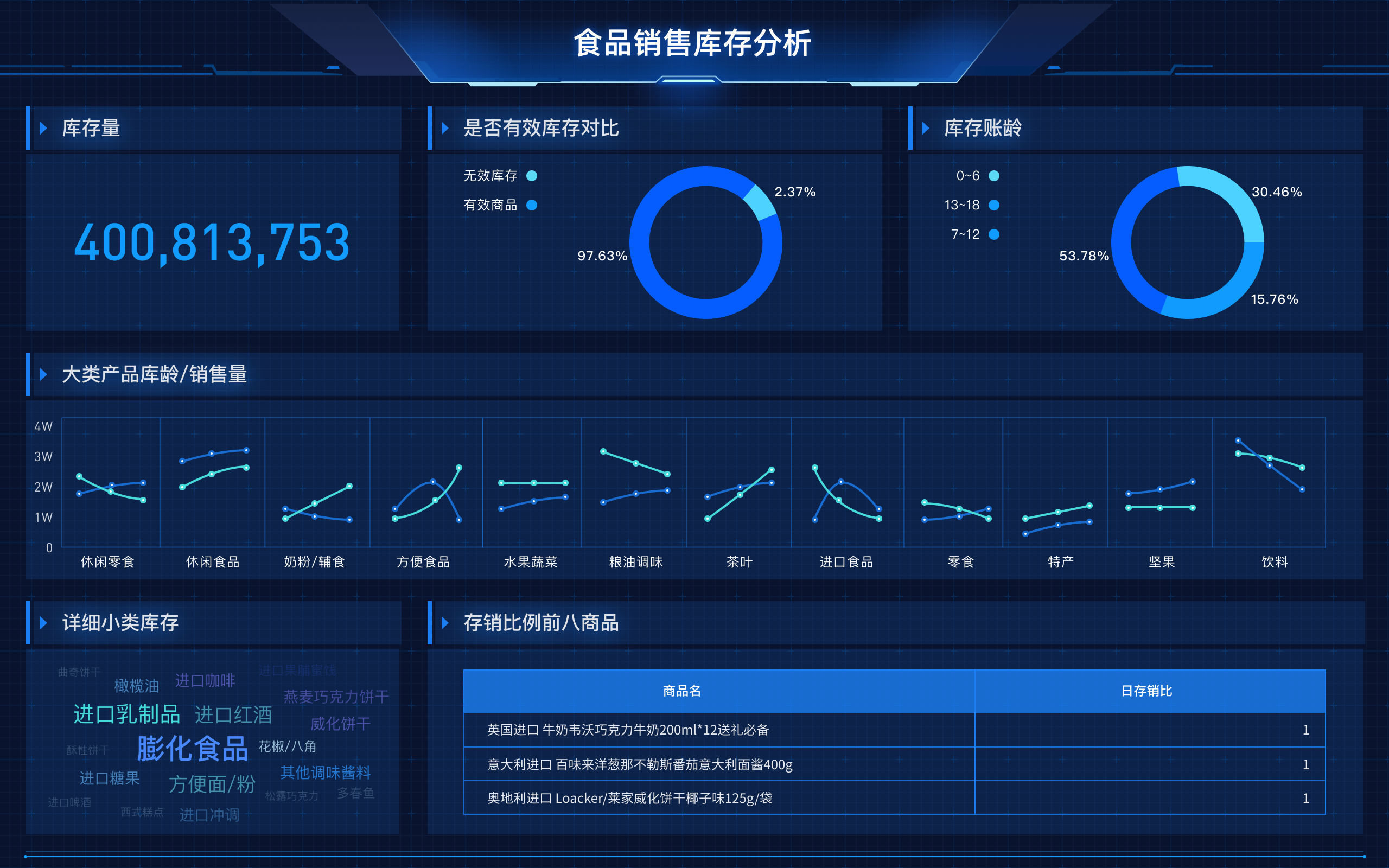
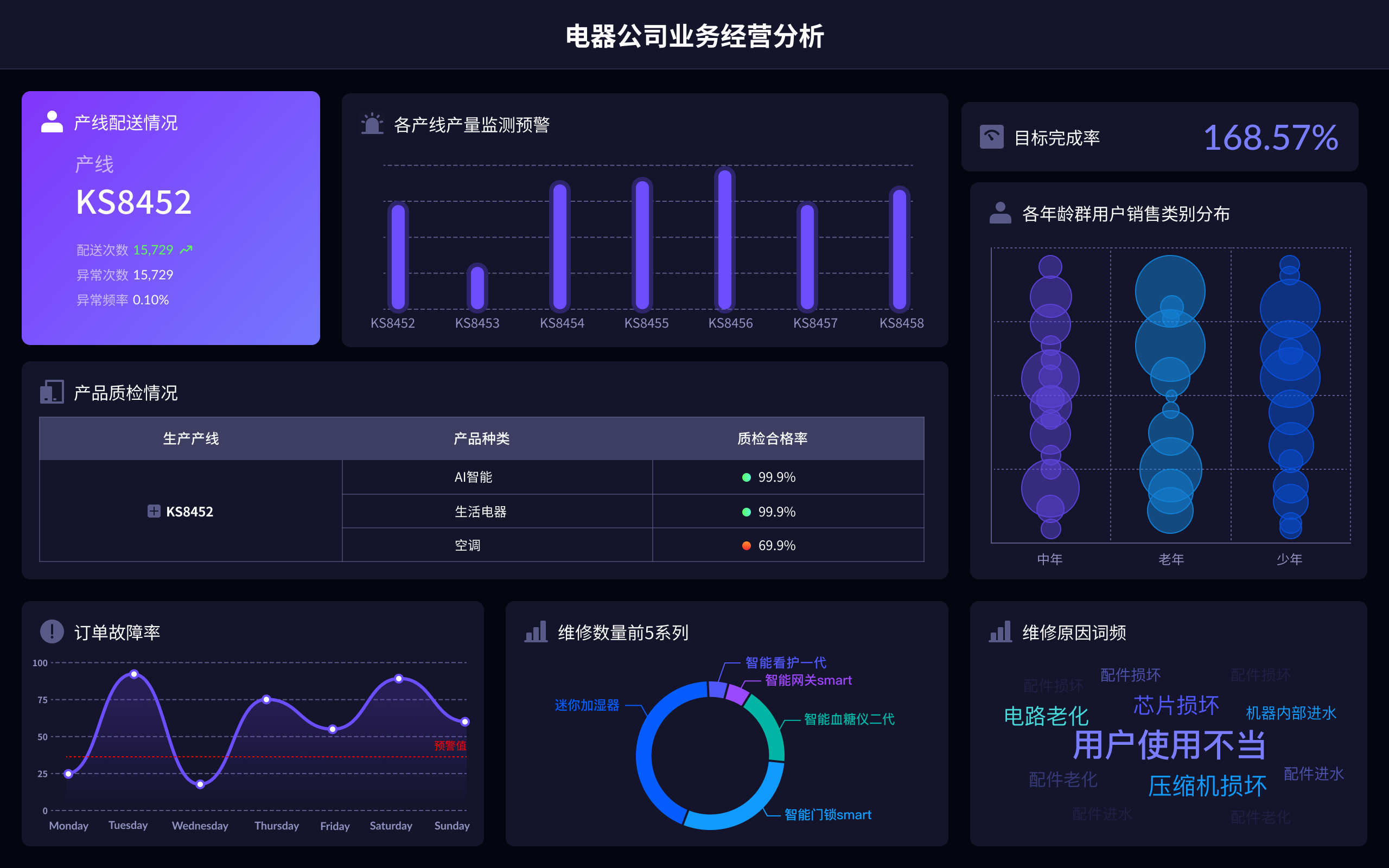
Intelligent data can unlock value through enhanced decision-making, improved efficiency, and personalized experiences. Enhanced decision-making involves using data analytics to derive actionable insights, which allows businesses to make informed decisions that can drive growth and innovation. For example, companies can use predictive analytics to forecast market trends, customer behavior, and operational efficiencies, thus enabling them to plan strategically and allocate resources more effectively. Improved efficiency is achieved by automating routine tasks and optimizing processes, which reduces costs and increases productivity. Personalized experiences involve tailoring products, services, and marketing efforts to individual customer preferences, thereby improving customer satisfaction and loyalty. By leveraging intelligent data, organizations can gain a competitive edge, boost profitability, and create value for stakeholders.
I. ENHANCED DECISION-MAKING
Enhanced decision-making is one of the primary ways intelligent data can unlock value. By using advanced data analytics, businesses can derive actionable insights from vast amounts of data. Predictive analytics is a powerful tool that allows companies to forecast future trends and behaviors. For instance, retail businesses can analyze purchasing patterns to predict future inventory needs, thus ensuring they stock the right products at the right times. This reduces the risk of overstocking or understocking, which can have significant financial implications.
Additionally, real-time analytics enables organizations to make immediate decisions based on current data. For example, in the finance sector, real-time analytics can help traders make quick decisions on buying or selling stocks, improving their chances of capitalizing on market opportunities. Furthermore, descriptive analytics helps in understanding historical data to identify patterns and trends, which can inform long-term strategic planning. By combining these various analytical approaches, businesses can create a comprehensive decision-making framework that leverages data to its fullest potential.
II. IMPROVED EFFICIENCY
Intelligent data plays a crucial role in improving efficiency within organizations. Automation of routine tasks is one of the key benefits. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can handle repetitive tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and customer service inquiries, freeing up human employees to focus on more complex and value-added activities. This not only increases productivity but also reduces the likelihood of errors, leading to better overall operational efficiency.
Moreover, process optimization is another significant advantage. By analyzing workflow data, businesses can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in their processes. For example, a manufacturing company might use data analytics to pinpoint stages in the production line where delays frequently occur. By addressing these issues, they can streamline operations, reduce downtime, and increase output. Supply chain optimization is another area where intelligent data can make a substantial impact. By analyzing data from various points in the supply chain, companies can identify opportunities to reduce costs, improve delivery times, and enhance overall supply chain performance.
III. PERSONALIZED EXPERIENCES
Creating personalized experiences for customers is a powerful way to unlock value using intelligent data. By analyzing customer data, businesses can gain insights into individual preferences, behaviors, and needs. This enables them to tailor products and services to meet specific customer requirements, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. For example, e-commerce platforms often use data analytics to recommend products based on a customer's browsing history and past purchases, providing a more personalized shopping experience.
Targeted marketing is another area where intelligent data can create significant value. By segmenting customers based on various criteria such as demographics, buying behavior, and preferences, businesses can design more effective marketing campaigns. This not only improves the chances of converting leads into customers but also ensures that marketing resources are used more efficiently. Customer journey mapping is another technique that benefits from intelligent data. By understanding the different touchpoints a customer interacts with before making a purchase, businesses can optimize these interactions to provide a seamless and enjoyable experience.
IV. COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
Leveraging intelligent data can provide organizations with a competitive edge. Market intelligence involves analyzing data from various sources to understand market trends, competitor strategies, and customer needs. By staying ahead of market trends, businesses can adapt quickly and innovate to meet changing demands. For example, a tech company might use market intelligence to identify emerging technologies and invest in research and development to stay ahead of competitors.
Customer insights derived from data analytics can also help businesses understand their customers better than their competitors do. This deeper understanding allows for the development of products and services that better meet customer needs, leading to increased market share. Operational excellence achieved through data-driven decision-making and process optimization can further enhance a company's competitive position by reducing costs and improving service quality.
V. PROFITABILITY
Intelligent data can significantly impact an organization's profitability. Revenue growth can be driven by identifying new business opportunities and optimizing sales strategies. For instance, by analyzing sales data, a company might identify high-performing products and focus its marketing efforts on promoting these items. Additionally, cost reduction is another critical area where data analytics can make a difference. By identifying inefficiencies and areas of waste, businesses can implement cost-saving measures that directly impact the bottom line.
Customer retention is another factor that influences profitability. By using data to understand customer behavior and preferences, businesses can implement strategies to retain existing customers, which is often more cost-effective than acquiring new ones. Pricing strategies can also be optimized using data analytics. By understanding the price sensitivity of different customer segments, businesses can set prices that maximize revenue while remaining competitive.
VI. STAKEHOLDER VALUE
Creating value for stakeholders is a crucial aspect of any business, and intelligent data plays a pivotal role in this regard. Shareholders benefit from increased profitability and competitive advantage, which can lead to higher stock prices and dividends. Employees benefit from improved efficiency and productivity, which can result in better job satisfaction and career development opportunities. Customers benefit from personalized experiences and high-quality products and services, which enhance their overall satisfaction and loyalty.
Suppliers and partners also benefit from more efficient and transparent supply chain processes, which can lead to stronger business relationships and better collaboration. Regulatory bodies benefit from improved compliance and reporting capabilities, which can result in a more stable and trustworthy business environment. By addressing the needs and expectations of all stakeholders, businesses can create a sustainable and mutually beneficial ecosystem.
VII. DATA GOVERNANCE AND ETHICS
The effective use of intelligent data also requires robust data governance and ethical considerations. Data privacy is a critical aspect, as businesses must ensure that they are collecting, storing, and using data in compliance with relevant laws and regulations. This involves implementing measures to protect customer data from breaches and misuse. Data quality is another important factor, as accurate and reliable data is essential for making informed decisions. Businesses must establish processes for data validation, cleansing, and maintenance to ensure the integrity of their data.
Ethical use of data involves being transparent with customers about how their data is being used and ensuring that data-driven decisions do not result in unfair or discriminatory practices. By adhering to high standards of data governance and ethics, businesses can build trust with their stakeholders and create a solid foundation for sustainable growth.
VIII. FUTURE TRENDS
The field of intelligent data is constantly evolving, and several future trends are worth noting. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are expected to play an increasingly important role in data analytics. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data more quickly and accurately than traditional methods, providing deeper insights and enabling more sophisticated decision-making.
Big Data is another trend that will continue to shape the landscape of intelligent data. As the volume of data generated by businesses and consumers grows exponentially, new tools and techniques will be required to manage and analyze this data effectively. Internet of Things (IoT) devices will also contribute to the proliferation of data, providing real-time insights into various aspects of business operations.
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize data security and transparency by providing a decentralized and tamper-proof way to store and verify data. Cloud computing will continue to be a key enabler, providing the scalability and flexibility needed to handle large datasets and complex analytics.
In conclusion, intelligent data unlocks value through enhanced decision-making, improved efficiency, and personalized experiences, among other benefits. By leveraging advanced data analytics and adhering to robust data governance practices, businesses can gain a competitive edge, boost profitability, and create lasting value for all stakeholders. The future of intelligent data holds exciting possibilities, and organizations that embrace these trends will be well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly data-driven world.
相关问答FAQs:
What is Smart Data and how does it differ from Big Data?
Smart Data refers to the high-quality, meaningful information that can be derived from vast quantities of raw data. Unlike Big Data, which emphasizes the volume, variety, and velocity of data, Smart Data focuses on the relevance and applicability of the information obtained. It involves the use of advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning techniques to filter out noise and extract actionable insights.
The distinction lies in the approach; while Big Data is about collecting and storing massive datasets, Smart Data prioritizes understanding and utilizing data in a way that enhances decision-making. For example, Smart Data can help businesses identify trends, customer preferences, and operational inefficiencies, allowing them to make informed strategic decisions. In this way, organizations can optimize their resources and create value through targeted actions.
How can organizations effectively mine value from Smart Data?
Organizations can effectively mine value from Smart Data by implementing a systematic approach to data analysis and decision-making. The process typically involves several key steps:
-
Data Integration: Combine data from multiple sources, including structured and unstructured data, to create a comprehensive view. This may involve utilizing data warehouses, data lakes, or cloud-based solutions to centralize information.
-
Data Cleaning and Preparation: Ensure that the data is accurate, complete, and formatted correctly. This step is crucial as it lays the foundation for reliable analysis. Removing duplicates, correcting errors, and filling in missing values are common practices.
-
Advanced Analytics: Employ statistical techniques, machine learning algorithms, and data visualization tools to analyze the data. Predictive analytics can be particularly useful for forecasting trends and behaviors, while descriptive analytics helps in understanding historical performance.
-
Actionable Insights: Focus on translating the analytical findings into actionable strategies. This could involve creating dashboards that highlight key performance indicators (KPIs) or developing reports that summarize insights for stakeholders.
-
Continuous Improvement: Implement a feedback loop that allows for ongoing monitoring and refinement of data strategies. Regularly assess the effectiveness of decisions made based on Smart Data and adjust approaches as necessary.
By adopting these practices, organizations can enhance their ability to extract meaningful insights from Smart Data, leading to better business outcomes, improved customer satisfaction, and increased operational efficiency.
What are some examples of industries that benefit from Smart Data mining?
Many industries can benefit significantly from Smart Data mining, each leveraging data insights to improve processes, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation. Some notable examples include:
-
Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, Smart Data can be utilized for predictive analytics to identify potential health risks in patients, optimize treatment plans, and streamline operations. By analyzing patient records, medical history, and real-time health data, healthcare providers can enhance patient care and reduce costs.
-
Retail: Retailers use Smart Data to understand consumer behavior, optimize inventory management, and personalize marketing strategies. By analyzing purchase patterns and customer feedback, businesses can offer tailored promotions, improve product placement, and enhance the overall shopping experience.
-
Finance: Financial institutions leverage Smart Data for risk assessment, fraud detection, and investment analysis. By analyzing transaction data and market trends, banks can make informed lending decisions, identify suspicious activities, and optimize their investment portfolios.
-
Manufacturing: In manufacturing, Smart Data mining can lead to improved supply chain management, predictive maintenance, and quality control. By analyzing production data, manufacturers can identify bottlenecks, reduce downtime, and enhance product quality.
-
Telecommunications: Telecommunication companies utilize Smart Data to improve customer service and network performance. By analyzing call data records and customer feedback, they can identify areas for improvement, reduce churn, and optimize service delivery.
These examples illustrate the versatility and value of Smart Data across various sectors, showcasing how organizations can harness data to drive growth and innovation.
本文内容通过AI工具匹配关键字智能整合而成,仅供参考,帆软不对内容的真实、准确或完整作任何形式的承诺。具体产品功能请以帆软官方帮助文档为准,或联系您的对接销售进行咨询。如有其他问题,您可以通过联系blog@fanruan.com进行反馈,帆软收到您的反馈后将及时答复和处理。