

Sean, Industry Editor
Aug 05, 2025
Analytical reasoning means using logic to solve problems by breaking complex information into smaller parts, finding patterns, and drawing conclusions based on facts. This type of reasoning combines analytical skills, critical thinking, and problem-solving. People use analytical reasoning skills every day, from making personal decisions to tackling business challenges. Employers highly value analytical reasoning, with 70% to 78% of companies listing it as a top skill for hiring and promotion. Analytical reasoning tests measure a person's ability to analyze data, identify patterns, and make sound decisions. Analytical reasoning plays a vital role in data-driven decision making, especially in business intelligence, where it helps professionals turn raw data into actionable insights. Analytical reasoning tests and reasoning skills help individuals adapt, innovate, and make better decisions in a fast-changing world.

Analytical reasoning is a cognitive process that helps individuals break down complex information into smaller, manageable parts. This process allows people to identify patterns, relationships, and underlying structures within data or situations. Analytical reasoning stands out as a specific type of reasoning that focuses on detailed analysis and decomposition of information. Unlike critical thinking, which broadly evaluates arguments and evidence, or logical reasoning, which checks the structure and validity of arguments, analytical reasoning centers on understanding how different components interact within a system.
Analytical reasoning enables individuals to analyze complex information, make logical deductions, and solve problems in both academic and real-world settings.
The table below highlights the differences between analytical reasoning and other forms of reasoning:
| Reasoning Type | Definition & Focus | Key Characteristics & Differentiation |
|---|---|---|
| Critical Thinking | Broad skill involving logic, reason, and evidence to make sound decisions and evaluate arguments. | Encompasses logic, reason, and evidence; evaluates arguments broadly; focuses on sound decision-making. |
| Logical Reasoning | Formal system of principles to evaluate argument validity, focusing on structure and consistency. | Emphasizes argument structure, validity, and avoiding fallacies; includes deductive and inductive logic. |
| Reason | Mental capacity to think rationally, analyze options, and infer conclusions. | Cognitive ability underlying reasoning; includes analytical, comparative, and causal reasoning. |
| Analytical Reasoning | Subset of reasoning involving breaking down complex information into parts for better understanding. | Focused on detailed analysis and decomposition of information; distinct from broader critical thinking and formal logic. |
Analytical reasoning often appears in educational settings, business intelligence, and daily life. It supports decision-making by helping people see connections, predict outcomes, and solve problems efficiently. Analytical reasoning skills are essential for students, professionals, and anyone who needs to interpret data or situations accurately.
Analytical reasoning involves several key elements that work together to support sharp analytical reasoning and effective problem-solving. Cognitive science and psychology describe analytical reasoning as a process that uses both intuitive and analytic thinking. Dual-process theories explain that people switch between quick, intuitive responses and slower, more deliberate analysis. Analytical reasoning activates when individuals detect conflicts, rationalize choices, and separate facts from assumptions.
Key elements of analytical reasoning include:
Tip: Analytical reasoning is not a linear or purely individual process. People often revisit earlier steps, refine their analysis, and collaborate with others to improve results.

Analytical reasoning skills also include logical reasoning, critical thinking, and the ability to interpret data without bias. Strong analytical reasoning depends on cognitive abilities like attention, memory, and openness to new ideas. Personality traits such as curiosity and willingness to engage in analytical thinking can enhance reasoning performance.
Educational research shows that analytical reasoning involves three main activities: analyze, evaluate, and create. These activities rely on cognitive processes like inductive, deductive, and analogical reasoning. Analytical reasoning is interdisciplinary and applies across subjects such as science, mathematics, and social studies. Verbal reasoning supports these processes by helping individuals communicate their analysis and conclusions clearly.
Analytical reasoning is essential for handling new and complex learning situations. It helps people make logical deductions, solve problems, and adapt to changing environments. Analytical reasoning skills prepare individuals to succeed in academic, professional, and everyday contexts.
Analytical reasoning plays a central role in making effective decisions. Individuals who use analytical reasoning can break down information, examine patterns, and apply logic to reach sound conclusions. In professional settings, analytical reasoning enables financial analysts to assess market trends and make profitable choices. Strategic planners use reasoning to anticipate market shifts and adapt strategies. Analytical reasoning also helps optimize resources by identifying inefficiencies and streamlining operations. Scientific studies show that analytical reasoning allows people to re-evaluate intuitive responses, consider contradictory evidence, and resist misinformation. This process leads to better decision outcomes. Analytical reasoning tests often measure these abilities, ensuring that individuals can make informed, data-driven decisions. Verbal reasoning supports this process by helping professionals communicate complex findings clearly to stakeholders.
Analytical reasoning complements artificial intelligence by adding human judgment and ethical considerations, which are essential for complex decisions.

Analytical reasoning is vital for solving complex problems. People with strong analytical skills can break down challenges into smaller parts, identify patterns, and use logic to find solutions. Analytical reasoning tests evaluate a person's ability to analyze situations, spot key issues, and devise effective solutions. These skills help individuals quickly understand new information and approach challenges efficiently. Analytical reasoning supports clear communication of findings and helps prioritize tasks. In unpredictable environments, such as customer success or leadership roles, analytical reasoning enables professionals to adapt plans and solve problems effectively. Verbal reasoning further enhances problem-solving by allowing individuals to explain their thought process and solutions to others.
Analytical reasoning drives significant business impact. Organizations that invest in analytical reasoning training see measurable improvements in performance and decision-making. A survey of Fortune 1000 executives found that nearly half of companies using data-driven decision making realized cost savings. Analytical reasoning helps businesses identify opportunities and threats earlier than competitors. Companies use SWOT analysis and competitor analysis to refine strategies and maintain a competitive edge. Analytical reasoning tests help organizations select employees who can solve problems effectively and make critical decisions. Talent analytics show that organizations with strong analytical reasoning programs achieve higher productivity, lower training costs, and improved employee satisfaction. Verbal reasoning ensures that teams can share insights and collaborate on strategic decisions.
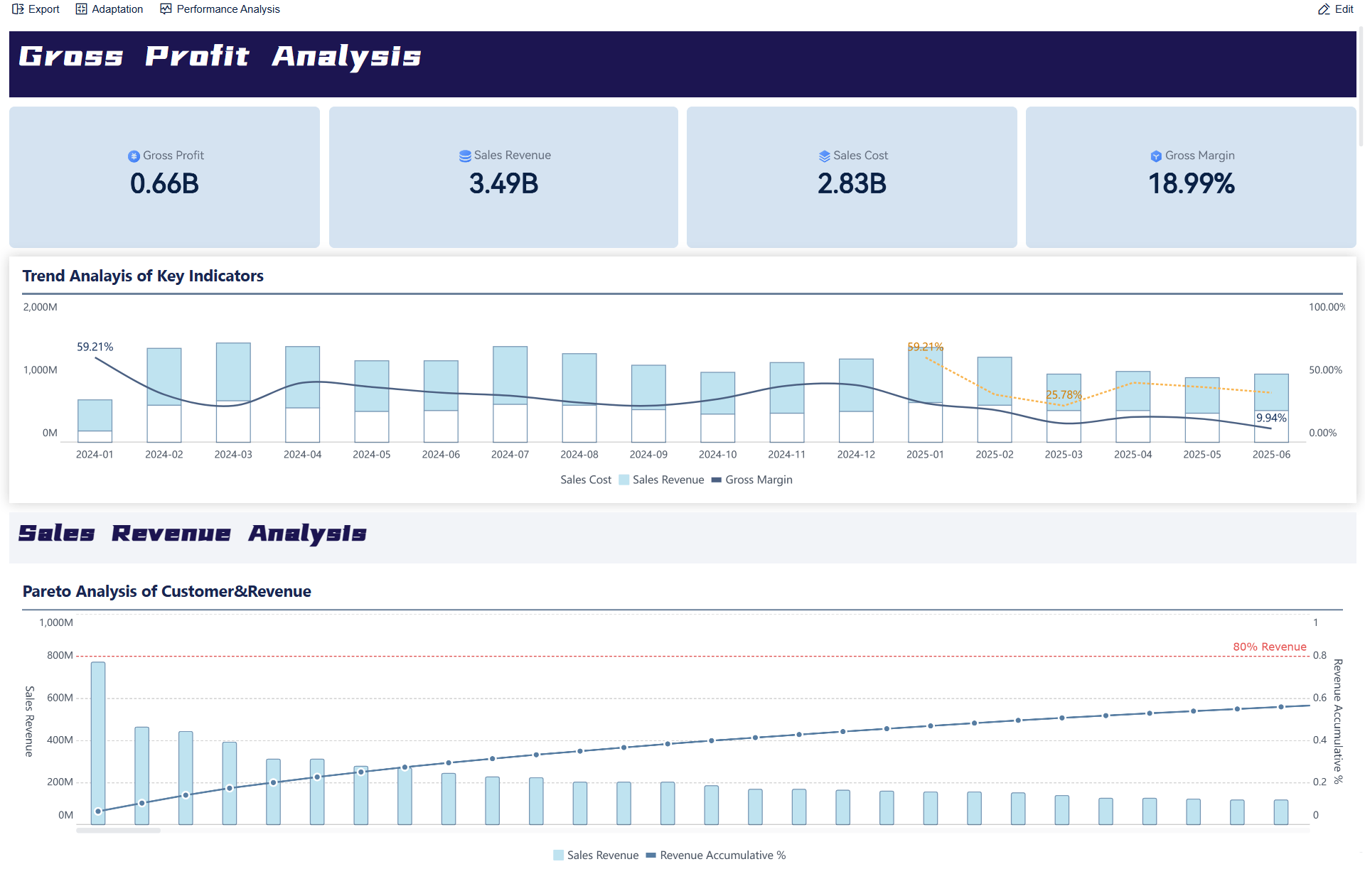
Analytical reasoning skills form the backbone of effective problem-solving and decision-making. Leading educational and psychological organizations highlight several core abilities that define strong analytical reasoning. These abilities help individuals break down complex information, identify patterns, and make logical decisions in both academic and real-world situations.
Recent research shows that executive functions, such as logical reasoning and the ability to resist cognitive biases, are essential for sharp analytical reasoning. These functions allow people to stay focused, avoid errors, and approach problems with a clear mind. Analytical reasoning skills also include the capacity to assess patterns, recognize probabilities, and think hypothetically. These skills support individuals as they analyze data, predict outcomes, and adapt to new challenges.
Key analytical reasoning skills include:
People with strong analytical reasoning abilities can approach complex tasks with confidence. They use these skills to solve problems, make informed decisions, and explain their reasoning to others. Analytical reasoning skills also support critical thinking skills, helping individuals think critically and avoid common mistakes.
Tip: Analytical reasoning skills improve with practice. Regularly challenging the mind with new problems helps build sharper analytical reasoning over time.
Anyone can strengthen analytical reasoning skills with the right strategies and consistent effort. Recent studies highlight several effective methods for building these abilities. Regular practice and active engagement play a key role in developing sharp analytical reasoning.
A recent study found that students who participated in a 12-week seminar focused on argument visualization showed significant improvements in analytical reasoning skills. The seminar encouraged students to map out the logical structure of complex arguments, revise their work, and receive detailed feedback. This hands-on approach led to better-structured written arguments and higher scores on standardized reasoning tests. The findings suggest that active learning, rather than passive reading, helps individuals develop strong analytical reasoning abilities.
People can also improve analytical reasoning by reading widely, analyzing case studies, and discussing complex topics with others. These activities expose individuals to new ideas and different ways of thinking. Over time, these habits build a solid foundation for analytical reasoning and prepare individuals to handle complex challenges in school, work, and daily life.
Note: Consistent practice and a willingness to learn from mistakes are key to developing analytical reasoning skills. Everyone can improve with time and effort.
Business intelligence platforms rely on analytical reasoning to turn raw data into valuable insights. FanRuan and its FineBI solution give users the tools to apply analytical reasoning in daily business tasks. FineBI supports users with features that make data analysis accessible and effective:
These features help business analysts and other users apply analytical reasoning to solve problems, improve performance, and make informed decisions.
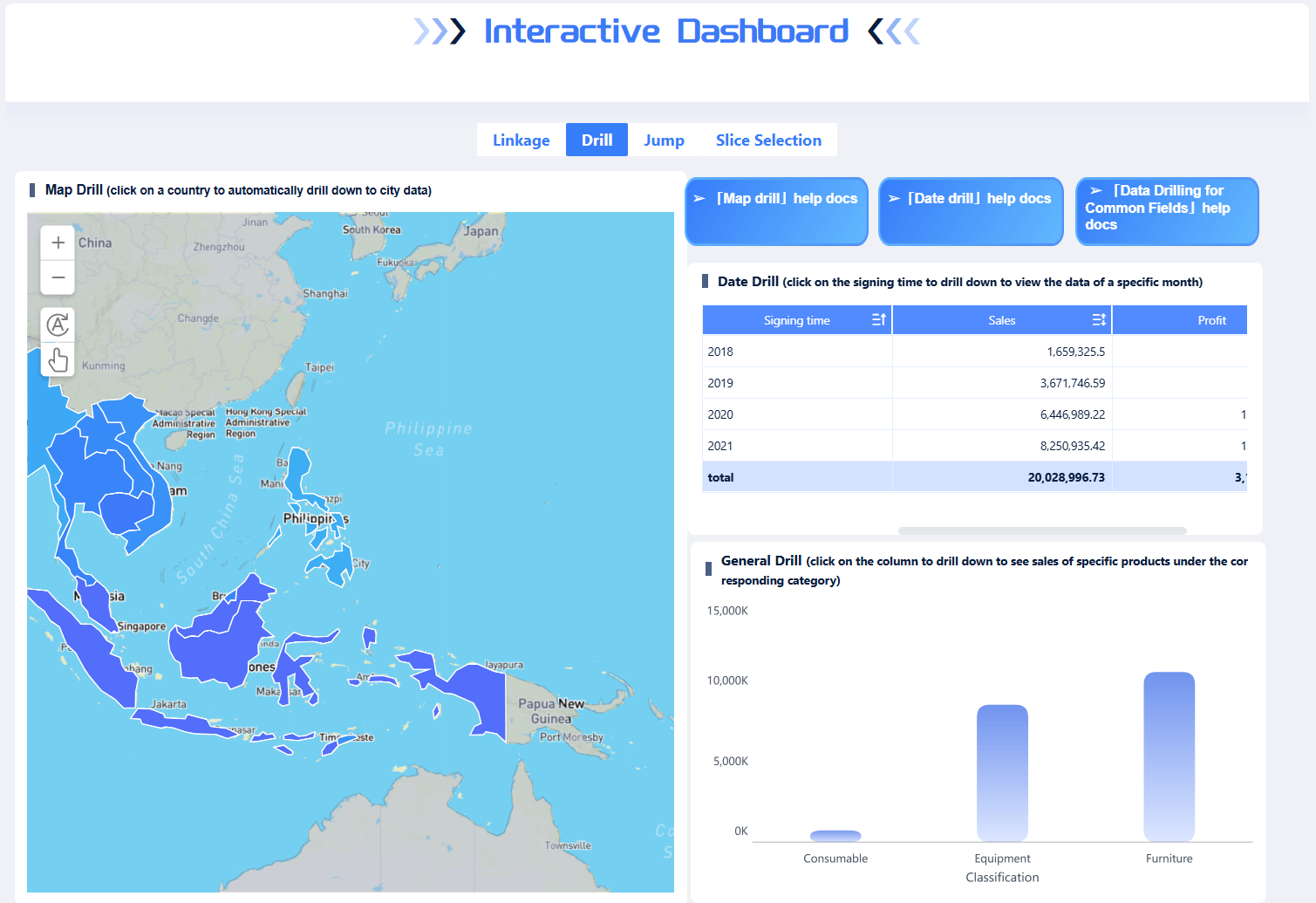
Organizations across industries use analytical reasoning in business intelligence to address specific challenges and improve results.
Advanced analytics in these sectors improves key performance indicators, reduces costs, and increases revenue. For example, predictive analytics can help retailers avoid stockouts, while manufacturers use data to reduce waste. Financial institutions use analytical reasoning to detect fraud and improve client loyalty. These real-world applications show how business intelligence platforms like FineBI empower organizations to make better decisions and achieve strategic goals.
FanRuan
https://www.fanruan.com/en/blogFanRuan provides powerful BI solutions across industries with FineReport for flexible reporting, FineBI for self-service analysis, and FineDataLink for data integration. Our all-in-one platform empowers organizations to transform raw data into actionable insights that drive business growth.
Analytical reasoning focuses on breaking down information and finding patterns. Critical thinking evaluates arguments and evidence. Both skills help people solve problems, but analytical reasoning looks deeper into details and relationships.
FineBI gives users self-service tools to explore data, create dashboards, and find trends. These features encourage users to practice analyzing information and making logical decisions based on real data.
Employers value analytical reasoning because it helps employees solve problems, make smart decisions, and adapt to new situations. Strong analytical skills lead to better business results and more effective teamwork.
Yes. Students can build analytical reasoning by solving puzzles, playing strategy games, and discussing real-world problems. Practice with different activities helps strengthen these skills over time.
Industries like manufacturing, finance, and retail use analytical reasoning to improve efficiency, manage risks, and understand customer needs. Business intelligence tools help these industries turn data into useful insights.

