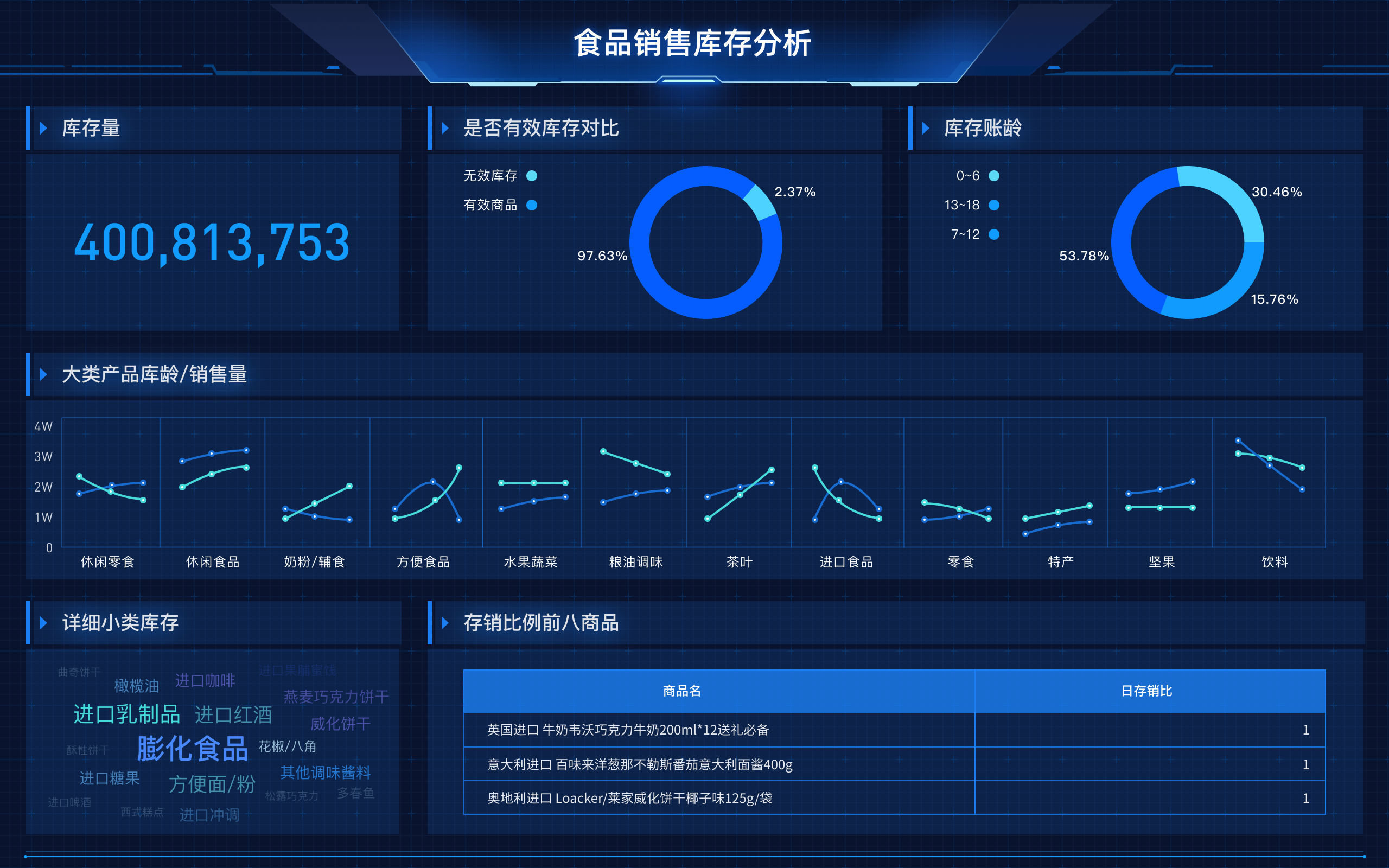
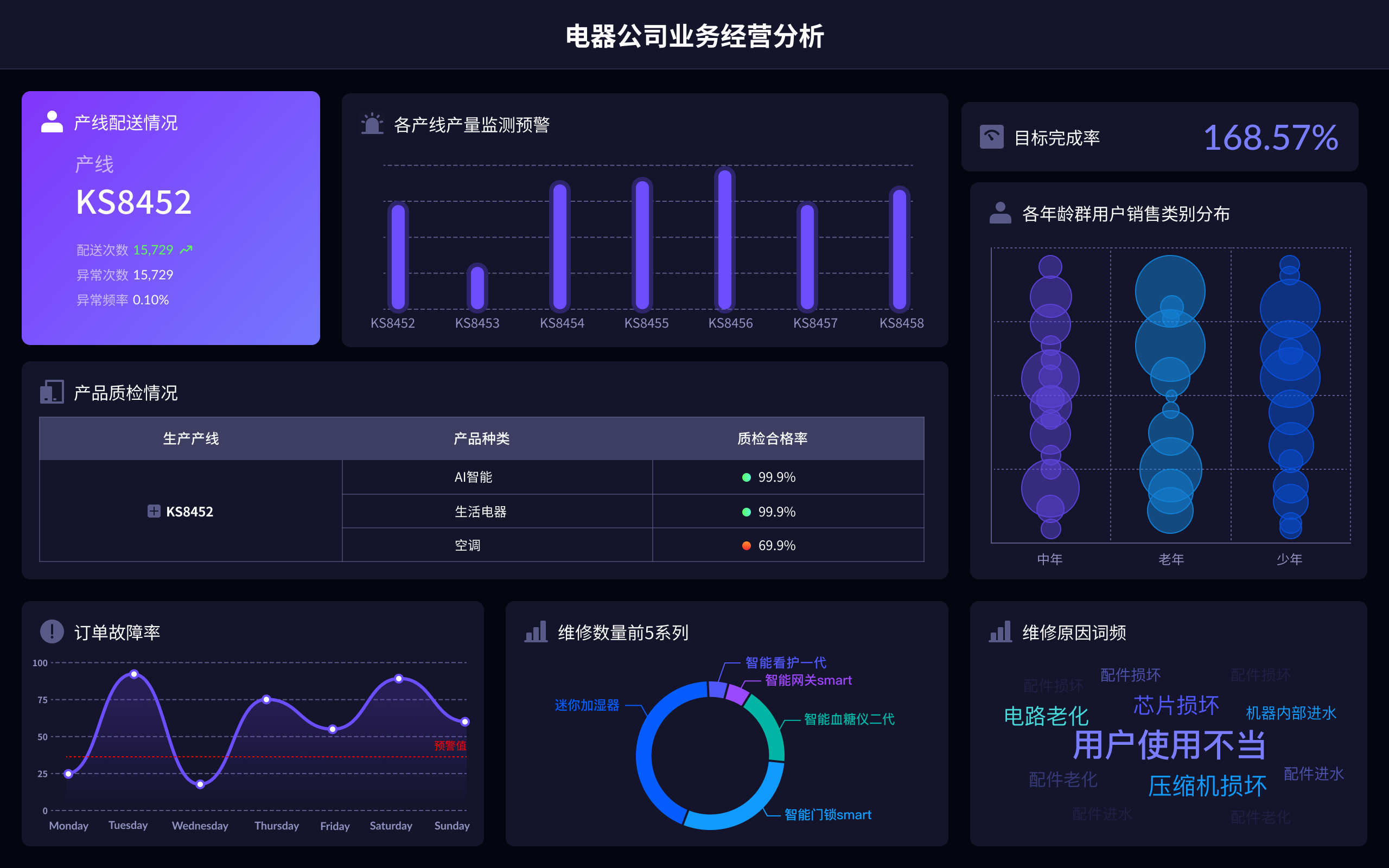
In the realm of accounting, the utilization of databases is paramount due to several compelling reasons: efficient data management, real-time financial reporting, enhanced data accuracy, improved compliance, scalability, and better decision-making. Efficient data management is perhaps the most critical aspect, as it allows accountants to store, retrieve, and manipulate vast amounts of financial data seamlessly. This capability significantly reduces the time and effort required to manage financial records, thereby increasing productivity and accuracy. For instance, a database can automatically update and reconcile financial transactions, ensuring that the data is always current and accurate. This feature is crucial for preparing timely financial reports and making informed business decisions.
I. EFFICIENT DATA MANAGEMENT
Efficient data management is the cornerstone of modern accounting practices. With the increasing volume of financial transactions and regulatory requirements, manual data handling has become impractical and error-prone. Databases enable accountants to store and organize financial data systematically, ensuring easy access and retrieval. This systematic storage allows for quick updates and modifications without compromising data integrity. For example, in a relational database, tables can be linked through unique identifiers, enabling seamless data integration from various sources. This integration facilitates comprehensive financial analysis and reporting. Moreover, databases support automated data entry and validation processes, reducing the likelihood of human errors and ensuring that the financial data remains accurate and reliable over time.
II. REAL-TIME FINANCIAL REPORTING
Real-time financial reporting is another significant benefit of using databases in accounting. Databases enable the instantaneous updating and retrieval of financial data, allowing accountants to generate up-to-date financial reports at any given moment. This capability is crucial for businesses that require timely insights into their financial performance to make strategic decisions. For instance, a company can monitor its cash flow, track expenses, and assess profitability in real-time, enabling it to respond swiftly to any financial anomalies or opportunities. Furthermore, real-time reporting enhances transparency and accountability, as stakeholders can access accurate and current financial information whenever needed. This transparency is particularly important for publicly traded companies and organizations subject to stringent regulatory requirements.
III. ENHANCED DATA ACCURACY
Enhanced data accuracy is a fundamental advantage of databases in accounting. Databases employ various mechanisms to ensure data accuracy, such as data validation rules, referential integrity, and transaction management. Data validation rules prevent the entry of invalid data by enforcing predefined criteria for data input. Referential integrity ensures that relationships between tables remain consistent, preventing orphaned records and data inconsistencies. Transaction management guarantees that all database operations are completed successfully before committing changes, ensuring data integrity even in the event of system failures. These mechanisms collectively contribute to maintaining high data accuracy, which is essential for generating reliable financial statements and conducting precise financial analysis.
IV. IMPROVED COMPLIANCE
Improved compliance with regulatory requirements is a critical aspect of using databases in accounting. Databases facilitate the implementation of internal controls and audit trails, ensuring that all financial transactions are accurately recorded and traceable. Internal controls help prevent fraudulent activities and ensure adherence to accounting standards and regulations. Audit trails provide a detailed record of all database activities, including data modifications, deletions, and access history. This traceability is crucial for regulatory compliance, as it enables auditors to verify the accuracy and completeness of financial records. Additionally, databases support data encryption and access controls, safeguarding sensitive financial information and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
V. SCALABILITY
Scalability is a vital benefit of using databases in accounting. Databases are designed to handle large volumes of data and can scale to accommodate the growing needs of a business. As a company expands, its financial data increases exponentially, necessitating a robust data management system that can handle this growth. Databases can efficiently manage large datasets, ensuring that data retrieval and processing times remain optimal. This scalability is essential for businesses operating in dynamic environments, as it allows them to maintain high-performance levels even as their data volumes increase. Moreover, databases can integrate with other business systems, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) and customer relationship management (CRM) systems, providing a unified platform for managing all business operations.
VI. BETTER DECISION-MAKING
Better decision-making is one of the most significant advantages of using databases in accounting. Databases provide accountants with accurate, comprehensive, and timely financial information, enabling them to make informed decisions. This information is critical for strategic planning, budgeting, and forecasting. For instance, a database can generate detailed financial reports, such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, providing a holistic view of the company's financial health. These reports help management identify trends, assess performance, and make data-driven decisions. Additionally, databases support advanced analytical tools, such as data mining and predictive analytics, which can uncover hidden patterns and provide valuable insights into future financial performance.
VII. COST-EFFECTIVENESS
Cost-effectiveness is another notable benefit of using databases in accounting. Databases streamline financial processes, reducing the time and resources required for data management. This efficiency translates into cost savings for businesses, as it minimizes the need for manual data entry and reduces the likelihood of errors that could result in financial losses. Additionally, databases support automation of routine accounting tasks, such as payroll processing, invoicing, and expense tracking, further reducing operational costs. By leveraging databases, businesses can achieve significant cost savings while maintaining high levels of accuracy and efficiency in their financial operations.
VIII. DATA SECURITY
Data security is a paramount concern in accounting, given the sensitive nature of financial information. Databases offer robust security features to protect financial data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats. These features include data encryption, user authentication, access controls, and regular security audits. Data encryption ensures that financial information is stored and transmitted securely, preventing unauthorized access. User authentication and access controls restrict access to the database, ensuring that only authorized personnel can view or modify financial data. Regular security audits help identify and address potential vulnerabilities, ensuring that the database remains secure. By implementing these security measures, businesses can safeguard their financial data and maintain the trust of their stakeholders.
IX. INTEGRATION CAPABILITIES
Integration capabilities are a significant advantage of using databases in accounting. Databases can seamlessly integrate with other business systems, such as ERP, CRM, and supply chain management systems, providing a unified platform for managing all business operations. This integration enables the seamless flow of financial data across different departments, facilitating comprehensive financial analysis and reporting. For example, an ERP system can automatically update the database with sales and inventory data, ensuring that financial records are always current and accurate. Similarly, a CRM system can provide customer payment information, enabling accurate revenue tracking and analysis. By integrating databases with other business systems, companies can achieve greater efficiency and accuracy in their financial operations.
X. CUSTOMIZATION AND FLEXIBILITY
Customization and flexibility are key benefits of using databases in accounting. Databases can be customized to meet the specific needs of a business, allowing for tailored data management solutions. This customization includes defining data structures, creating custom reports, and implementing specific business rules and workflows. Flexibility is another critical aspect, as databases can adapt to changing business requirements and regulatory standards. For instance, a company can modify its database schema to accommodate new accounting standards or expand its reporting capabilities to meet emerging business needs. This customization and flexibility ensure that the database remains relevant and valuable to the business over time.
XI. AUDIT TRAILS AND TRANSPARENCY
Audit trails and transparency are crucial for maintaining the integrity of financial data. Databases provide detailed audit trails that record all database activities, including data modifications, deletions, and access history. These audit trails enable auditors to verify the accuracy and completeness of financial records, ensuring compliance with accounting standards and regulations. Transparency is another critical aspect, as databases provide a clear and traceable record of all financial transactions. This transparency is essential for building trust with stakeholders, as it ensures that financial information is accurate, reliable, and verifiable. By maintaining detailed audit trails and transparency, businesses can enhance their credibility and accountability.
XII. TIME-SAVING
Time-saving is a significant benefit of using databases in accounting. Databases automate many routine accounting tasks, such as data entry, reconciliation, and reporting, reducing the time and effort required for these activities. Automation ensures that these tasks are completed quickly and accurately, freeing up accountants to focus on more strategic activities. For example, a database can automatically generate financial reports, eliminating the need for manual data compilation and analysis. This automation not only saves time but also reduces the likelihood of errors, ensuring that financial information is always accurate and up-to-date. By leveraging databases, businesses can achieve greater efficiency and productivity in their accounting operations.
XIII. ENHANCED COLLABORATION
Enhanced collaboration is another notable benefit of using databases in accounting. Databases provide a centralized platform for storing and sharing financial data, enabling seamless collaboration among team members. This centralized platform ensures that all team members have access to the same accurate and up-to-date information, facilitating effective communication and decision-making. For instance, multiple accountants can work on the same financial records simultaneously, making updates and modifications in real-time. This collaboration enhances the efficiency and accuracy of financial operations, as team members can easily share insights, identify issues, and resolve discrepancies. By fostering enhanced collaboration, databases contribute to more effective and cohesive accounting practices.
XIV. REDUCED RISK OF DATA LOSS
Reduced risk of data loss is a critical advantage of using databases in accounting. Databases offer robust data backup and recovery mechanisms, ensuring that financial data is protected against loss or corruption. These mechanisms include regular data backups, off-site storage, and disaster recovery plans. Regular data backups ensure that a copy of the financial data is always available, even in the event of system failures or data corruption. Off-site storage provides an additional layer of protection, safeguarding data against physical damage or theft. Disaster recovery plans outline the steps to be taken in the event of a data loss incident, ensuring that the business can quickly restore its financial data and resume operations. By implementing these data protection measures, businesses can minimize the risk of data loss and ensure the continuity of their accounting operations.
XV. DATA ANALYTICS AND INSIGHTS
Data analytics and insights are significant benefits of using databases in accounting. Databases support advanced analytical tools and techniques, such as data mining, predictive analytics, and business intelligence. These tools enable accountants to analyze large volumes of financial data, uncover hidden patterns, and gain valuable insights into the company's financial performance. For example, data mining can identify trends and anomalies in financial data, providing insights into revenue growth, cost reduction, and profitability. Predictive analytics can forecast future financial performance, helping businesses make proactive decisions. Business intelligence tools can generate comprehensive financial reports and dashboards, providing a holistic view of the company's financial health. By leveraging data analytics and insights, businesses can make data-driven decisions and achieve better financial outcomes.
XVI. STANDARDIZATION OF FINANCIAL DATA
Standardization of financial data is a crucial benefit of using databases in accounting. Databases enforce consistent data formats and structures, ensuring that financial data is standardized and uniform. This standardization is essential for accurate financial reporting and analysis, as it enables the comparison and aggregation of data from different sources. For instance, a database can enforce consistent data entry formats for financial transactions, ensuring that all records follow the same structure. This consistency facilitates accurate data aggregation and analysis, enabling businesses to generate reliable financial reports. Moreover, standardization ensures compliance with accounting standards and regulations, as it provides a clear and consistent record of financial transactions. By standardizing financial data, businesses can achieve greater accuracy and reliability in their accounting practices.
XVII. ENHANCED CUSTOMER SERVICE
Enhanced customer service is another notable benefit of using databases in accounting. Databases enable businesses to maintain accurate and comprehensive financial records for their customers, ensuring timely and accurate billing, payments, and account management. This accuracy enhances customer satisfaction, as customers can trust that their financial transactions are handled correctly. For example, a database can track customer payments and generate accurate invoices, ensuring that customers are billed correctly and on time. Additionally, databases can provide customer service representatives with real-time access to financial information, enabling them to quickly address customer inquiries and resolve issues. By providing accurate and timely financial information, databases contribute to enhanced customer service and satisfaction.
XVIII. ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY
Environmental sustainability is a significant advantage of using databases in accounting. Databases reduce the need for paper-based financial records, contributing to environmental sustainability by minimizing paper usage and waste. This reduction in paper usage not only supports environmental conservation efforts but also reduces the costs associated with printing, storage, and disposal of paper records. Moreover, digital financial records are easier to store, retrieve, and manage, further enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of accounting practices. By adopting databases, businesses can achieve greater environmental sustainability while improving the efficiency and accuracy of their financial operations.
XIX. HISTORICAL DATA ANALYSIS
Historical data analysis is a crucial benefit of using databases in accounting. Databases enable businesses to store and analyze historical financial data, providing valuable insights into past performance and trends. This historical analysis is essential for strategic planning, budgeting, and forecasting. For example, a database can store financial data for multiple years, enabling businesses to analyze trends in revenue, expenses, and profitability over time. This analysis helps identify patterns and anomalies, providing insights into the factors driving financial performance. By leveraging historical data analysis, businesses can make informed decisions and develop effective strategies for future growth and success.
XX. IMPROVED RESOURCE ALLOCATION
Improved resource allocation is a significant advantage of using databases in accounting. Databases provide accurate and comprehensive financial information, enabling businesses to allocate resources more effectively. This accurate information is critical for budgeting, forecasting, and financial planning. For instance, a database can provide detailed insights into cash flow, expenses, and profitability, helping businesses identify areas where resources can be optimized. By leveraging this information, businesses can allocate resources to high-impact areas, reduce costs, and improve overall financial performance. Improved resource allocation contributes to better financial outcomes and supports the long-term success of the business.
In conclusion, the utilization of databases in accounting offers a myriad of benefits, including efficient data management, real-time financial reporting, enhanced data accuracy, improved compliance, scalability, and better decision-making. These advantages collectively contribute to the efficiency, accuracy, and reliability of accounting practices, enabling businesses to achieve better financial outcomes and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements. By leveraging the power of databases, businesses can enhance their financial operations and support their long-term growth and success.
相关问答FAQs:
Why Do Accountants Need Databases?
In today's fast-paced business environment, the role of accountants has evolved significantly. With the advent of technology, particularly in the realm of data management, databases have become an essential tool for accountants. Here are some key reasons why databases are crucial for the accounting profession.
1. Efficient Data Management
One of the primary reasons accountants utilize databases is the efficient management of vast amounts of financial data. Traditional methods of record-keeping, such as spreadsheets, can quickly become cumbersome and error-prone when dealing with large datasets. Databases provide a structured way to store, retrieve, and manage financial information.
For example, a relational database allows accountants to organize data into tables, making it easier to access specific information without sifting through numerous documents. This structured approach not only saves time but also enhances accuracy, which is critical in maintaining financial integrity.
2. Enhanced Data Analysis
Databases empower accountants to perform complex data analysis with ease. With advanced querying capabilities, accountants can extract valuable insights from financial data, allowing for better decision-making. Tools like SQL (Structured Query Language) enable accountants to write queries that can analyze trends, calculate ratios, and generate financial reports.
Moreover, data visualization tools can be integrated with databases to present findings in a more digestible format. This capability transforms raw data into actionable insights, allowing accountants to identify patterns and anomalies that could impact the financial health of an organization.
3. Improved Collaboration and Accessibility
In an increasingly globalized world, collaboration among team members is essential. Databases facilitate this collaboration by allowing multiple users to access and work on the same data simultaneously. Cloud-based databases, in particular, enable accountants to collaborate in real-time, regardless of their physical location.
This accessibility is particularly important for businesses that operate in multiple locations or have remote teams. Accountants can share reports, financial statements, and other critical documents instantly, ensuring that everyone is on the same page and can make informed decisions based on the most current data.
4. Enhanced Security and Compliance
Financial data is highly sensitive and must be protected against unauthorized access and breaches. Databases offer robust security features that help safeguard this information. Access controls can be implemented to restrict who can view or modify data, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive financial information.
In addition to security, compliance with financial regulations is paramount. Databases can be designed to maintain an audit trail, capturing changes made to financial data. This feature is vital for demonstrating compliance with laws and regulations, such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act in the United States, which mandates strict controls over financial reporting.
5. Automation of Repetitive Tasks
Databases can significantly reduce the time spent on repetitive tasks through automation. For instance, routine data entry, report generation, and reconciliation processes can be automated using database management systems. This automation not only increases efficiency but also minimizes the risk of human error.
Accountants can set up scheduled tasks that run automatically, ensuring that reports are generated and sent to stakeholders at regular intervals. This frees up valuable time for accountants to focus on more strategic activities, such as financial planning and analysis.
6. Integration with Other Systems
Modern accounting practices often involve multiple software systems, such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems, CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software, and payroll systems. Databases serve as a central hub that can integrate data from these various systems, creating a comprehensive view of an organization's financial health.
This integration is crucial for accurate financial reporting and analysis. For example, by linking sales data from a CRM system with accounting data, accountants can gain insights into revenue trends and customer profitability, informing strategic business decisions.
7. Support for Decision-Making
In a world where data-driven decision-making is becoming the norm, databases provide accountants with the tools they need to support this process. By enabling access to historical financial data and trends, databases empower accountants to offer valuable insights during strategic planning sessions.
Additionally, predictive analytics can be applied to database information, helping accountants forecast future financial performance based on historical data. This ability to anticipate trends and outcomes is invaluable for organizations aiming to stay ahead of the competition.
Conclusion
The integration of databases into the accounting profession has transformed how accountants manage, analyze, and report financial data. From efficient data management to enhanced security and compliance, the advantages are numerous. As technology continues to evolve, accountants who leverage database systems will be better equipped to navigate the complexities of modern finance, ultimately driving greater value for their organizations.
FAQs
1. What are the main benefits of using databases in accounting?
Databases provide numerous advantages for accountants, including efficient data management, enhanced data analysis capabilities, improved collaboration and accessibility, robust security measures, automation of repetitive tasks, integration with other systems, and support for data-driven decision-making. These benefits contribute to greater accuracy, efficiency, and effectiveness in financial reporting and analysis.
2. How do databases enhance the accuracy of financial data?
Databases enhance accuracy by providing a structured environment for data storage and retrieval. They minimize the risk of human error associated with manual data entry and enable accountants to create standardized processes for data management. Additionally, features such as access controls and audit trails help ensure that only authorized personnel can modify sensitive financial information.
3. Can small businesses benefit from using databases in their accounting practices?
Absolutely. Small businesses can greatly benefit from using databases for accounting purposes. While the scale may differ from larger organizations, the advantages remain the same. Databases can help small businesses efficiently manage their financial data, automate tasks, and generate reports, allowing them to focus on growth and strategic decision-making. Additionally, many affordable database solutions are available that cater specifically to the needs of small businesses.
本文内容通过AI工具匹配关键字智能整合而成,仅供参考,帆软不对内容的真实、准确或完整作任何形式的承诺。具体产品功能请以帆软官方帮助文档为准,或联系您的对接销售进行咨询。如有其他问题,您可以通过联系blog@fanruan.com进行反馈,帆软收到您的反馈后将及时答复和处理。