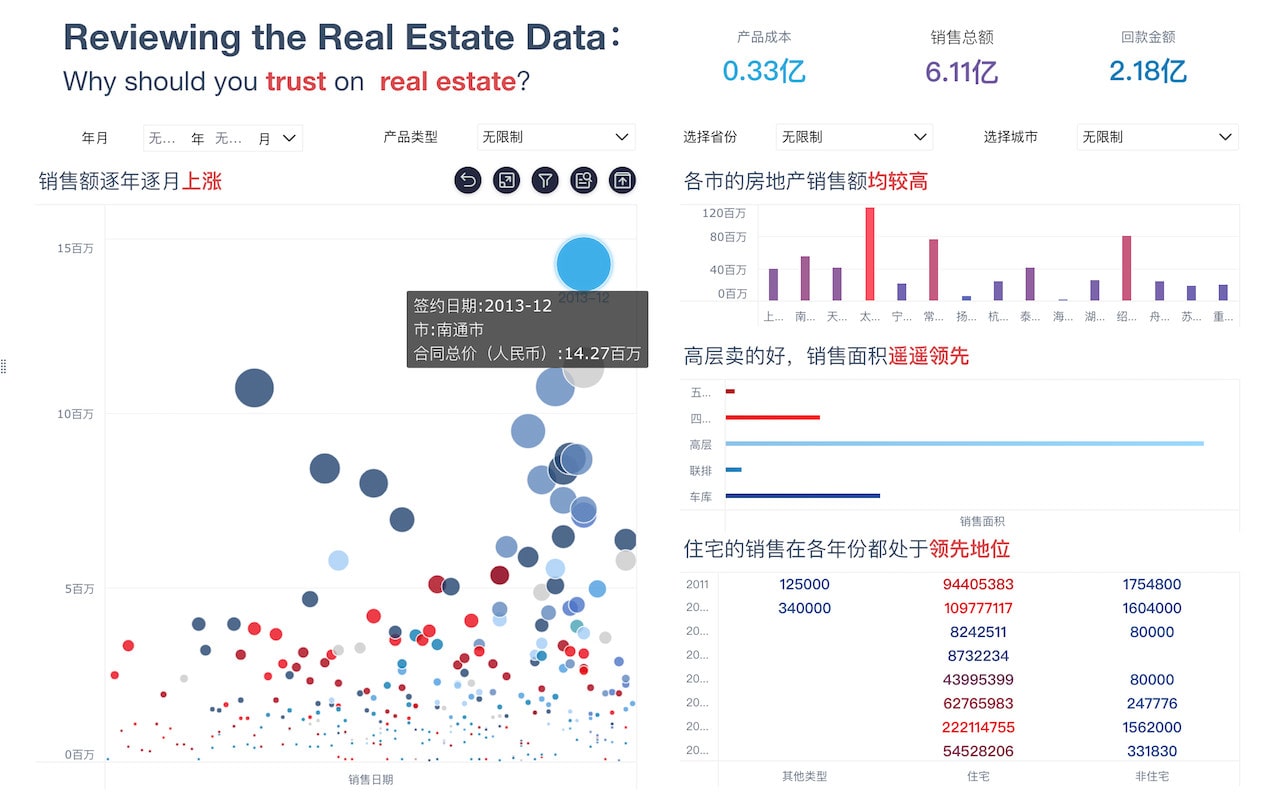
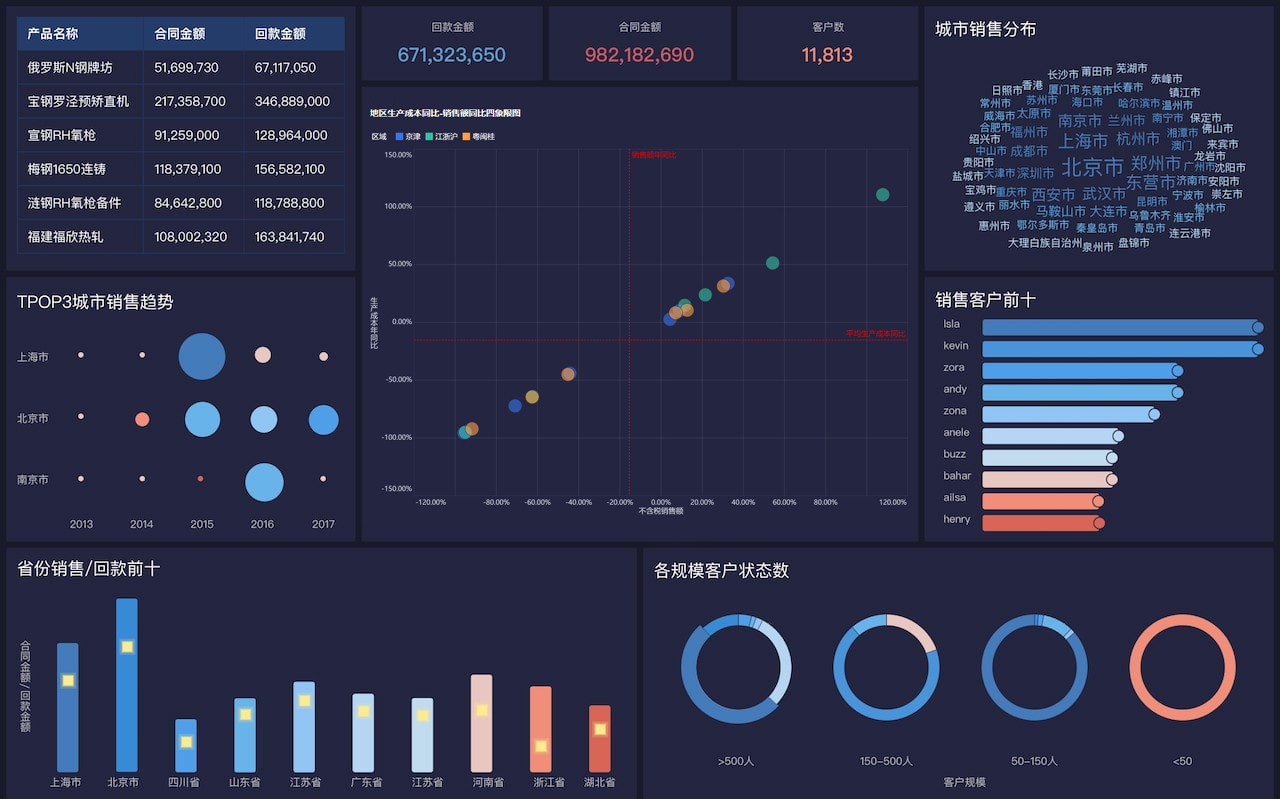
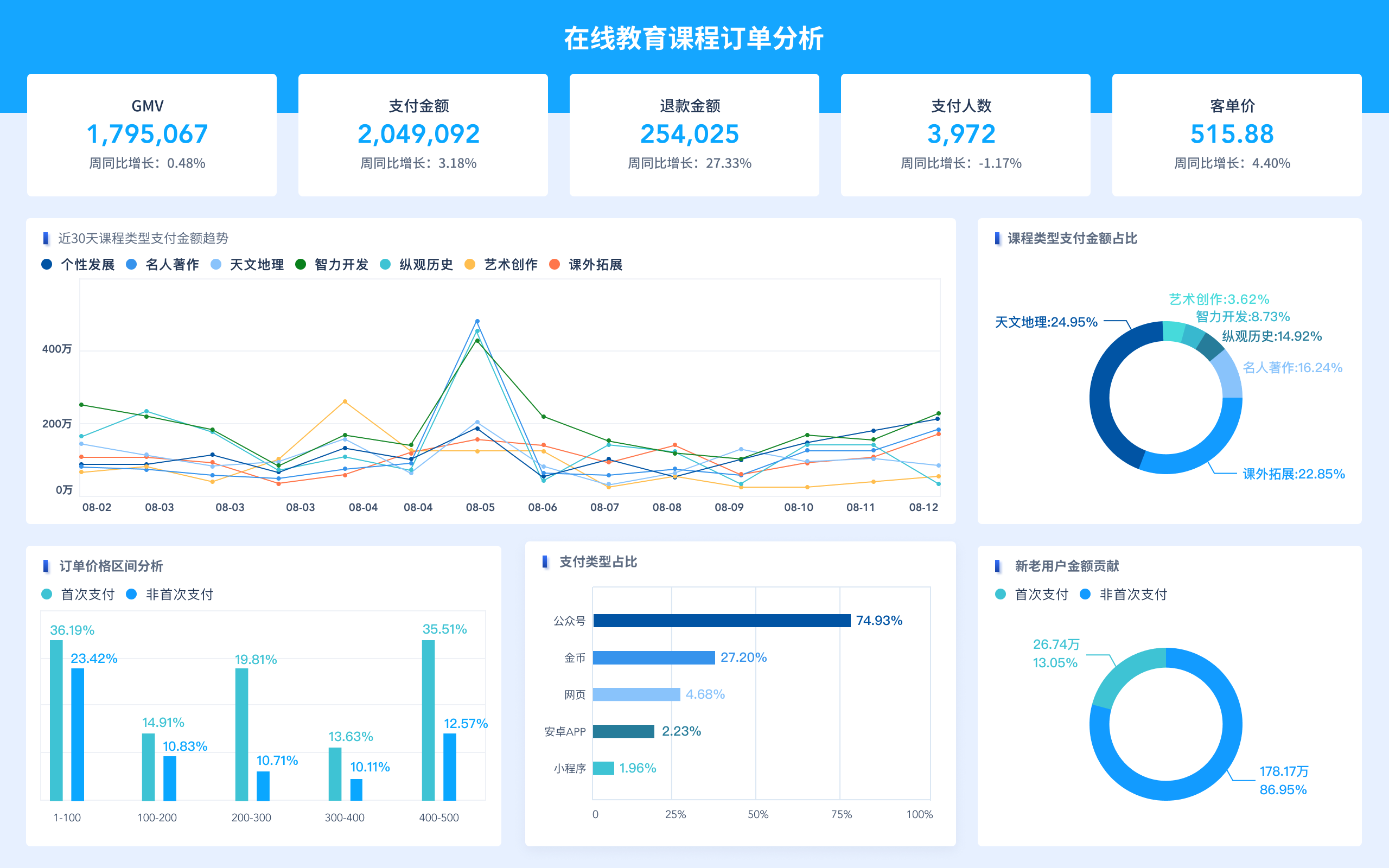
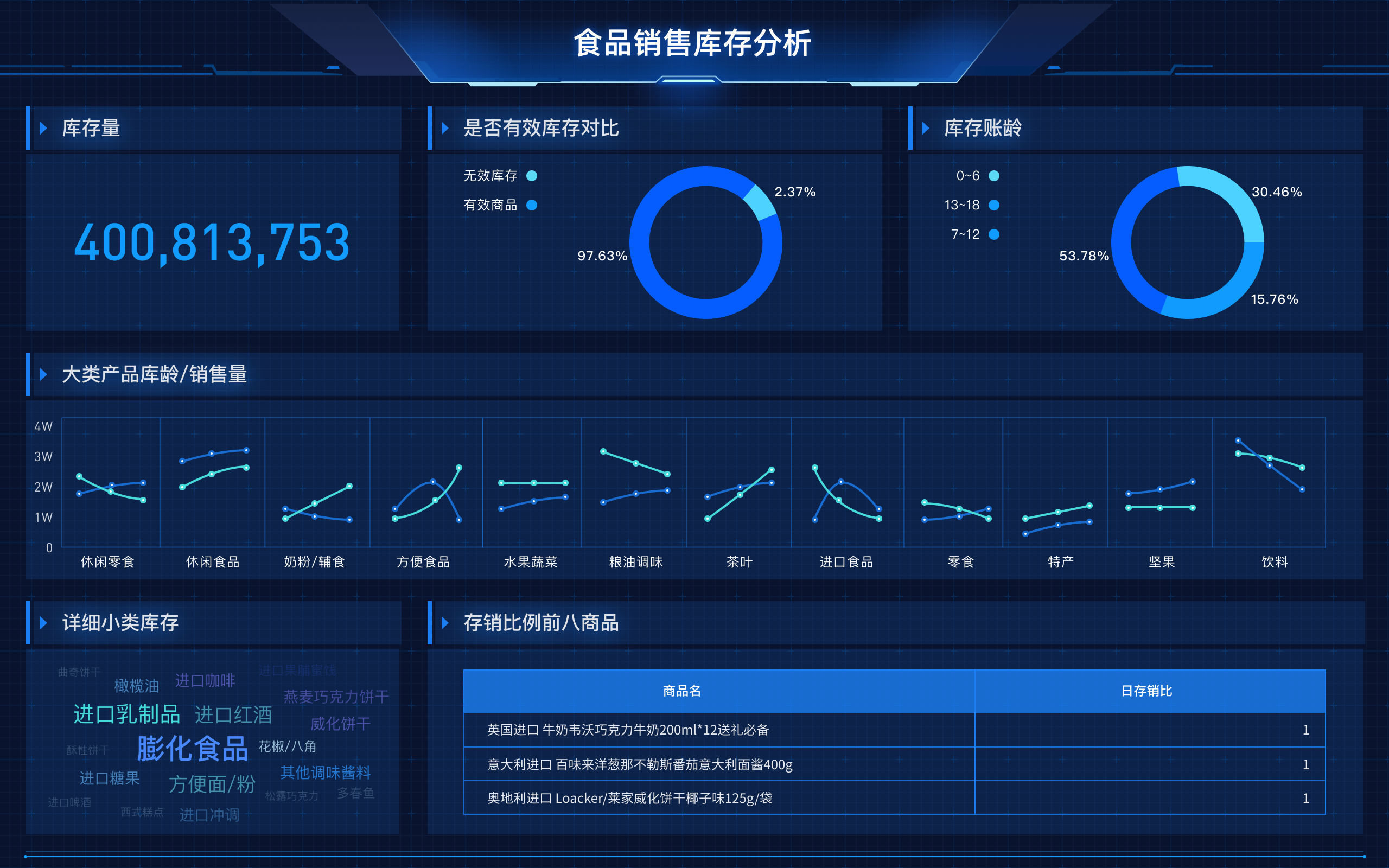
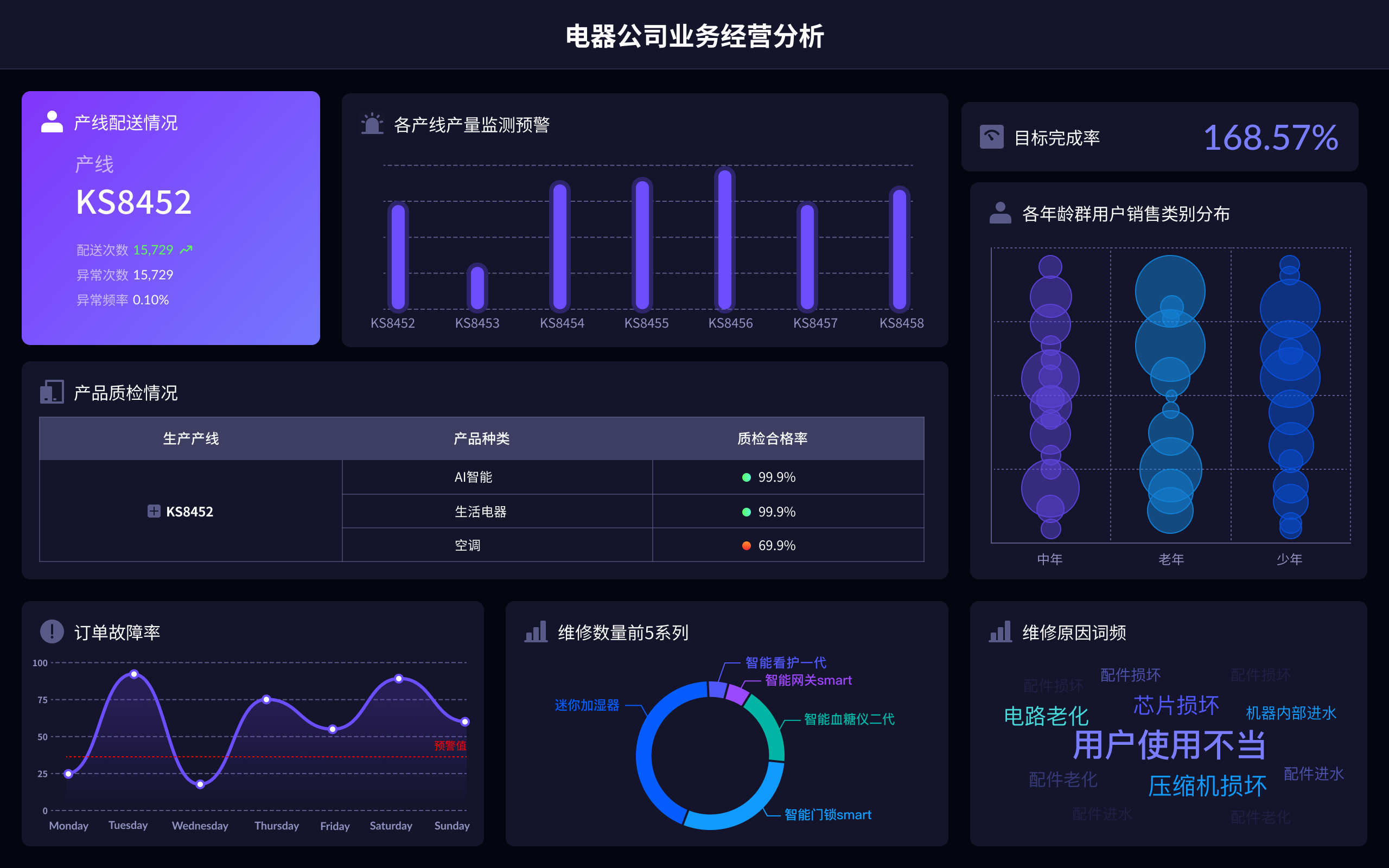
Legally harnessing data value involves compliance with data protection laws, maintaining transparency with data subjects, and implementing robust security measures. Compliance with laws such as GDPR, CCPA, and other regional data protection regulations ensures that data collection, storage, and processing are conducted within legal boundaries. Transparency with data subjects involves informing them about what data is being collected, how it will be used, and obtaining their consent. Robust security measures, including encryption and access controls, protect data from unauthorized access and breaches. For example, GDPR mandates that organizations must have a lawful basis for data processing, which can be consent, contractual necessity, legal obligation, vital interests, public task, or legitimate interests. This not only keeps the organization on the right side of the law but also fosters trust with consumers, leading to better business outcomes.
I、COMPLIANCE WITH DATA PROTECTION LAWS
Compliance with data protection laws is crucial for any organization looking to harness data value legally. Different regions have different regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, and the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) in Singapore. These laws are designed to protect individuals' privacy and provide guidelines on how data should be collected, processed, and stored.
GDPR is one of the most comprehensive data protection laws and applies to any organization that processes the data of EU citizens. It requires organizations to have a lawful basis for data processing, such as consent, contractual necessity, or legitimate interests. Additionally, GDPR mandates that organizations implement data protection by design and by default, conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs), and appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) where necessary.
CCPA grants California residents specific rights regarding their personal information. It includes the right to know what data is being collected, the right to delete personal information, the right to opt-out of the sale of their data, and the right to non-discrimination for exercising these rights. Organizations must update their privacy policies to include these rights and provide mechanisms for consumers to exercise them.
PDPA in Singapore requires organizations to obtain consent before collecting, using, or disclosing personal data. It also mandates that organizations ensure the accuracy of personal data, protect it from unauthorized access, and cease retention of data once it is no longer needed.
By complying with these regulations, organizations can avoid hefty fines and legal consequences, build trust with consumers, and improve their overall data governance practices.
II、TRANSPARENCY WITH DATA SUBJECTS
Transparency with data subjects is essential for building trust and ensuring legal compliance. It involves clearly communicating with individuals about what data is being collected, how it will be used, and obtaining their consent. This can be achieved through privacy policies, consent forms, and regular communication.
Privacy Policies are a critical tool for transparency. They should be easy to understand and accessible, providing detailed information about the types of data collected, the purposes for which it is used, and any third parties with whom the data may be shared. A well-crafted privacy policy helps users make informed decisions about their data and demonstrates the organization's commitment to privacy.
Consent Forms are another important aspect of transparency. They should clearly explain what individuals are consenting to and provide options for different levels of consent. For example, a consent form might allow users to opt-in to data collection for specific purposes, such as marketing or research. This granular approach to consent helps ensure that users are fully aware of how their data will be used and can make choices that align with their preferences.
Regular Communication with data subjects helps maintain transparency over time. This might include updates to privacy policies, notifications of any data breaches, or information about new data processing activities. Keeping users informed about how their data is being handled fosters trust and allows them to exercise their rights under data protection laws.
By prioritizing transparency, organizations can build stronger relationships with their customers, reduce the risk of data-related disputes, and enhance their reputation as responsible data stewards.
III、ROBUST SECURITY MEASURES
Implementing robust security measures is critical to protecting data from unauthorized access, breaches, and other threats. This involves a combination of technical, administrative, and physical controls designed to safeguard data throughout its lifecycle.
Technical Controls include encryption, access controls, and network security measures. Encryption ensures that data is unreadable to unauthorized users, both in transit and at rest. Access controls limit who can access data based on their role and responsibilities, reducing the risk of insider threats. Network security measures, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, help protect data from external attacks.
Administrative Controls involve policies, procedures, and training designed to ensure that data is handled securely. This includes conducting regular security assessments, implementing data classification schemes, and establishing incident response plans. Training employees on data security best practices is also crucial, as human error is often a significant factor in data breaches.
Physical Controls protect data from physical threats, such as theft or damage. This might include securing data centers with access controls, surveillance cameras, and environmental controls to prevent damage from fire or water. Physical security is an often-overlooked aspect of data protection but is essential for comprehensive security.
By implementing robust security measures, organizations can protect their data from a wide range of threats, comply with legal requirements, and demonstrate their commitment to data protection. This not only reduces the risk of costly data breaches but also enhances the organization's reputation and trustworthiness.
IV、DATA MINIMIZATION
Data minimization is a key principle in data protection laws, requiring organizations to collect and process only the data that is necessary for their specific purposes. This reduces the risk of data breaches and helps ensure compliance with legal requirements.
Purpose Limitation involves defining the specific purposes for which data is collected and ensuring that data is not used for unrelated purposes. This helps organizations focus on collecting only the data they need and reduces the risk of unnecessary data exposure.
Data Retention Policies are essential for data minimization. These policies define how long data should be retained and when it should be deleted. By regularly reviewing and updating data retention policies, organizations can ensure that they are not holding onto data longer than necessary.
Anonymization and Pseudonymization are techniques that can help minimize the risk associated with data processing. Anonymization involves removing all personally identifiable information (PII) from data, making it impossible to link the data back to an individual. Pseudonymization replaces PII with pseudonyms, allowing data to be used for analysis without exposing the identities of individuals.
By adhering to data minimization principles, organizations can reduce the amount of data they need to protect, making it easier to manage and secure. This not only helps ensure compliance with data protection laws but also reduces the potential impact of data breaches.
V、DATA SUBJECT RIGHTS
Respecting and facilitating data subject rights is a fundamental aspect of legally harnessing data value. Data protection laws grant individuals certain rights regarding their personal data, and organizations must have processes in place to honor these rights.
Right to Access allows individuals to request access to their personal data and obtain information about how it is being processed. Organizations must provide this information in a clear and understandable format, typically within a specified timeframe.
Right to Rectification allows individuals to request corrections to their personal data if it is inaccurate or incomplete. Organizations must have processes in place to quickly and accurately update data upon request.
Right to Erasure, also known as the "right to be forgotten," allows individuals to request the deletion of their personal data under certain conditions. Organizations must evaluate these requests and delete data when appropriate, while also considering any legal obligations to retain data.
Right to Data Portability allows individuals to request a copy of their personal data in a commonly used and machine-readable format. This enables individuals to transfer their data to another organization if they choose.
Right to Object allows individuals to object to the processing of their personal data for certain purposes, such as direct marketing. Organizations must respect these objections and cease processing data for the specified purposes.
By respecting data subject rights, organizations can build trust with their customers, comply with legal requirements, and demonstrate their commitment to ethical data practices. This not only enhances the organization's reputation but also reduces the risk of legal disputes and penalties.
VI、DATA GOVERNANCE
Strong data governance practices are essential for legally harnessing data value. Data governance involves establishing policies, procedures, and standards for data management to ensure data quality, security, and compliance.
Data Stewardship involves assigning roles and responsibilities for data management. Data stewards are responsible for overseeing the quality and integrity of data, ensuring compliance with data protection laws, and implementing data governance policies.
Data Quality Management focuses on ensuring that data is accurate, complete, and reliable. This involves regular data audits, data cleansing processes, and validation procedures to identify and correct any issues with data quality.
Data Security Governance involves establishing policies and procedures to protect data from unauthorized access and breaches. This includes implementing security controls, conducting regular security assessments, and ensuring compliance with relevant security standards.
Compliance Monitoring is essential for ensuring that data management practices align with legal requirements. This involves regularly reviewing and updating policies, conducting compliance audits, and addressing any identified issues promptly.
By implementing strong data governance practices, organizations can ensure that their data is managed effectively and securely. This not only helps ensure compliance with data protection laws but also enhances the overall value and reliability of data.
VII、ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONS
Ethical considerations are crucial for legally harnessing data value. Organizations must consider the ethical implications of their data practices and ensure that they are acting in the best interests of data subjects.
Informed Consent is an ethical cornerstone of data collection and processing. Organizations must ensure that data subjects are fully informed about how their data will be used and have given their explicit consent. This involves clear and transparent communication, avoiding any deceptive or misleading practices.
Fairness and Non-Discrimination involve ensuring that data processing activities do not result in unfair or discriminatory outcomes. This includes avoiding biases in data collection and analysis, and ensuring that data-driven decisions are fair and equitable.
Accountability and Responsibility require organizations to take responsibility for their data practices and be accountable for any negative impacts. This involves establishing mechanisms for oversight and accountability, such as data ethics committees or independent audits.
Respect for Privacy is a fundamental ethical principle. Organizations must ensure that they respect individuals' privacy rights and take steps to protect their personal data from unauthorized access and misuse.
By prioritizing ethical considerations, organizations can build trust with their customers, enhance their reputation, and ensure that their data practices align with societal values and expectations.
VIII、DATA ANALYTICS AND INSIGHTS
Data analytics and insights are essential for deriving value from data while ensuring legal compliance. This involves using advanced analytical techniques to extract meaningful insights from data, while adhering to data protection laws and ethical principles.
Descriptive Analytics involves analyzing historical data to understand past trends and patterns. This can provide valuable insights into customer behavior, operational efficiency, and market trends. Organizations must ensure that descriptive analytics activities comply with data protection laws and respect data subject rights.
Predictive Analytics uses statistical models and machine learning algorithms to predict future outcomes based on historical data. This can help organizations make informed decisions and identify opportunities for growth. It is essential to ensure that predictive analytics models are free from biases and do not result in discriminatory outcomes.
Prescriptive Analytics goes a step further by recommending specific actions based on predictive insights. This can help organizations optimize their operations and improve decision-making. Organizations must ensure that prescriptive analytics activities are transparent and accountable, and that they respect data subject rights and ethical principles.
Data Visualization is a powerful tool for communicating insights from data. Effective data visualization can help stakeholders understand complex data and make informed decisions. Organizations must ensure that data visualizations are accurate, unbiased, and comply with data protection laws.
By leveraging data analytics and insights, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data while ensuring legal compliance and ethical integrity. This not only enhances business outcomes but also builds trust with customers and stakeholders.
IX、CROSS-BORDER DATA TRANSFERS
Cross-border data transfers involve the movement of data across national boundaries and are subject to specific legal and regulatory requirements. Organizations must ensure that cross-border data transfers comply with data protection laws and protect the privacy rights of data subjects.
Adequacy Decisions are issued by data protection authorities to determine whether a third country provides an adequate level of data protection. If a country has an adequacy decision, data can be transferred to that country without additional safeguards. Organizations must be aware of the adequacy status of countries to which they transfer data.
Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) are legal tools that provide safeguards for cross-border data transfers. SCCs are pre-approved by data protection authorities and must be included in contracts between data exporters and importers. Organizations must ensure that SCCs are properly implemented and adhered to.
Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs) are internal policies that allow multinational organizations to transfer data within their corporate group while ensuring compliance with data protection laws. BCRs must be approved by data protection authorities and provide comprehensive data protection safeguards.
Data Transfer Impact Assessments (DTIAs) involve evaluating the risks associated with cross-border data transfers and implementing appropriate safeguards. Organizations must conduct DTIAs to ensure that data transfers do not expose data subjects to undue risks.
By ensuring compliance with cross-border data transfer requirements, organizations can legally and securely transfer data across national boundaries. This not only helps protect data subjects' privacy rights but also facilitates international business operations.
X、DATA BREACH RESPONSE
A robust data breach response plan is essential for legally harnessing data value. Data breaches can have significant legal, financial, and reputational impacts, and organizations must be prepared to respond effectively.
Incident Response Planning involves establishing a comprehensive plan for responding to data breaches. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, establishing communication protocols, and outlining steps for containment, investigation, and remediation.
Data Breach Notification requirements vary by jurisdiction, but generally involve notifying affected individuals and data protection authorities within a specified timeframe. Organizations must be aware of the notification requirements in their respective jurisdictions and ensure timely and accurate reporting.
Root Cause Analysis involves investigating the cause of the data breach and identifying any vulnerabilities or weaknesses in security controls. This helps organizations understand how the breach occurred and implement measures to prevent future incidents.
Remediation and Recovery involve addressing the impact of the data breach and restoring normal operations. This may include repairing or replacing affected systems, enhancing security controls, and providing support to affected individuals.
Post-Incident Review is essential for learning from the data breach and improving future response efforts. This involves evaluating the effectiveness of the response plan, identifying any gaps or weaknesses, and implementing improvements.
By having a robust data breach response plan in place, organizations can minimize the impact of data breaches, comply with legal requirements, and demonstrate their commitment to data protection. This not only helps protect data subjects' privacy rights but also enhances the organization's resilience and reputation.
XI、CONCLUSION
Legally harnessing data value requires a comprehensive approach that involves compliance with data protection laws, transparency with data subjects, robust security measures, data minimization, respect for data subject rights, strong data governance, ethical considerations, data analytics and insights, cross-border data transfers, and a robust data breach response plan. By prioritizing these elements, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data while ensuring legal compliance and ethical integrity. This not only enhances business outcomes but also builds trust with customers and stakeholders, ultimately leading to long-term success.
相关问答FAQs:
如何合法挖掘数据价值?
在当今的数据驱动时代,数据已经成为一种重要的资产。合法挖掘数据价值不仅可以帮助企业提升竞争力,还能促进创新和决策的科学化。然而,如何在法律框架内有效地挖掘和利用数据呢?以下是一些常见的疑问与解答。
1. 数据挖掘的法律限制有哪些?
数据挖掘涉及多个法律领域,包括知识产权、隐私保护和消费者权益。为了合法挖掘数据,企业需要遵循相关法律法规,如通用数据保护条例(GDPR)或加州消费者隐私法案(CCPA)。这些法律规定了数据收集、存储和使用的具体要求,确保用户的个人信息不会被滥用。此外,企业在使用第三方数据时,应确保获得合法的授权和使用许可,以避免侵犯他人权利。
2. 如何确保数据挖掘过程的透明性和合规性?
确保数据挖掘过程的透明性和合规性至关重要。企业应采取多项措施,以建立信任并遵循法律要求。首先,清晰地向用户说明数据收集的目的和使用方式,确保用户在知情的情况下同意数据使用。其次,建立内部合规流程,定期审查数据使用情况,并评估合规性。此外,企业可以实施隐私保护技术,例如数据匿名化和加密,进一步降低数据泄露的风险。
3. 在合法挖掘数据价值时,如何平衡商业利益与用户隐私?
在数据挖掘过程中,企业需要在追求商业利益与保护用户隐私之间找到平衡。这一平衡可以通过多种方式实现。例如,企业可以采取负责任的数据使用政策,确保数据的使用仅限于提升用户体验和服务质量。同时,企业应积极倾听用户的反馈,了解他们对数据使用的期望和顾虑,及时调整数据策略。此外,建立明确的用户数据访问和删除权利,赋予用户对自己数据的控制权,也有助于增强用户的信任感,进而促进企业的可持续发展。
通过以上问题的解答,希望能够帮助企业更好地理解如何合法挖掘数据价值,建立健康的数据生态。
本文内容通过AI工具匹配关键字智能整合而成,仅供参考,帆软不对内容的真实、准确或完整作任何形式的承诺。具体产品功能请以帆软官方帮助文档为准,或联系您的对接销售进行咨询。如有其他问题,您可以通过联系blog@fanruan.com进行反馈,帆软收到您的反馈后将及时答复和处理。