The manufacturing in Malay sector plays a crucial role in driving Malaysia’s economic growth and influencing global trade. The nation transitioned from an agriculture-based economy to a thriving industrial hub, fueled by robust government support. Today, high-value manufacturing enhances product quality and boosts competitiveness. The sector’s significance is evident in these key statistics:
| Aspect | Fact |
|---|---|
| E&E output share | 34.4% of total manufacturing output |
| Export share | 34.4% of total exports (E&E); 10% (chemicals) |
| Industrial parks | Over 500 parks, 140,000 km of roads, 60+ airports, and 7 major seaports |
| Workforce | Skilled, business-friendly, and a global hub |
You can see the importance of manufacturing in Malaysia’s economy through its strong contribution to the country’s GDP. In 2023, the sector made up 23.02% of Malaysia’s GDP. The GDP from manufacturing reached 95,676 MYR Million in Q1 2025. Analysts expect this number to rise to 97,309 MYR Million by the end of Q2 2025 and continue growing in the coming years. This steady performance shows how manufacturing in malay supports national growth.
The sector also plays a key role in employment and exports. Here is a snapshot of recent trends:
| Month | Manufacturing PMI | Employment Trend | Export Orders Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| March 2025 | 48.8 | Employment fell | New export orders declined sharply |
| April 2025 | 48.6 | Slight drop in employment | New export orders declined (6th month) |
| May 2025 | 48.8 | Employment unchanged | New export orders declined (softest rate) |
PMI values below 50 show contraction, but employment stabilized in May 2025 after several months of decline. Export orders have dropped for six months, but the rate of decline is slowing. This data highlights the sector’s resilience and ability to adapt.
You will notice positive growth trends in Malaysia’s manufacturing industry. Job advertisements in this sector increased by 12.6%, making it the top industry for job ads for two years in a row. The Malaysian central bank forecasts GDP growth between 4.0% and 5.0% for 2024. The Asian Development Bank projects a similar rate at 4.6%. These numbers reflect strong domestic demand and stable employment.
Government initiatives, such as the New Industrial Master Plan 2030, focus on economic integration, digitalization, and green growth. These policies attract both foreign and domestic investment, especially in high-value-added manufacturing. The sector leads the country’s Industrial Production Index, supported by new industrial parks and infrastructure. You will find a diverse range of industries here, including electronics, rubber, palm oil, chemicals, and more. This diversity helps Malaysia remain competitive and resilient in the global market.
Malaysia’s manufacturing in malay sector stands out for its diversity and global reach. You will find a wide range of industries, from high-tech electronics to traditional food processing. This diversity helps the country stay resilient and competitive.
You will notice that electronics and semiconductors form the backbone of Malaysia’s manufacturing exports. The country supplies about 40% of its total exports from this sector. Malaysia ranks first in Southeast Asia for STEM education, which means you have access to a skilled workforce. Major companies like Renesas Semiconductor, Micron, and ON Semiconductor operate here, producing microcontrollers, memory chips, and power management devices. The semiconductor market is expected to reach over US$18 billion by 2025, with strong growth ahead. Malaysia’s strategic location and world-class infrastructure, such as ports and highways, make it a global hub for electronics manufacturing.
You will see a robust automotive and machinery sector in Malaysia. The industry covers everything from passenger cars and electric vehicles to advanced machinery and robotics. Over 3,000 enterprises employ more than 200,000 people. The sector produces engines, chassis, electronics, and safety systems. Companies use AI and robotics to improve efficiency and product quality. Malaysia’s competitive labor costs and government incentives attract global players and support local innovation.
Tip: The automotive sector is moving toward Industry 4.0, using smart technologies for better production and sustainability.
Food and agribusiness play a vital role in Malaysia’s manufacturing landscape. You will find companies processing palm oil, rubber, cocoa, and seafood. This sector supports both local consumption and exports. Many small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) operate here, adding to the sector’s diversity. The industry also faces challenges such as environmental sustainability and the need for green practices.
Chemicals and pharmaceuticals contribute about 6% to Malaysia’s GDP. The country ranks as the fourth-largest methanol producer in the world and second in Southeast Asia for ammonia and urea. Annual output grows by around 4.5%. The government offers tax incentives to attract investment, making Malaysia a top destination for chemical manufacturing. The pharmaceutical market is also expanding, driven by health awareness and an aging population. By 2025, the sector is expected to reach US$1.74 billion in revenue.
You will see that Malaysia’s manufacturing in malay sector relies on a multicultural workforce, with employees from Bangladesh, Nepal, and India. Training in cultural intelligence helps teams work better together. The government supports the sector with tax breaks, investment allowances, and a focus on high-value jobs. This approach ensures Malaysia remains a leader in manufacturing across Southeast Asia.
You can see a major shift happening in Malaysia’s manufacturing sector. Factories now use more digital tools and smart technologies. This change is called digital transformation. It helps companies work faster, make better products, and stay competitive.
Malaysia’s government supports this shift. Programs like MyDigital and the National Policy on Industry 4.0 (Industry4WRD) encourage factories to adopt new technologies. The digital transformation market in Malaysia is growing quickly, with an expected annual growth rate of almost 19% from 2025 to 2033. Big tech companies such as IBM, Microsoft, and Google work with local firms to build a strong digital ecosystem.
Note: Some factories face challenges like cybersecurity risks, a shortage of skilled workers, and old equipment that does not work well with new systems. Urban areas like Kuala Lumpur and Selangor lead in digital adoption because they have better infrastructure.
A recent study in Malaysian factories showed that digital transformation brings many benefits. Managers reported better supply chain management, higher efficiency, and more chances for innovation. However, they also pointed out barriers such as lack of skills, limited funding, and not enough support for employees to learn new tools.
You will notice that smart factories are becoming more common in Malaysia. These factories use advanced technology to connect machines, people, and systems. This approach is part of Industry 4.0, which focuses on automation, data exchange, and real-time monitoring.
Key technologies in smart factories include:
Malaysia’s National Policy on Industry 4.0 highlights important success metrics for smart factories:
You can see the benefits of smart factories in daily operations. Automation and optimization increase efficiency. Real-time monitoring improves product quality. Companies save money by reducing waste and energy use. Smart factories also adapt quickly to market changes and new product demands.
The manufacturing sector contributed over 23% to Malaysia’s GDP in 2021. Experts expect this number to rise above 50% by 2025 as more companies adopt Industry 4.0 technologies. Large companies lead the way, but small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are starting to follow. Adoption rates for Industry 4.0 tools range from 15% to 20% among top firms, while less than 21% of SMEs have started using these technologies.
You can unlock even more value from manufacturing in malay by using advanced data analytics. FanRuan and its FineBI platform help you collect, integrate, and analyze data from many sources. These tools support both business operations and manufacturing control.
FineBI lets you connect to over 60 types of data sources, including databases, cloud platforms, and APIs. You can bring together sales, inventory, and supply chain data into one dashboard. This helps you:
FineBI’s self-service features mean you do not need to be a data expert. You can drag and drop charts, filter data, and create reports without writing code. The platform supports role-based access, so you control who sees sensitive information.
Tip: FineBI’s AI-powered module, FineChatBI, lets you ask questions in plain language and get instant answers. This makes data analysis easy for everyone in your company.
You can use FanRuan’s FineDataLink to integrate data from machines, sensors, and business systems. This creates a real-time view of your factory floor. With FineBI, you can:
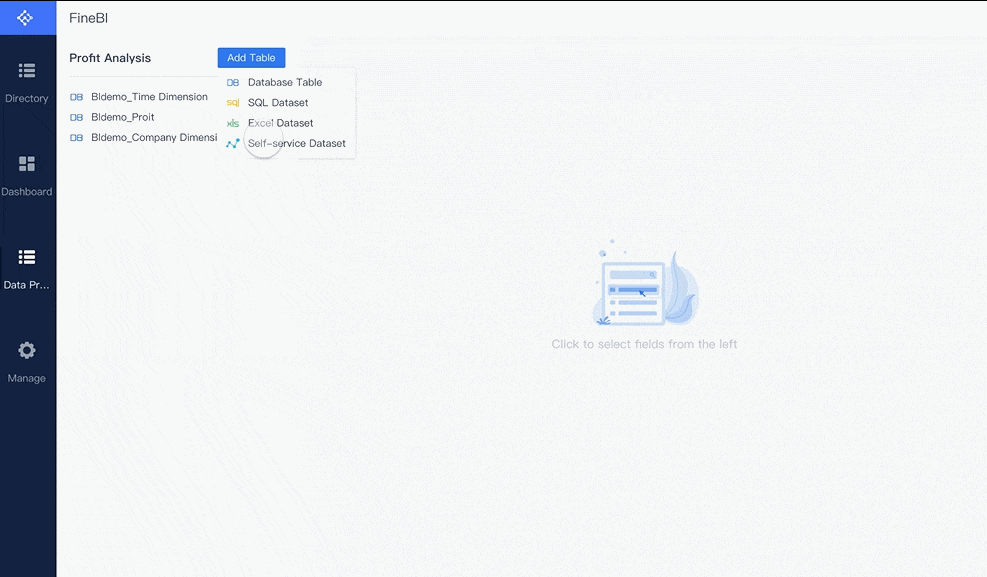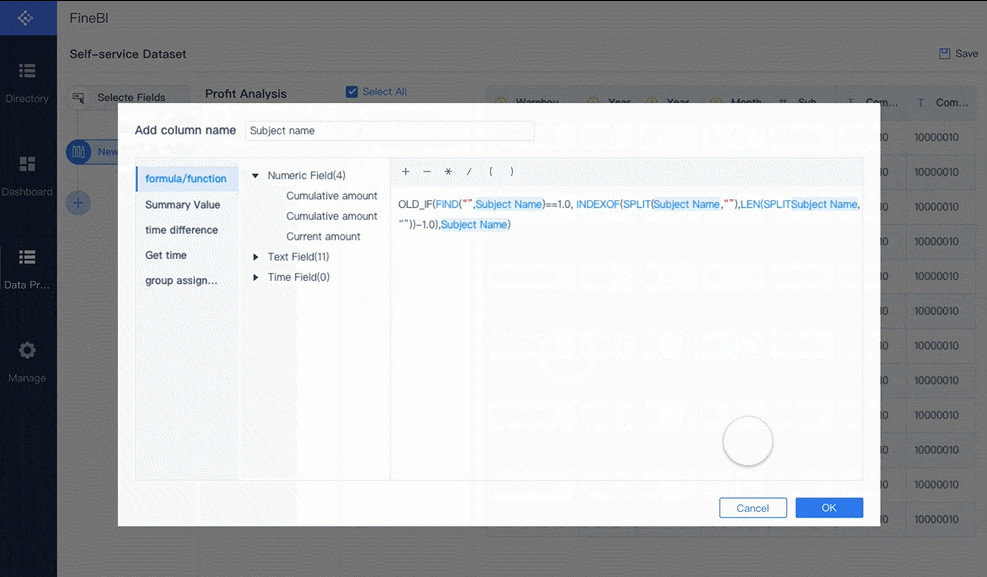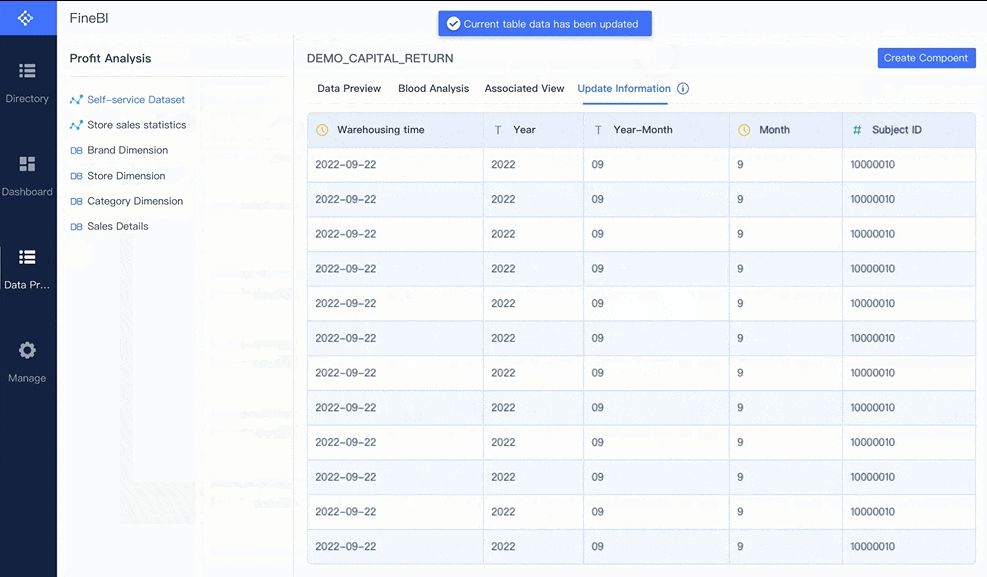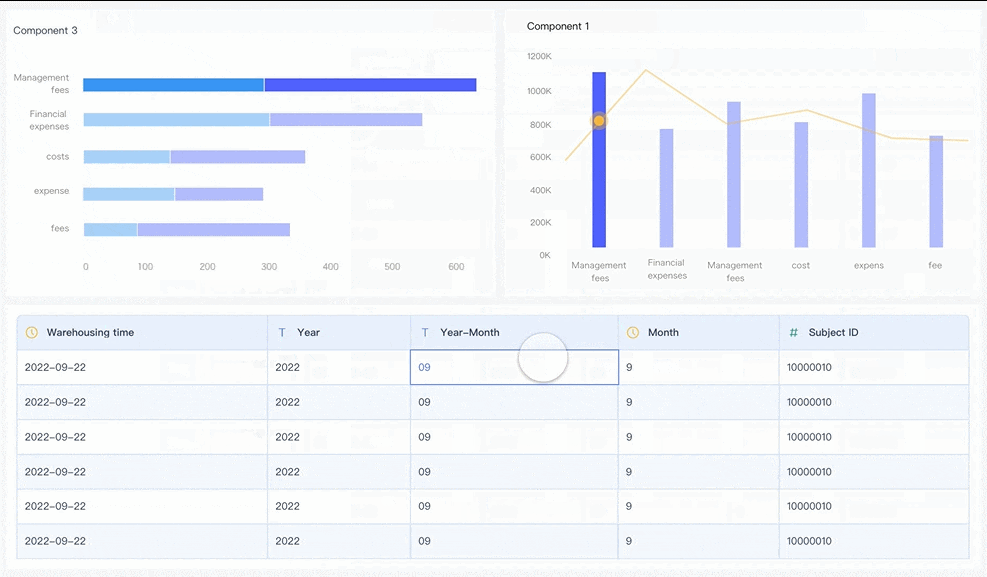
FineBI supports real-time alerts and automated reporting. You get notified when something goes wrong, so you can act fast. The platform’s visual dashboards help you see patterns and make better decisions.
Malaysia’s government encourages companies to use data analytics and smart manufacturing tools. Incentives and training programs help businesses modernize and stay competitive. By adopting solutions like FanRuan and FineBI, you can lead the way in digital transformation and smart manufacturing in malay.
Malaysia offers you many opportunities if you want to invest in manufacturing in malay. The country’s strategic location, strong infrastructure, and government support make it attractive for both local and foreign investors. You can benefit from a wide range of incentives and a growing export market, but you will also face challenges such as labor shortages, regulatory complexity, and global competition.
You will find Malaysia’s investment climate very supportive. The government approved RM83.7 billion in investments in Q1 2024, which is a 13% increase from last year. You can see the main incentives in the table below:
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Investment Figures | RM83.7 billion approved investments in Q1 2024, 13% YoY increase |
| Tax Incentives | Pioneer Status (5 years tax exemption), Investment Tax Allowance (60%-100% for 5-10 years) |
| Relocation Incentives | 0% tax rate for 10-15 years for new companies with large investments |
| Special Economic Zones (SEZ) | Income tax, import duty, and stamp duty exemptions in zones like Iskandar Malaysia, Johor-Singapore SEZ |
| Malaysia Digital (MD) Status | Reduced tax rates (0%-15%) and ITA of 30%-100% on capital expenditure |
| Green Incentives | Tax exemptions for green tech projects, 70% tax exemption for solar leasing up to 10 years |
These incentives help you reduce costs and encourage you to invest in advanced manufacturing, green technology, and digital transformation.
Malaysia’s export market continues to grow. In Q2 2024, exports reached RM368.78 billion, up 5.8% from last year. Key products include electronics, petroleum, and palm oil. Top export markets are Singapore, China, and the United States. You can see the trade growth with major partners in the chart below:
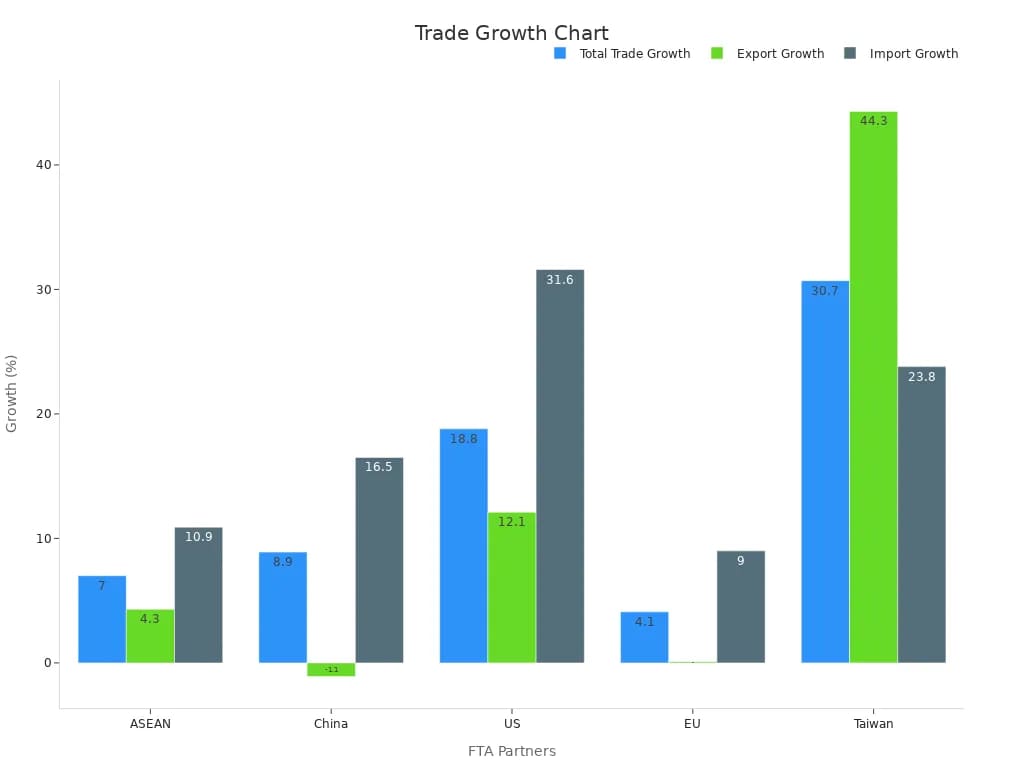
Malaysia’s ongoing free trade agreement talks with the EU could open new doors for exports, especially in high-tech and green products. You must follow strict export regulations, use proper packaging, and provide the right documents to access these markets smoothly.
You may face challenges finding skilled workers for advanced manufacturing in malay. Many companies report skill gaps, especially in digital and technical roles. These gaps come from changes in technology, social factors, and the need for new training methods. You need to invest in upskilling your team and use digital tools like FineBI to make data-driven decisions and improve productivity.
Malaysia enforces strong competition laws and regulatory standards. The Malaysia Competition Commission (MyCC) actively monitors the market, focusing on fair practices and preventing abuse of dominance. For example, the MyCC proposed a large fine against a major ride-hailing company for unfair practices. Regulatory bodies also work to speed up processes, such as reducing insurance claim times by 55%. You must stay updated on regulations and global standards to remain competitive. Digital solutions like FineBI help you track compliance, analyze market trends, and respond quickly to changes.
You need to understand the legal and regulatory framework before starting your business in Malaysia. The country offers a clear process for company registration, licensing, and compliance. Here is a summary of the main requirements:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Company Registration Documents | Memorandum and Articles of Association (company charter), Declaration of Compliance, Statutory Declaration |
| Governing Laws | Companies Act 2016, Industrial Coordination Act 1975 |
| Licensing Thresholds | License required if capital ≥ RM2.5 million or ≥ 75 full-time employees |
| SME Definition | Manufacturing SMEs: annual revenue < RM50 million or < 200 employees |
| Foreign Equity | Up to 100% foreign equity allowed for licensed manufacturers |
| Regulatory Improvements | Simplified incorporation, online platforms, streamlined permits |
| Free Zones | Free Industrial Zones (FIZ) and Free Commercial Zones (FCZ) for duty-free imports/exports |
| Fiscal Incentives | Pioneer Status (15 years tax exemption), Investment Tax Allowance (10 years) |
| Licensing Authority | Malaysian Investment Development Authority (MIDA) |
| Additional References | Bilateral treaties, NPDIR, trade facilitation initiatives |
If you plan to manufacture pharmaceuticals, you must follow strict rules. The National Pharmaceutical Regulatory Agency (NPRA) oversees product quality and safety. The agency holds international certifications and aligns with global standards. You must appoint a local representative or set up a registered business. Product registration requires detailed documents, including quality and safety reports. You need to comply with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) and prepare for inspections. Import licenses and Good Distribution Practice (GDP) are also necessary. Registration fees apply, and you must renew approvals regularly.
Tip: Approvals from the EU or US can speed up some steps, but you still need to meet all Malaysian requirements.
You will benefit from building strong local partnerships. Local partners help you understand the market, culture, and regulations. They can connect you with suppliers, distributors, and government agencies. Many successful companies work with Malaysian SMEs to access skilled labor and local networks. You can join industry associations or attend trade fairs to meet potential partners. These relationships help you adapt quickly and solve problems on the ground.
You can gain a competitive edge by using advanced data solutions. Platforms like FanRuan and FineBI help you connect, manage, and analyze data from different sources. With FineBI, you can create dashboards to track sales, inventory, and production in real time. You do not need coding skills to use its drag-and-drop features. FineDataLink lets you integrate machine and business data for a complete view of your operations. Real-time alerts and automated reports help you make fast decisions. By adopting these tools, you improve efficiency, reduce risks, and support your growth in Malaysia’s manufacturing sector.
You have seen how Malaysia’s manufacturing industry grows stronger with digital transformation.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Market CAGR | 7.5% (2025–2031) |
| Market Value (2031) | USD 4.3 billion |
| Key Technologies | AI, IoT, blockchain, RPA |
| Workforce Focus | Digital skills, training, change management |
Explore digital tools like FanRuan and FineBI to stay ahead. For more insights, connect with local experts or join industry events.
Click the banner below to try FineBI for free and empower your enterprise to transform data into productivity!

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles

Best Self-Service Tools for Analytics You Should Know
See which self-service tools for analytics let business users access data, build dashboards, and make decisions faster—no IT help needed.
Lewis
Dec 29, 2025

Understanding Predictive Analytics Services in 2026
Predictive analytics services use data and AI to forecast trends, helping businesses make informed decisions, reduce risks, and improve efficiency in 2026.
Lewis
Dec 30, 2025

What is Distribution Analysis in Mathematics and Statistics
Distribution analysis in mathematics and statistics examines how data values spread, helping identify patterns and predict outcomes accurately.
Lewis
Dec 28, 2025