You interact with digital resources every day. Administrative metadata helps you manage these resources by recording key details such as creation date, modification date, file size, format, and access rights. This metadata gives you control and clarity over your files, making it easier to track changes and maintain resource integrity. By using administrative metadata, you improve the efficiency and reliability of your digital resource management.
You rely on metadata management to organize, access, and protect your digital resources. Administrative metadata plays a central role in this process. It works alongside descriptive metadata to give you a complete picture of your digital assets. While descriptive metadata helps you identify and locate resources by providing titles, authors, and subjects, administrative metadata focuses on the technical and operational details that keep your files usable and secure.
The table below shows how different types of administrative metadata support metadata management:
| Type of Administrative Metadata | Description |
|---|---|
| Technical Metadata | Details about the file's creation, quality control, and access control. |
| Preservation Metadata | Information necessary for the long-term preservation of the resource. |
| Rights Metadata | Data regarding the rights management and licensing of the resource. |
You use these types of metadata to ensure your files remain accessible, authentic, and protected. In large-scale repositories, administrative metadata works with descriptive metadata to make digital assets easy to find and retrieve. The following table highlights how each type contributes to metadata management:
| Type of Metadata | Description |
|---|---|
| Technical Metadata | Information about the technical aspects of the asset, such as file type, size, creation date, etc. |
| Rights Metadata | Details about intellectual property rights, including licensing information and copyright status. |
| Preservation Metadata | Information necessary for archiving and long-term preservation, such as source and authenticity. |
By combining administrative metadata with descriptive metadata, you create a robust metadata management system that supports both discovery and long-term stewardship of your digital resources.
Administrative metadata has a direct impact on the preservation of your digital assets. You need to know who owns the data, who can access it, and how long you should keep it. Administrative metadata provides this crucial information. It documents data ownership, access permissions, and retention policies. This information helps you maintain data accessibility over time and ensures you follow legal and organizational rules.
You can see the importance of administrative metadata in data preservation through these points:
Preservation metadata, a type of administrative metadata, captures essential information that supports long-term digital preservation actions. It includes provenance information, rights management, and technical details necessary for maintaining the usability of preserved digital objects. Northwestern University Libraries emphasizes the creation of preservation metadata to sustain digital preservation efforts.
Administrative metadata, which encompasses critical details like creation date, format, and access rights, plays a vital role in preserving records. It ensures that files are not only discoverable but also interpretable over time, thereby significantly reducing the risk of data loss or corruption.
You face increasing demands for compliance and security in digital environments. Administrative metadata helps you meet these demands. It creates a tamper-proof history of your digital assets, which legal teams can use to authenticate evidence and ensure the integrity and chain of custody. Compliance officers benefit from this metadata because it simplifies verification during regulatory checks and audits.
Administrative metadata also supports your security efforts. IT managers can quickly identify unauthorized actions or security breaches by reviewing metadata records. Maintaining accurate and up-to-date metadata is crucial for compliance and security. Regular reviews of data governance policies help you incorporate new metadata requirements during audits. Metadata audits ensure compliance and help eliminate potential liabilities, such as data leakage or unauthorized use. Evaluating metadata can identify areas for improvement, enhancing system performance and compliance.
Note: You should always keep your metadata management practices current. This approach helps you protect your digital assets and meet regulatory requirements.
By focusing on administrative metadata, you strengthen your overall metadata management strategy. You ensure your digital resources remain secure, compliant, and accessible for years to come.

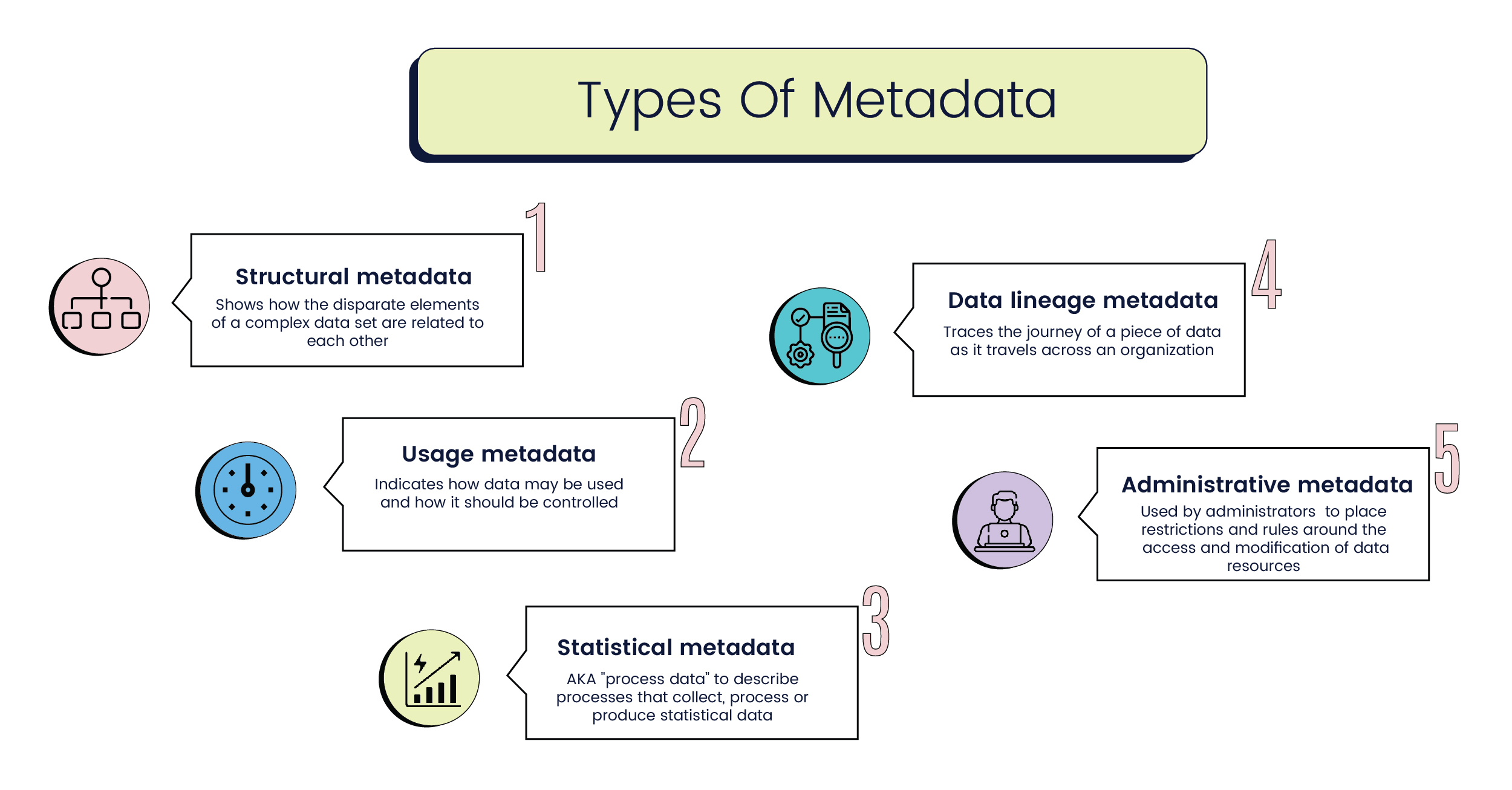
You encounter different types of metadata when you manage digital resources. Understanding these types of metadata helps you organize, preserve, and use your files effectively. Administrative metadata includes several categories, each serving a unique purpose. You also work with structural metadata, which connects different parts of a digital object and supports navigation.
Preservation metadata helps you keep digital resources safe and usable over time. You use this type of metadata to record important details about the history, authenticity, and rights of your files. Preservation metadata answers questions like who created the file, what changes have been made, and what actions you need to take to keep the file accessible.
| Key Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Provenance | Tracks who has owned or managed the digital object. |
| Authenticity | Confirms if the digital object is genuine. |
| Preservation activity | Records actions taken to preserve the digital object. |
| Technical environment | Lists what is needed to use the digital object. |
| Rights management | Details intellectual property rights for the digital object. |
Preservation metadata supports the longevity and authenticity of your digital resources. It provides technical and administrative details that help you maintain files for the long term.
Provenance metadata tracks the history and ownership of your digital assets. You rely on this type of metadata to verify where your data came from and how it has changed. Provenance metadata creates a documented trail that shows the origin, modifications, and custody of your files.
You use provenance metadata to build trust in your digital assets. It helps you confirm that your files are accurate and reliable.
Technical metadata describes the technical details of your digital files. You use this type of metadata to understand file formats, media types, and source information. Technical metadata is essential for interoperability between systems and for transforming files when needed.
| Technical Metadata Element | Description |
|---|---|
| File Format Information | Explains the structure and encoding of the file. |
| Media Specific Information | Lists attributes like resolution or codecs for media files. |
| Source Information | Documents where the data came from. |
Technical metadata helps you migrate and transform digital files. It provides the information you need to load, access, and convert data across different systems. You also use technical metadata to support structural metadata, which organizes and connects parts of your digital objects.
Note: You should always combine administrative metadata with structural metadata and other types of metadata. This approach gives you a complete view of your digital resources and supports effective management.
You need rights metadata to manage digital resources responsibly. This type of metadata records who owns a file, what you can do with it, and how you can share or reproduce it. Rights metadata protects your organization from legal risks and helps you respect intellectual property.
You use rights metadata to answer important questions about your digital assets. Who holds the rights? What are the usage restrictions? Can you share or modify the resource? Rights metadata gives you clear answers and helps you avoid unauthorized use.
The table below shows the core components of rights metadata:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Rights Management | Information about rights held in and over the resource. |
| Intellectual Property Rights | Details regarding intellectual property rights, copyright, and property rights. |
| Rights Holder Information | Contact information for rights holders and specification of rights holder entities. |
| Rights Management Statement | A statement that may include accessibility, reproduction rights, and securing permissions for use. |
You rely on rights metadata to ensure compliance with legal standards. This metadata provides critical details about ownership, usage rights, and restrictions. You can protect intellectual property and manage the distribution of digital content effectively. When you tag your digital assets with rights metadata, you create a clear record of usage rights and copyright permissions. This practice supports efficient rights management and reduces the risk of unauthorized usage.
Rights metadata also helps you maintain transparency in your organization. You can track who owns each asset and what permissions exist. This information supports audits and helps you respond to legal inquiries quickly.
If you want to streamline rights metadata management, you can use a data integration platform like FineDataLink. FineDataLink helps you organize, synchronize, and tag your digital assets with accurate metadata. You can automate metadata workflows and ensure that your rights metadata stays up to date across all systems.
Tip: Always review your rights metadata regularly. This habit helps you stay compliant and protects your organization from legal challenges.
You see administrative metadata at work in many industries. Libraries use metadata to track digital collections, ensuring each file remains accessible and authentic. Hospitals rely on metadata to manage patient records, supporting privacy and compliance. Businesses use metadata to organize documents, making it easier for teams to find and understand information.
A well-defined metadata strategy helps you protect sensitive data and maintain compliance with privacy regulations. You can measure the impact of administrative metadata by checking data quality, regulatory adherence, and workflow efficiency. Metadata management is vital for meeting regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. You gain accountability for your data assets and can demonstrate legal compliance.
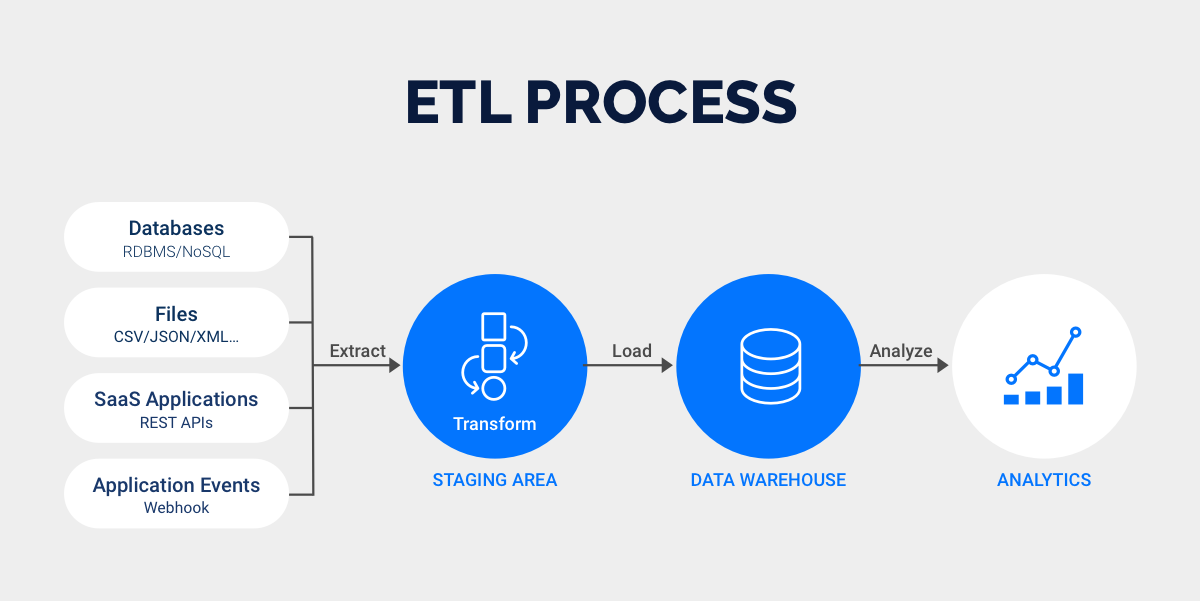
You can streamline metadata management using FineDataLink. This platform supports real-time data synchronization across more than 100 data sources, including SaaS applications, databases, and cloud environments. You benefit from a low-code, drag-and-drop interface that simplifies complex ETL tasks. FineDataLink enables quick API creation without coding, which boosts integration efficiency.
FineDataLink helps you automate metadata workflows, maintain consistency, and enhance data governance. You can ensure that metadata remains accurate and up to date across all systems.
NTT DATA Taiwan used administrative metadata to build a unified data platform. The company integrated backend systems like ERP, POS, and CRM using ETL processes. This approach allowed businesses to visualize data and provide role-specific insights for decision-making. Employees gained the ability to perform self-service analysis, improving operational efficiency and supporting data-driven strategies. Administrative metadata played a key role in ensuring data integrity, compliance, and accessibility throughout the organization.

You may encounter several challenges when managing administrative metadata. Inconsistent metadata formats and terminologies often create confusion and make it difficult to search for information. Errors or missing details in metadata can lead to misclassification of digital assets and reduce trust in your data. Fragmented systems disrupt workflows and lower the value of your enterprise data.
You might also face issues such as missing relationships between metadata elements, which makes it hard to track data lineage. Solutions built by non-metadata professionals can result in poorly defined fields. The lack of consistent standards increases implementation and maintenance costs. Choosing inadequate tools for managing metadata can expose sensitive information and make it harder to control access.
When you do not address these issues, you risk having scattered, duplicated, or outdated digital assets. This disorganization wastes resources and creates security vulnerabilities. In fields like sustainable development, poor metadata management can cause the loss of valuable insights and harm data integrity.
You can overcome these challenges by following best practices for metadata management. Start by assigning a dedicated metadata administration team. This team will develop and coordinate your metadata processes. Define a clear metadata strategy that aligns with your data goals and outlines responsibilities.
Standardization ensures that everyone uses the same language and structure for metadata. Using a dedicated tool, such as FineDataLink, helps you collect and use metadata efficiently. FineDataLink supports real-time synchronization and automation, making it easier to maintain accurate metadata across all systems.
You should measure your success by tracking key performance indicators like accuracy, access frequency, and support for business processes. Strong governance and continuous improvement help you maintain high-quality metadata and support your organization’s goals.
You have seen that administrative metadata forms the backbone of effective digital resource management. It supports tasks like resource management, archiving, and rights administration. You benefit from metadata because it adds context, improves understanding, and streamlines your work.
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Data Governance | You gain a structured approach to managing data assets. |
| Improved Compliance | You can track data lineage and enforce policies. |
| Increased Data Security | You classify and protect sensitive information. |
When you prioritize metadata management, you set your organization up for long-term success. FineDataLink gives you the tools to automate and maintain high-quality metadata, making your data management more reliable and secure.
Enterprise Data Integration: A Comprehensive Guide
What is enterprise data and why does it matter for organizations
Understanding Enterprise Data Centers in 2025
Enterprise Data Analytics Explained for Modern Businesses

The Author
Howard
Engineer Data Management & Ahli Data Research Di FanRuan
Related Articles
What is a data management platform in 2025
A data management platform in 2025 centralizes, organizes, and activates business data, enabling smarter decisions and real-time insights across industries.
Howard
Dec 22, 2025

Top 10 Database Management Tools for 2025
See the top 10 database management tools for 2025, comparing features, security, and scalability to help you choose the right solution for your business.
Howard
Dec 17, 2025

Best Data Lake Vendors For Enterprise Needs
Compare top data lake vendors for enterprise needs. See which platforms offer the best scalability, integration, and security for your business.
Howard
Dec 07, 2025