A supply and demand graph helps you visualize how supply and demand interact in any market. You see the supply curve show how much producers want to sell at different prices, while the demand curve reveals how much buyers want at those same prices. When supply increases, the supply curve shifts, and you notice changes in the market. When demand rises, the demand curve shifts, and the market responds. Every point on the supply and demand graph tells you something about supply, demand, and price. In business, you use supply and demand graphs to make decisions about pricing, production, and inventory.
Supply and demand graphs are not just for classrooms. You find them in business meetings and dashboards because they help you spot trends quickly. Many educational programs, like introductory economics courses, use supply and demand graphs to teach how markets work and how prices form. Today, tools like FineBI from FanRuan make it simple to analyze these graphs. With FineBI, you can:
With these tools, you can explore supply and demand changes, track how supply and demand curves shift, and understand the impact on your business. A supply and demand graph becomes a powerful tool when you have the right data and visualization platform.
You see the terms supply and demand in every economics textbook. Supply means the amount of a good or service that producers are willing to offer at each price. Demand means the amount of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy at each price. The law of demand says that when the price goes up, people buy less. When the price drops, people buy more. The demand curve shows this relationship as a downward slope. On the other hand, the law of supply says that when the price rises, producers want to sell more. When the price falls, they supply less. The supply curve slopes upward. These two forces shape every market. You use a supply and demand graph to see how they interact and to find the price where buyers and sellers agree.
A supply and demand chart has several key parts. You need to know these to read any supply and demand diagram:
Tip: Always check that the axes are labeled and the curves are clear. This helps you avoid confusion when you look at a supply and demand chart.
You can read a supply and demand graph by following a few simple steps:
You can use tools like FineBI by FanRuan to make this process easier. FineBI lets you drag and drop your data to create a supply and demand diagram in seconds. You can combine data from different sources, update your charts in real time, and share your findings with your team. This helps you spot trends and make better decisions in your business.
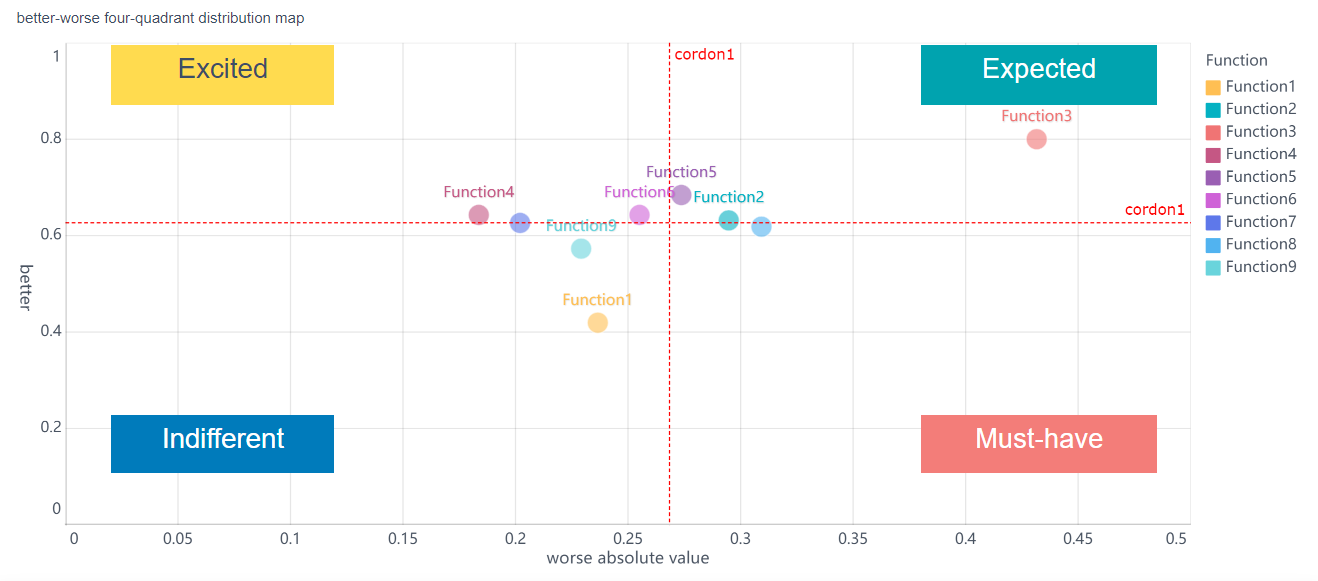
The KANO Model helps you understand demand in product development. It sorts features into three main types:
| Feature Category | Customer Expectation | Impact on Satisfaction | Relation to Supply and Demand |
|---|---|---|---|
| Must-be | Expected by customers | Absence causes dissatisfaction; presence does not increase satisfaction | Represents basic demand; must be supplied to avoid dissatisfaction |
| Performance | Desired features | Satisfaction increases with implementation | Reflects direct supply-demand relationship; more supply leads to more satisfaction |
| Attractive | Unexpected delights | Presence increases satisfaction; absence does not cause dissatisfaction | Represents latent demand; supply can create new demand and delight customers |
You use the KANO Model to decide which features to supply in your product. Must-be features are basic needs. If you do not supply them, customers feel unhappy. Performance features make customers happier as you supply more of them. Attractive features surprise and delight customers, even if they did not expect them. By using the KANO Model, you match your supply to customer demand and make smarter choices about what to build next.
A supply and demand graph, a supply and demand chart, or a supply and demand diagram all help you see these relationships clearly. When you use data visualization tools like FineBI, you can turn complex data into easy-to-read charts. This helps you understand your market, forecast trends, and make decisions that keep your business ahead.
When you look at a supply and demand graph, you see the point where the supply and demand curves cross. This intersection is called the equilibrium. At this spot, the quantity of goods that producers want to sell matches exactly with the quantity that consumers want to buy. You call this balance the market equilibrium. The price at this point is the equilibrium price, and the amount traded is the equilibrium quantity.
If you set the price higher than the equilibrium, you get a surplus. Producers supply more than buyers want, so goods pile up. Sellers then lower prices to clear out the extra stock. If you set the price below equilibrium, you get a shortage. Buyers want more than producers supply, so products run out quickly. This pushes prices up. These forces keep moving the market toward equilibrium.
Let’s look at a real-world example. In the gasoline market, the equilibrium price is $1.40 per gallon. At this price, both the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded are 600 million gallons. If the price rises above $1.40, you see a surplus. If the price drops below $1.40, you see a shortage. The table below shows how this works:
| Price (per gallon) | Quantity Demanded (millions) | Quantity Supplied (millions) |
|---|---|---|
| $1.00 | 800 | 500 |
| $1.20 | 700 | 550 |
| $1.40 (Equilibrium) | 600 | 600 |
| $1.60 | 550 | 640 |
| $1.80 | 500 | 680 |
You can also see this relationship in the following chart:
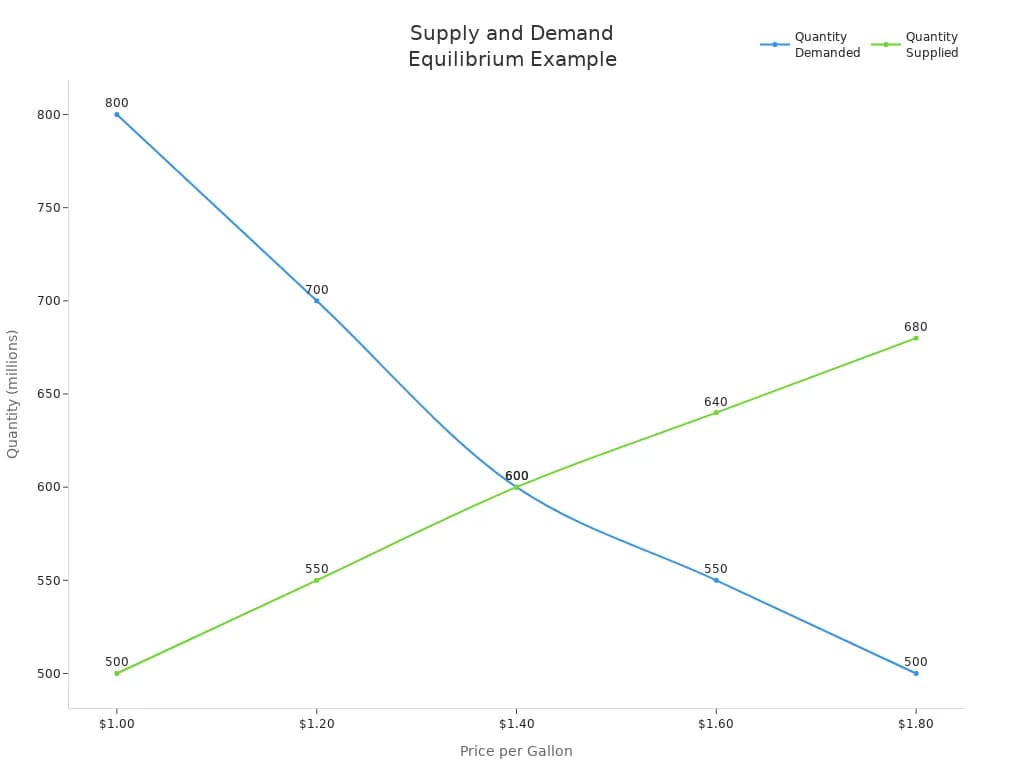
This graph makes it easy to spot the equilibrium. You see how the market moves toward this point, no matter where the price starts.
Tip: In a perfectly competitive market, equilibrium happens when many buyers and sellers interact freely, and everyone has the same information.
Markets do not stay the same forever. You often see the equilibrium change when outside factors shift the supply or demand. When the supply curve moves, it means producers can offer more or less at every price. When the demand curve moves, it means buyers want more or less at every price.
Common reasons for shifts include:
For example, when hydraulic fracturing (fracking) technology improved in North America, oil producers could supply much more oil. This shift in supply caused oil prices to fall sharply, which also changed the equilibrium in the oil market. You can see similar effects in other industries when new competitors enter or when input costs rise or fall.
When the supply curve shifts right (increases), you get a new equilibrium with a lower price and higher quantity. When the demand curve shifts right (increases), you get a new equilibrium with a higher price and higher quantity. The opposite happens if supply or demand decreases.
Note: You can use FineBI dashboards to track these changes in real time. FineBI lets you visualize how shifts in supply or demand affect market equilibrium. In manufacturing or supply chain management, you can monitor inventory, production, and sales data. This helps you respond quickly to changes and keep your business running smoothly.
By understanding how equilibrium works and how shifts in supply or demand change the market, you can make better decisions. You can set prices, plan production, and manage inventory with confidence. FineBI gives you the tools to see these changes as they happen, so you always stay ahead in your market.
You use supply and demand graphs every day in manufacturing, procurement, and inventory management. These graphs help you see how much product to make, when to order materials, and how to avoid shortages or excess stock. In a real case, a modular bathroom pod manufacturer improved efficiency by mapping supply and demand with operations science tools. The team used production system optimization to track throughput, cycle time, and inventory. By analyzing supply and demand, they found bottlenecks and set the right inventory levels. This led to better scheduling and fewer delays.
Many companies use supply and demand data to forecast needs and adjust quickly. For example, big data helps you predict demand by looking at past sales and current trends. Real-time tracking systems show you where your supply is at any moment, so you can avoid running out or having too much. Companies like General Electric use digital twins to simulate supply and demand scenarios, reducing waste and improving throughput. Amazon uses predictive analytics to keep the right amount of supply on hand, making sure demand is always met. These strategies help you respond to changes in the market and keep your business running smoothly.
Tip: Update your supply and demand analysis often. Some businesses do this daily, while others review weekly or monthly. Frequent updates help you react fast to market changes and keep your supply chain efficient.
You can make better decisions when you see your supply and demand data clearly. FineBI gives you powerful tools to visualize this information. With interactive dashboards, you can spot trends in supply and demand quickly. Self-service analytics let you explore data on your own, without waiting for IT support. Real-time data visualization means you get instant feedback as the market shifts.
FineBI connects to many data sources, so you always have the latest supply and demand numbers. You can use drag-and-drop features to build reports and dashboards that show how supply and demand interact in your market. Predictive analytics in FineBI help you forecast demand and plan your supply, reducing the risk of stockouts or overstocking.

When you integrate supply and demand analysis into your business intelligence workflow, you gain a complete view of your operations. This helps you find inefficiencies, optimize inventory, and improve supply chain performance. Companies that use business intelligence tools like FineBI report better decision-making, higher productivity, and cost savings. You move from reacting to problems to planning ahead, staying competitive in any market.
Elasticity measures how much one economic variable responds when another changes. In the context of supply and demand, elasticity tells you how sensitive buyers and sellers are to price changes. You calculate elasticity as the percentage change in one variable divided by the percentage change in another. For example, price elasticity of demand shows how much the quantity demanded changes when the price changes. If a small price increase causes a big drop in demand, you say demand is elastic. If demand hardly changes, it is inelastic.
On a supply and demand graph, elasticity affects the slope of the curves. A flatter demand curve means buyers react strongly to price changes, showing high elasticity. A steeper demand curve means buyers do not change their behavior much, showing low elasticity. The same idea applies to the supply curve. When you look at products like luxury goods or airline tickets, you see high elasticity. People buy less when prices rise. For basic goods, like salt, demand is less elastic because people need them no matter the price.
| Product Category | Price Elasticity Type | Consumer Behavior and Demand Response |
|---|---|---|
| Luxury Goods | High Elasticity | Demand decreases when prices rise as consumers delay purchases or seek alternatives; demand increases when prices fall. |
| Airline Tickets | High Elasticity | Demand fluctuates with price; consumers may postpone travel or choose other transport if prices rise. |
| Fast Food | High Elasticity | Demand sensitive to price; consumers switch to home cooking or cheaper options if prices increase. |
| OTT Platforms | High Elasticity | Consumers switch subscriptions based on price and content availability. |
| Furniture & Décor | High Elasticity | Consumers compare prices and quality; demand drops if prices rise relative to alternatives. |
Understanding elasticity helps you predict how changes in price will affect both supply and demand, which is key for setting prices and planning production.
Many outside factors can shift supply or demand in a market. These factors can move the curves left or right, changing the equilibrium price and quantity. You often see these shifts when governments change policies, when new technology appears, or when global events happen.
| External Factor Category | Description | Examples of Impact on Supply or Demand |
|---|---|---|
| Political | Government actions like trade or tax policy | Stimulus programs, new taxes, or tariffs can change supply or demand. |
| Economic | Changes in the economy | Inflation or unemployment can reduce demand or increase supply costs. |
| Social | Shifts in population or behavior | More people working from home can change demand for office supplies. |
| Technological | New inventions or processes | Automation can increase supply by lowering costs. |
| Environmental | Natural events or health crises | Pandemics can reduce supply by closing factories or change demand for certain goods. |
| Legal | New laws or regulations | Health and safety rules can increase production costs, shifting supply. |
Note: Taxes and regulations usually increase production costs, shifting the supply curve to the left. Subsidies or new technology can lower costs, shifting supply to the right. Sometimes, taxes on products like cigarettes aim to reduce demand by making them more expensive.
You need to watch these external influences because they can quickly change the balance between supply and demand. By tracking these changes, you can adjust your business strategy and stay ahead of market shifts.
Understanding supply and demand gives you a strong foundation for business success. You can set prices, manage inventory, and plan production by tracking how supply and demand interact. FineBI from FanRuan lets you visualize supply and demand, making it easier to spot trends and act quickly.
| Business Insight | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Price setting | You adjust supply and demand to avoid shortages or excess stock. |
| Equilibrium price | You match supply with demand for efficient planning. |
| Demand elasticity | You see how demand changes with price, guiding your supply decisions. |
| External factors | You respond to shifts in supply or demand from outside events. |
| Market response | You adapt supply and demand to stay ahead of changes. |
Mastering supply and demand analysis helps you make smarter decisions and build a resilient business.
Click the banner below to try FineBI for free and empower your enterprise to transform data into productivity!
Understanding the Kano Model: A Comprehensive Guide (with Kano Model Examples)

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles

Top 8 Data Visualization softwares You Should Try in 2025
Compare the top 8 data visualization software for 2025, including FineReport, Tableau, Power BI, and more to find the best fit for your business needs.
Lewis
Dec 19, 2025
10 Must-Have Data Visualization Tools for Modern Businesses
Compare the top 10 data visualization tools for 2025 to boost business insights, streamline analytics, and empower smarter decision-making.
Lewis
Dec 17, 2025

7 Leading Big Data Visualization Tools for the Year Ahead
Compare the top big data visualization tools for 2025 to find advanced analytics, scalability, and interactive dashboards for your business.
Lewis
Dec 17, 2025