A business intelligence engineer in 2025 transforms raw data into actionable insights that drive fast, informed decisions and foster a data-driven culture. Companies rely on these professionals to enable real-time analytics, automate data preparation, and simplify complex data architectures using advanced BI tools and cloud solutions. BI engineers help organizations respond swiftly to market trends, empower non-technical users through self-service BI, and align data strategies with business outcomes. With the adoption of BI-as-a-Service and the growing dominance of cloud BI, organizations gain flexible, secure, and scalable analytics. This role directly impacts operational efficiency, competitive advantage, and strategic growth.
Every demo in this article was designed using FineBI. Ready to unlock smarter insights? Click below to start your free FineBI trial and see what’s possible!
A business intelligence engineer in 2025 starts each day by reviewing the latest data flows and system dashboards. They check for any issues in data pipelines and ensure that all scheduled ETL procedures run smoothly overnight. Many large enterprises now use platform engineering to automate routine maintenance, so BI engineers spend less time on manual tasks and more time on analysis. They focus on aligning their work with key business metrics, not just department requests. This approach helps them deliver insights that matter most to the company’s goals.
BI engineers use advanced BI tools, such as FineBI and FineChatBI, to automate data preparation and reporting. They often collaborate with business users, helping them access self-service analytics and interpret results. AI and automation handle repetitive jobs, like data cleansing or basic reporting, freeing BI engineers to work on complex analysis and strategic projects. They also participate in regular meetings with stakeholders to understand new business needs and adjust analytics priorities.
Tip: BI engineers use natural language processing and AI-powered assistants to automate data queries, making it easier for everyone in the company to get answers quickly.
A typical day might include:
The bi engineer job description in 2025 covers a wide range of technical and analytical duties. These professionals design and manage ETL pipelines, ensuring that data moves smoothly from source systems into data warehouses. They build and maintain data warehouses and marts, making sure data is accurate, secure, and easy to access. Collaboration is key, as BI engineers work closely with analysts and developers to create data models that support efficient reporting and analysis.
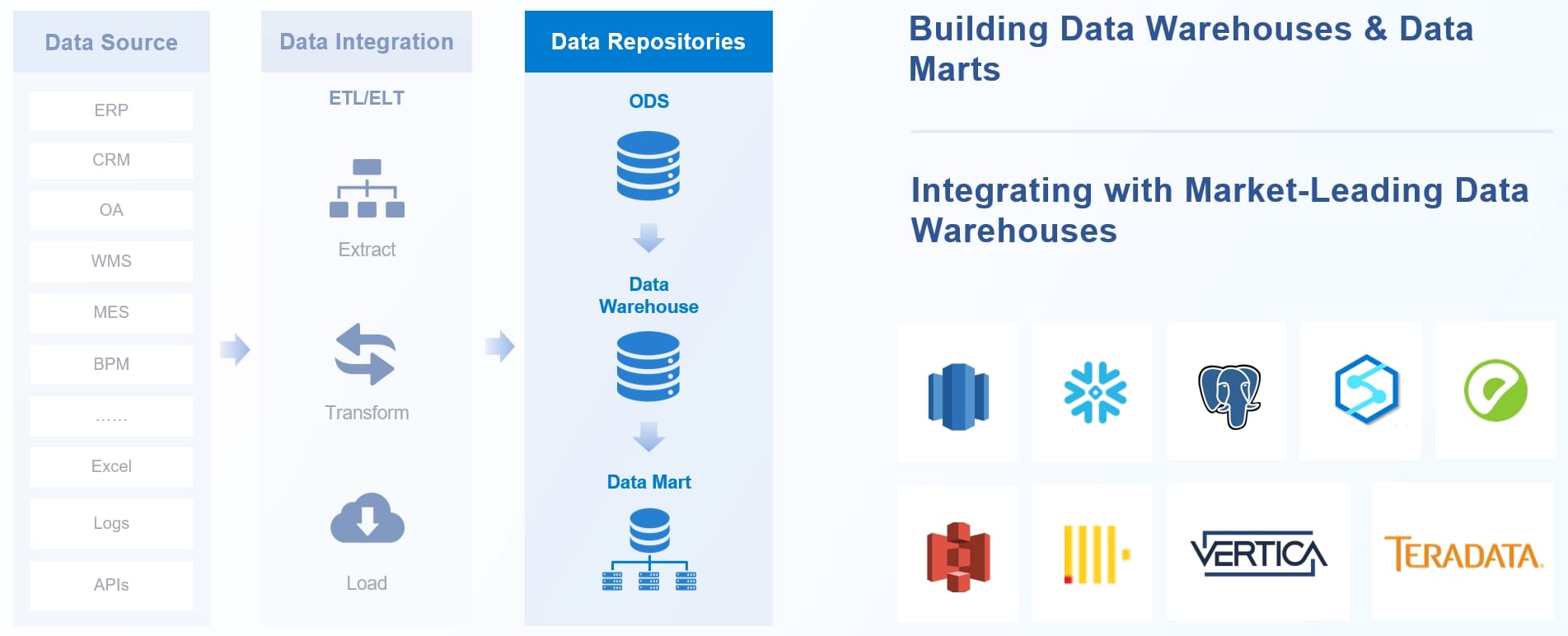
Their roles and responsibilities include:
BI engineers also play a vital role in integrating AI and automation into analytics workflows. While many routine data preparation tasks are automated, BI engineers validate data, interpret results, and guide business strategy. New specialized roles, such as "BI Engineer – AI Integration" and "Analytics Translator," have emerged, reflecting the growing need for both technical and business skills.
Different industries rely on BI engineers for unique tasks. For example, in marketing, they analyze campaign performance and customer segments. In sales, they track pipelines and forecast revenue. Retail and e-commerce companies depend on BI engineers for supply chain analysis and real-time inventory reporting. Finance teams use their expertise for risk management and fraud detection. The table below shows how responsibilities vary by industry:
| Industry | Key BI Engineer Responsibilities in 2025 |
|---|---|
| Marketing | Campaign analysis, customer segmentation, ROI dashboards. |
| Sales | Pipeline tracking, revenue forecasting, win/loss analysis. |
| Retail & E-commerce | Sales forecasting, supply chain analysis, CRM, procurement, inventory visibility. |
| Finance | Expense tracking, risk management, cash flow optimization, fraud detection. |
| Human Resources | Attrition trends, diversity hiring, engagement metrics. |
| Telecommunications | Network performance, customer retention, data leakage prevention. |
| Healthcare | Treatment plans, hospital operations, patient forecasting, drug development cycles. |
| Supply Chain & Logistics | Inventory planning, delivery route assessment, vendor reliability tracking. |
| Manufacturing | Maintenance planning, cost/resource tracking. |
Business intelligence engineers drive measurable business outcomes for organizations in 2025. They help companies move beyond simple activity tracking to measuring how data skills and analytics impact performance and profit. High-performing teams use BI platforms to link skill development and analytics projects directly to business results, such as increased revenue or reduced costs.
BI engineers align their projects with strategic priorities and key performance indicators. They work closely with stakeholders to ensure that analytics efforts support company goals. This ongoing engagement makes BI initiatives more relevant and impactful.
Modern BI engineers enable organizations to scale analytics through self-service tools, enterprise-grade support, and strong governance. By integrating AI-powered analytics, they help extract value from complex data, supporting faster and more informed decision-making. This leads to improved operational performance and a stronger competitive edge.
Organizations see real financial benefits from the work of BI engineers. For example:
Note: High-performing companies invest in cloud and AI, reflecting the essential role of BI engineers in digital transformation, growth, and cost efficiency.
Business intelligence engineers in 2025 need a broad set of technical skills to manage modern bi workflows. They use AI-enhanced tools to automate dashboard prototyping and validate model outputs. These professionals understand how to build and maintain data pipelines, using real-time analytics platforms such as Azure Stream Analytics and Kafka. They master low-code and no-code platforms, including FineBI, Power Apps, and Tableau Prep, which allow them to extend functionality with Python or JavaScript. Cloud-native data engineering is essential, so they work with data warehouses like Snowflake and BigQuery. They use infrastructure as code tools, such as Terraform, and orchestrate etl procedures with Apache Airflow. Data ethics and privacy remain important, so they embed privacy by design and audit for fairness. Business intelligence engineers also collaborate across business units to align bi strategies with company goals.
Tip: Mastering both traditional etl and AI-driven automation helps business intelligence engineers deliver faster, more reliable reporting and visualization.
Soft skills play a vital role in the success of a business intelligence engineer. Communication and storytelling help them explain complex bi insights to both technical and non-technical audiences. Collaboration and team leadership guide cross-functional teams and align bi initiatives with business goals. Strategic thinking and planning allow them to translate data into actionable strategies. Critical thinking and problem-solving support informed decision-making. Adaptability and change management help them navigate rapid changes in technology and the market. Emotional intelligence and interpersonal skills foster strong relationships and influence decisions. Creativity and innovation encourage new approaches to data challenges.
| Skill Category | Description of Use in Cross-Functional Teams |
|---|---|
| Collaboration | Work with data engineers, analysts, stakeholders, and users to ensure data accuracy, governance, and alignment with business needs. |
| Communication | Clearly convey information verbally and in writing; summarize discussions to avoid miscommunication; share ideas; keep supervisors and stakeholders informed. |
| Interpersonal Skills | Foster respectful, tactful, and diplomatic interactions; promote open and transparent communication across all levels. |
| Peer Relationships | Find common ground, solve problems cooperatively, gain trust, encourage collaboration, and represent interests fairly. |
| Customer Focus | Prioritize internal and external customers, build trust, solve problems promptly, adapt positively to changes, and incorporate feedback. |
Note: Business intelligence engineers often lead requirements gathering and develop training programs to empower business users.
Modern bi engineers rely on advanced tools to streamline data pipelines, reporting, and visualization. FineBI stands out as a self-service bi platform that enables users to connect, analyze, and share data across the organization. It supports real-time reporting, flexible etl, and robust data governance. FineChatBI adds conversational analytics, allowing users to interact with data using natural language. These tools reduce the need for coding and make bi accessible to everyone. FineDataLink helps integrate and transform data from multiple sources, supporting efficient etl procedures and building high-quality data layers for bi. Together, these solutions enable business intelligence engineers to deliver fast, accurate insights and support strategic decision-making.
Tip: Using FineBI and FineChatBI, business intelligence engineers can automate reporting and visualization, empower business users, and maintain strong data governance.
Business intelligence engineer and business intelligence analyst play distinct roles in a modern bi team. The engineer focuses on building and maintaining the technical foundation for bi. They design scalable data pipelines, optimize data models, and ensure data quality. The engineer works with tools like FineBI and FineDataLink to automate data integration and support real-time analytics. Their job includes managing data warehouses, setting up ETL workflows, and implementing security measures.
The business intelligence analyst interprets data and creates actionable insights. They develop dashboards and reports using bi platforms. The analyst works closely with stakeholders to understand business needs. They translate raw data into visualizations and recommendations that help leaders make decisions. The analyst uses bi tools to explore trends, measure performance, and identify opportunities.
The table below highlights the main differences:
| Role | Main Focus | Typical Tasks | Tools Used |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business Intelligence Engineer | Data infrastructure | Build pipelines, manage warehouses, automate ETL | FineBI, FineDataLink |
| Business Intelligence Analyst | Data analysis and reporting | Create dashboards, interpret data, advise teams | FineBI, FineChatBI |
Note: Both roles require strong bi skills, but the engineer emphasizes technical architecture while the analyst focuses on business insights.
Collaboration drives success in bi teams. Engineers and analysts work together to deliver reliable, insightful business intelligence. The engineer builds and maintains the data infrastructure. The analyst transforms raw data into dashboards and reports. They meet regularly to gather requirements and translate business needs into technical solutions.
Together, engineers and analysts combine technical and analytical skills. They enable organizations to make data-driven decisions using bi platforms like FineBI and FineChatBI. Their teamwork ensures that business intelligence supports growth and efficiency.

Business intelligence engineers see strong career growth in 2025. Most professionals start as BI analysts, focusing on data analysis and reporting. They move into BI engineer roles, where they build and maintain data pipelines and dashboards. The next step is BI developer, who creates front-end BI solutions and software. Senior professionals become BI architects, designing system roadmaps and translating business needs into technical plans. Leadership roles such as BI manager involve overseeing teams and managing department performance.
Industry trends drive demand for BI engineers. The rise of Generative BI and AI-powered data agents increases the need for experts who can implement and manage advanced BI systems. Companies invest more in AI and data, creating new opportunities for BI engineers in areas like HR, procurement, and supplier diversity.
Tip: BI engineers who learn AI integration and cloud platforms gain access to the fastest-growing roles in the field.
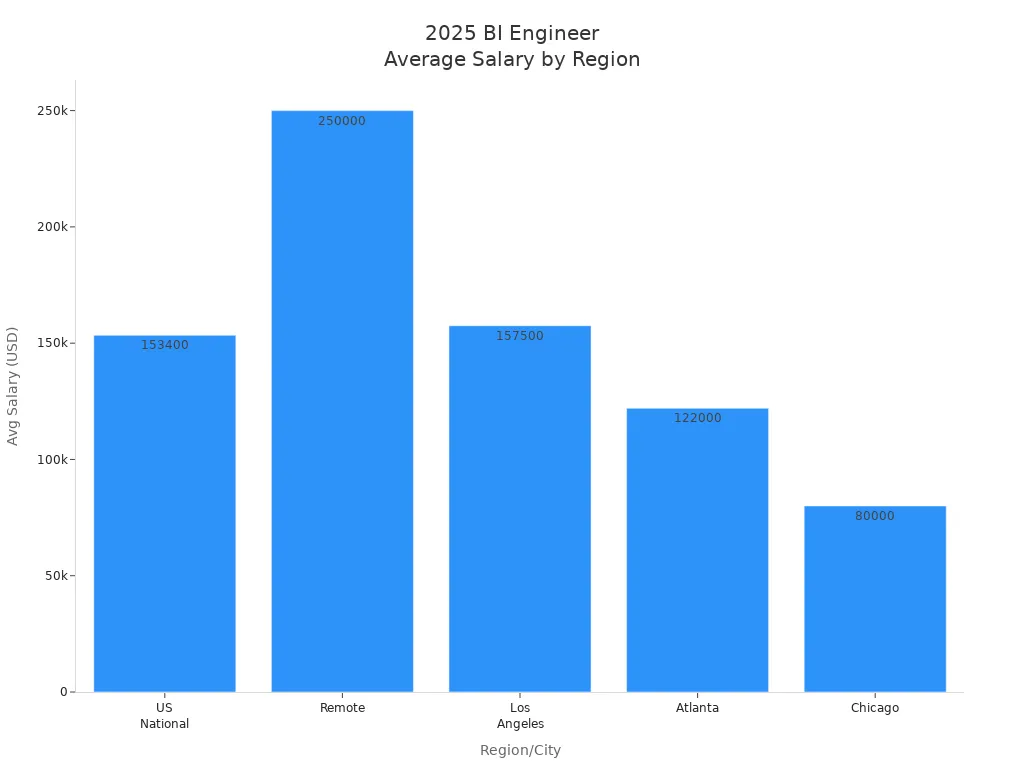
The average business intelligence engineer salary in the United States reaches $153,400 in 2025. Remote roles offer even higher pay, up to $250,000. Salaries vary by city, with Los Angeles at $157,500 and Atlanta at $122,000. Chicago reports lower averages at $80,000. BI developers earn between $60,000 and $187,000, with total compensation averaging $160,775.
| Region/City | Average Salary (2025) | Comparison to National Average |
|---|---|---|
| United States | $153,400 | N/A |
| Remote | $250,000 | +39% |
| Los Angeles, CA | $157,500 | +3% |
| Atlanta, GA | $122,000 | -25% |
| Chicago, IL | $80,000 | -90% |
BI engineers earn less than data engineers and data scientists, but more than data analysts. BI architects command higher salaries, reflecting their seniority.
| Role | Average Salary (2025, USD) |
|---|---|
| Business Intelligence Developer | $110,000 |
| Data Analyst | $95,000 |
| Data Engineer | $120,000 |
| Data Scientist | $125,000 |
| BI Architect | $130,000 |
Aspiring BI engineers need a bachelor's degree in fields such as Data Science, Computer Science, Business Administration, Mathematics, or Information Systems. Many professionals pursue certifications in BI tools like Tableau, Power BI, or SAP BusinessObjects. Practical skills in SQL, data modeling, and dashboard creation are essential. Some choose advanced degrees for specialized roles. Employers value a mix of technical expertise and business knowledge.
Recommended certifications include SAP Certified Application Associate, Tableau Business Intelligence Analyst Professional Certificate, and Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst Associate. Online programs from Coursera, TDWI, and Qlik offer flexible learning options. BI engineers who combine technical skills with business understanding stand out in the job market.
Note: The demand for BI engineers continues to grow as organizations expand their use of AI and data-driven decision-making.
Business intelligence engineers shape the future by turning data into real business value. They master AI-driven analytics, cloud platforms, and self-service tools to deliver fast, actionable insights. Key trends include natural language processing, no-code machine learning, and real-time analysis. To stay ahead, aspiring engineers should:
Staying curious and adaptable ensures long-term success in this dynamic field.
What Does a Business Intelligence Developer Do in 2025
10 Business Intelligence Jobs Hiring Now That You Should Know
A business intelligence engineer reviews data pipelines, builds dashboards, and meets with teams. They solve data problems and help others use BI tools. They focus on making data easy to understand.
Business intelligence engineers use FineBI for self-service analytics and FineChatBI for conversational data queries. They also use SQL, Python, and cloud platforms like Snowflake or BigQuery.
FineBI lets users create dashboards without coding. It connects to many data sources and supports real-time analysis. Business users can explore data, find trends, and share insights quickly.
A future BI engineer needs skills in data modeling, SQL, and dashboard design. They should learn cloud platforms and AI tools. Strong communication and teamwork help them succeed.
Business intelligence engineering offers strong job growth and high salaries. Companies need experts who turn data into business value. The role supports digital transformation and helps organizations make better decisions.

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles
What is a Business Intelligence System and How Does It Work
A business intelligence system collects, analyzes, and visualizes data, turning raw information into actionable insights for smarter business decisions.
Lewis
Jan 04, 2026

Top 3 Retail Management Software Picks
Compare the top 3 retail management software. See features, pricing, and which solution fits your business needs for inventory and sales.
Lewis
Dec 30, 2025

What Are Enterprise BI Solutions and How Do They Work
Enterprise BI solutions unify business data, enabling real-time analytics, secure collaboration, and smarter decision-making across your organization.
Lewis
Dec 22, 2025