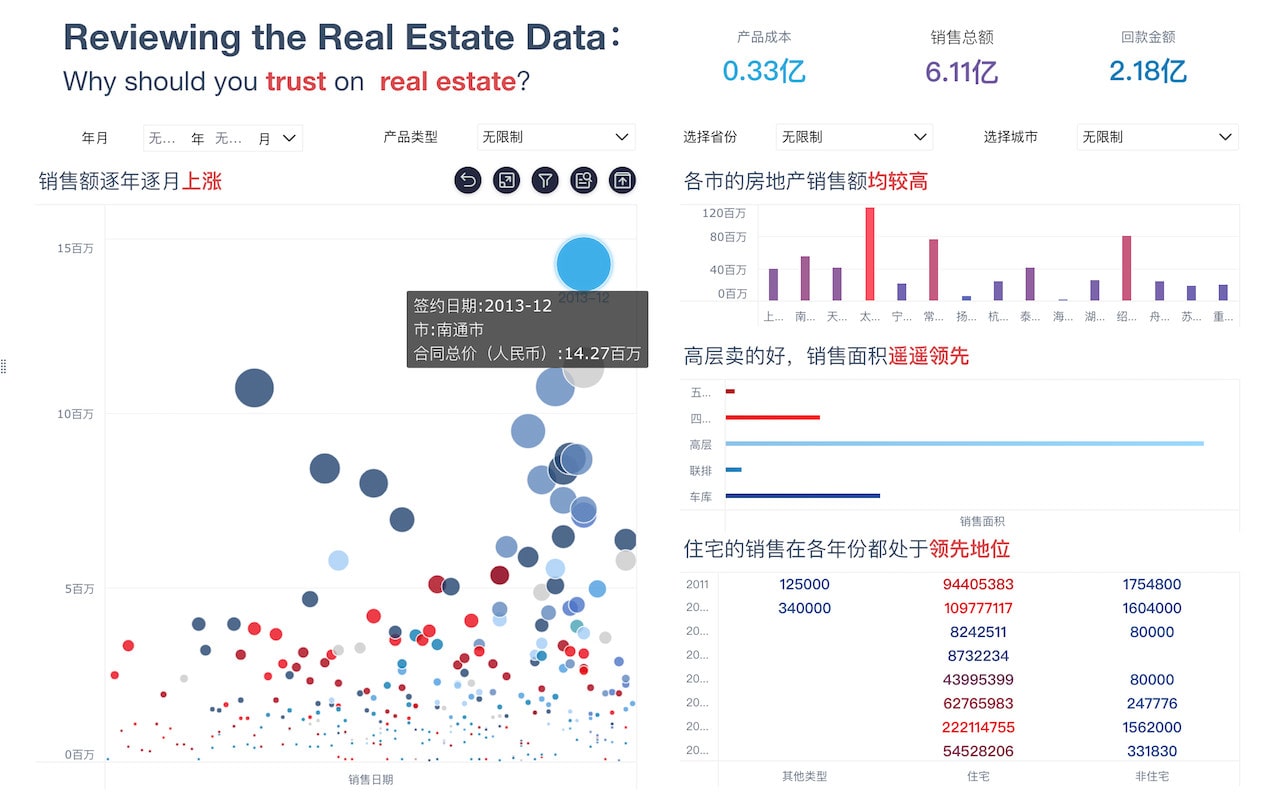
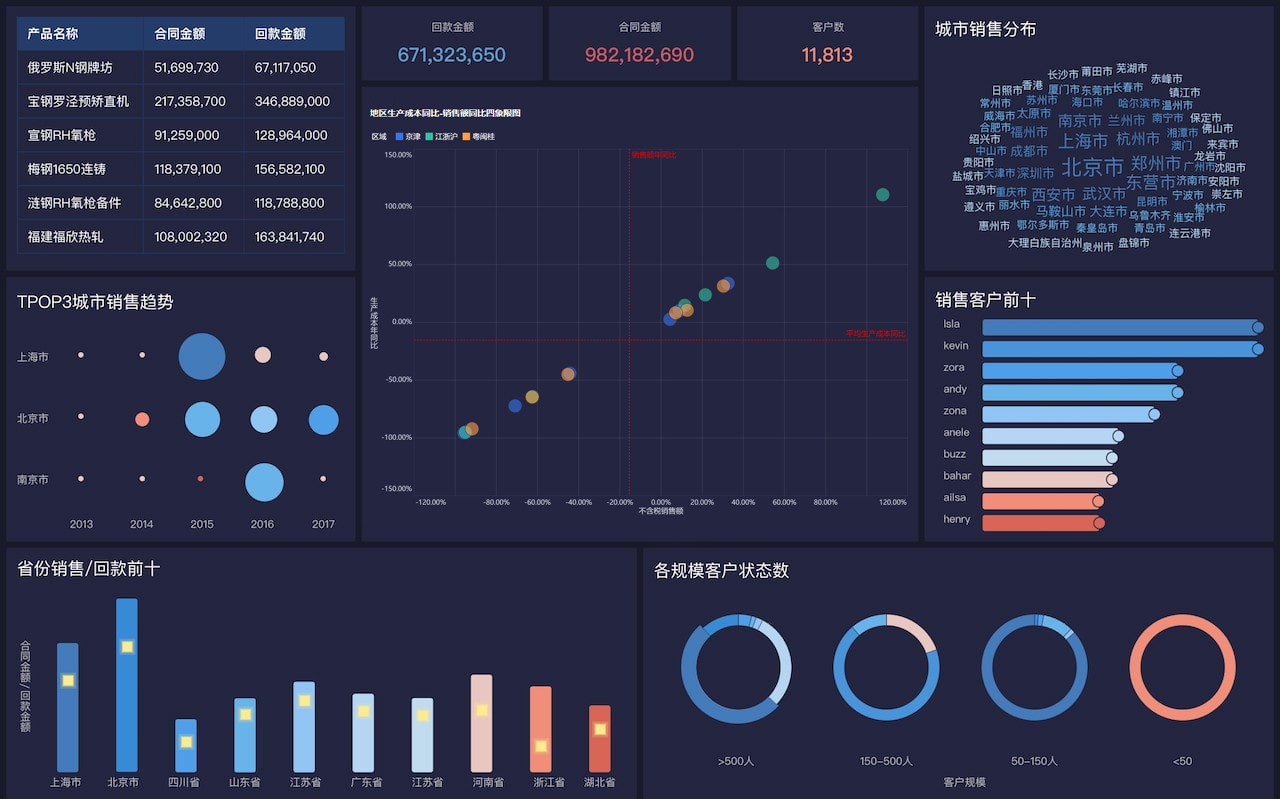
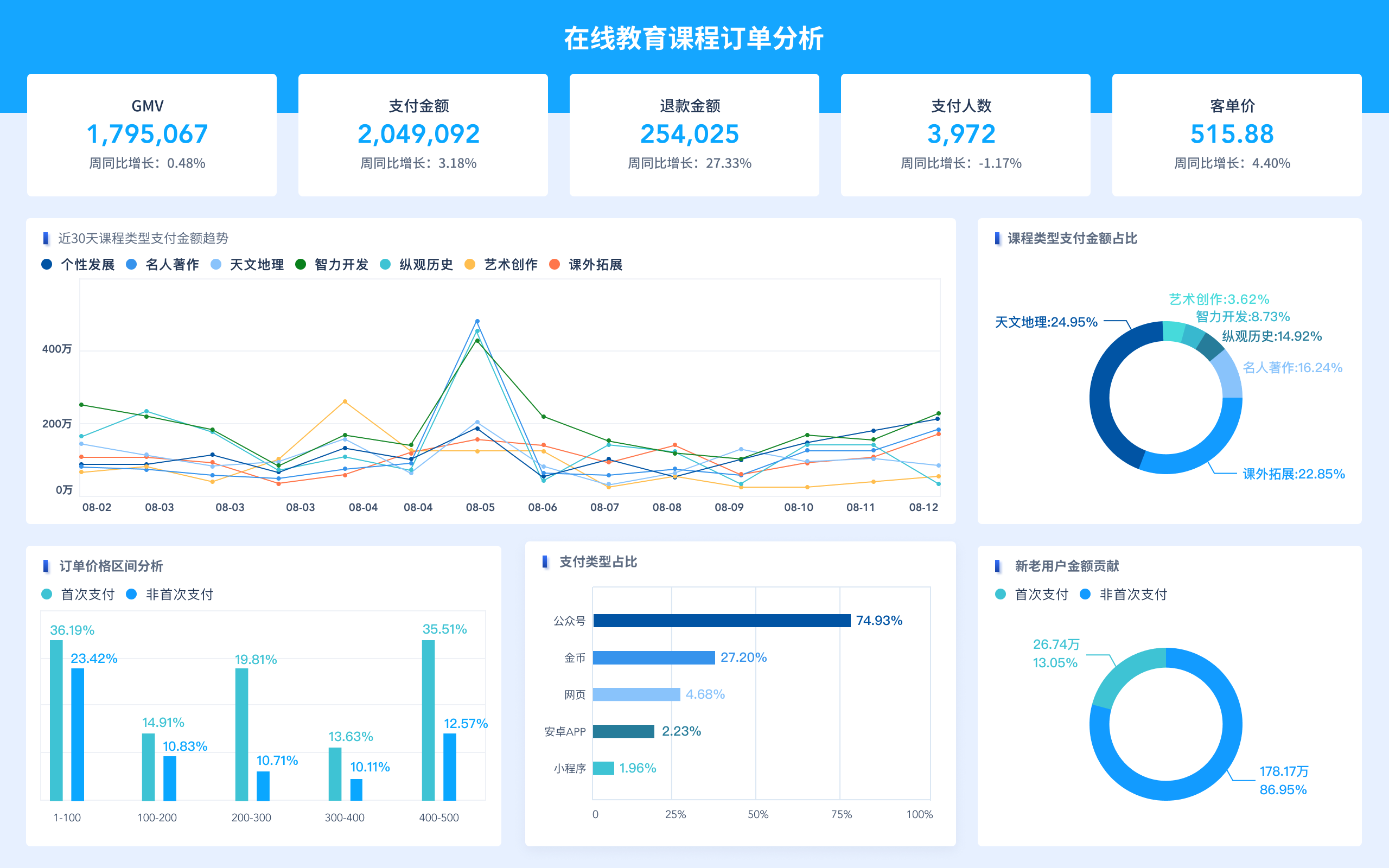
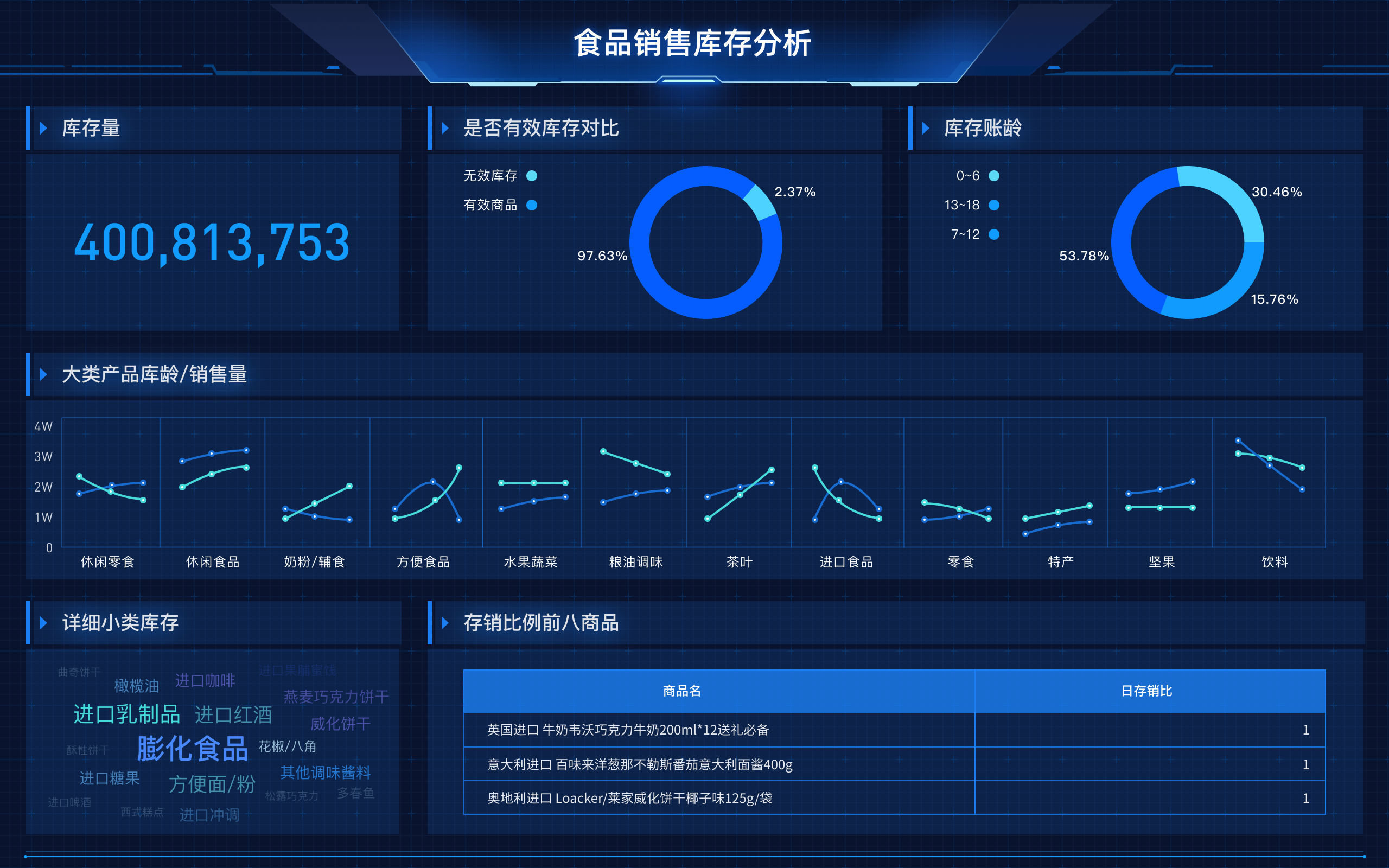
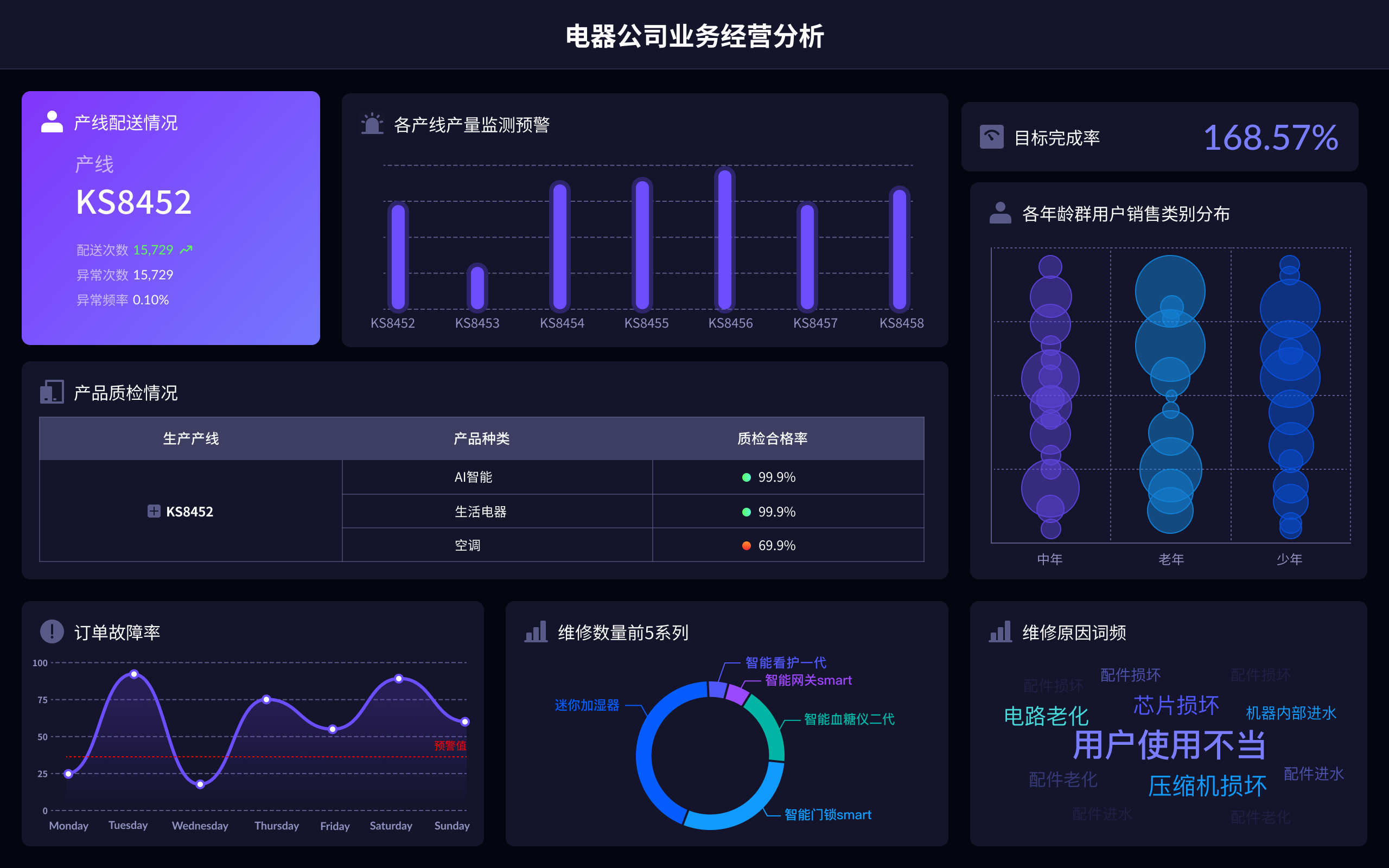
When faced with data mining problems, it is crucial to understand the data, preprocess the data, select appropriate algorithms, evaluate the models, and interpret the results. One of the most critical steps is to preprocess the data, as this involves cleaning, transforming, and normalizing the data to ensure it is in the best possible state for analysis. Without proper preprocessing, the results of data mining can be misleading or incorrect. This step includes handling missing values, removing duplicates, and scaling numerical features, which can significantly impact the performance of machine learning models.
I、UNDERSTAND THE DATA
Understanding the data is the initial and perhaps the most crucial step in facing data mining problems. This involves gaining a deep insight into the dataset's nature, its structure, and its inherent characteristics. By understanding the data, you can make informed decisions on how to approach the problem. This step involves several sub-tasks such as:
- Domain Knowledge: Acquiring knowledge about the domain from which the data originates. This helps in making sense of the data and identifying relevant features.
- Data Types: Identifying the different types of data (e.g., numerical, categorical, text, image) and understanding their distribution.
- Data Sources: Knowing where the data comes from and how it was collected to assess its reliability and potential biases.
- Descriptive Statistics: Utilizing statistical techniques to summarize and describe the main features of the dataset. This includes measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and measures of variability (range, variance, standard deviation).
II、PREPROCESS THE DATA
Preprocessing the data is essential to ensure that the data is in a suitable format for analysis. This step can be broken down into several key activities:
- Data Cleaning: This involves identifying and correcting errors in the data, such as missing values, outliers, and duplicate records. Methods for handling missing values include imputation techniques (mean, median, mode substitution) or using algorithms that can handle missing data natively.
- Data Transformation: Transforming data into a format that is appropriate for analysis. This can include normalization (scaling data to a standard range), encoding categorical variables (using techniques like one-hot encoding), and creating new features (feature engineering) that can enhance the performance of models.
- Data Integration: Combining data from different sources to provide a unified view. This might involve merging tables from different databases or integrating data from different formats (e.g., CSV, JSON, XML).
- Data Reduction: Reducing the volume of data while maintaining its integrity. Techniques such as dimensionality reduction (PCA, LDA) and sampling can be used to achieve this.
III、SELECT APPROPRIATE ALGORITHMS
Choosing the right algorithms is crucial for effective data mining. Different algorithms are suited to different types of problems and data. Key considerations include:
- Type of Problem: Determining whether the problem is supervised (classification, regression) or unsupervised (clustering, association). Each type of problem requires different algorithms.
- Algorithm Suitability: Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of various algorithms. For instance, decision trees are easy to interpret but can overfit, while neural networks are powerful but require large amounts of data and computational resources.
- Performance Metrics: Selecting appropriate metrics to evaluate the performance of the algorithms. For classification, metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score are important. For regression, metrics like mean squared error (MSE), mean absolute error (MAE), and R-squared are commonly used.
- Scalability: Considering whether the algorithm can handle the size and complexity of the data. Some algorithms may perform well on small datasets but struggle with larger ones.
IV、EVALUATE THE MODELS
Evaluating the models is a critical step to ensure that they perform well on unseen data. This involves:
- Cross-Validation: Using techniques like k-fold cross-validation to assess the model's performance on different subsets of the data. This helps in understanding the model's generalization capability.
- Hyperparameter Tuning: Optimizing the model's hyperparameters to improve performance. Techniques like grid search, random search, and Bayesian optimization can be used to find the best hyperparameter values.
- Model Comparison: Comparing different models to select the best one. This can involve comparing different algorithms or different versions of the same algorithm with various hyperparameters.
- Validation Metrics: Using appropriate validation metrics to evaluate the model's performance. It's important to choose metrics that align with the business objectives and the nature of the problem.
V、INTERPRET THE RESULTS
Interpreting the results is crucial to derive actionable insights from the data mining process. This involves:
- Understanding Model Outputs: Interpreting the outputs of the models in the context of the business problem. This might involve understanding feature importance, decision boundaries, and the impact of different variables on the predictions.
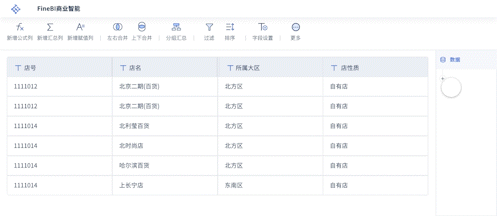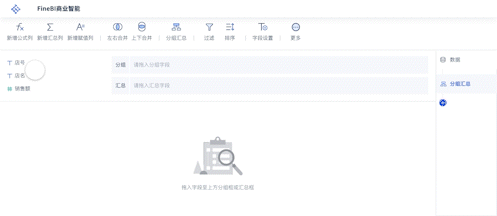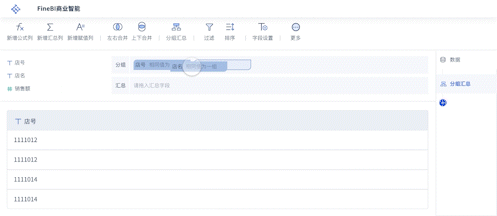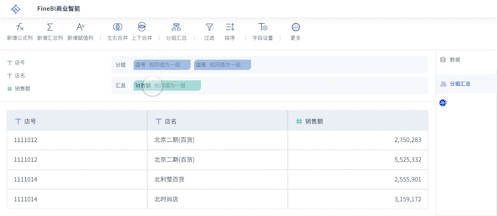
- Visualizations: Using visualizations to communicate the results effectively. Techniques like bar charts, line graphs, scatter plots, and heat maps can help in understanding the data and the model's performance.
- Business Insights: Translating the technical results into business insights that can drive decision-making. This involves communicating the findings to stakeholders in a clear and concise manner, highlighting the key takeaways and potential actions.
VI、DEPLOY AND MONITOR THE MODELS
Once the models are developed and evaluated, they need to be deployed into a production environment where they can be used to make real-time decisions. This involves:
- Deployment Strategy: Deciding on how the models will be deployed, whether it's batch processing, real-time scoring, or embedded into applications.
- Monitoring: Continuously monitoring the model's performance to ensure it remains effective. This involves tracking metrics like accuracy, precision, and recall over time, and identifying any degradation in performance.
- Maintenance: Updating the models as new data becomes available or as the business problem evolves. This might involve retraining the models periodically or incorporating new features.
VII、DOCUMENTATION AND COMMUNICATION
Thorough documentation and effective communication are essential for the success of data mining projects. This involves:
- Documentation: Keeping detailed records of the data preprocessing steps, the algorithms used, the hyperparameters, and the evaluation results. This ensures that the work can be reproduced and understood by others.
- Communication: Effectively communicating the results and insights to stakeholders. This involves creating reports, presentations, and dashboards that summarize the key findings and their implications for the business.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging with stakeholders throughout the process to ensure that their needs and expectations are met. This involves regular updates, soliciting feedback, and incorporating their input into the analysis.
In conclusion, facing data mining problems requires a structured approach that includes understanding the data, preprocessing it, selecting appropriate algorithms, evaluating the models, interpreting the results, deploying and monitoring the models, and documenting and communicating the findings. By following these steps, you can ensure that your data mining efforts are effective and drive meaningful business insights.
相关问答FAQs:
如何识别数据挖掘问题的根源?
在数据挖掘过程中,明确问题的根源是成功的第一步。数据挖掘问题通常源于数据本身的质量、数量或复杂性。质量不高的数据可能包含噪声、缺失值或错误,而这些都会直接影响挖掘结果。此外,数据的规模也会影响处理的难易程度,过大的数据集可能导致性能瓶颈。为了识别问题的根源,可以通过数据探索和可视化技术来分析数据的特征、分布和潜在异常。这一过程不仅可以帮助发现数据中的潜在问题,还能为后续的建模和分析提供有价值的洞见。
在数据挖掘中,如何选择合适的算法?
选择合适的算法是数据挖掘中的关键步骤,直接影响到结果的有效性和可解释性。不同的问题类型(如分类、回归、聚类等)适用不同的算法。例如,若目标是进行分类,可以选择决策树、随机森林或支持向量机等算法。聚类问题则可以考虑K-means或层次聚类等方法。选择算法时,还需考虑数据的特性,如数据的规模、维度、数据分布等。此外,模型的可解释性和计算复杂度也应纳入考虑范围。通过对比不同算法的性能,可以使用交叉验证等方法来评估算法的效果,从而选择最适合的方案。
如何处理数据挖掘中的伦理问题?
在数据挖掘过程中,伦理问题越来越受到关注。处理数据时必须遵循隐私保护和数据安全的原则。确保数据的收集和使用符合相关法律法规是首要任务。例如,某些数据(如个人身份信息)在未获得用户同意的情况下不得使用。此外,应当在数据处理过程中考虑公平性,避免算法歧视和偏见。为了保持透明度,企业可以向用户公开数据使用政策并提供选择权。通过实施这些措施,不仅可以保护用户的隐私,还能增强用户对数据挖掘工作的信任,从而为企业带来更好的声誉和长期利益。
本文内容通过AI工具匹配关键字智能整合而成,仅供参考,帆软不对内容的真实、准确或完整作任何形式的承诺。具体产品功能请以帆软官方帮助文档为准,或联系您的对接销售进行咨询。如有其他问题,您可以通过联系blog@fanruan.com进行反馈,帆软收到您的反馈后将及时答复和处理。