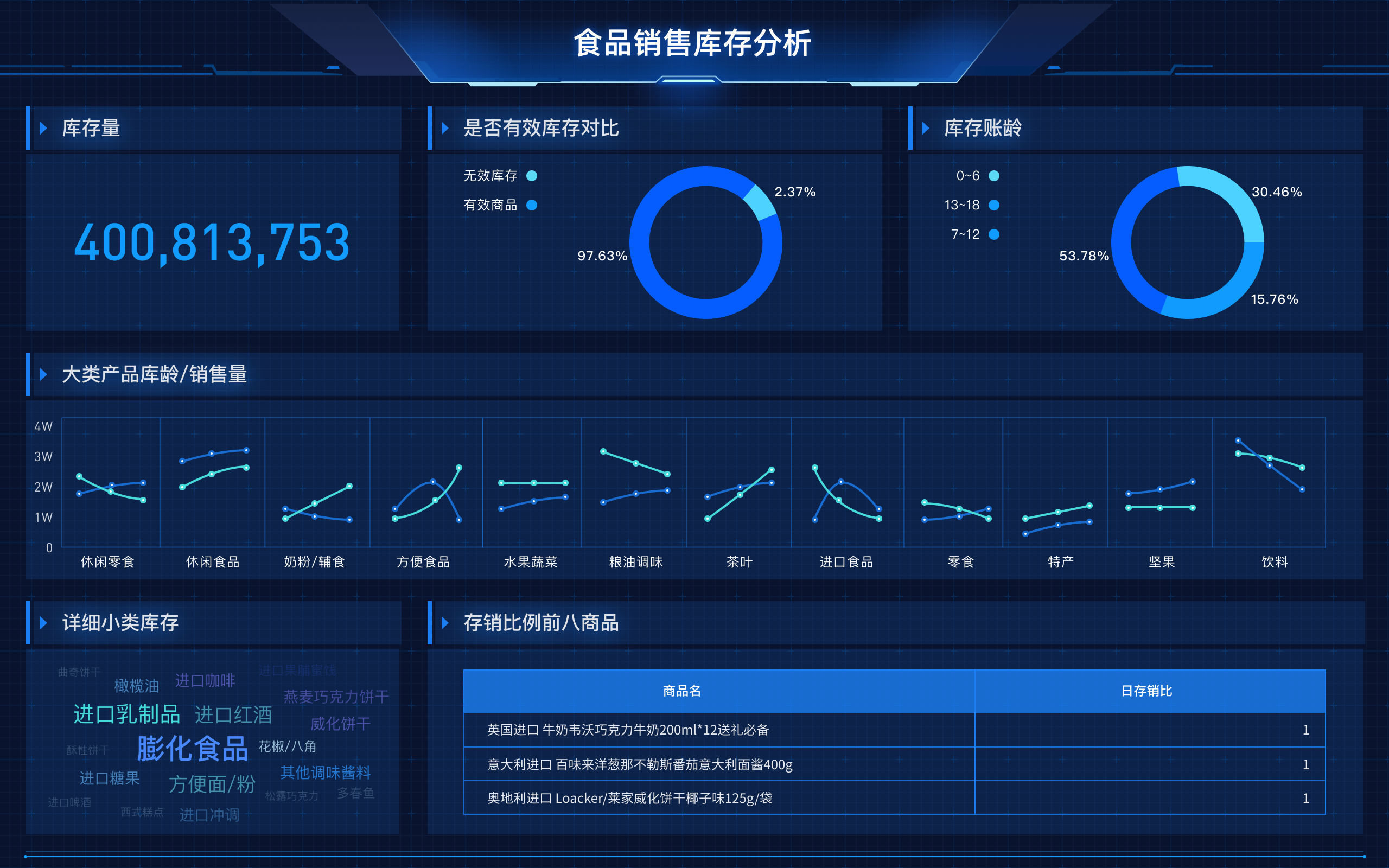
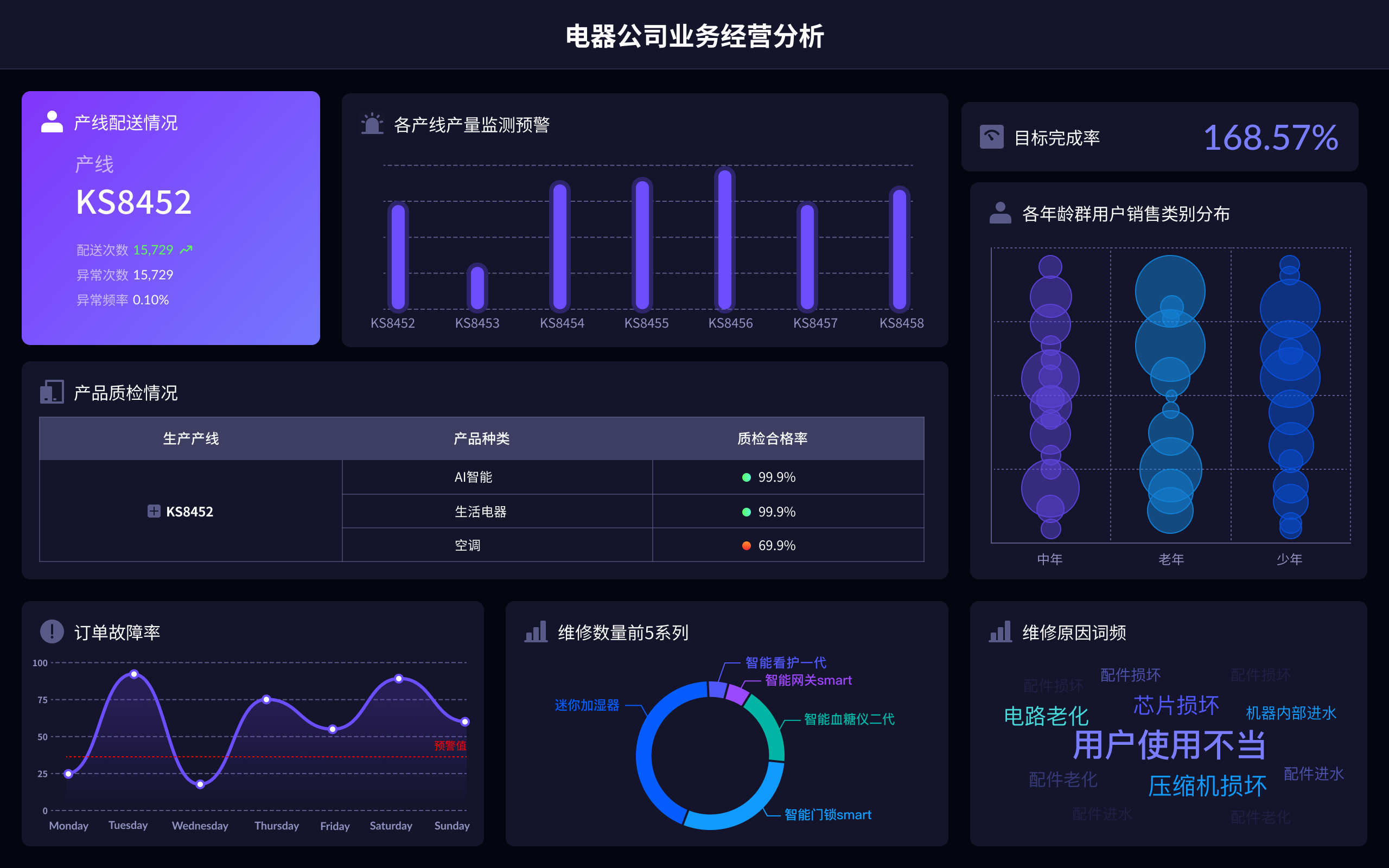
Visual Data Dashboard is how you would say 可视化数据大屏 in English. Visual Data Dashboard refers to a user interface that organizes and presents information in an easily understandable format using various types of charts and graphs.
I、DEFINITION AND IMPORTANCE
A Visual Data Dashboard is a comprehensive display of key data points and performance indicators, visually represented to facilitate quick insights and decision-making. These dashboards integrate data from multiple sources, providing a cohesive view. They are crucial for businesses to monitor metrics, track performance, and identify trends or anomalies. For instance, a retail company might use a Visual Data Dashboard to monitor sales performance across different regions, products, and time periods. This allows managers to quickly pinpoint underperforming areas and devise strategies to improve them.
II、KEY COMPONENTS OF A VISUAL DATA DASHBOARD
Data Integration: Combining data from various sources into a unified display. This ensures that all relevant information is available in one place, providing a holistic view of performance metrics.
Visualization Tools: Utilizing charts, graphs, and maps to represent data visually. These tools help in simplifying complex data sets, making it easier to understand patterns and correlations.
User Interface (UI): The design and layout of the dashboard, which should be intuitive and user-friendly. A well-designed UI enhances usability and ensures that users can easily navigate and interpret the data.
Real-Time Updates: Implementing real-time data updates to ensure that the information displayed is current and accurate. This feature is particularly important for monitoring ongoing processes and making timely decisions.
Interactivity: Allowing users to interact with the data, such as drilling down into specific metrics, filtering data, or adjusting time frames. Interactivity increases the flexibility and usefulness of the dashboard.
III、BENEFITS OF USING VISUAL DATA DASHBOARDS
Improved Decision-Making: By providing a clear and concise overview of key performance indicators (KPIs), dashboards enable faster and more informed decision-making. Managers can quickly identify issues and opportunities, leading to more strategic and effective actions.
Enhanced Data Comprehension: Visual representations of data make it easier to understand complex information. Graphs and charts can highlight trends, outliers, and correlations that might be missed in traditional reports.
Time Efficiency: Dashboards save time by aggregating data from multiple sources and presenting it in a single view. This eliminates the need to manually compile and analyze data from different systems.
Performance Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of performance metrics allows for timely intervention and adjustments. Dashboards can alert users to deviations from expected performance, enabling proactive management.
Collaboration and Communication: Dashboards facilitate better communication and collaboration among team members by providing a shared view of key metrics. This ensures that everyone is on the same page and working towards common goals.
IV、APPLICATIONS OF VISUAL DATA DASHBOARDS
Business Intelligence (BI): In BI, dashboards are used to monitor and analyze business performance. They provide insights into sales, marketing, finance, operations, and other critical areas.
Healthcare: Dashboards help healthcare providers track patient outcomes, monitor resource utilization, and manage operational efficiency. For example, a hospital might use a dashboard to track patient admission rates, bed occupancy, and staff allocation.
Education: Educational institutions use dashboards to track student performance, enrollment trends, and resource allocation. Dashboards can display data on student attendance, grades, and retention rates, helping educators identify areas for improvement.
Manufacturing: In manufacturing, dashboards are used to monitor production processes, quality control, and supply chain management. They can provide real-time updates on production rates, defect rates, and inventory levels.
Retail: Retailers use dashboards to track sales performance, customer behavior, and inventory management. A dashboard can show sales trends, customer demographics, and stock levels, helping retailers optimize their operations.
V、BEST PRACTICES FOR CREATING EFFECTIVE VISUAL DATA DASHBOARDS
Identify Key Metrics: Determine the most important metrics to track based on your business goals and objectives. Focus on KPIs that provide actionable insights.
Simplify the Design: Keep the design clean and uncluttered. Use white space effectively and avoid overloading the dashboard with too much information.
Use Appropriate Visualizations: Choose the right type of visualization for each data set. For example, use line charts for trends over time, bar charts for comparisons, and pie charts for proportions.
Ensure Data Accuracy: Regularly update the data and verify its accuracy. Inaccurate data can lead to incorrect conclusions and poor decision-making.
Provide Context: Include contextual information, such as benchmarks or historical data, to help users understand the significance of the metrics. Annotations and explanatory notes can also be helpful.
Make It Interactive: Allow users to interact with the dashboard, such as by filtering data or drilling down into specific details. This enhances the flexibility and usability of the dashboard.
VI、TOOLS FOR CREATING VISUAL DATA DASHBOARDS
FineReport: A powerful tool for creating comprehensive and customizable data reports and dashboards. FineReport offers a wide range of visualization options and supports data integration from multiple sources. FineReport官网
FineVis: Another robust tool from FanRuan, FineVis is designed for advanced data visualization and analysis. It provides intuitive drag-and-drop features, making it easy to create complex visualizations. FineVis官网
Tableau: Widely used for its powerful visualization capabilities, Tableau allows users to create interactive and shareable dashboards with a variety of data sources.
Power BI: A Microsoft product that integrates well with other Microsoft tools, Power BI offers strong data visualization and business analytics capabilities.
QlikView: Known for its associative data model, QlikView allows users to explore data freely and discover insights hidden in their data sets.
Google Data Studio: A free tool that integrates well with other Google products, Google Data Studio allows users to create dynamic and interactive dashboards with ease.
Domo: A cloud-based platform that provides a wide range of data visualization options and integrates with various data sources, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes.
Incorporating Visual Data Dashboards into your business strategy can significantly enhance your ability to monitor performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. By following best practices and leveraging the right tools, you can create dashboards that provide valuable insights and drive business success.
相关问答FAQs:
可视化数据大屏英语怎么说?
可视化数据大屏的英语表达通常是“Data Visualization Dashboard”或“Data Visualization Display”。在现代商业和科技环境中,这些术语被广泛使用,主要指的是将复杂数据以图形或图表的形式呈现,以便于用户理解和分析。数据可视化大屏通常集成多种数据源,通过实时更新的信息为决策提供支持。
可视化数据大屏的应用场景有哪些?
可视化数据大屏在多个领域都有广泛的应用。首先,在商业领域,企业可以通过大屏实时展示销售数据、市场趋势和客户反馈,以便做出快速决策。其次,在教育领域,学校和教育机构利用可视化数据大屏展示学生的学习进度、考试成绩等信息,以便教师和家长进行分析与讨论。此外,政府部门也会使用可视化数据大屏展示社会经济发展指标、公共服务质量等数据,增强透明度和公众参与感。
如何制作一个有效的可视化数据大屏?
制作一个有效的可视化数据大屏需要多个步骤。首先,明确目标受众和展示目的,了解观众希望从数据中获取哪些信息。其次,选择合适的数据源,确保数据的准确性和时效性。在设计时,应该采用清晰、简洁的图表和颜色方案,以便于观众快速理解。最后,定期更新和维护数据大屏,确保信息的实时性和相关性。通过用户反馈不断改进展示效果,也是提升可视化数据大屏质量的重要环节。
本文内容通过AI工具匹配关键字智能整合而成,仅供参考,帆软不对内容的真实、准确或完整作任何形式的承诺。具体产品功能请以帆软官方帮助文档为准,或联系您的对接销售进行咨询。如有其他问题,您可以通过联系blog@fanruan.com进行反馈,帆软收到您的反馈后将及时答复和处理。