Data redundancy refers to the unnecessary duplication of data within a storage system. You might think of it as a sneaky foe that can complicate data management. While it can enhance system performance by enabling faster data access, excessive redundancy often leads to inefficiencies. It increases storage costs and can cause data inconsistencies. Understanding data redundancy is crucial for effective data management. Tools like FineDataLink and FineBI help manage and analyze data efficiently, ensuring you maintain data integrity and continuity.
What is Data Redundancy?
Definition of Data Redundancy
Data redundancy occurs when you store the same piece of data in multiple locations within a database or storage system. This practice ensures that you have backup copies of your data, which can be crucial in case of data corruption or loss. By maintaining redundant data, you can continue operations smoothly even when unexpected issues arise. This approach is particularly beneficial for disaster recovery and high availability systems, where uninterrupted access to data is essential.
Importance of Understanding Data Redundancy
Understanding data redundancy is vital for several reasons. First, it plays a critical role in maintaining data integrity and continuity. By having duplicate copies of data, you can ensure system reliability and fault tolerance. This means that even if one data source fails, you can still access the information from another location. Additionally, data redundancy enhances system performance by enabling faster data access and improving data availability.
Moreover, data redundancy is a key component of effective backup strategies. It allows for quick data recovery after catastrophic events, minimizing downtime and ensuring that you can access your data when needed. However, it's important to note that while data redundancy offers numerous benefits, it can also lead to increased storage costs. Storing multiple copies of the same data consumes more space than necessary, which can be costly for organizations.
How Does Data Redundancy Occur?
Data redundancy can manifest in various ways, particularly within database and file-based systems. Understanding these occurrences helps you manage data more effectively and avoid potential pitfalls.
Occurrence in Database Systems
In database systems, data redundancy often arises from poor design or lack of normalization. When you store the same data in multiple tables, it can lead to inconsistencies and errors. For instance, if you update a customer's address in one table but forget to do so in another, you end up with conflicting information. This inconsistency can undermine data integrity and lead to flawed conclusions.
Examples of Redundancy in Databases
- Customer Information Duplication: Imagine a scenario where customer details are stored in both the orders and customer tables. If a customer's contact information changes, you must update it in both places. Failing to do so results in discrepancies.
- Product Details Repetition: In some databases, product details might be stored in multiple tables for ease of access. However, this practice can lead to outdated or incorrect data if not managed properly.
- Employee Records: Storing employee records in different departments' databases can cause redundancy. Each department might have its own version of an employee's data, leading to inconsistencies.
Occurrence in File-Based Systems
File-based systems also experience data redundancy, often due to manual processes or lack of centralized control. When you save the same file in different folders or drives, it consumes unnecessary storage space and complicates data management.
Examples of Redundancy in File Systems
- Document Copies: You might save multiple copies of the same document across different folders for easy access. While convenient, this practice can lead to confusion about which version is the most current.
- Media Files: Storing the same images or videos in various locations on your computer or network can quickly eat up storage space. It also makes it challenging to manage and organize your media library.
- Backup Files: Creating multiple backups of the same files without a clear strategy can result in redundant data. While backups are essential for data recovery, excessive redundancy increases storage costs and management complexity.
Managing data redundancy effectively is crucial for maintaining data integrity and accuracy. By understanding how redundancy occurs, you can implement strategies to minimize its impact, ensuring your data remains reliable and consistent.
Advantages of Data Redundancy
Data redundancy offers several benefits that enhance your data management practices. By understanding these advantages, you can make informed decisions about how to implement redundancy in your systems.
Data Backup and Recovery
- Ensures Data Security: Data redundancy acts as a safety net for your information. When you store multiple copies of data, you protect against data loss due to hardware failures, accidental deletions, or cyber-attacks. This redundancy ensures that you can recover your data quickly and efficiently.
- Facilitates Quick Recovery: In the event of data corruption or loss, redundant data allows you to restore operations with minimal downtime. You can access backup copies swiftly, ensuring business continuity and reducing the impact of data-related disruptions.
- Supports Archiving Strategies: Redundant data plays a crucial role in archiving strategies. By maintaining multiple versions of data, you can track changes over time and retrieve historical data when needed. This capability proves invaluable for audits, compliance, and long-term data retention.
Improved Data Availability
- Enhances System Performance: Redundant data improves system performance by enabling faster data retrieval. When you have multiple copies of data, you can distribute the load across different storage locations, reducing access times and improving user experience.
- Increases Data Reliability: By having duplicate data, you ensure that your systems remain reliable and fault-tolerant. If one data source becomes unavailable, you can seamlessly switch to another, maintaining uninterrupted access to critical information.
- Boosts Data Accessibility: Data redundancy enhances accessibility by providing multiple pathways to the same information. This setup ensures that users can access data from various locations, improving collaboration and decision-making across your organization.
Data redundancy, when managed effectively, offers significant advantages in terms of backup, recovery, and availability. By leveraging these benefits, you can enhance your data management strategies, ensuring that your systems remain robust and resilient.
Disadvantages of Data Redundancy
Increased Storage Costs
Data redundancy significantly impacts your storage expenses. When you store multiple copies of the same data, you require additional storage resources. This need for extra space leads to escalating costs. As your organization accumulates more data, the expenses associated with acquiring, maintaining, and expanding storage infrastructure can strain your budget.
Consider the following points:
- Escalating Costs: More data means more storage, which translates to higher costs. This can be a serious issue if you're trying to keep expenses low to increase profits.
- Cloud Storage: If you rely on cloud services, remember that they don't come cheap. The more redundant data you store, the more you'll spend on these services.
- Infrastructure Maintenance: Maintaining and updating redundant data requires additional overhead and resources, further increasing costs.
By understanding these cost implications, you can make informed decisions about managing data redundancy effectively.
Data Inconsistency Issues
Data redundancy can lead to data inconsistencies if not properly managed. When you have multiple copies of data, updating all instances simultaneously becomes challenging. This can result in discrepancies and errors, undermining data integrity.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Unintentional Duplicity: Sometimes, data gets duplicated unintentionally. This can cause problems for your database, making it harder for users to access accurate information.
- Data Integrity: Ensuring data consistency across all copies is crucial. Failing to update data in all locations can lead to conflicting information, which can affect decision-making.
- Complex Data Management: Managing redundant data complicates data processing and retrieval. It requires more effort to ensure that all copies remain consistent and up-to-date.
Understanding these issues helps you recognize the importance of managing data redundancy carefully. By addressing these challenges, you can maintain data accuracy and reliability in your systems.
Strategies to Manage Data Redundancy
Effectively managing data redundancy is crucial for maintaining data integrity and optimizing storage. You can employ several strategies to address redundancy issues and ensure efficient data management.
Data Normalization
Data normalization is a powerful technique that helps you organize your data efficiently. By structuring your data into smaller, related tables, normalization reduces duplication and enhances data consistency. This process involves breaking down larger tables into smaller ones and establishing relationships between them using foreign keys. As a result, each piece of data gets stored only once, minimizing redundancy.
Benefits of Data Normalization:
- Reduces Storage Costs: By eliminating unnecessary duplication, you save on storage space, which translates to cost savings.
- Enhances Data Integrity: With normalized data, you can update and manage information more easily, reducing the risk of inconsistencies.
- Optimizes Data Management: Normalization streamlines your database, making it more efficient and reliable.
Implementing data normalization ensures that your data remains structured and organized, allowing for easier updates and management without risking data integrity.
Deduplication Technologies
Deduplication technologies offer another effective strategy for managing data redundancy. These technologies identify and eliminate duplicate copies of data, significantly reducing storage space and costs. Deduplication is particularly beneficial in backup and recovery scenarios, where redundant data can quickly accumulate.
Advantages of Deduplication Technologies:
- Efficient Storage Utilization: By removing duplicate data, you optimize your storage resources, ensuring proper utilization.
- Cost Savings: Reducing the amount of stored data lowers storage expenses, making deduplication a cost-effective solution.
- Improved Data Protection: Deduplication enhances data protection by ensuring that only unique data gets stored, reducing the risk of data loss.
By incorporating deduplication technologies into your data management strategy, you can maintain data integrity while optimizing storage and reducing costs.
Role of FanRuan in Managing Data Redundancy
FanRuan plays a pivotal role in managing data redundancy, ensuring that your data remains consistent and reliable. By leveraging advanced technologies, FanRuan provides solutions that help you maintain data integrity and optimize storage efficiency.
FineDataLink's Real-Time Data Synchronization
FineDataLink offers a robust platform for real-time data synchronization. This feature ensures that your data remains up-to-date across multiple systems. By synchronizing data in real time, you can reduce the chances of redundant data entries. This approach not only minimizes storage costs but also enhances data accuracy.
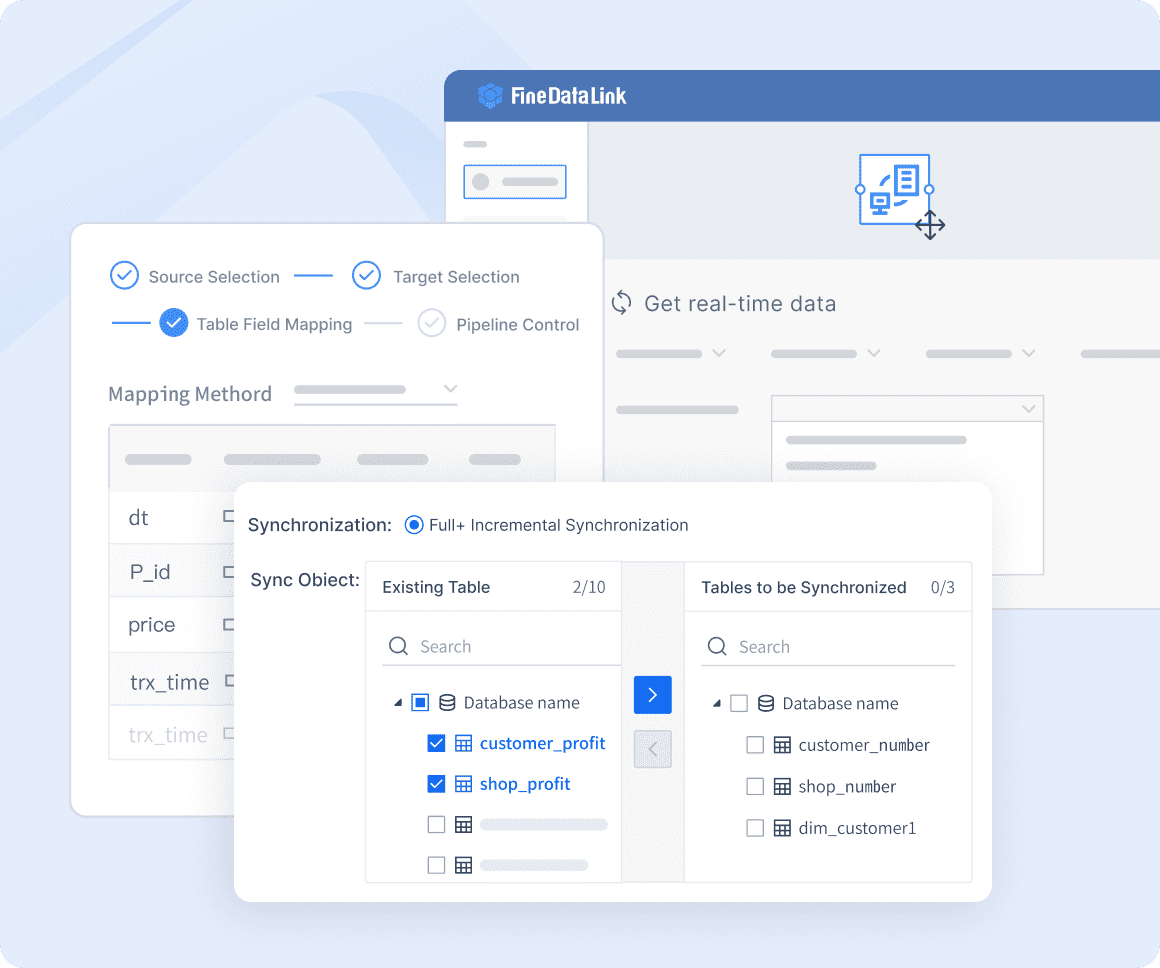
- Real-Time Updates: FineDataLink allows you to synchronize data instantly, ensuring that all systems reflect the most current information. This capability is crucial for maintaining data consistency and avoiding discrepancies.
- Efficient Data Management: With FineDataLink, you can streamline your data management processes. The platform's low-code approach simplifies complex tasks, making it easier for you to manage data across various sources.
- Enhanced Data Connectivity: FineDataLink supports integration with diverse data sources, enabling seamless data flow. This connectivity ensures that you can access and manage data efficiently, reducing the risk of redundancy.
FineBI's Data Analysis and Visualization
FineBI empowers you to analyze and visualize data effectively. By transforming raw data into actionable insights, FineBI helps you make informed decisions. This capability is essential for identifying and addressing data redundancy issues.
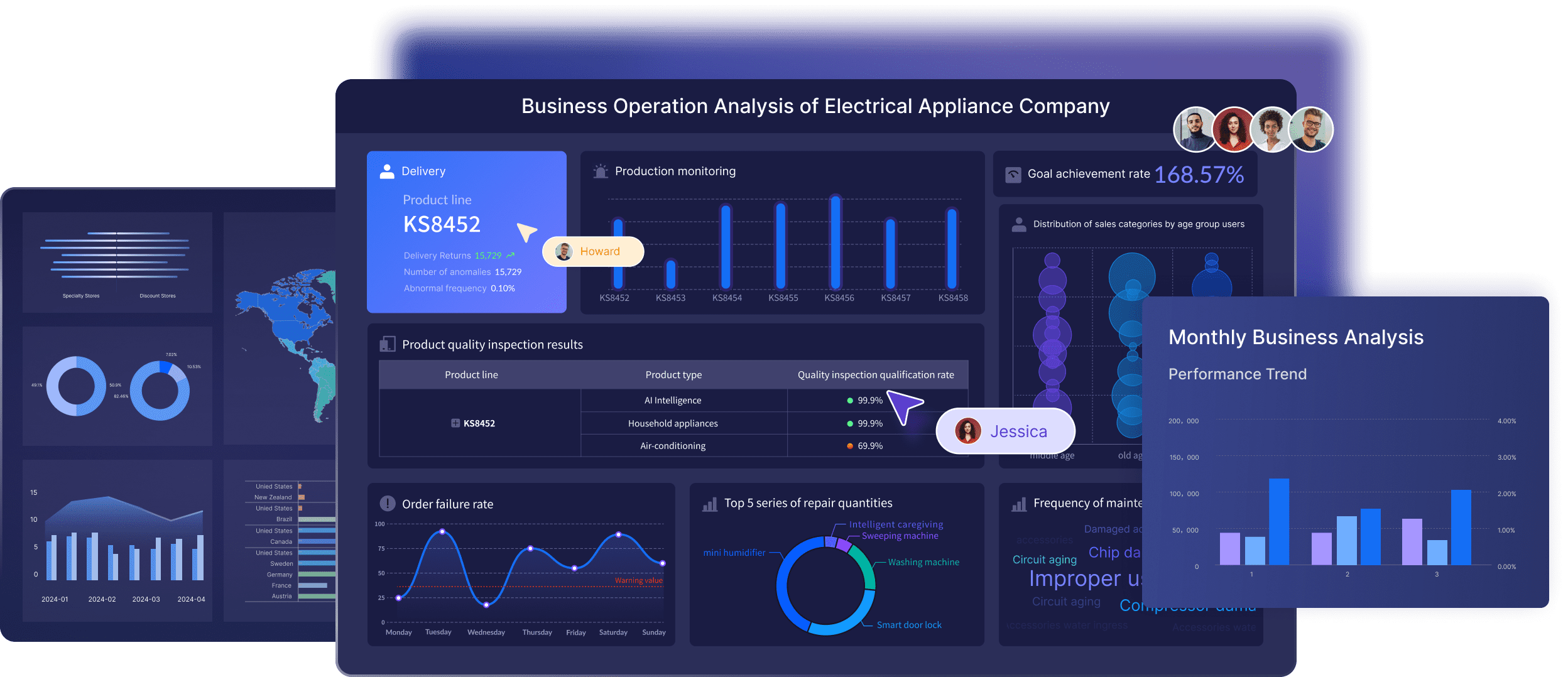
- Comprehensive Data Analysis: FineBI provides tools for in-depth data analysis. You can explore data trends and patterns, helping you identify areas where redundancy may occur.
- Interactive Visualizations: With FineBI, you can create interactive visualizations that make data interpretation easier. These visualizations allow you to spot anomalies and redundancies quickly, facilitating proactive data management.
- User-Friendly Interface: FineBI's intuitive interface makes it accessible to users with varying levels of expertise. You can easily navigate the platform, ensuring that you can manage and analyze data without difficulty.
By utilizing FineDataLink and FineBI, you can effectively manage data redundancy. These tools provide you with the capabilities needed to maintain data integrity, optimize storage, and enhance overall data management practices.
Practical Use Cases of Data Redundancy
Data redundancy plays a crucial role in various sectors, ensuring data availability and reliability. By understanding its practical applications, you can leverage redundancy to enhance your data management strategies.
Use in Cloud Storage Solutions
Cloud storage solutions often rely on data redundancy to ensure data availability and integrity. When you store data in the cloud, providers typically create multiple copies across different locations. This practice safeguards your data against potential loss due to hardware failures or natural disasters.
- Enhanced Data Security: Cloud providers use redundancy to protect your data. By storing multiple copies, they ensure that even if one server fails, your data remains accessible.
- Improved Disaster Recovery: Redundant data storage in the cloud facilitates quick recovery during disasters. You can restore your data swiftly, minimizing downtime and maintaining business continuity.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud storage solutions offer scalable redundancy options. You can adjust the level of redundancy based on your needs, ensuring optimal storage utilization and cost-effectiveness.
"Data redundancy in cloud storage ensures that your information is always available, even in the face of unexpected challenges."
Use in Enterprise Data Management
In enterprise environments, data redundancy supports robust data management practices. By maintaining duplicate data, organizations can enhance system performance and reliability.
- System Performance Optimization: Redundant data allows you to distribute workloads across multiple systems. This setup reduces access times and improves overall system performance.
- Data Integrity and Consistency: Enterprises use redundancy to maintain data integrity. By synchronizing data across systems, you ensure that all copies remain consistent and up-to-date.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Many industries require data redundancy to meet compliance standards. By storing multiple copies, you can ensure that your organization adheres to legal and regulatory mandates.
Tools like FineDataLink and FineBI play a pivotal role in managing data redundancy within enterprises. FineDataLink offers real-time data synchronization, ensuring that your data remains consistent across systems. FineBI provides comprehensive data analysis and visualization capabilities, helping you identify and address redundancy issues effectively.
By understanding these practical use cases, you can implement data redundancy strategies that enhance your data management practices, ensuring reliability and efficiency across your organization.
Summary of Key Points in Data Redundancy
Recap of Data Redundancy Definition
Data redundancy involves storing the same piece of data in multiple locations within a storage system. This practice ensures data availability and reliability, especially during unexpected events like data corruption or loss. While redundancy can enhance system performance by providing faster data access, it also poses challenges. Excessive redundancy can lead to inefficiencies, increased storage costs, and potential data inconsistencies. You must understand these aspects to manage your data effectively.
Recap of Management Strategies
Managing data redundancy requires strategic approaches to maintain data integrity and optimize storage. Here are some key strategies:
- Data Normalization: This technique involves organizing data into smaller, related tables to reduce duplication. By doing so, you enhance data consistency and save on storage costs.
- Deduplication Technologies: These tools identify and eliminate duplicate data copies, optimizing storage utilization and reducing costs. Deduplication is particularly useful in backup scenarios where redundant data can accumulate quickly.
- Real-Time Data Synchronization: Platforms like FineDataLink offer real-time data synchronization, ensuring that your data remains consistent across multiple systems. This approach minimizes the risk of redundant data entries and enhances data accuracy.
- Data Analysis and Visualization: Tools like FineBI empower you to analyze and visualize data effectively. By transforming raw data into actionable insights, you can identify and address redundancy issues proactively.
"Complexity in redundancy management can consume valuable IT resources and personnel time. It may also increase the risk of synchronization failures, compromising data integrity."
By implementing these strategies, you can manage data redundancy effectively, ensuring that your systems remain robust and resilient. Understanding these management techniques allows you to optimize your data management practices, maintaining data integrity and continuity.
Understanding and managing data redundancy is crucial for maintaining data integrity and optimizing storage. You should apply effective strategies to enhance your data management practices. Consider using data normalization and deduplication technologies to reduce redundancy. FanRuan's products, FineDataLink and FineBI, offer valuable tools for efficient data management. FineDataLink provides real-time data synchronization, while FineBI empowers you with comprehensive data analysis and visualization capabilities. By leveraging these solutions, you can ensure robust and resilient data systems, ultimately improving your organization's data management efficiency.
FAQ
Data redundancy occurs when you store the same piece of data in multiple locations within a database or storage system. This practice can ensure data availability and reliability, especially during unexpected events like data corruption or loss. However, excessive redundancy may lead to inefficiencies and increased storage costs.
Several factors contribute to data redundancy. Poor database design often results in unnecessary duplication. Lack of data governance and improper backup practices also play a role. User behavior, such as saving multiple copies of files, can further exacerbate redundancy issues. Additionally, legal requirements and system migrations might necessitate data replication.
Data redundancy offers several benefits. It enhances data availability and reliability by providing backup copies. This redundancy ensures quick recovery during data loss events. It also supports high availability systems and load balancing, improving overall system performance. Moreover, redundancy can help meet regulatory compliance and fault tolerance requirements.
While redundancy strengthens data protection, it can lead to inefficiencies. Storing multiple copies increases storage costs and complicates data management. Duplicate entries slow down query processing and require consistent updates, which can lead to errors if not managed correctly. Redundancy can also decrease performance and increase security risks.
You can employ several strategies to manage data redundancy. Data normalization helps organize data efficiently, reducing duplication. Establishing a single source of truth and implementing data governance policies further minimize redundancy. Utilizing data deduplication tools and conducting regular audits ensure data integrity. Leveraging cloud data management services offers scalable redundancy options.
FineDataLink provides real-time data synchronization, ensuring that your data remains consistent across multiple systems. This minimizes redundant data entries and enhances data accuracy. FineBI empowers you to analyze and visualize data effectively, helping you identify and address redundancy issues proactively. These tools optimize data management practices, maintaining data integrity and continuity.
Continue Reading About Data Redundancy
10 Game-Changing Project Management Reporting Types!
Unlock project success with 10 must-know reporting types! Track progress, manage risks, and stay on budget like a pro.
Lewis
Mar 03, 2025
10 Must-Have Marketing Agency Reporting Tools for Your Success
Optimize your agency's performance with top reporting tools. Explore analytics, social media, SEO, and more for data-driven decisions and efficiency.
Lewis
Oct 09, 2024
15 Best Software Reporting Tools for 2025
Explore the top 15 software reporting tools for 2025. Compare features, pricing, and usability to find the best fit for your business needs.
Lewis
Oct 08, 2024
2025 Best Data Integration Solutions and Selection Guide
Explore top data integration solutions for 2025, enhancing data management and operational efficiency with leading platforms like Fivetran and Talend.
Howard
Dec 19, 2024
2025 Data Pipeline Examples: Learn & Master with Ease!
Unlock 2025’s Data Pipeline Examples! Discover how they automate data flow, boost quality, and deliver real-time insights for smarter business decisions.
Howard
Feb 24, 2025
Augmented Analytics: Unlock the Core Concepts & Benefits!
Discover augmented analytics—where AI and ML automate data prep and insights, revolutionizing decision-making for smarter, faster business strategies!
Lewis
Mar 04, 2025