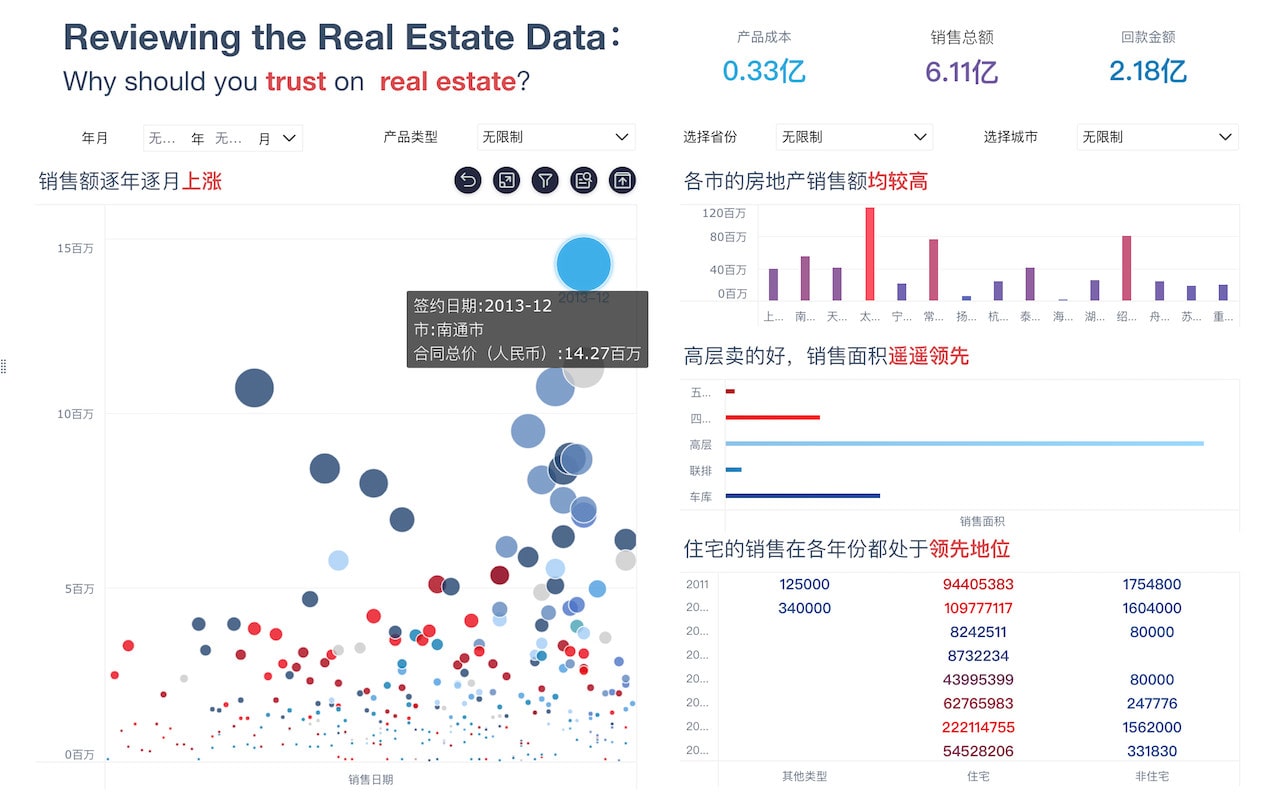
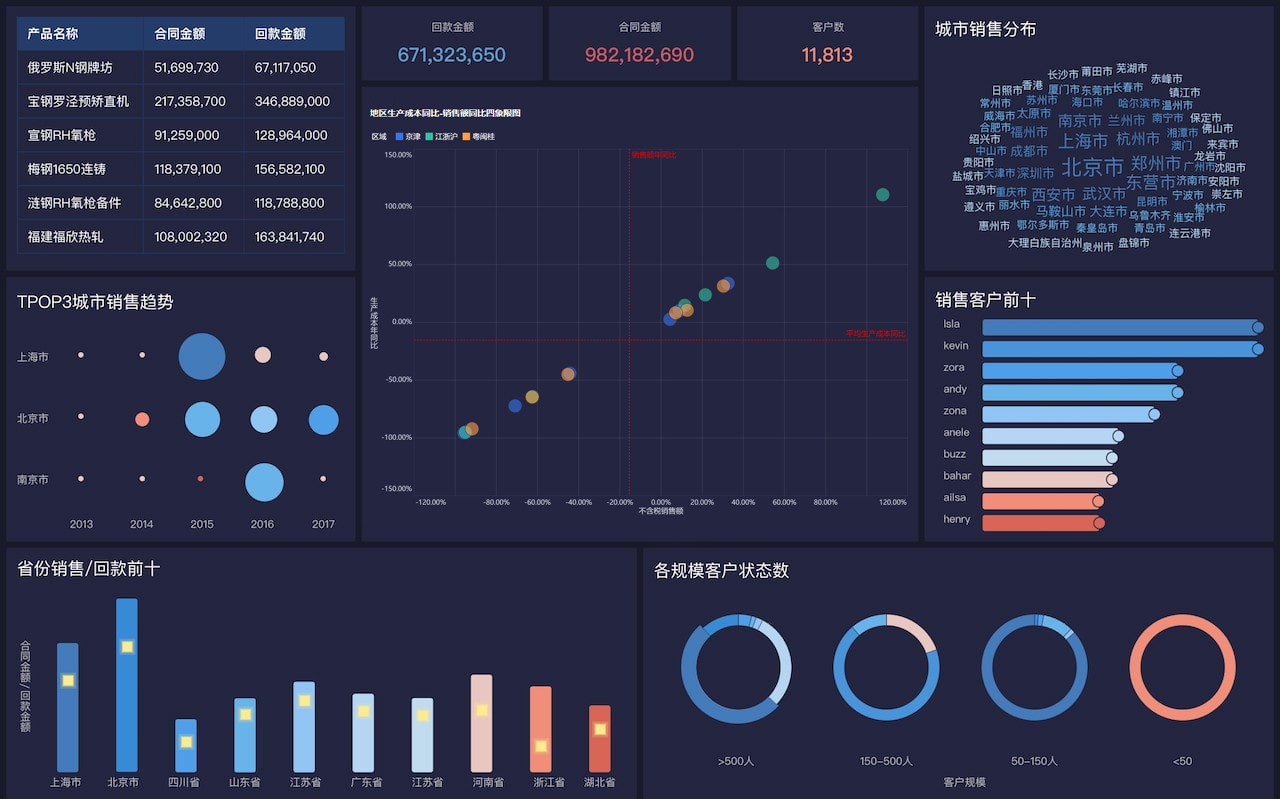
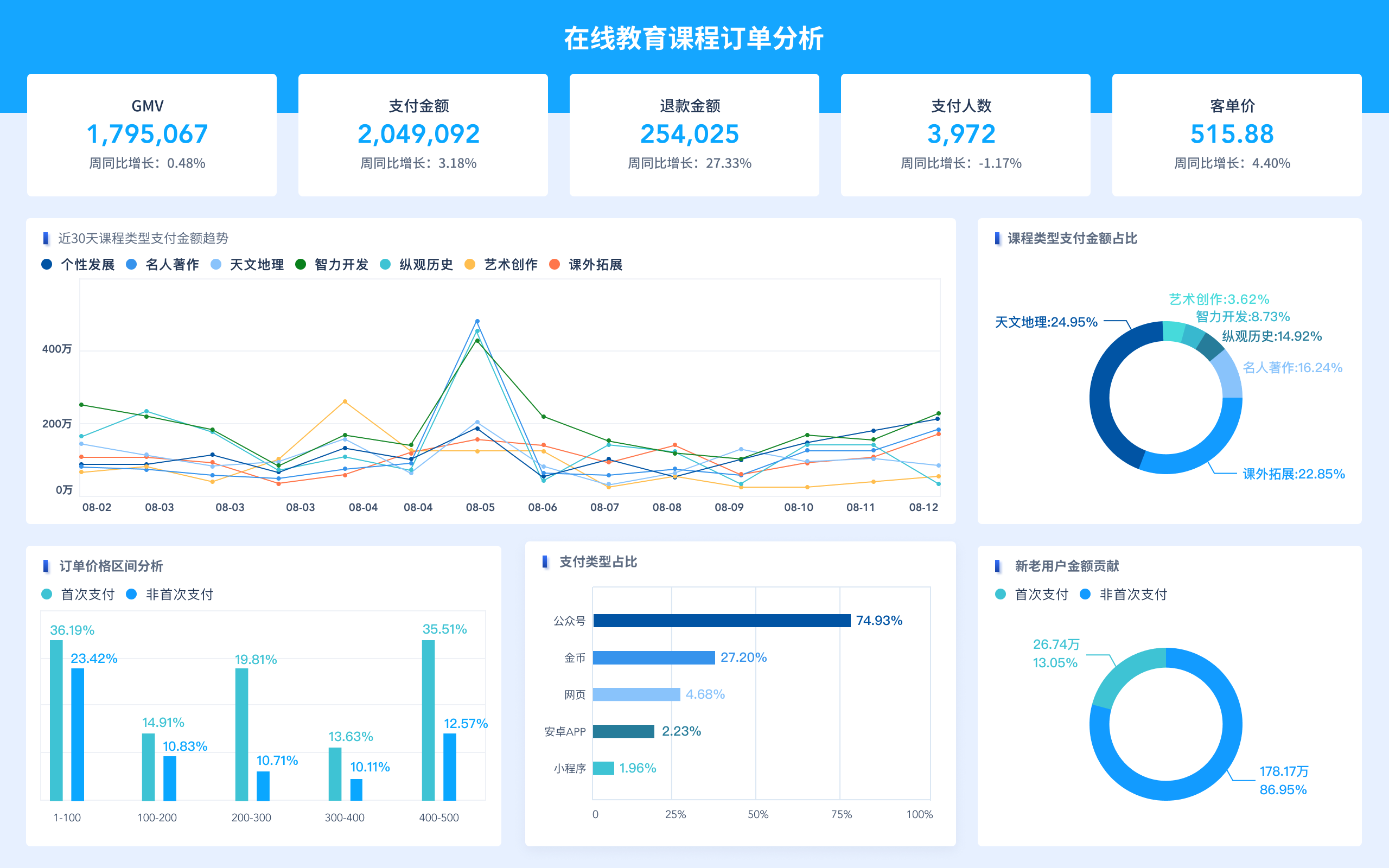
Anycasting没有数据库因为其主要功能是优化互联网流量、减少延迟、提高可靠性。Anycasting技术通过将同一IP地址分配给多个地理上分散的服务器节点,从而根据请求的源位置动态地将流量路由到最近的节点。这种机制是基于DNS和路由协议的,而不是传统的数据库。数据库主要用于存储和管理数据,而Anycasting侧重于网络流量的动态分配和优化。在这种模式下,数据库的使用并不适用,因为Anycasting的核心是基于实时路由和负载均衡的动态调整,不涉及静态数据存储和查询。
一、ANYCASTING的工作原理
Anycasting通过将同一IP地址分配给多个地理上分散的服务器节点来实现流量优化。这些服务器节点通常称为“anycast节点”。当用户发送请求时,DNS会将请求解析到最接近用户的anycast节点。这种机制使得流量可以根据地理位置动态地分配,从而显著减少延迟和提高服务的可用性。
DNS解析是Anycasting的核心部分。DNS服务器会根据用户的地理位置和网络拓扑,将请求解析到最近的anycast节点。这种解析过程是动态的,可以根据网络状况实时调整。路由协议如BGP(边界网关协议)也在Anycasting中扮演了重要角色。BGP可以根据网络流量和拓扑结构,动态调整路由路径,将流量引导到最优节点。
二、ANYCASTING的优势
Anycasting的主要优势包括减少延迟、提高可靠性、增强安全性。减少延迟是因为请求被路由到最近的节点,从而缩短数据传输的物理距离。提高可靠性是因为多个节点可以提供冗余服务,即使某个节点出现故障,流量也可以自动切换到其他可用节点。增强安全性是因为攻击者很难同时攻击多个分散的节点,从而提升了服务的抗攻击能力。
减少延迟是Anycasting的一个显著优势。当用户请求被路由到最近的节点时,数据传输的物理距离缩短了,从而显著减少了延迟。这对于实时应用如视频流、在线游戏和金融交易等非常重要。延迟减少不仅提升了用户体验,还能提高业务的竞争力。
三、ANYCASTING的应用场景
Anycasting广泛应用于内容分发网络(CDN)、域名系统(DNS)、分布式拒绝服务(DDoS)防护等领域。在CDN中,Anycasting可以将内容分发到离用户最近的节点,提高内容加载速度。在DNS中,Anycasting可以提高解析速度和可靠性。在DDoS防护中,Anycasting可以将攻击流量分散到多个节点,从而减轻单个节点的负担,提高防护效果。
内容分发网络(CDN)是Anycasting的一个典型应用场景。CDN通过将内容缓存到多个地理分散的节点,利用Anycasting将用户请求路由到最近的缓存节点,从而显著提高内容加载速度。这种机制不仅提升了用户体验,还能减轻源服务器的负担,提高整体服务的可用性和可靠性。
四、ANYCASTING的挑战与解决方案
尽管Anycasting有许多优势,但它也面临一些挑战,如路由复杂性、负载均衡、成本问题。路由复杂性是因为Anycasting需要动态调整路由路径,这增加了网络管理的复杂性。负载均衡是因为不同节点的负载可能不均衡,需要有效的负载均衡算法来优化资源利用。成本问题是因为部署和维护多个anycast节点需要较高的成本。
路由复杂性是Anycasting面临的一个主要挑战。由于Anycasting依赖于动态路由调整,网络管理员需要不断监控和优化路由路径,以确保流量能够高效地分配到最优节点。这需要借助先进的路由协议和网络监控工具,如BGP监控和流量分析工具,来实现动态路由优化。
五、ANYCASTING与数据库的区别
Anycasting和数据库在功能和用途上有明显区别。Anycasting主要用于网络流量优化、实时路由调整、负载均衡,而数据库主要用于数据存储、数据管理、数据查询。Anycasting不涉及静态数据的存储和管理,而是基于实时的网络流量和地理位置进行动态调整。数据库则主要用于存储和管理大量的结构化和非结构化数据,支持复杂的数据查询和分析。
数据存储与管理是数据库的核心功能。数据库系统如SQL和NoSQL数据库,能够高效地存储和管理大量数据,支持复杂的查询和分析操作。这与Anycasting的实时路由和流量优化功能有本质上的区别。数据库系统通常用于企业应用、电子商务、数据分析等需要大量数据管理和查询的场景,而Anycasting则用于需要高效网络流量分配和优化的场景。
六、ANYCASTING技术的发展趋势
随着互联网技术的不断发展,Anycasting技术也在不断演进。未来的发展趋势包括更智能的路由算法、与边缘计算的结合、增强的安全性。更智能的路由算法可以通过人工智能和机器学习来优化流量分配和路由选择。与边缘计算的结合可以进一步减少延迟,提高服务的实时性和响应速度。增强的安全性则可以通过更先进的加密和认证技术来提升服务的抗攻击能力。
更智能的路由算法是Anycasting未来发展的一个重要方向。通过引入人工智能和机器学习技术,Anycasting系统可以实时分析网络流量和拓扑结构,自动调整路由路径,优化流量分配。这不仅可以提高网络效率,还能更好地应对网络流量的动态变化,提高服务的可靠性和可用性。
七、ANYCASTING与边缘计算的结合
Anycasting与边缘计算的结合可以进一步提升服务质量。边缘计算通过将计算和存储资源部署在靠近用户的边缘节点,可以显著减少延迟,提高服务的实时性。当Anycasting与边缘计算结合时,可以将用户请求路由到最近的边缘节点,不仅提高了内容加载速度,还能减少核心网络的负担,提升整体网络的效率和可靠性。
边缘计算在Anycasting中的应用,主要体现在实时性和响应速度的提升。边缘节点可以缓存常用内容和数据,利用Anycasting将用户请求路由到最近的边缘节点,从而实现快速响应。这对于需要高实时性的应用,如视频流、在线游戏和物联网设备等,具有重要意义。
八、ANYCASTING的未来前景
Anycasting作为一种先进的网络流量优化技术,未来前景广阔。随着互联网应用的不断增长,对高效、可靠、安全的网络服务需求也在不断增加。Anycasting可以通过动态路由调整和负载均衡,满足这些需求。未来,随着人工智能、边缘计算等新技术的融合,Anycasting的性能和功能将得到进一步提升,为用户提供更优质的网络服务。
人工智能的融合将是Anycasting未来发展的一个重要方向。通过引入人工智能技术,Anycasting系统可以实现更智能的流量预测和路由优化,自动调整路由路径和负载分配,提高网络效率和服务质量。这将使Anycasting在应对复杂网络环境和动态流量变化方面,具备更强的适应性和灵活性。
总之,Anycasting作为一种高效的网络流量优化技术,通过动态路由调整和负载均衡,显著提升了网络服务的质量和可靠性。尽管面临一些挑战,但通过不断技术创新和优化,Anycasting在未来将发挥越来越重要的作用,为用户提供更加高效、可靠的网络服务。
相关问答FAQs:
What is Anycasting and How Does It Work?
Anycasting is a network addressing and routing method that allows multiple servers to share the same IP address. When a request is made to that IP, the network routes it to the nearest or most optimal server based on the current network conditions. This technique is widely used in content delivery networks (CDNs) and for optimizing the performance of various services, including DNS resolution.
The essence of anycasting lies in its ability to direct user requests to the closest server, thus reducing latency and improving response times. This mechanism is particularly useful in scenarios where high availability and fault tolerance are critical. For instance, if one server goes down, the traffic can be automatically redirected to another operational server sharing the same IP address.
Why Does Anycasting Not Have a Database?
1. Nature of Anycasting: Statelessness
Anycasting operates in a stateless manner, meaning it does not maintain or require any session or user data to function effectively. Since the primary goal of anycasting is to direct traffic based on network topology, it doesn’t need to store user-specific information. This is different from traditional databases, which are designed to store, manage, and retrieve data.
In a typical database system, data is organized into structured formats, allowing for complex queries and transactions. Anycasting, on the other hand, focuses solely on routing packets and handling requests as they come. Each packet is treated independently, and once it reaches its destination, the server processes it without needing to reference any previous interactions.
2. Load Distribution and Scalability
Anycasting is inherently designed for load distribution across multiple servers. When multiple servers share the same IP address, they can handle incoming traffic collectively. This setup allows for seamless scalability because new servers can be added to the network without changing the existing IP address.
In such a distributed environment, maintaining a centralized database would not be practical. Each server can operate independently, processing requests and serving content without needing to consult a database. This reduces the complexity of managing stateful information and allows for rapid scaling in response to varying traffic loads.
3. Focus on Performance and Reliability
The primary objectives of anycasting are performance optimization and reliability. By routing requests to the nearest server, anycasting minimizes latency and ensures faster response times. If a server becomes unavailable, the network can quickly reroute traffic to another server without any disruption.
In contrast, databases introduce additional latency because of the time taken to retrieve and process data. For applications where speed and reliability are crucial, relying on a database could hinder performance. Therefore, anycasting is designed to prioritize direct server communication over the complexities that come with database interactions.
What Are the Use Cases for Anycasting?
1. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
One of the most prominent uses of anycasting is in CDNs. These networks distribute content across multiple servers located in different geographical areas. By using anycasting, CDNs can ensure that users receive content from the nearest server, which significantly reduces load times and enhances the overall user experience.
CDNs leverage anycasting to manage high volumes of traffic, especially during peak times. When a popular event occurs or a viral video is released, the ability to direct users to the closest server helps in handling surges in traffic efficiently.
2. DNS Resolution
Anycasting is also widely utilized in DNS resolution. DNS servers can be deployed in multiple locations, all sharing the same IP address. When a user attempts to resolve a domain name, the request is routed to the nearest DNS server. This not only speeds up the resolution process but also provides redundancy in case one server fails.
The use of anycasting in DNS enhances the resilience and reliability of the entire domain name system, making it less susceptible to attacks and outages.
3. DDoS Mitigation
Anycasting can be an effective strategy for mitigating Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. By distributing the traffic across multiple servers, anycasting can help absorb and dissipate the impact of the attack. Instead of overwhelming a single server, the malicious traffic is spread out, making it more manageable.
This strategy helps maintain service availability even under attack, providing a layer of protection for critical online services.
What Are the Benefits of Anycasting?
1. Enhanced Performance
One of the most significant benefits of anycasting is improved performance. By directing user requests to the nearest server, anycasting reduces latency and speeds up response times. This is especially crucial for applications that require real-time interaction, such as gaming or video conferencing.
2. Increased Reliability
Anycasting contributes to increased reliability by providing redundancy. If one server becomes unavailable, the network automatically reroutes traffic to another operational server. This ensures that services remain accessible even in the face of server failures.
3. Simplified Network Management
With anycasting, network management becomes more straightforward. Since multiple servers can share the same IP address, adding or removing servers from the network does not require reconfiguration of the IP addressing scheme. This flexibility simplifies maintenance and scaling efforts.
4. Geographic Load Balancing
Anycasting allows for effective geographic load balancing. By routing users to the nearest server, anycasting ensures that no single server becomes a bottleneck. This is particularly beneficial for global applications, where users are spread out across different regions.
Conclusion
Anycasting is a powerful networking technique that offers a range of benefits, including enhanced performance, increased reliability, and simplified network management. Its stateless nature and focus on optimizing traffic routing make it an ideal solution for various applications, such as content delivery networks, DNS resolution, and DDoS mitigation.
By understanding the principles of anycasting and its advantages, organizations can better leverage this technology to improve their online services and provide a seamless experience for users around the globe.
本文内容通过AI工具匹配关键字智能整合而成,仅供参考,帆软不对内容的真实、准确或完整作任何形式的承诺。具体产品功能请以帆软官方帮助文档为准,或联系您的对接销售进行咨询。如有其他问题,您可以通过联系blog@fanruan.com进行反馈,帆软收到您的反馈后将及时答复和处理。