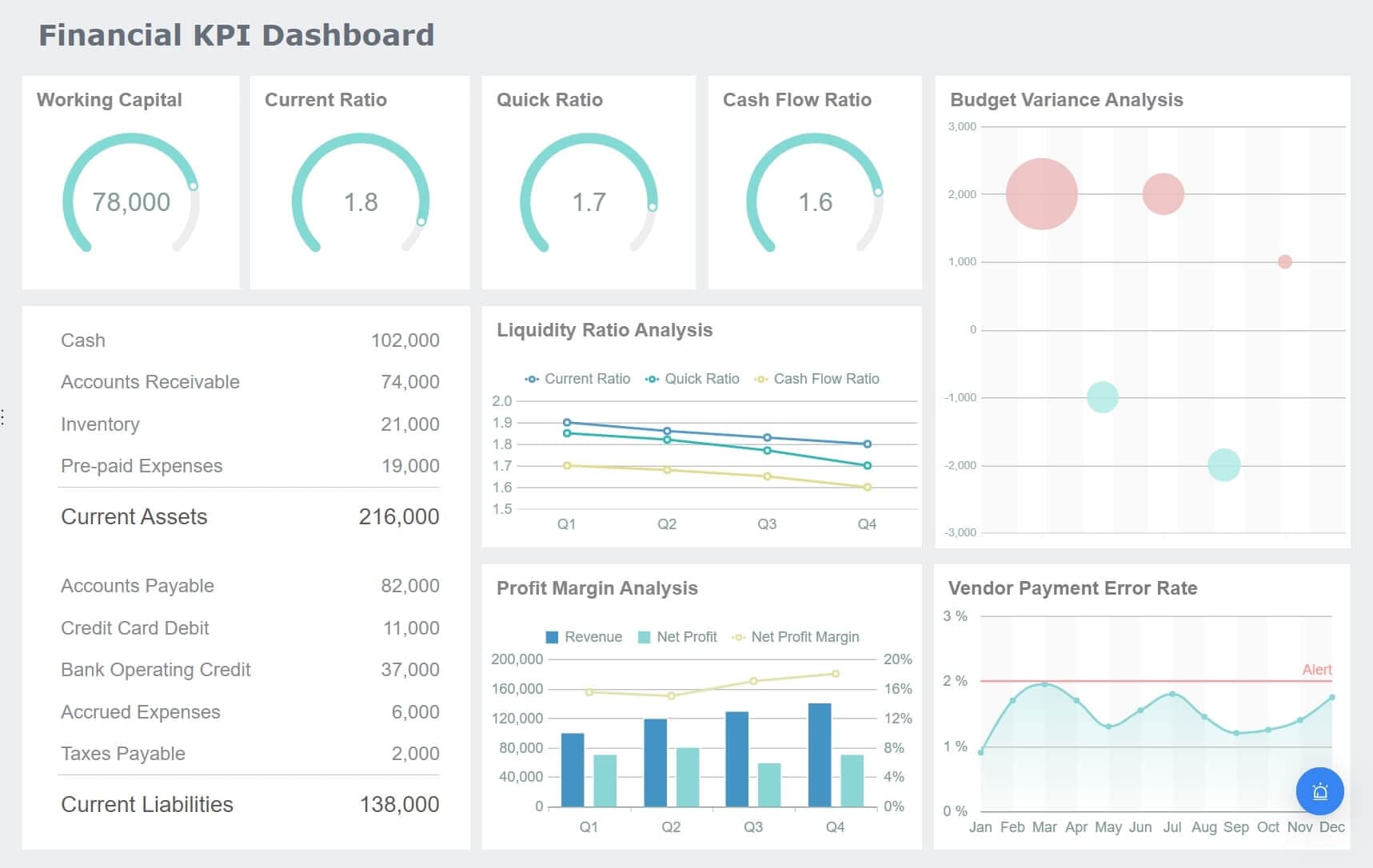
Descriptive analytics serves as a fundamental tool in data analysis, focusing on understanding past events by examining historical data. This approach provides businesses with valuable insights into patterns and trends, enabling them to make informed decisions. In today's fast-paced business environment, descriptive analytics plays a crucial role in enhancing operational efficiency and strategic planning. Tools like FineReport and FineBI empower organizations to harness the power of descriptive analytics, offering user-friendly interfaces for data visualization and reporting. These tools facilitate the transformation of complex datasets into actionable insights, driving business growth and innovation.

Descriptive analytics serves as a foundational element in the realm of data analytics. It focuses on analyzing historical data to provide insights into past events, patterns, and trends. By employing techniques such as exploratory data analysis and data visualization, organizations can derive actionable insights that drive strategic decision-making and optimize operations.
Descriptive analytics involves summarizing data to reveal key insights. This process includes calculating summary measures like averages, totals, percentages, or ratios relevant to the subject being analyzed. It simplifies complex datasets by providing clear summaries, often utilizing data visualization techniques to make the information more accessible and understandable.
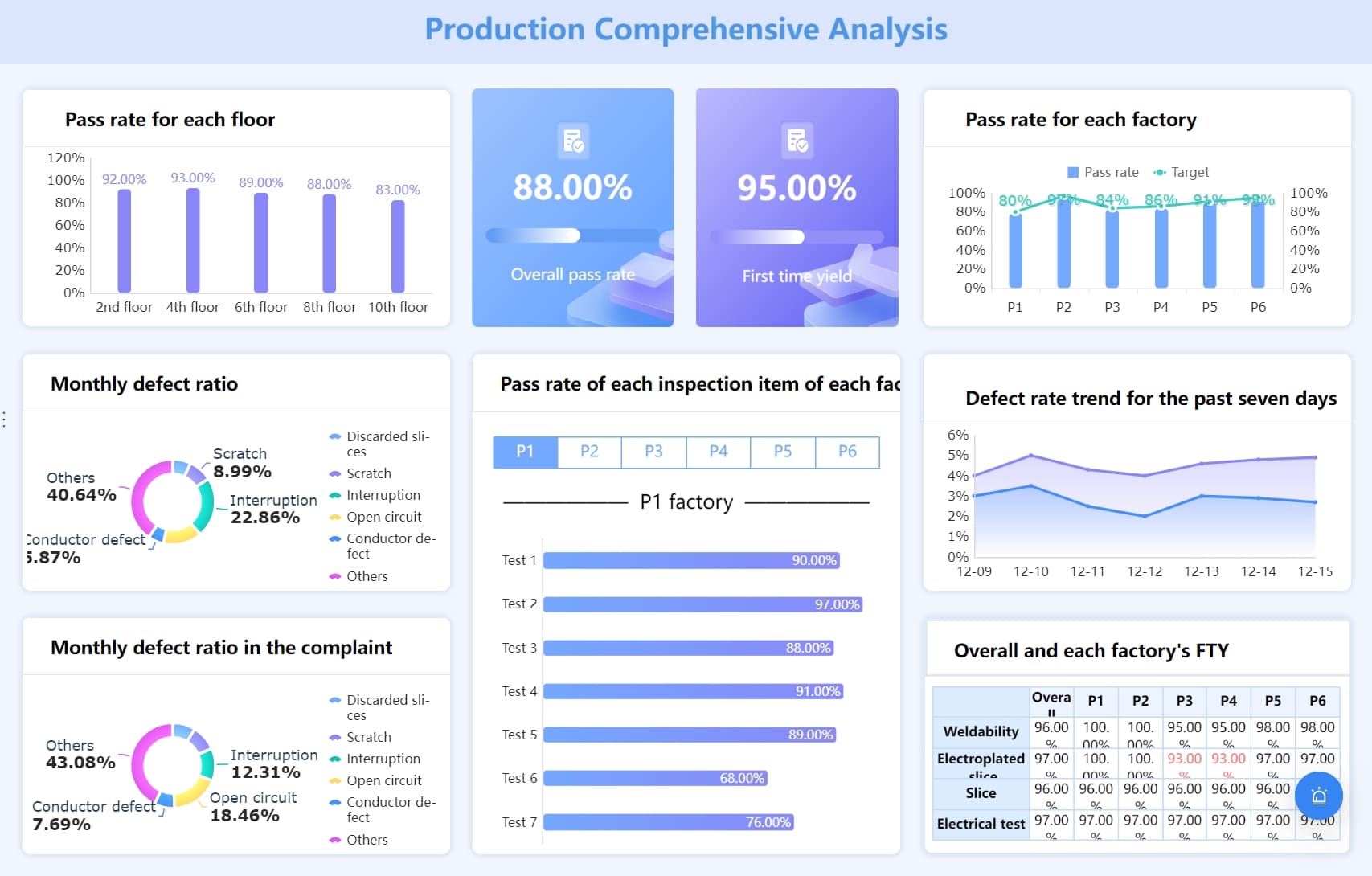
The roots of descriptive analytics can be traced back to the early days of statistical analysis. As businesses began to collect more data, the need to understand and interpret this information became crucial. Over time, descriptive analytics evolved, incorporating advanced tools and technologies to enhance its effectiveness. Today, it remains a vital component of business intelligence, offering a solid foundation for tracking trends and gauging performance over time.
Descriptive analytics is a cornerstone of data analysis, offering organizations a thorough understanding of past events. By examining historical data, it allows businesses to assess their performance, recognize recurring trends, and gain insights into key patterns. This retrospective view is crucial for making well-informed decisions, refining strategies, and ensuring continuous improvement. Without this foundation, organizations may struggle to identify underlying factors that influence their operations and outcomes.
Descriptive analytics serves as the essential first phase in the broader data analysis framework. It organizes raw data into meaningful summaries, transforming complex information into an easily understandable format. This step is invaluable for identifying patterns and trends that might otherwise be overlooked. By painting a clear picture of what has occurred, descriptive analytics paves the way for more advanced approaches like predictive and prescriptive analytics, which build on the insights derived from historical data to forecast future events and optimize decision-making.
The practical advantages of descriptive analytics for businesses are vast. By measuring performance against predefined benchmarks, it helps organizations pinpoint strengths and areas in need of improvement. The insights it offers into customer behavior, preferences, and interactions enable businesses to fine-tune their marketing efforts, ensuring they target the right audience more effectively. Furthermore, descriptive analytics enhances reporting capabilities, allowing businesses to create comprehensive, data-driven reports that are critical for both internal decision-making and external communications with stakeholders. Overall, descriptive analytics equips businesses with the tools to make better, data-backed decisions and drive sustained success.
Descriptive analytics is built upon several essential components that transform raw data into actionable insights. Each component, from data collection to data processing, plays a critical role in ensuring the analysis is both comprehensive and accurate. Together, these elements enable organizations to derive meaningful information from large data sets, ultimately informing better decision-making.
Data collection forms the cornerstone of descriptive analytics. It involves the systematic gathering of data from a variety of sources to ensure that the analysis captures a full spectrum of relevant information. A diverse and well-structured data collection process is essential for a robust analysis, as it provides the raw material necessary for generating valuable insights.
To conduct effective descriptive analytics, organizations draw on multiple data sources, each contributing unique information to the analysis:
For descriptive analytics to yield accurate and actionable insights, maintaining high standards of data quality and integrity is essential. The accuracy of the analysis is directly linked to the quality of the data being used. Poor data quality—characterized by errors, duplicates, or inconsistencies—can lead to flawed conclusions and misguided strategies. Therefore, organizations must implement rigorous data validation procedures, ensuring that the data is accurate, consistent, and reliable.
Effective data validation processes involve checking for anomalies, correcting errors, and eliminating duplicates. By ensuring data quality at the outset, businesses can confidently rely on their descriptive analytics to guide decision-making, making the insights derived from their analysis both trustworthy and impactful.
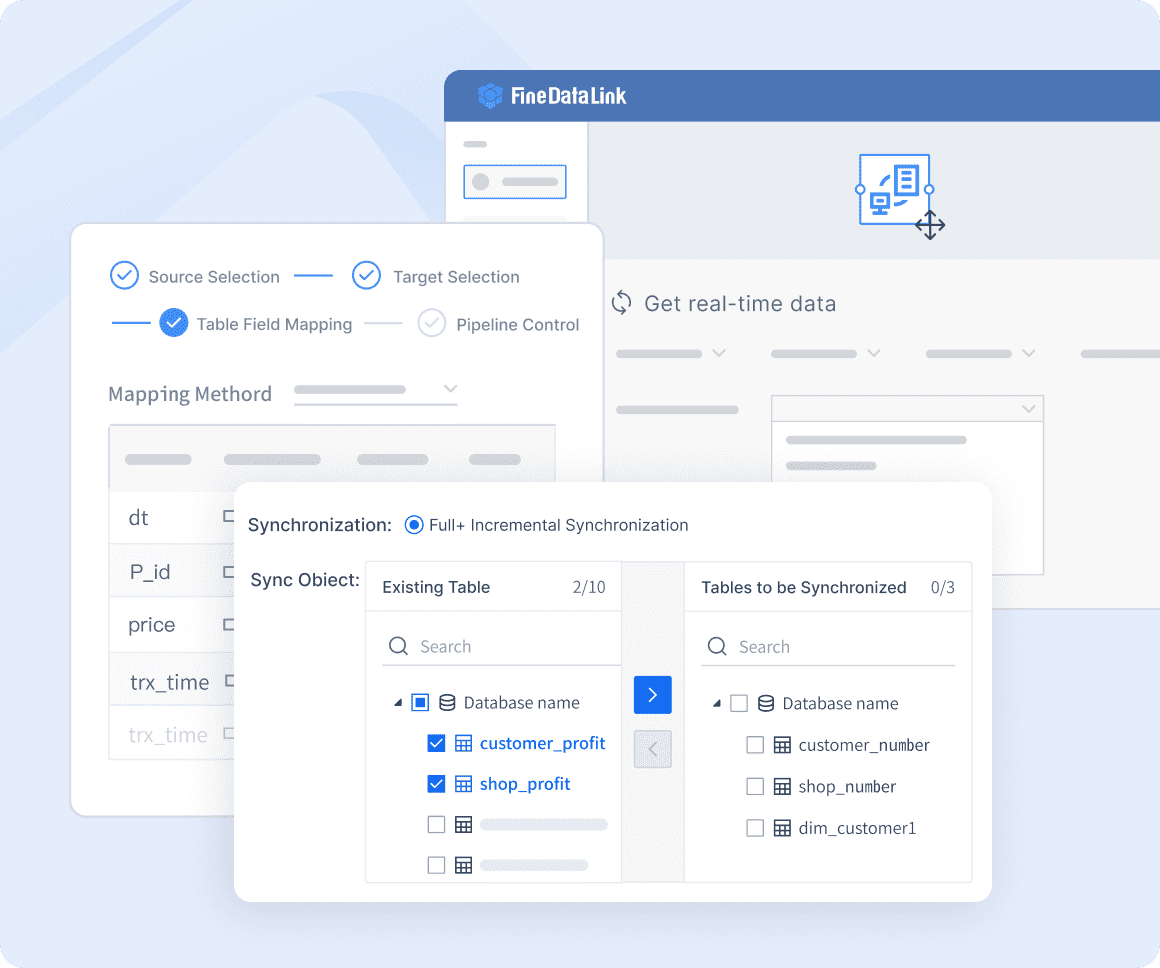
After data is collected, it must undergo processing to prepare it for meaningful analysis. This critical step transforms raw data into a structured format that can be easily interpreted. A range of techniques and tools is employed during this phase to enhance the data’s usability and ensure it’s ready for insightful analysis.
Descriptive analytics utilizes several key techniques to refine and organize data, making it more actionable:
A variety of tools and technologies are available to facilitate the data processing phase in descriptive analytics, each offering unique functionalities that cater to different aspects of the analysis:
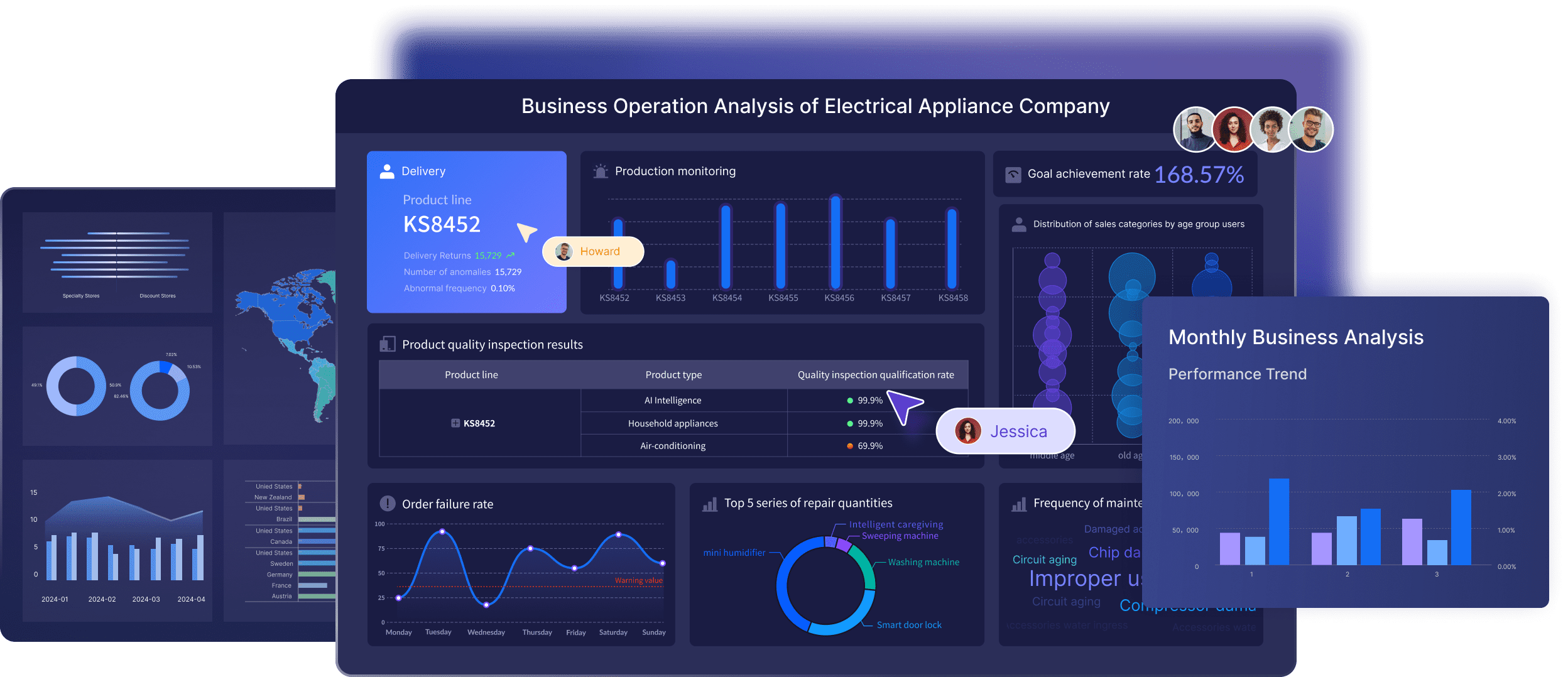
By applying these techniques and leveraging advanced tools, descriptive analytics transforms raw and unstructured data into actionable insights. This process enables organizations to better understand past events, uncover valuable patterns, and make informed decisions that are grounded in data. The end result is a clearer view of historical performance, which is essential for future planning and strategy development.
Descriptive analytics encompasses several crucial processes that convert raw data into valuable insights. These processes ensure the data is accurate, well-organized, and ready for comprehensive analysis, forming the foundation for meaningful interpretations.
Data cleaning is a critical, foundational step in the descriptive analytics process. It ensures that the dataset is free from errors, inconsistencies, and redundancies, which are essential for producing accurate and reliable results. Without this step, faulty data can lead to misleading conclusions and suboptimal decisions.
Error Detection and Correction: This method involves carefully scrutinizing the dataset for typographical errors, missing values, and incorrect entries. Analysts use automated tools and manual reviews to detect anomalies and correct them, ensuring the dataset reflects reality. For instance, ensuring that numerical values are within expected ranges or checking for misplaced data entries can drastically improve data integrity.
Duplicate Removal: Removing duplicate entries is essential to prevent the distortion of results. Duplicates can skew statistical outcomes and lead to overrepresentation of certain data points. By eliminating these redundancies, analysts guarantee that each record is unique, contributing to more precise and trustworthy analysis.
Data Standardization: Standardizing data formats is crucial for consistency across the dataset. This includes ensuring uniform formats for dates, currency, and other units of measurement. For instance, aligning all date formats (e.g., DD/MM/YYYY) or converting currency values to a single standard prevents misinterpretation during analysis and simplifies comparisons.
Outlier Detection and Handling: Outliers—data points that deviate significantly from other observations—can skew results and lead to misinterpretation. Identifying these anomalies is a vital part of the cleaning process. Analysts may choose to remove outliers if they are deemed irrelevant or adjust them if they represent valuable but extreme data. Proper handling of outliers ensures that the analysis is reflective of typical patterns, without being distorted by rare, atypical events.
The data cleaning process, while essential, is not without its challenges. Incomplete data, inconsistencies in formatting, and the sheer volume of data to be processed can all pose significant obstacles to obtaining accurate insights. However, with the right strategies and tools, these challenges can be effectively managed to ensure the quality of the data and the reliability of descriptive analytics.
Key Challenges
Effective Solutions
To overcome these challenges, analysts implement several strategies to maintain data integrity and streamline the cleaning process:
By addressing these challenges with proactive solutions—such as automated tools, validation rules, and consistent data audits—organizations can overcome the complexities of data cleaning. These efforts not only improve the accuracy and quality of their data but also enhance the reliability of descriptive analytics, providing a solid foundation for effective decision-making and future analysis.
Data aggregation is a crucial component of descriptive analytics, allowing organizations to condense large datasets into meaningful, digestible insights. By summarizing data, this process makes it easier to detect patterns, trends, and correlations that drive informed decision-making.
Various tools and platforms facilitate the aggregation process, each offering unique capabilities that cater to different levels of analysis:
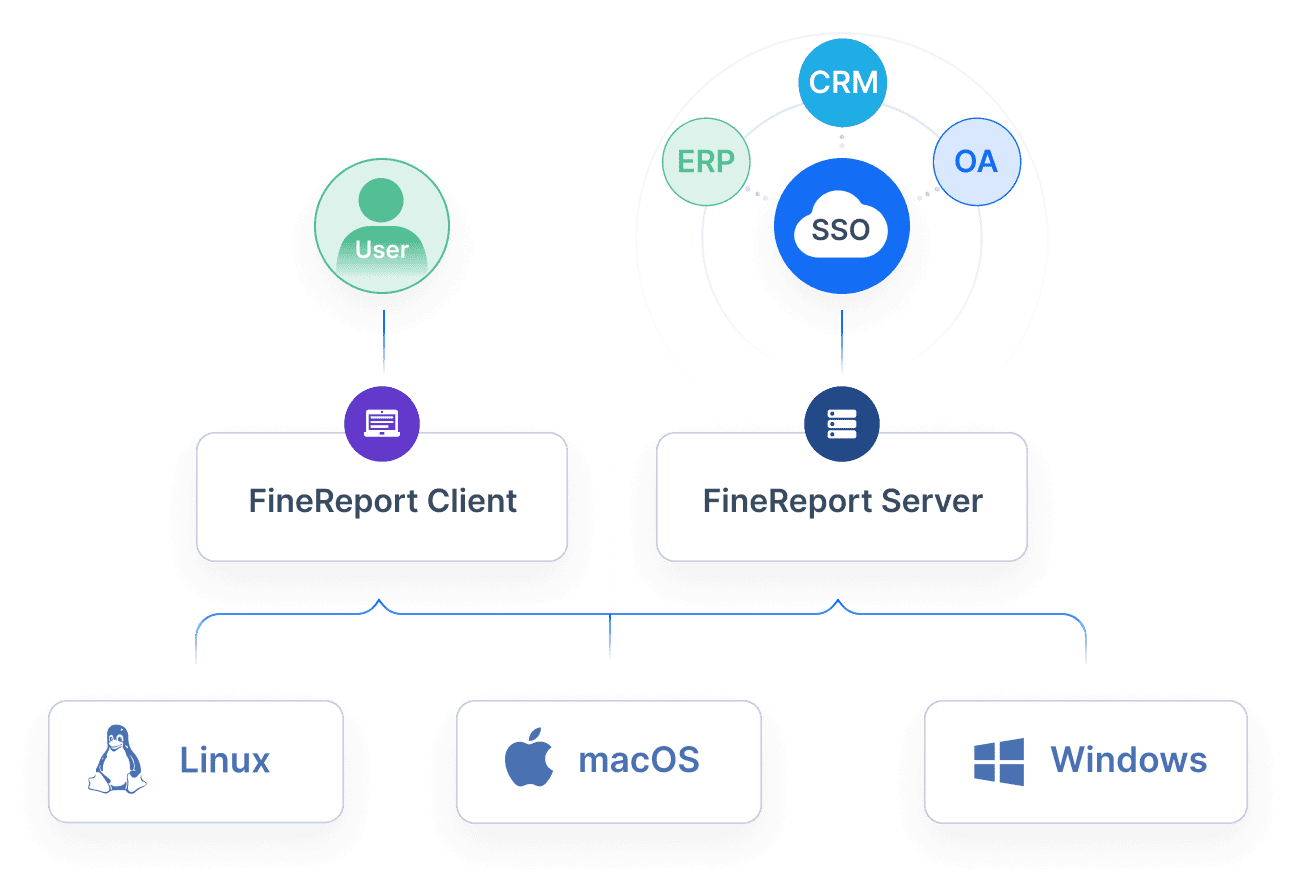
By carefully aggregating data, organizations can transform raw datasets into actionable insights that reveal historical trends and performance metrics. The process ensures that the data is structured, reliable, and ready for further exploration. With clean, consolidated data, businesses can enhance their understanding of past events and leverage this knowledge to guide future strategies and optimize operations.
Descriptive analytics serves as a cornerstone in various business applications, offering crucial insights that drive data-driven decision-making and strategic planning. This section delves into how businesses leverage descriptive analytics across different industries, highlighting the capabilities of FanRuan's FineBI and its transformative impact on market research and beyond.

FineBI, developed by FanRuan Software, is a cutting-edge business intelligence tool designed to unlock the potential of data through advanced analytics and visualization. With its user-friendly interface and powerful analytical features, FineBI empowers organizations to analyze vast datasets, uncover trends, and generate actionable insights. Its versatility makes it a valuable asset across multiple sectors, providing a comprehensive platform for both data discovery and performance optimization.
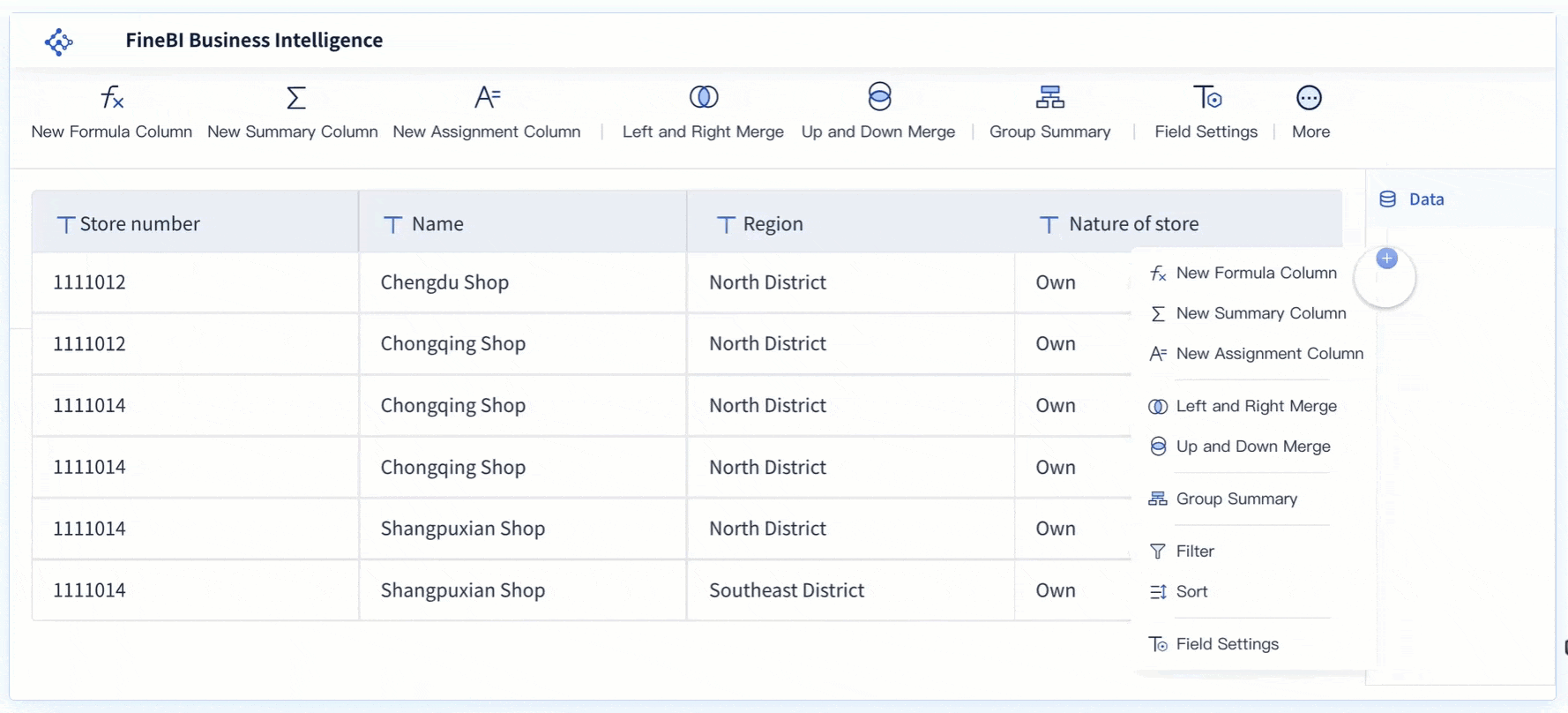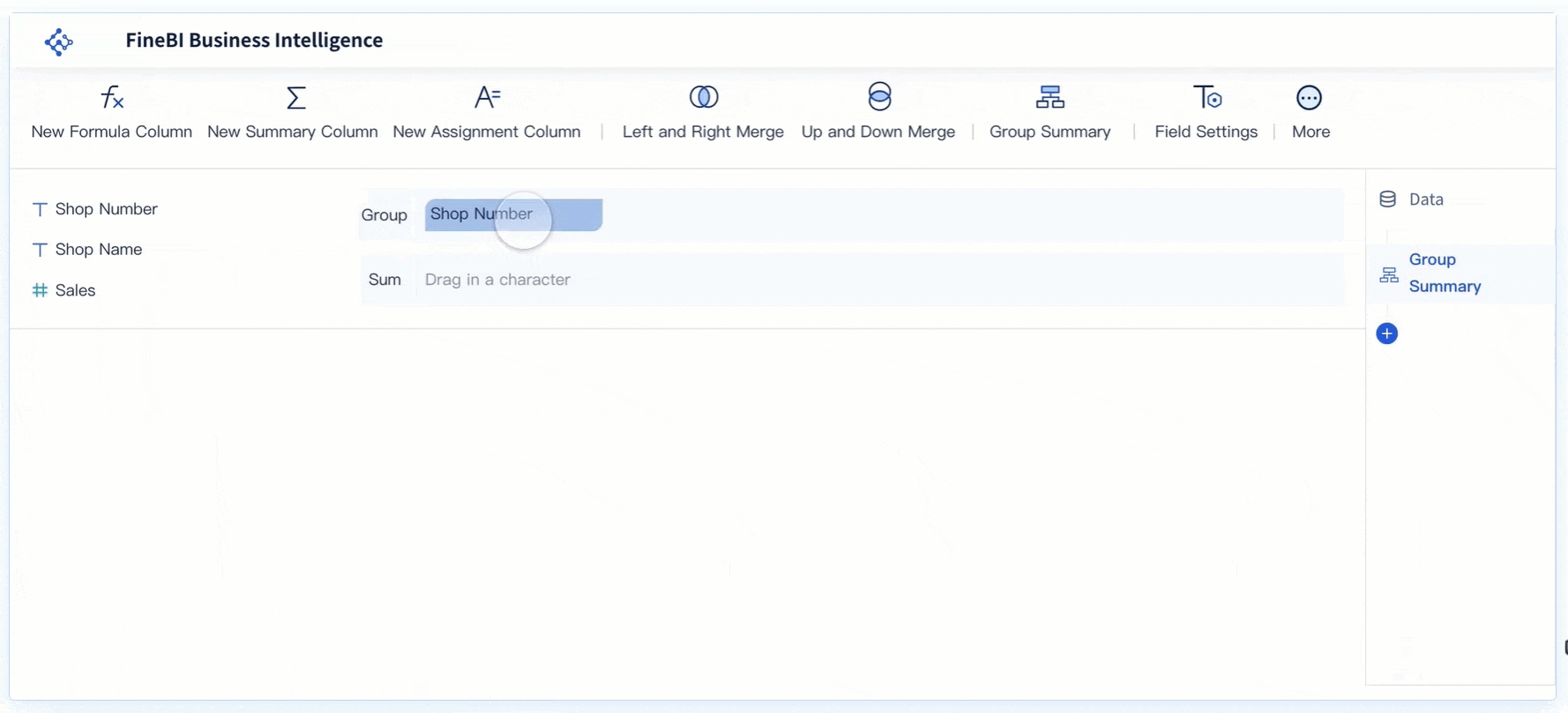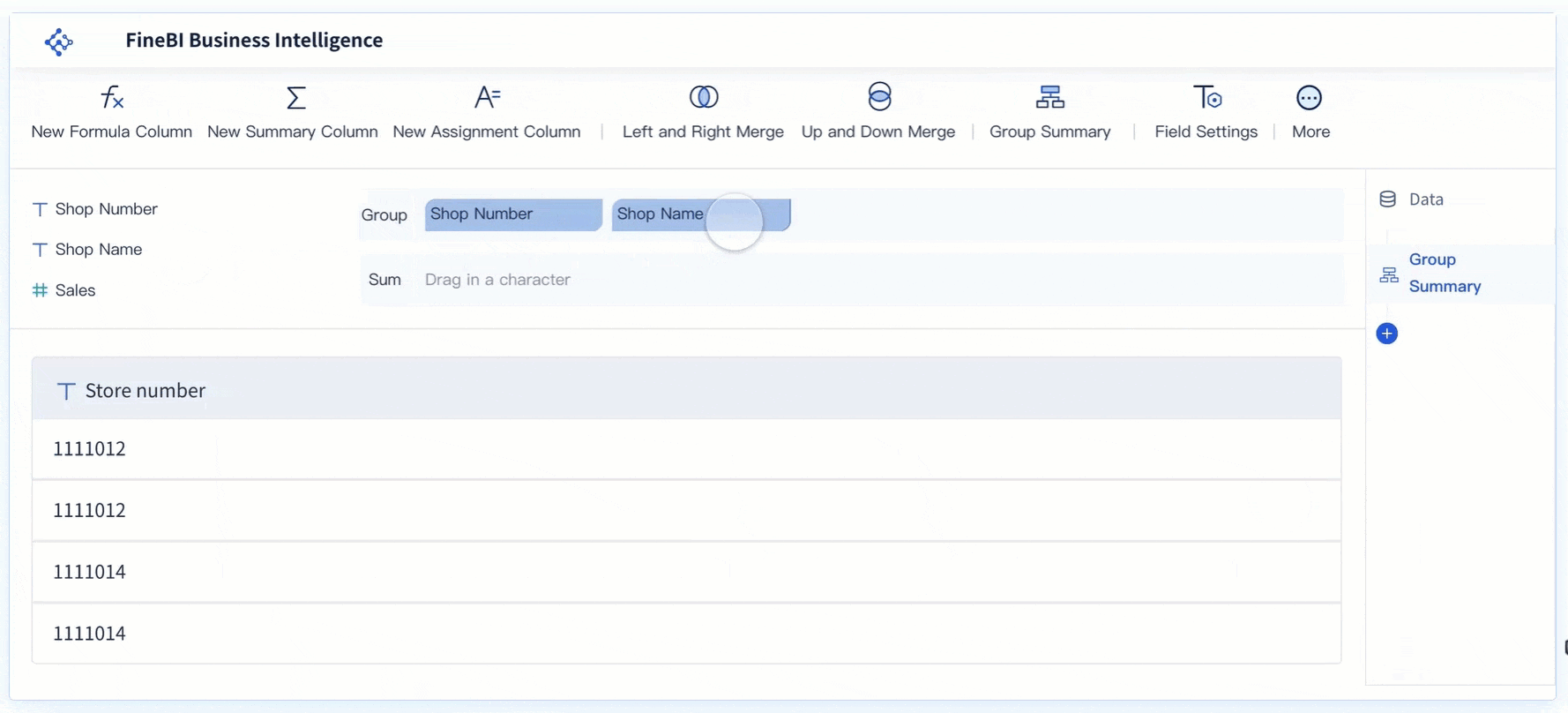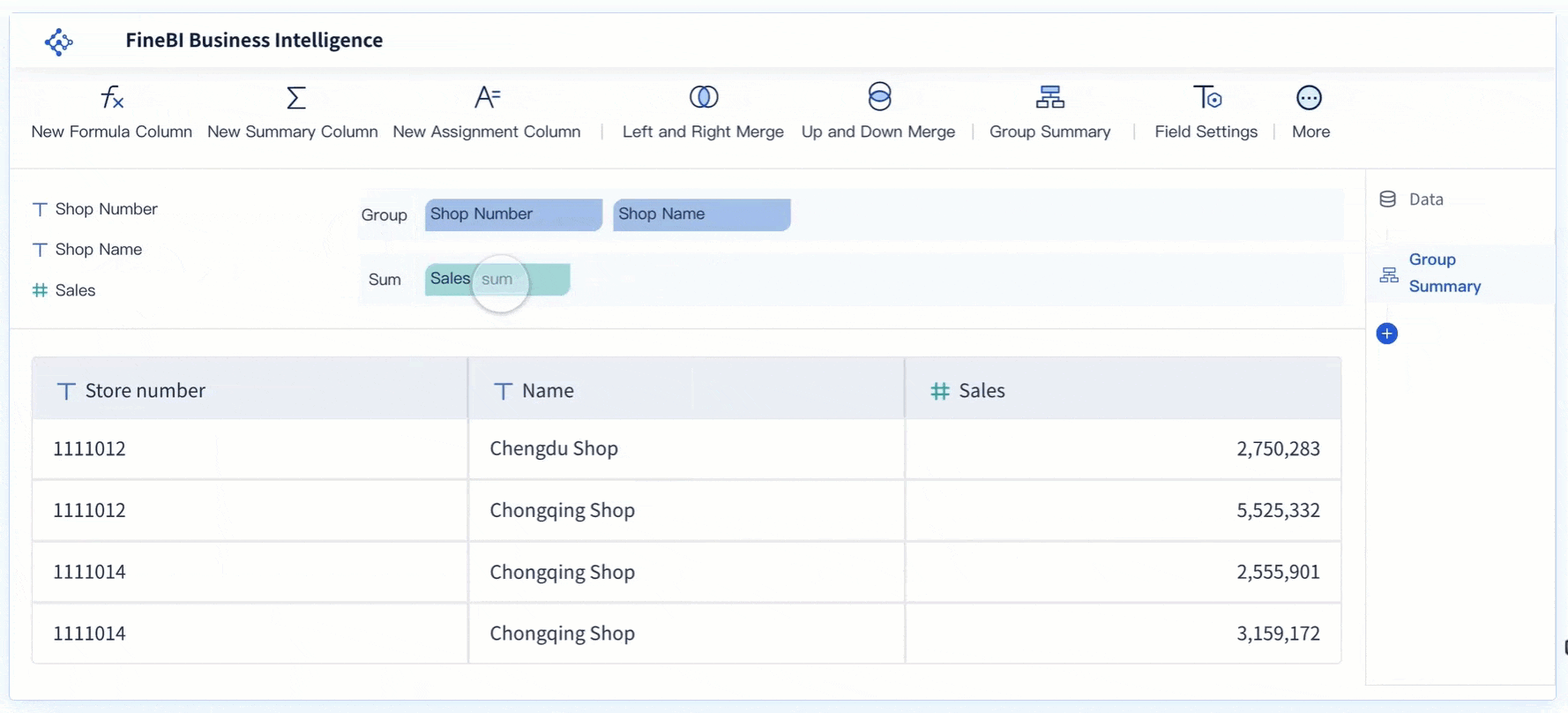
Retail Sector: FineBI enables retailers to dive deep into sales analytics, track inventory levels in real time, and gain insights into customer preferences. By visualizing sales trends and analyzing customer behavior, retailers can make informed decisions about inventory management and personalize marketing strategies to align with consumer demand. This not only helps in reducing stockouts or overstocking but also improves overall customer satisfaction and profitability.
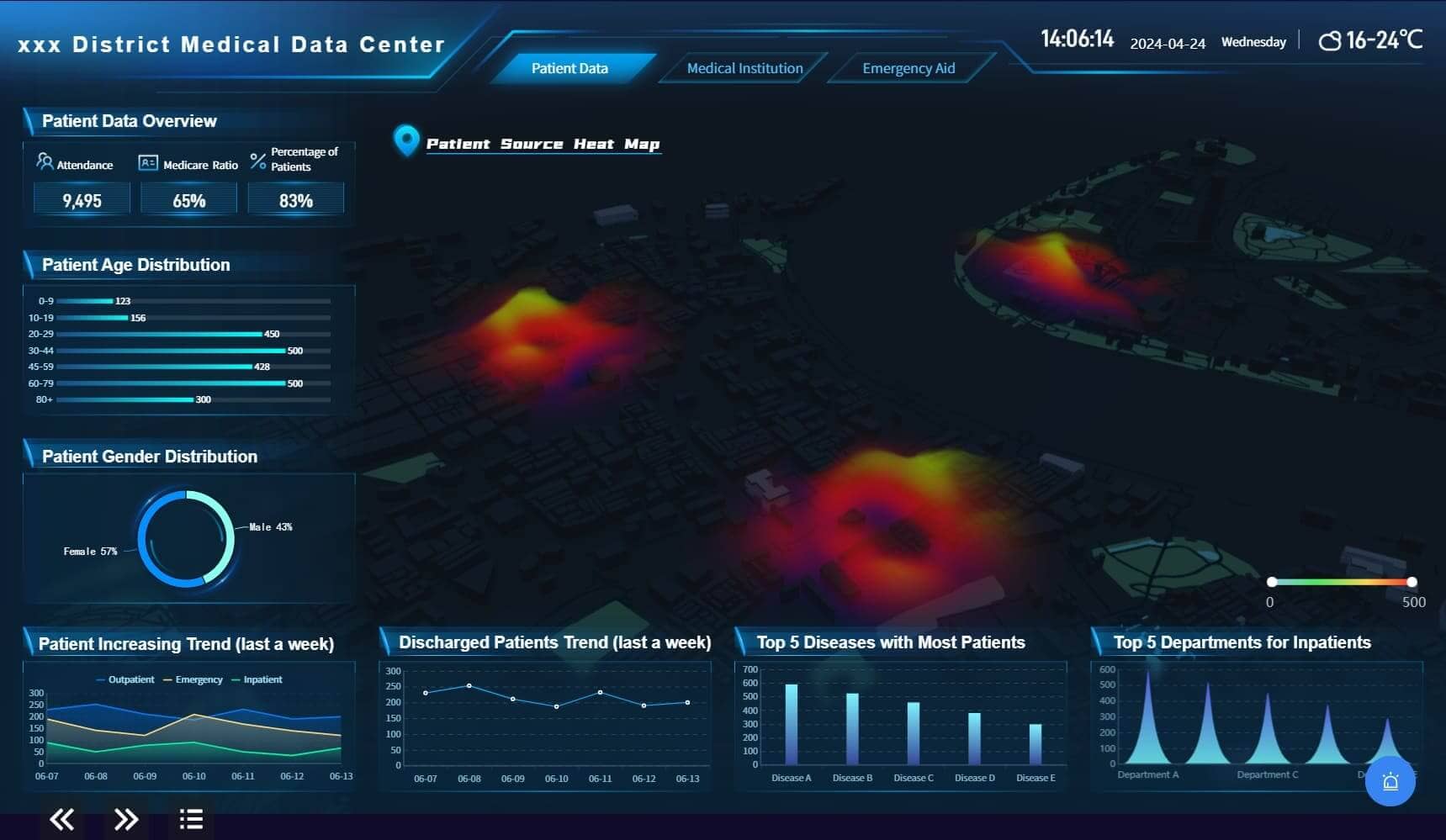
Healthcare: In the healthcare industry, FineBI supports hospitals and medical facilities in monitoring patient data, optimizing resource allocation, and improving service quality. By tracking key performance metrics such as patient outcomes and hospital efficiency, healthcare providers can enhance the quality of care while streamlining operations. FineBI also aids in identifying patterns in patient data that can be used to forecast demand for services, optimize staffing, and improve patient management.
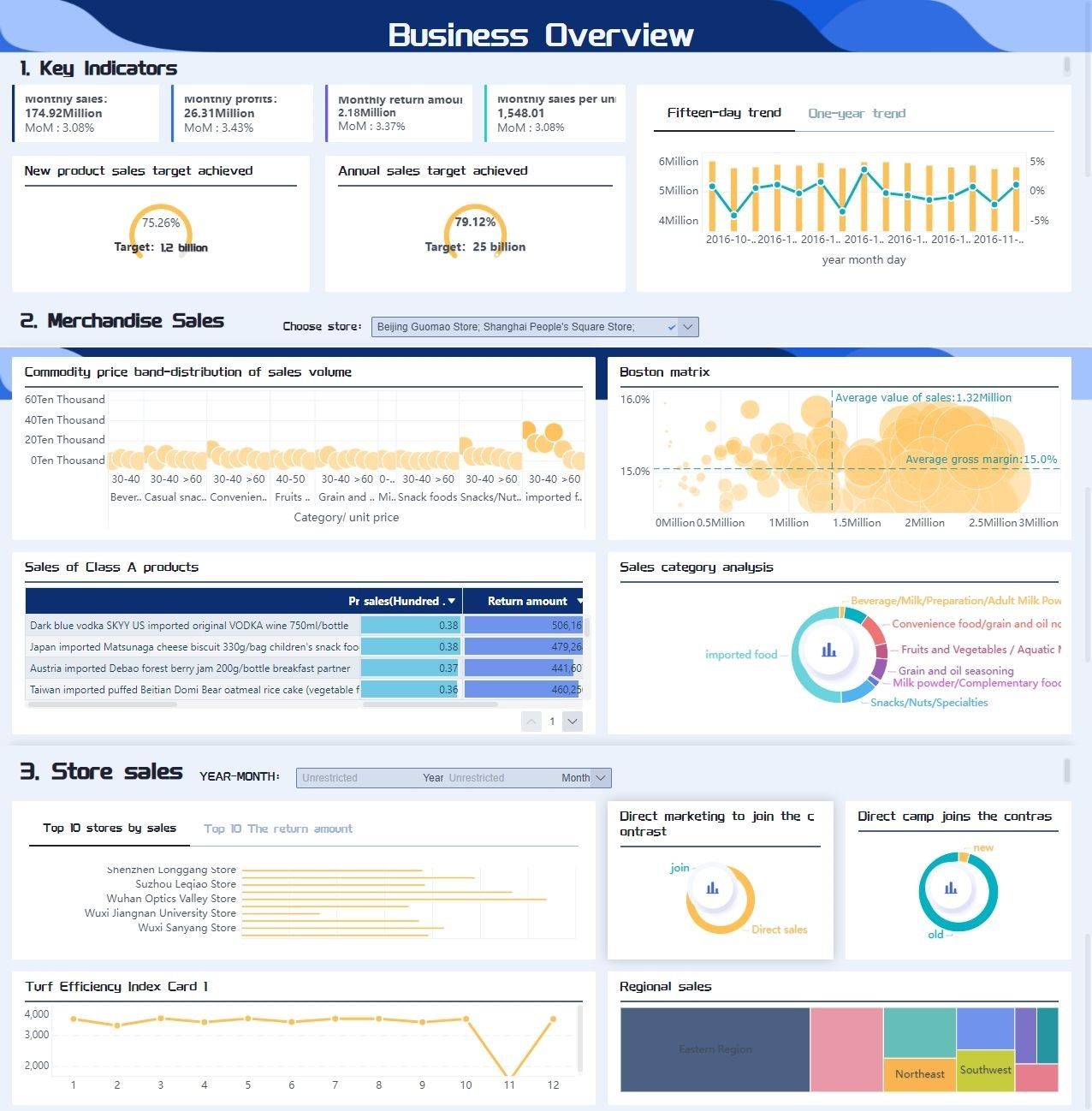
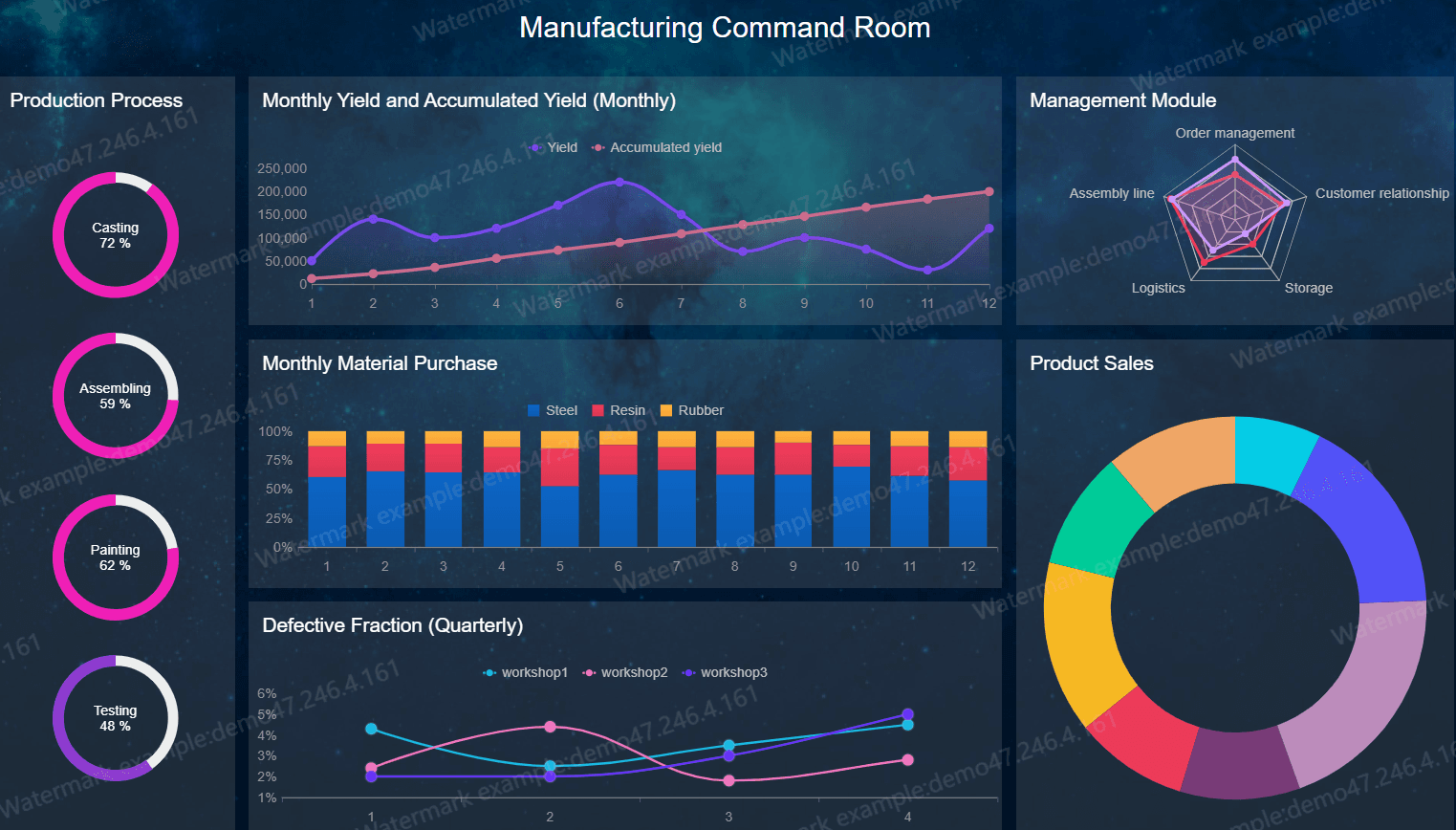
Manufacturing: Manufacturers rely on FineBI to closely monitor production processes, detect inefficiencies, and improve quality control. By analyzing data from various stages of production, manufacturers can identify bottlenecks, reduce waste, and optimize their workflows. This data-driven approach leads to higher productivity, better resource management, and ultimately, improved product quality and cost savings.
Finance: Financial institutions leverage FineBI for transaction analysis, risk assessment, and regulatory compliance. The platform helps identify fraudulent activities, optimize investment portfolios, and ensure that financial operations adhere to compliance standards. FineBI’s real-time reporting capabilities enable financial analysts to track key metrics like liquidity, risk exposure, and profitability, providing a solid foundation for strategic decision-making and risk management.
In all these sectors, FineBI’s ability to transform raw data into valuable insights empowers businesses to enhance their operations, minimize risk, and improve decision-making. By utilizing descriptive analytics, organizations can unlock the potential hidden within their data, leading to more accurate forecasts, efficient processes, and a competitive edge in the market.
FineBI has a profound impact on decision-making processes across various industries by transforming how organizations interpret and act on data. With its real-time data visualization and analysis capabilities, FineBI enables decision-makers to access up-to-the-minute insights, allowing them to respond swiftly and accurately to changing circumstances. The platform simplifies complex datasets into intuitive visual formats, making critical information accessible to stakeholders at all levels—from executives to frontline managers.
This accessibility ensures that informed decisions are made with confidence, grounded in clear, data-driven insights. By enhancing both the speed and accuracy of decision-making, FineBI not only improves operational efficiency but also cultivates a data-driven culture within organizations. This shift towards data-centric decision-making empowers businesses to stay competitive, adapt to market trends, and seize opportunities based on robust, actionable intelligence.
Descriptive analytics is fundamental to market research, providing businesses with crucial insights into consumer behavior and market dynamics. By leveraging this analytical approach, organizations gain a clearer understanding of their markets, allowing them to make data-backed decisions that drive growth and innovation.
Descriptive analytics enables market researchers to uncover emerging trends and patterns. By examining historical sales data, tracking social media interactions, and analyzing consumer feedback, companies can anticipate shifts in market demand. This foresight allows businesses to adapt their strategies proactively, keeping them ahead of competitors and positioning them to capitalize on new opportunities. The ability to spot trends early provides a competitive edge in fast-evolving industries.
Understanding consumer behavior is key to creating effective marketing strategies. Descriptive analytics offers a deep dive into customer preferences, purchasing habits, and demographic profiles. These insights allow businesses to segment their audiences more precisely, enabling the development of targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific customer groups. This tailored approach not only enhances customer engagement but also strengthens brand loyalty, leading to higher retention rates and increased lifetime value.
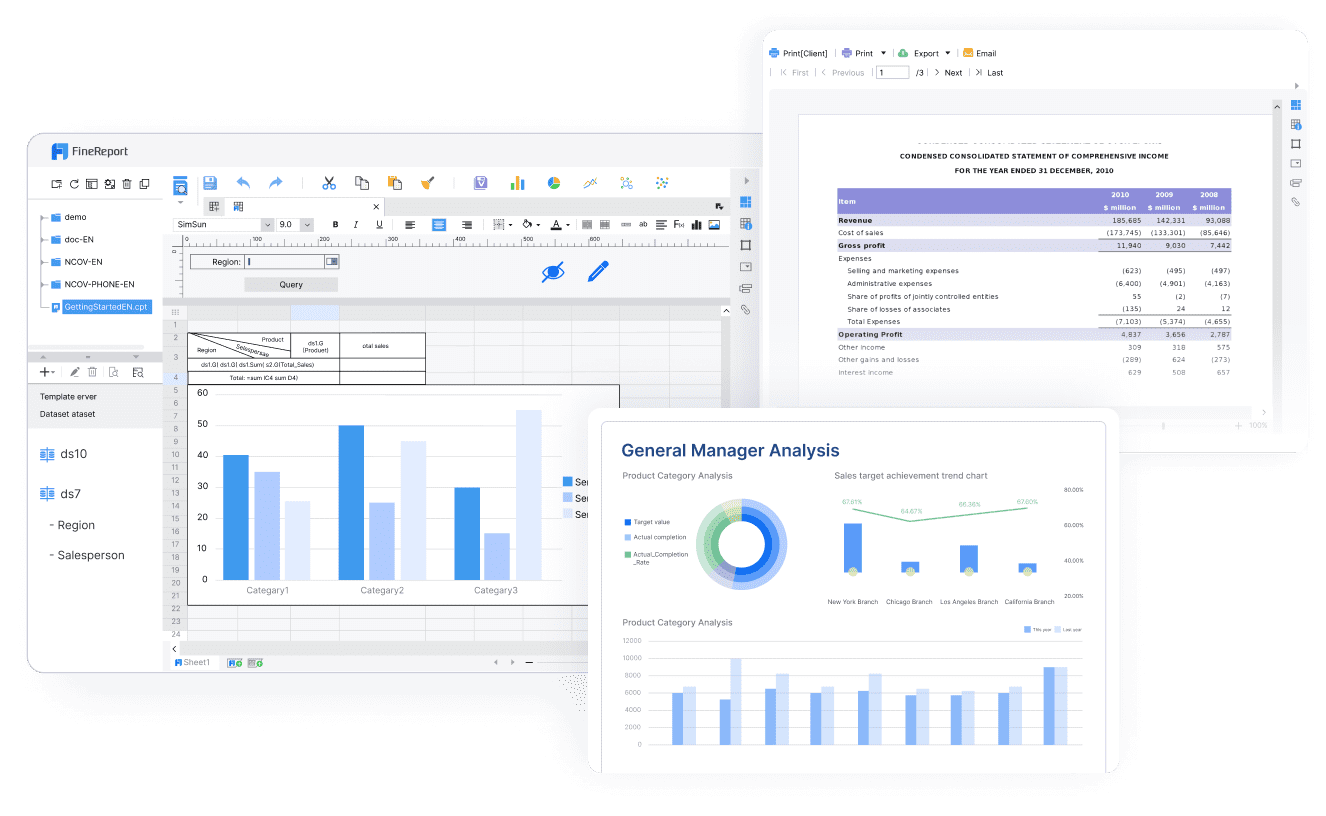
FanRuan's tools, FineReport and FineBI, play vital roles in market research applications. FineReport’s flexible report design and extensive visualization options allow businesses to craft detailed, easy-to-interpret reports that communicate insights clearly. Meanwhile, FineBI’s self-service analytics empower users to explore data independently, fostering a culture of data-driven decision-making. These tools collectively enhance the ability of organizations to transform raw data into actionable insights, improving decision-making and enabling more agile, informed strategies.
Descriptive analytics serves as a foundational tool in data analysis, but it is essential to understand how it compares to other forms of analytics. This section explores the differences and applications of descriptive analytics in relation to predictive and prescriptive analytics.
Descriptive analytics focuses on summarizing historical data to provide insights into past events. It answers the question, "What happened?" by using data aggregation and data visualization techniques. In contrast, predictive analytics aims to forecast future outcomes based on historical data patterns. It addresses the question, "What could happen?" by employing statistical models and machine learning algorithms.
"Predictive analytics is about understanding the future, while descriptive analytics is about understanding the past," says a data science expert.
Organizations should use descriptive analytics when they need to understand historical performance and identify patterns. It is ideal for generating reports and dashboards that summarize past data. FineReport excels in this area by offering flexible report design and diverse visualization options.
Predictive analytics becomes valuable when businesses want to forecast future trends and make proactive decisions. It is particularly useful in scenarios where anticipating customer behavior or market changes can provide a competitive advantage. FineBI supports predictive analytics by enabling users to explore data trends and patterns, facilitating informed decision-making.
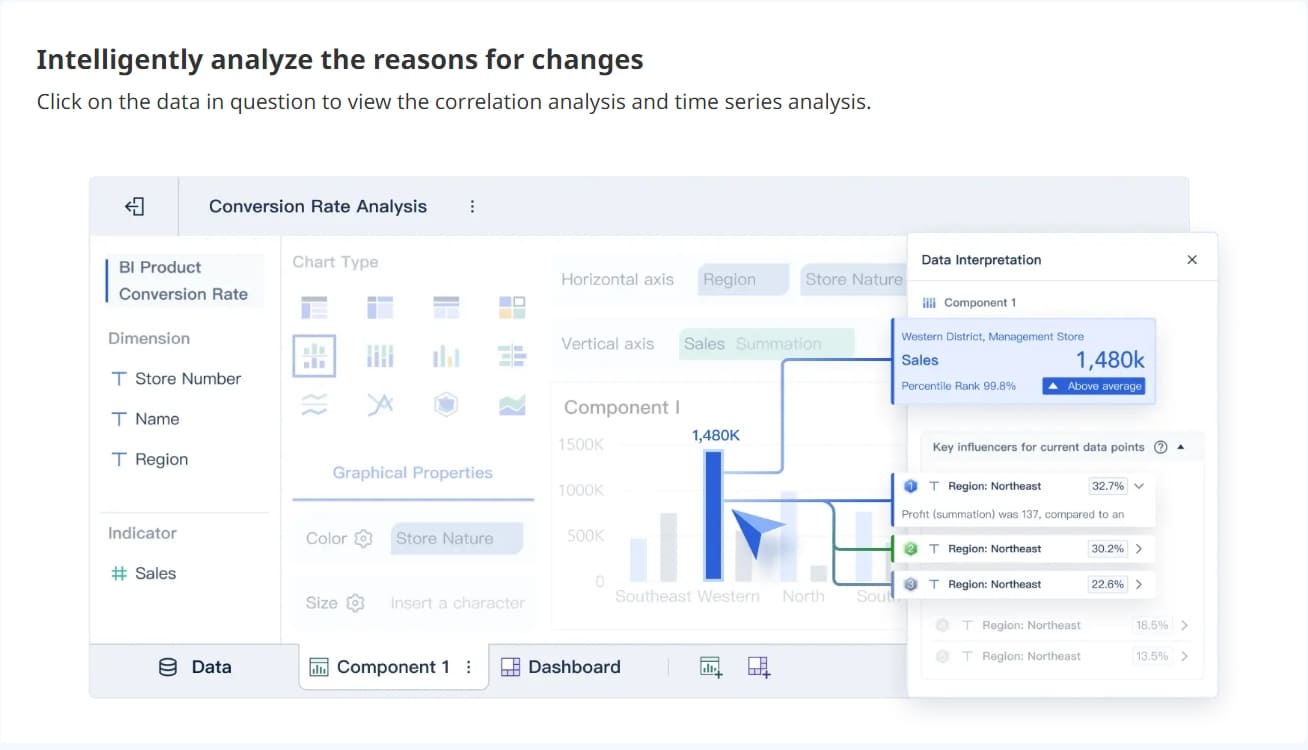
While descriptive analytics explains what has happened, prescriptive analytics goes a step further by recommending actions based on insights. It answers the question, "What should we do?" by analyzing data to suggest the best course of action.
"Prescriptive analytics not only predicts future outcomes but also suggests ways to achieve desired results," notes a business strategist.
Descriptive analytics is widely used in reporting and performance measurement. Businesses leverage tools like FineReport to create detailed reports that communicate insights clearly. FineBI enhances this process by allowing users to independently explore data and generate visual insights.
Prescriptive analytics finds applications in areas where decision-making is critical. It is used in supply chain optimization, resource allocation, and risk management. By analyzing data and recommending actions, prescriptive analytics helps organizations optimize operations and achieve strategic goals.
Descriptive analytics has proven its value in various industries through successful implementations. Netflix, for instance, utilizes descriptive analytics to identify trends in viewer preferences. By analyzing historical viewing data, Netflix determines which TV shows and movies are popular among different demographics. This insight influences their content creation, marketing strategies, and partnerships, ensuring they cater to audience demands effectively.
In the retail sector, companies analyze sales data to understand customer purchasing patterns. This analysis helps optimize inventory management, marketing strategies, and product assortment. Retailers can adjust stock levels based on consumer demand, reducing waste and increasing profitability. FineReport plays a crucial role in this process by providing flexible report design and diverse visualization options, enabling retailers to create detailed reports that communicate insights clearly.
From these implementations, businesses have learned the importance of asking clear questions with achievable answers. Descriptive analytics allows organizations to understand website users and evaluate marketing campaign performance. By leveraging tools like FineBI, businesses can independently explore data and generate visual insights, fostering a culture of data-driven decision-making. This approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also improves customer engagement and brand loyalty.
In the healthcare industry, hospitals use descriptive analytics to monitor patient data and manage resources. By analyzing historical patient outcomes, healthcare providers can improve service delivery and streamline operations. FineBI empowers healthcare professionals to visualize patient data, track key performance indicators, and identify areas for improvement.
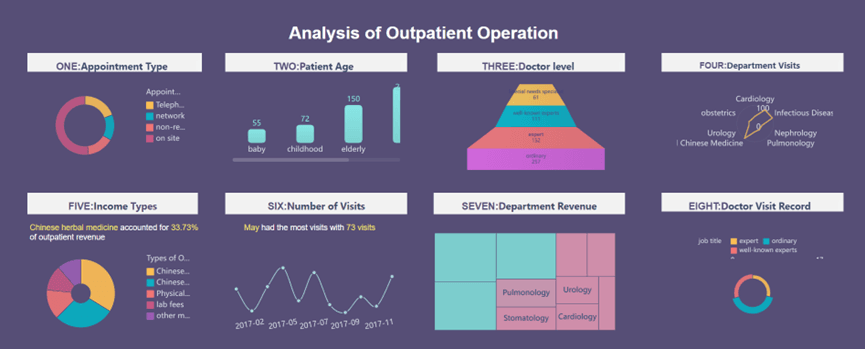
The manufacturing sector also benefits from descriptive analytics. Manufacturers monitor production processes to identify bottlenecks and improve quality control. By analyzing operational data, they enhance productivity and reduce waste. FineReport supports this process by offering robust tools for data visualization and reporting, enabling manufacturers to create detailed reports that highlight key insights.
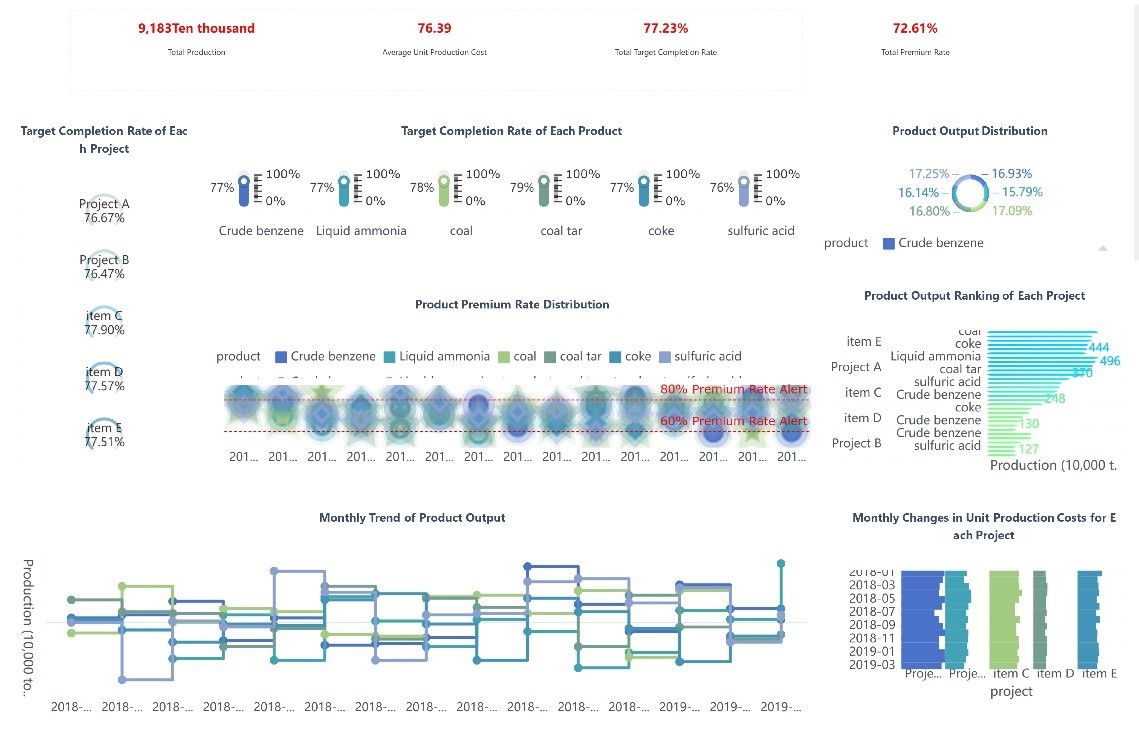
These industry-specific cases demonstrate the transformative power of descriptive analytics. In healthcare, improved patient outcomes and resource management lead to enhanced service delivery. In manufacturing, increased productivity and reduced waste contribute to operational efficiency. FineBI and FineReport play integral roles in these outcomes by providing user-friendly interfaces for data visualization and reporting. These tools facilitate the transformation of complex datasets into actionable insights, driving business growth and innovation.
Descriptive analytics offers valuable insights into historical data, yet it presents several challenges and limitations that organizations must navigate to maximize its effectiveness.
Data privacy remains a significant concern in descriptive analytics. Organizations collect vast amounts of data, often containing sensitive information. Ensuring this data's security and privacy is paramount. Analysts must adhere to strict data protection regulations to prevent unauthorized access and breaches. They must also balance the need for comprehensive analysis with the ethical obligation to protect individual privacy.
Descriptive analytics focuses on summarizing past events, which limits its scope. It does not predict future outcomes or provide reasons for observed patterns. This limitation can hinder organizations from adopting more advanced analytical techniques that offer proactive insights. Descriptive analytics serves as a foundational tool, but relying solely on it may prevent businesses from exploring predictive or prescriptive analytics, which can drive strategic growth.
Organizations can overcome the limitations of descriptive analytics by adopting several strategies:

The future of descriptive analytics lies in its integration with more advanced techniques. As technology evolves, organizations will increasingly leverage AI and machine learning to enhance descriptive analytics. These advancements will enable businesses to derive deeper insights from historical data, paving the way for more informed decision-making. Additionally, the focus on data ethics will grow, ensuring that organizations gather and interpret information accurately and fairly.
Descriptive analytics often raises questions among those new to the field. Here are some frequently asked questions that provide clarity and understanding.
Descriptive analytics involves analyzing historical data to understand past events. It summarizes data to identify patterns and trends, offering a clear picture of what has happened. This type of analytics serves as a foundation for more advanced analytics, such as predictive and prescriptive analytics.
Descriptive analytics follows a structured process:
Descriptive analytics offers several advantages:
Businesses use descriptive analytics to summarize past events and report general trends. It plays a crucial role in areas like market research, where it helps identify connections between variables and trends. By analyzing survey and focus group data, businesses can gain insights into consumer behavior and preferences.
Descriptive analytics finds applications across various sectors:
Descriptive analytics provides tangible benefits by asking well-formulated questions with clear, achievable answers. It supports performance evaluation and enhances reporting capabilities, facilitating better communication within and outside the organization.
Several tools support descriptive analytics:
Descriptive analytics continues to evolve, offering organizations a solid foundation for understanding past events and driving informed decision-making. As data generation increases, its importance and applications will only grow.
Descriptive analytics serves as a cornerstone in data analysis, offering businesses insights into past performance and operational effectiveness. By summarizing and visualizing data, it enables easy understanding and interpretation, facilitating informed decision-making. As technology advances, the future of descriptive analytics will likely involve integration with predictive and prescriptive analytics, enhancing its value. Businesses can leverage these insights to drive strategic growth and optimize operations. In conclusion, descriptive analytics remains an indispensable tool for organizations aiming to understand historical trends and make data-driven decisions.

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles

Self-Service Analytics Defined and Why You Need It
Self-service analytics lets you analyze data without IT help, empowering faster, data-driven decisions and boosting agility for your business.
Lewis
Jan 04, 2026

Best Self-Service Tools for Analytics You Should Know
See which self-service tools for analytics let business users access data, build dashboards, and make decisions faster—no IT help needed.
Lewis
Dec 29, 2025

Understanding Predictive Analytics Services in 2026
Predictive analytics services use data and AI to forecast trends, helping businesses make informed decisions, reduce risks, and improve efficiency in 2026.
Lewis
Dec 30, 2025