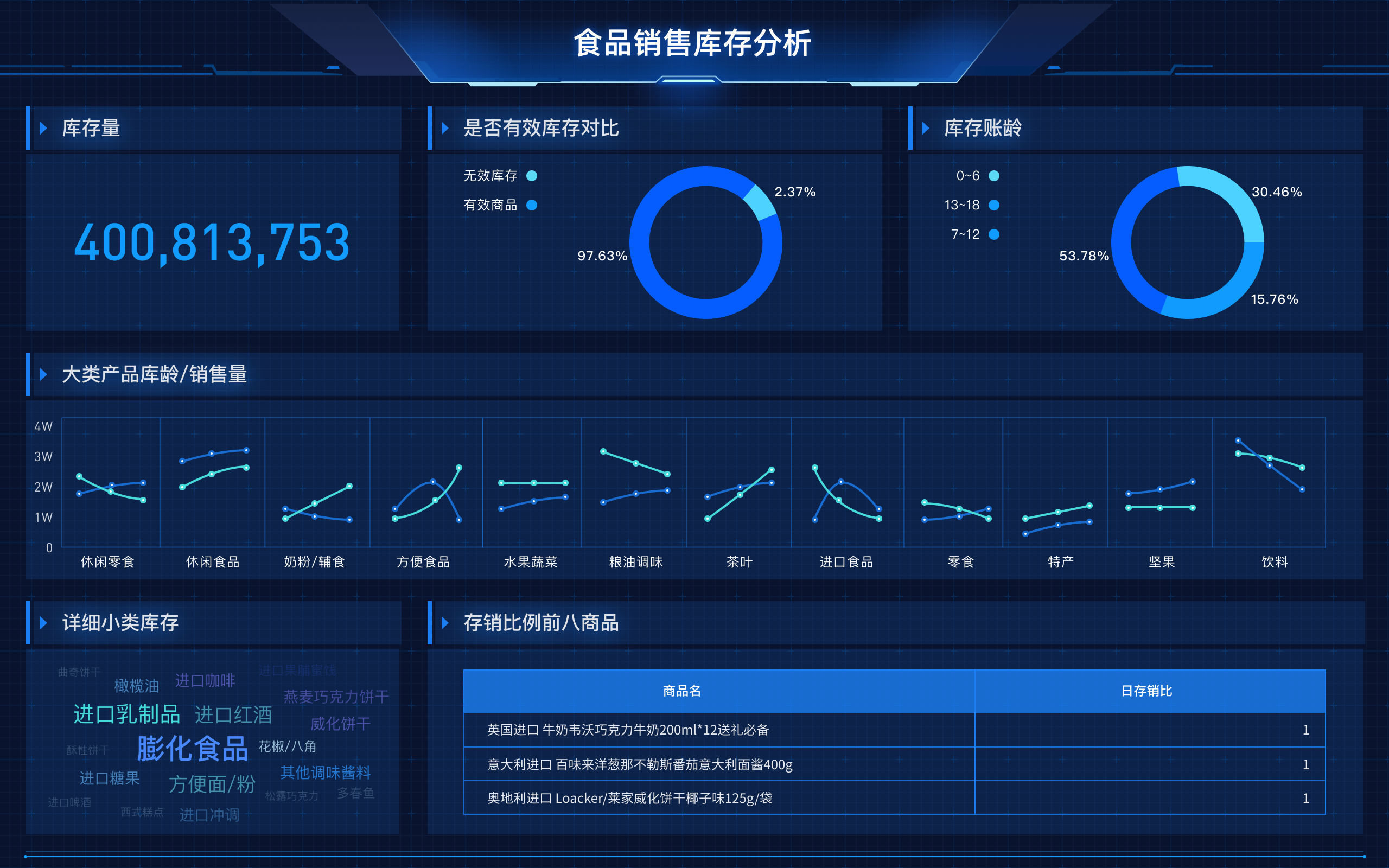
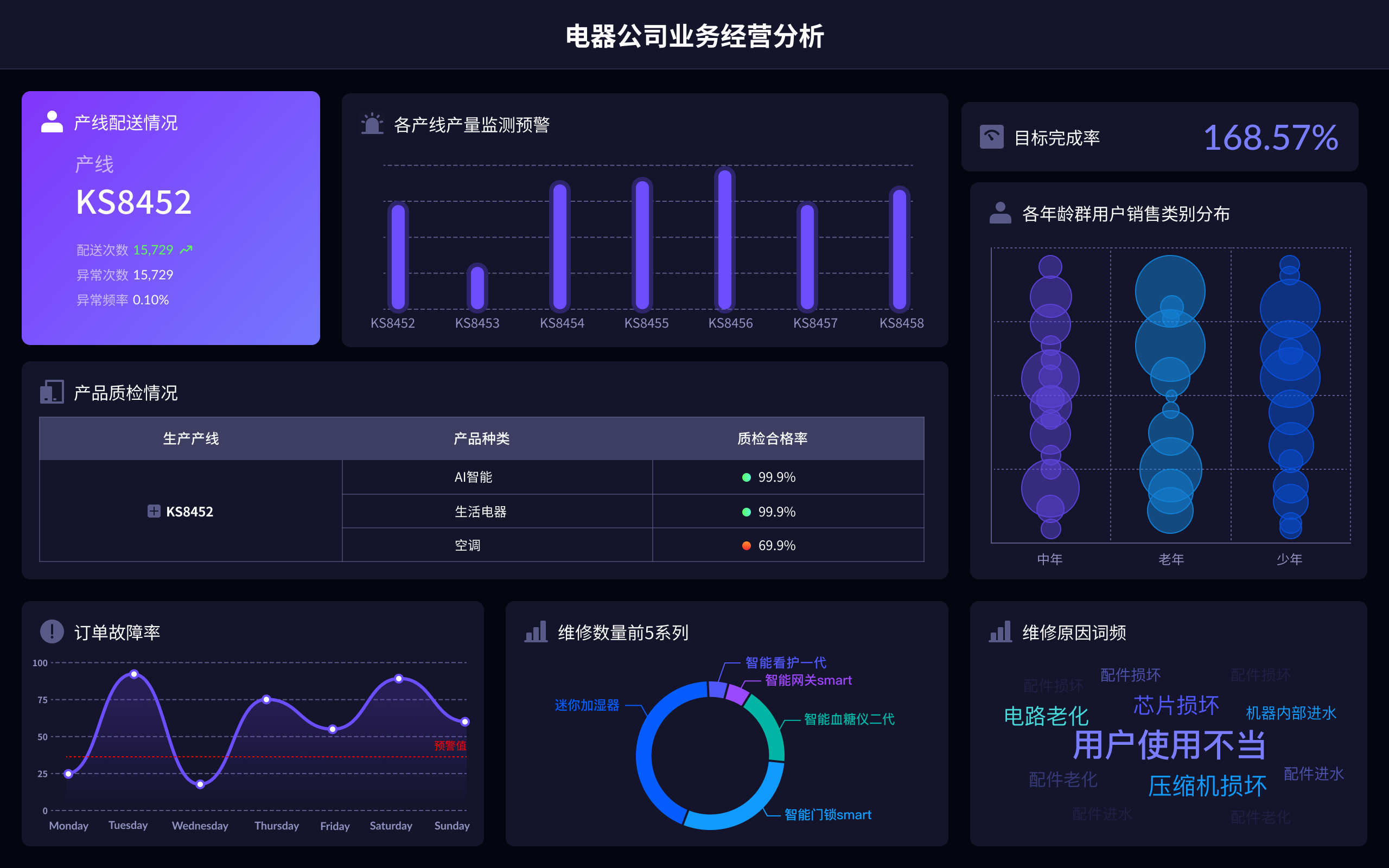
数据仓库(Data Warehouse)是一个用于存储和管理大量结构化数据的系统,旨在支持商业智能活动、分析和报告。 数据仓库通过从多个不同来源的数据整合、整理和存储,提供一个统一的、易于访问的数据视图,帮助企业做出数据驱动的决策。它的核心特点包括数据集成、数据一致性、数据查询优化和历史数据存储。数据仓库通常与数据湖和数据集市一起使用,以满足不同的分析需求。数据集成是数据仓库的重要功能之一,它通过将来自不同来源的数据进行转换和整合,提供一个一致且统一的数据视图,方便数据分析师和决策者进行分析和报告。这不仅提高了数据的准确性和一致性,还减少了数据冗余和重复存储,提高了数据管理的效率。
一、数据仓库的定义与特性
数据仓库是一个面向主题、集成的、不可变的、随时间变化的数据集合,用于支持管理决策。面向主题意味着数据仓库围绕特定的业务主题(如客户、销售、产品等)组织数据,而不是围绕企业的应用程序。数据集成指的是将来自不同来源的数据整合在一起,使其在数据仓库中表现为统一的格式和结构。数据仓库的数据通常是不可变的,这意味着一旦数据被加载到数据仓库中,它通常不会被更新或删除,而是保持历史记录以供分析。数据仓库的数据是随时间变化的,反映了业务活动的历史。
数据仓库的特性使其成为商业智能应用的理想选择。它的面向主题特性使得用户可以方便地围绕特定的业务问题进行分析。集成特性确保数据的一致性和准确性,不同来源的数据可以在数据仓库中以统一的格式呈现,方便分析人员进行多维度的数据分析。不可变性保证了数据的完整性和可靠性,用户可以对历史数据进行回溯和分析。数据仓库的数据随着时间的变化不断累积,提供了丰富的历史数据支持趋势分析和预测。
二、数据仓库的架构
数据仓库的架构通常包括三个层次:数据源层、数据仓库层和数据访问层。数据源层负责从各种外部数据源收集数据,这些数据源可以是关系数据库、文件系统、云存储等。数据仓库层是核心,它存储和管理从数据源层收集并经过清洗和转换的数据。数据访问层提供了用户访问数据仓库的接口,包括查询工具、报告生成工具和分析工具。
数据仓库的架构设计需要考虑性能、可扩展性、数据完整性和安全性。在性能方面,数据仓库需要支持大量并发用户的快速查询响应,因此通常使用专门的数据库技术(如列式存储、并行处理)来优化查询性能。在可扩展性方面,数据仓库需要能够随着数据量的增长而扩展,因此通常设计为模块化的、可扩展的架构。在数据完整性方面,数据仓库需要确保数据的一致性和准确性,因此通常使用数据校验和清洗技术来保证数据质量。在安全性方面,数据仓库需要保护敏感数据免受未经授权的访问,因此通常采用加密、访问控制等安全措施。
三、数据仓库的实施过程
实施数据仓库通常包括多个步骤:需求分析、数据建模、ETL开发、数据加载、数据验证和用户培训。需求分析是实施数据仓库的第一步,目的是了解企业的业务需求和数据需求,为数据仓库的设计提供基础。数据建模是根据需求分析的结果设计数据仓库的数据模型,通常包括概念模型、逻辑模型和物理模型。ETL开发是数据仓库实施的核心步骤,涉及到数据的提取、转换和加载过程。数据加载是将经过ETL处理的数据加载到数据仓库中。数据验证是对加载到数据仓库中的数据进行验证,以确保数据的准确性和完整性。用户培训是数据仓库实施的最后一步,目的是帮助用户了解如何使用数据仓库进行数据查询和分析。
数据仓库的实施过程需要团队协作,包括IT人员、业务分析师和项目经理等角色。IT人员负责技术实现,包括数据建模、ETL开发和数据加载等技术工作。业务分析师负责需求分析和用户培训,确保数据仓库能够满足业务需求。项目经理负责项目的整体协调和管理,确保数据仓库项目按时、按预算完成。
四、数据仓库的优势与挑战
数据仓库的主要优势包括:提高数据访问速度、支持复杂查询、提供一致的数据视图和支持历史数据分析。通过数据仓库,用户可以快速访问和分析大量数据,支持复杂的查询和分析需求。数据仓库提供了一致的数据视图,使用户能够从不同的角度查看和分析数据。此外,数据仓库存储了大量的历史数据,可以用于趋势分析和预测。
然而,数据仓库的实施也面临一些挑战:数据质量、数据集成、性能优化和成本控制。数据质量是数据仓库成功的关键,必须确保数据的准确性、一致性和完整性。数据集成是一个复杂的过程,需要将来自不同来源的数据整合到一起,通常需要大量的数据清洗和转换工作。性能优化是数据仓库设计的重要考虑因素,需要使用专门的技术和工具来提高查询性能。成本控制是实施数据仓库的一个重要挑战,需要在性能、可扩展性和成本之间找到平衡。
五、数据仓库的应用场景
数据仓库广泛应用于各行各业,支持多种业务应用场景。在零售行业,数据仓库用于分析销售数据、库存数据和客户行为数据,支持营销决策和供应链优化。在金融行业,数据仓库用于分析客户交易数据、风险数据和市场数据,支持风险管理和市场分析。在制造业,数据仓库用于分析生产数据、质量数据和供应链数据,支持生产优化和质量控制。在医疗行业,数据仓库用于分析患者数据、医疗记录和临床数据,支持医疗决策和健康管理。
数据仓库在这些应用场景中发挥了重要作用,通过提供一致的、全面的和易于访问的数据视图,帮助企业提高决策效率和业务绩效。数据仓库的应用不仅限于大型企业,中小型企业也可以通过数据仓库实现数据驱动的决策,提高竞争力和市场响应能力。
六、未来数据仓库的发展趋势
随着技术的发展和业务需求的变化,数据仓库也在不断演变。未来的数据仓库将更加智能化、灵活化和云化。智能化体现在数据仓库将集成更多的人工智能和机器学习技术,支持自动化的数据分析和预测。灵活化体现在数据仓库将更加模块化和可扩展,支持不同的业务需求和数据规模。云化体现在数据仓库将更多地部署在云环境中,支持更高的可扩展性和灵活性。
未来的数据仓库将更加注重实时数据处理和分析,支持实时决策和快速响应。数据仓库将与数据湖、数据集市和实时分析系统紧密结合,形成一个完整的数据管理和分析生态系统。随着数据量的不断增加和数据类型的多样化,数据仓库将支持更多的数据类型和格式,包括结构化数据、半结构化数据和非结构化数据。
总之,数据仓库在未来将继续发挥重要作用,通过不断创新和技术进步,支持企业实现数据驱动的决策,提高业务效率和竞争力。数据仓库的发展将为企业提供更多的机会和挑战,帮助企业在数字化转型的道路上取得成功。
相关问答FAQs:
What is a Data Warehouse?
A data warehouse is a centralized repository designed to store, manage, and analyze large volumes of structured and unstructured data from different sources. It acts as a bridge between operational databases and analytical tools, providing a consolidated view of an organization’s data. By integrating data from various sources, a data warehouse enables organizations to perform complex queries and generate insightful reports, facilitating better decision-making processes.
Data warehouses are typically optimized for read-heavy operations, meaning that they are designed to efficiently handle large volumes of queries that analyze historical data. They often employ techniques such as data modeling and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, which ensure that the data is cleaned, transformed, and loaded into the warehouse in a structured format. This allows for faster retrieval and analysis.
The architecture of a data warehouse usually consists of three key components: the data source layer, the data storage layer, and the presentation layer. The data source layer includes various databases and external data sources from which data is extracted. The data storage layer is where the data is organized and stored, often using star or snowflake schemas for efficient querying. Finally, the presentation layer allows users to interact with the data through visualization tools and reporting interfaces.
Overall, data warehouses play a crucial role in business intelligence, enabling organizations to gain insights from their data, track performance, and identify trends over time.
What are the Benefits of Using a Data Warehouse?
Utilizing a data warehouse offers numerous advantages to organizations looking to make data-driven decisions. One of the primary benefits is the ability to consolidate data from multiple sources, which provides a holistic view of the organization's information. By having a single source of truth, businesses can reduce discrepancies and inconsistencies that often arise from using disparate systems.
Another significant advantage is the improved query performance. Data warehouses are optimized for complex queries and reporting, which allows users to access and analyze data quickly. This efficiency is especially beneficial for organizations that require real-time insights to respond to market changes or operational challenges.
Data warehouses also enhance data quality and accuracy. Through the ETL process, data is cleansed and transformed to ensure that it is reliable and consistent. This focus on data integrity is essential for making informed decisions based on accurate information.
Moreover, a data warehouse supports advanced analytics and business intelligence initiatives. Organizations can leverage data mining, predictive analytics, and machine learning algorithms to uncover hidden patterns and trends, ultimately driving strategic initiatives and improving business outcomes.
Lastly, by providing historical data analysis capabilities, data warehouses enable organizations to perform trend analysis and forecasting. This capability is invaluable for strategic planning, resource allocation, and identifying potential areas for growth or improvement.
How Does a Data Warehouse Differ from a Database?
Understanding the distinction between a data warehouse and a database is crucial for organizations that want to leverage their data effectively. While both serve as storage solutions for data, they are designed for different purposes and have distinct characteristics.
A database is primarily focused on transaction processing and is optimized for CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations. It is best suited for managing real-time data and supporting day-to-day operations. Databases are structured to handle high volumes of transactions and maintain data integrity, making them ideal for applications such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems or enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
In contrast, a data warehouse is designed for analytical processing. It is optimized for read-heavy operations and complex queries, allowing users to analyze historical data and generate reports. Data warehouses store large amounts of data from multiple sources and are structured to support fast retrieval and analysis, which is essential for business intelligence activities.
Another key difference lies in the data model. Databases typically utilize a normalized schema to reduce redundancy and ensure data integrity. In contrast, data warehouses often employ denormalized schemas, such as star or snowflake schemas, to optimize query performance and simplify data retrieval.
Additionally, the frequency of data updates varies between the two. Databases are updated in real-time, reflecting the current state of the data. Data warehouses, however, are updated periodically through ETL processes, which means they may not always reflect the most current data but instead provide a historical perspective for analysis.
Ultimately, while databases and data warehouses both play essential roles in data management, their different purposes, structures, and functionalities make them suitable for distinct types of tasks within an organization.
本文内容通过AI工具匹配关键字智能整合而成,仅供参考,帆软不对内容的真实、准确或完整作任何形式的承诺。具体产品功能请以帆软官方帮助文档为准,或联系您的对接销售进行咨询。如有其他问题,您可以通过联系blog@fanruan.com进行反馈,帆软收到您的反馈后将及时答复和处理。