The main difference between a chart vs graph comes down to how you display and understand your data. You use a chart to organize information visually, often to compare parts or show categories. In contrast, you use a graph to illustrate relationships or trends, especially how things change over time. Understanding this distinction helps you select the right tool for clear communication and avoids common mistakes, such as assuming all charts are interchangeable or that more detail always leads to better understanding. FineBI makes it easy for you to choose and create the best visual for your needs, helping you share insights quickly and accurately.

You use charts to turn numbers and facts into pictures that make sense at a glance. A chart is a visual tool that helps you organize and present information clearly. When you look up the difference between charts and graphs, you will see that charts often show categories, parts of a whole, or comparisons. Charts make it easier for you to spot patterns, trends, and outliers in your data. You do not need to be a data expert to understand charts. They help you see the story behind the numbers.
Many types of charts exist, each with its own best use. Here is a table that shows some of the most common chart types and when you might use them:
| Chart Type | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|
| Line chart | Trend analysis, time series data, comparing multiple data series |
| Bar chart | Comparing categories, ranking items, frequency distribution |
| Stacked bar chart | Comparing categories with multiple subdivisions |
| Column chart | Comparing categories, ranking items, frequency distribution |
| Pie chart | Showing relative proportions, highlighting parts of a whole |
| Donut chart | Similar to pie charts, but with a hole in the middle |
| Box plot | Comparing distributions, understanding data spread |
| Dual axis chart | Comparing different data types, highlighting trends |
| Bubble chart | Showing multivariate data, visualizing trends and patterns |
| Funnel chart | Visualizing sales or marketing funnels, conversion analysis |
| Heatmap | Pattern recognition, correlation analysis, risk assessment |
| Gantt chart | Project planning, task scheduling |
Charts help you in many daily situations.
FineBI gives you powerful tools to create and use charts with ease. You do not need coding skills to build clear and attractive charts. Here is how FineBI supports you:
| Feature Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Chart Variety | You can choose from many chart types, such as column, line, and pie charts, for different needs. |
| Customization | FineBI lets you adjust colors, sizes, and labels to make your charts stand out. |
| Dashboard Creation | You can combine charts and other components into a dashboard for a complete view. |
| Intuitive Charts | FineBI offers easy-to-use chart options for all skill levels. |
| Custom Chart Options | You can create combination charts for flexible data exploration. |
| Dashboard Functionality | FineBI helps you organize charts so you can spot key issues at a glance. |
With FineBI, you can turn raw data into clear, useful charts in minutes. This makes it simple for you to share insights and make informed choices. When you understand the difference between charts and graphs, you can pick the right visual for your message and audience.

You use graphs to show how things relate to each other or how they change over time. When you search online, you will find that graphs help you turn numbers into pictures that reveal patterns, trends, and relationships. Unlike charts, graphs often focus on showing connections between data points. You can use graphs to make sense of complex information quickly. Your brain processes visual data faster than reading tables or lists, so graphs help you spot important details at a glance.
Many types of graphs exist, each with a special purpose. Here are some of the most common types you will see in science and business:
You can use these graphs to answer questions like, “How did sales change this year?” or “Is there a link between study time and test scores?” Each type of graph gives you a different way to look at your data.
You use graphs in many parts of your daily life. In school, teachers use graphs to show class performance or attendance. At work, you might use graphs to track sales, monitor project progress, or compare results from different teams. When you look at the news, you often see graphs that explain trends in the economy or health statistics. Graphs make it easier for you to turn raw data into insights you can act on. They help you see patterns, spot outliers, and understand relationships that might not be obvious from numbers alone.
Analyzing Relationship Patterns: Look for patterns in your graph to gain insights and identify trends. Patterns like clusters, bridges, and outliers can reveal important information about the structure and behavior of your data.
FineBI gives you powerful tools to create and explore graphs, even if you have no technical background. You can use the drag-and-drop interface to build graphs without writing any code. FineBI processes your data in real time, so your graphs always show the latest information. You can prepare your data easily with built-in tools, making it simple to get your graphs ready for analysis. FineBI works on your computer and mobile devices, so you can view and share graphs anywhere. The in-memory computing engine keeps your graphs fast and responsive, even with large datasets. With FineBI, you can turn complex data into clear, interactive graphs that help you make better decisions.
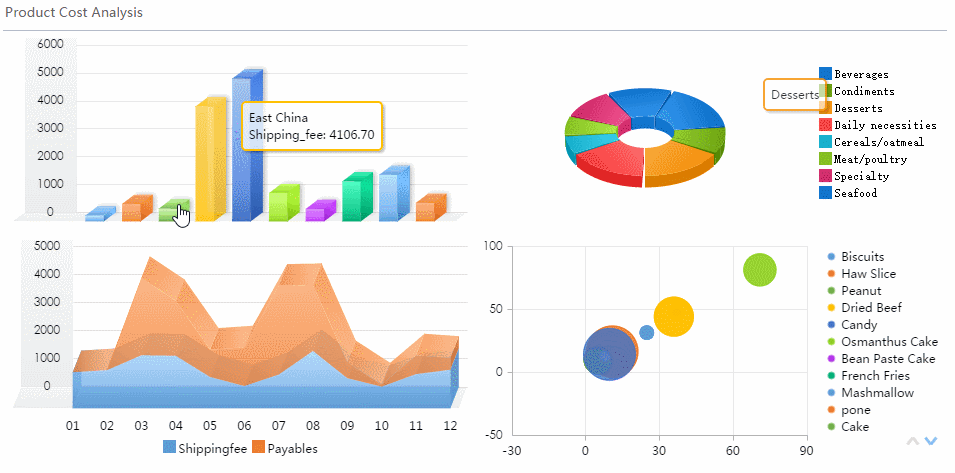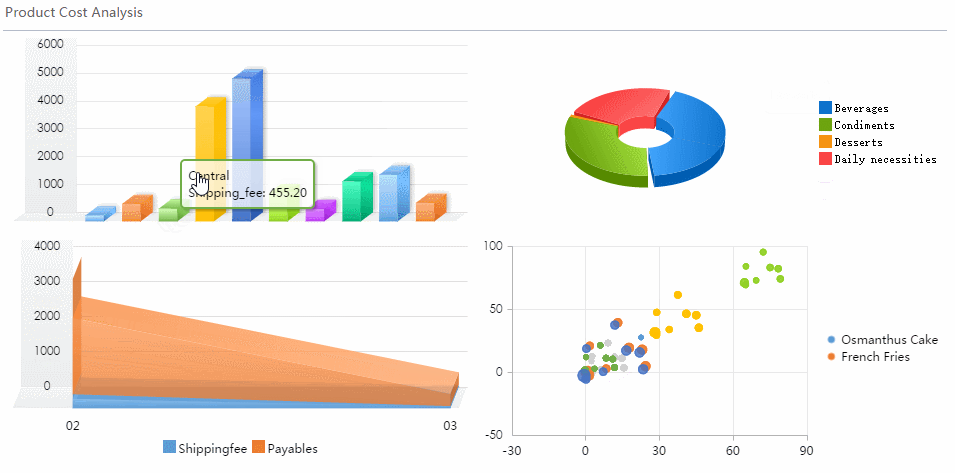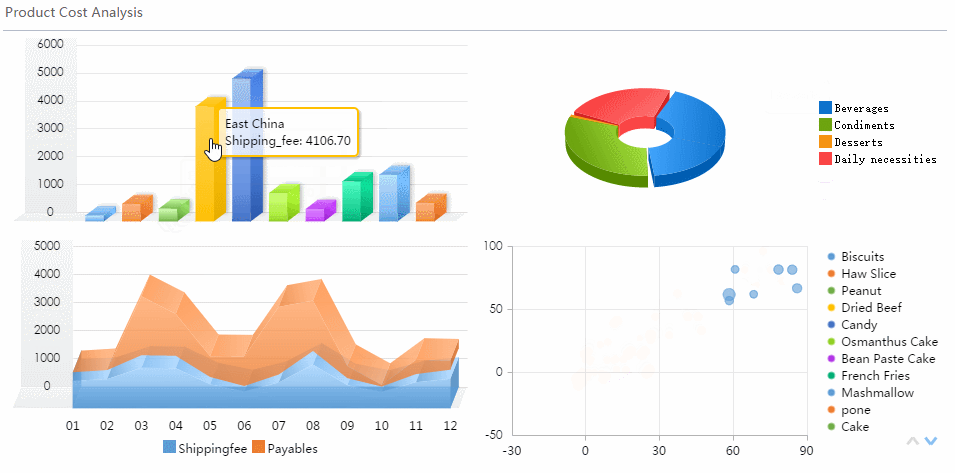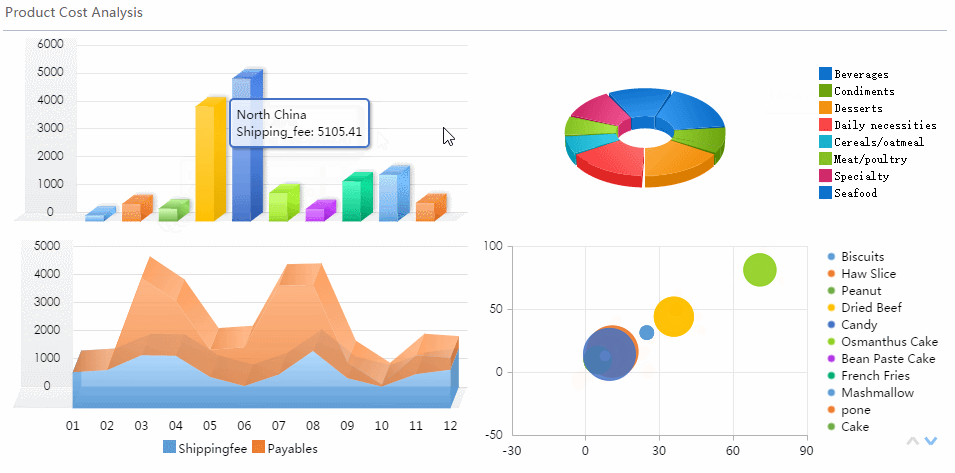
You often wonder about the difference between charts and graphs when choosing how to present your data. The table below helps you see the main distinctions at a glance. You can use this as a quick reference when deciding which visual tool fits your needs.
| Feature | Charts | Graphs |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | You can represent both numbers and categories. | You usually visualize numbers and relationships. |
| Types | You use pie charts, bar charts, column charts, and more. | You often use line graphs, scatter plots, and histograms. |
| Axes | You may see categories on one axis and numbers on the other. | You see data points plotted on x and y axes. |
| Purpose | You organize and compare information visually. | You show how things change or relate over time. |
| Visual Focus | You highlight categories, proportions, or comparisons. | You focus on trends, patterns, and relationships. |
| Context | You use charts for quick insights in business or daily life. | You use graphs for deeper analysis in academic or technical settings. |
You need to understand the difference between charts and graphs to choose the right visual for your message. Here are the main distinctions explained in simple terms:
Tip: When you choose between a chart vs graph, think about your audience and your goal. If you want to compare categories or show proportions, use a chart. If you want to reveal trends or relationships, use a graph.
You can see that the difference between charts and graphs is not just about how they look. It is about how you use them to communicate information clearly and effectively.
Choosing between a chart or a graph can feel confusing. You want your data to be clear and easy to understand. Here are some practical tips to help you decide:
Experts recommend that you keep your visualizations simple. Avoid clutter and information overload. Choose the most effective chart type for your data.
When you understand the difference between graphs and charts, you can select the best tool for your message. Charts work well for comparing categories or showing proportions. Graphs help you reveal trends, patterns, or relationships.
You need to match your data type to the right visual. This step makes your information clear and meaningful. Here is a table to guide your choice:
| Data Type | Recommended Visualization |
|---|---|
| Continuous Data | Line charts |
| Categorical Data | Bar charts |
| Large Datasets | Scatter plots |
| Small Datasets | Pie charts |
Ask yourself what you want to show:
When you know the difference between graphs and charts, you can answer these questions and pick the right visual.
FineBI helps you choose and create the best visual for your data. You do not need technical skills to use FineBI. The platform guides you through each step:
FineBI recommends the best chart or graph based on your data type. For continuous data, you can use line charts to show trends. For categories, bar charts help you compare groups. If you have a large dataset, scatter plots reveal patterns. FineBI’s workflow makes it easy to match your data to the right visual.
You can preview your charts before sharing them. FineBI’s dashboard lets you organize multiple charts and graphs for a complete view. You can apply filters and customize styles to highlight key insights.
When you use FineBI, you avoid common mistakes. You do not need to worry about the difference between graphs and charts. FineBI’s smart recommendations and intuitive design help you communicate your message clearly.
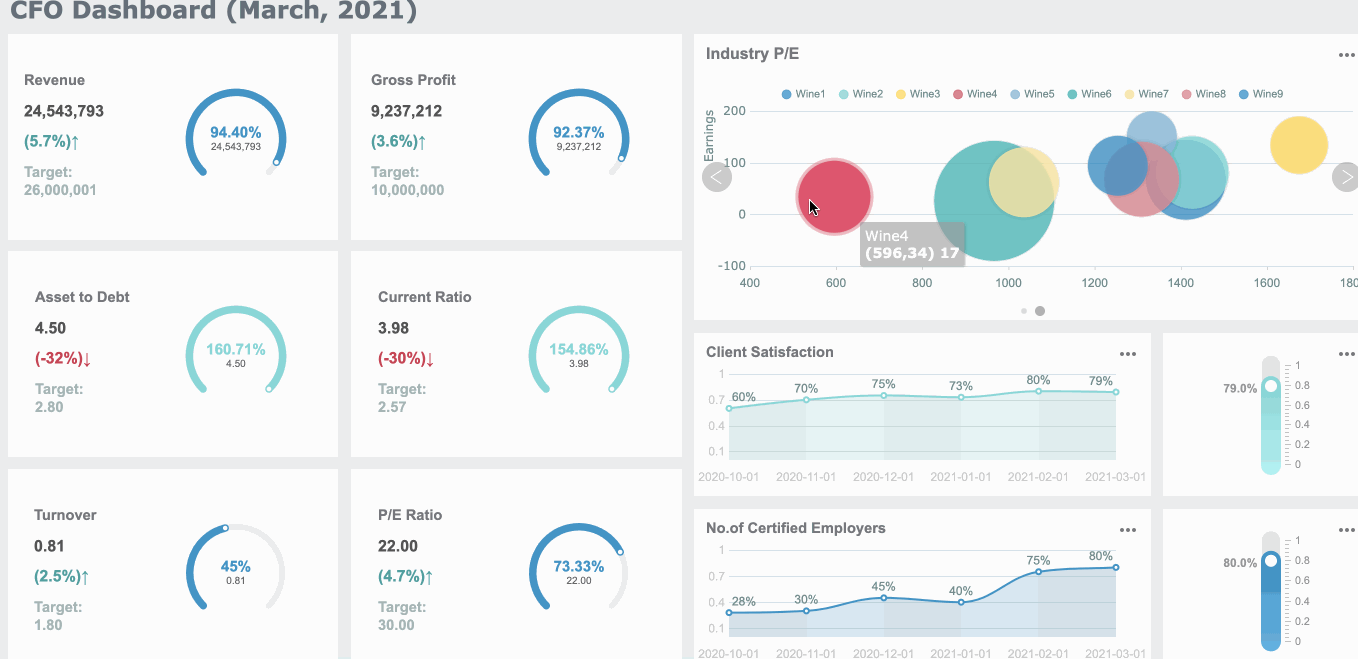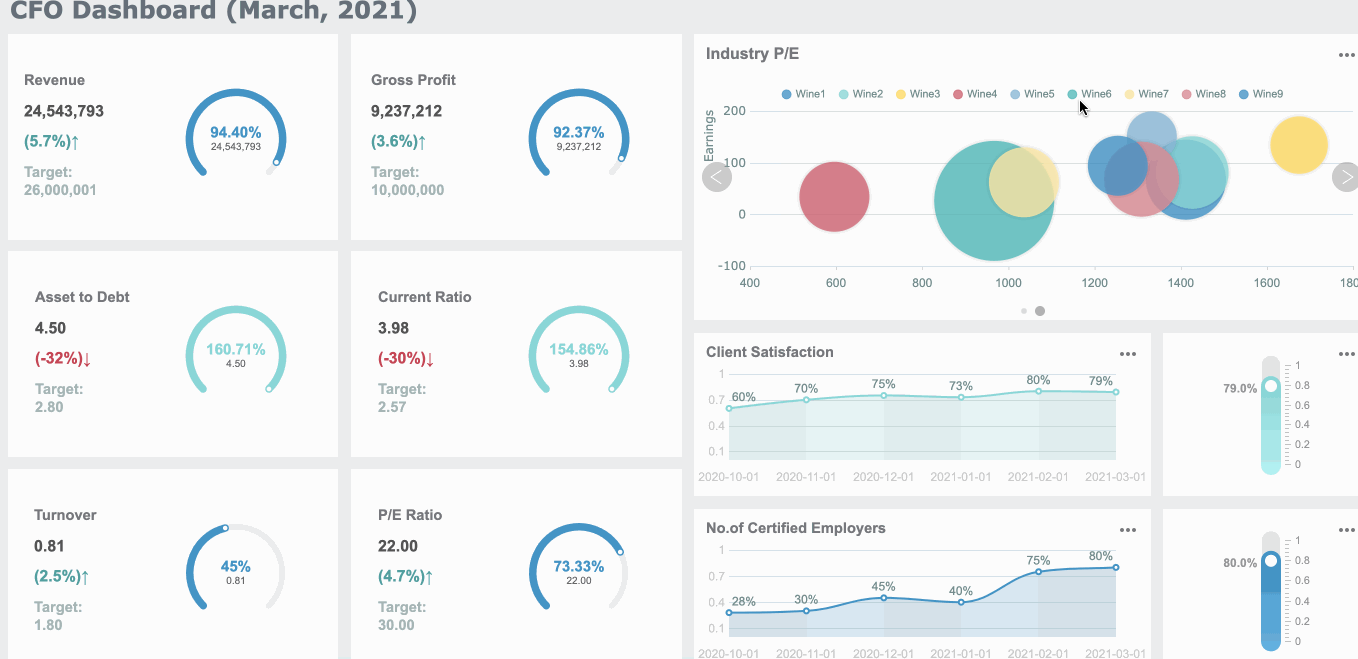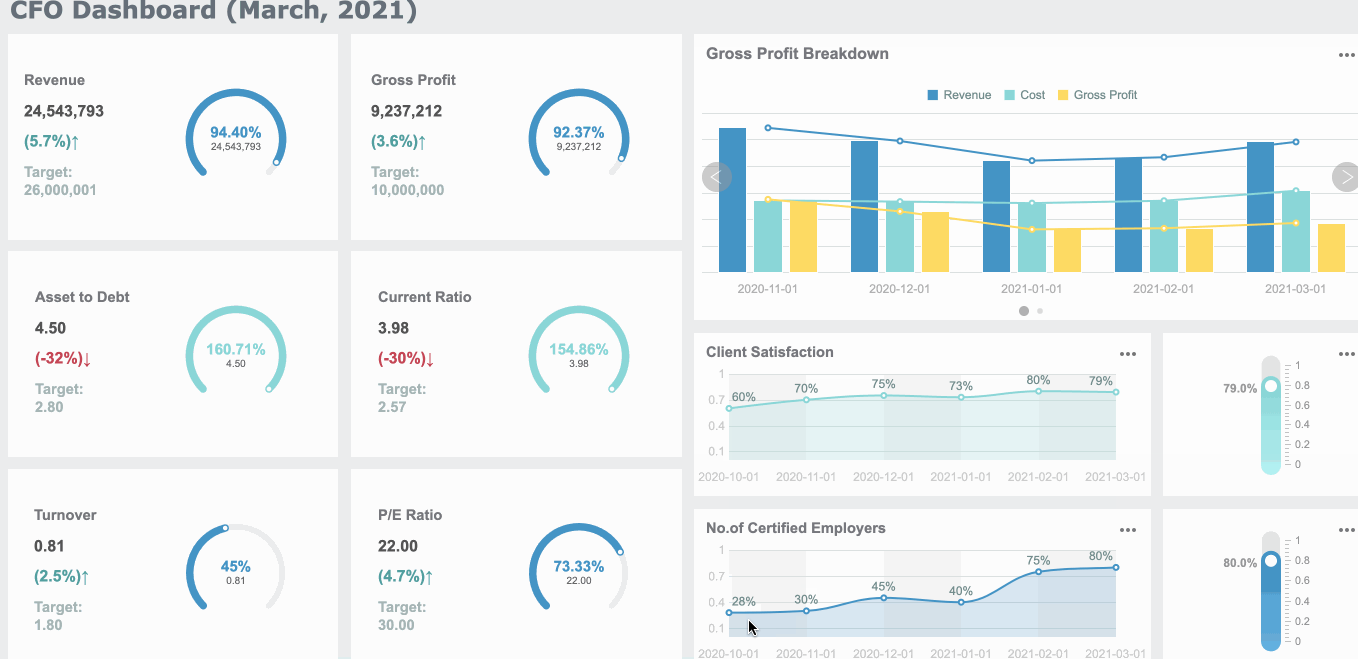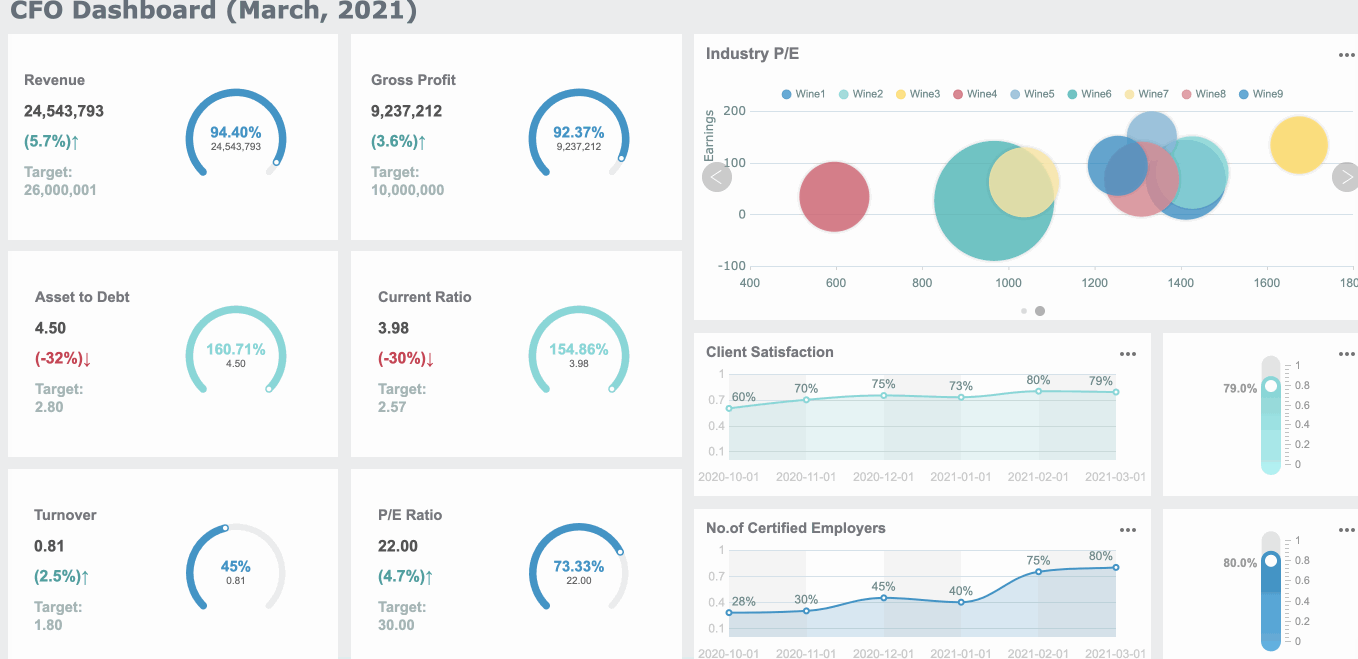
You want to understand your spending habits. You collect data from your bank statements and receipts. You organize this information into categories like groceries, rent, and entertainment. You use charts to see where your money goes each month. Bar charts help you compare spending across categories. Pie charts show the proportion of each expense. These visual representations of data make it easy to spot patterns and identify unnecessary costs. You can reduce expenses by seeing which categories take up the most money. When you use graphs, you track changes in your spending over time. Line graphs reveal trends, such as rising utility bills or decreasing grocery costs. FineBI lets you create these visuals quickly. You drag and drop your data, choose the best chart or graph, and see your financial health at a glance.
Charts and graphs help you organize expenses, compare financial items, and support better decision-making for long-term planning.
| Benefit of Charts for Tracking Expenses | Description |
|---|---|
| Shows Spending Patterns | Helps you identify where money is spent. |
| Aids in Cost Reduction | Visualisation highlights unnecessary costs. |
| Comparison of Financial Items | Enhances understanding of overall financial health. |
You manage a small business and want to track sales performance. You use time series charts to see how sales change month by month. Line graphs show trends and help you spot seasonal patterns. Bar charts let you compare sales across products or regions. You break down sales data to find what drives growth. FineBI makes this process simple. You connect your sales data, select the right visualisation, and analyze results in real time. You see clear directional indicators, which help you make quick decisions. You can share dashboards with your team and improve meeting efficiency.
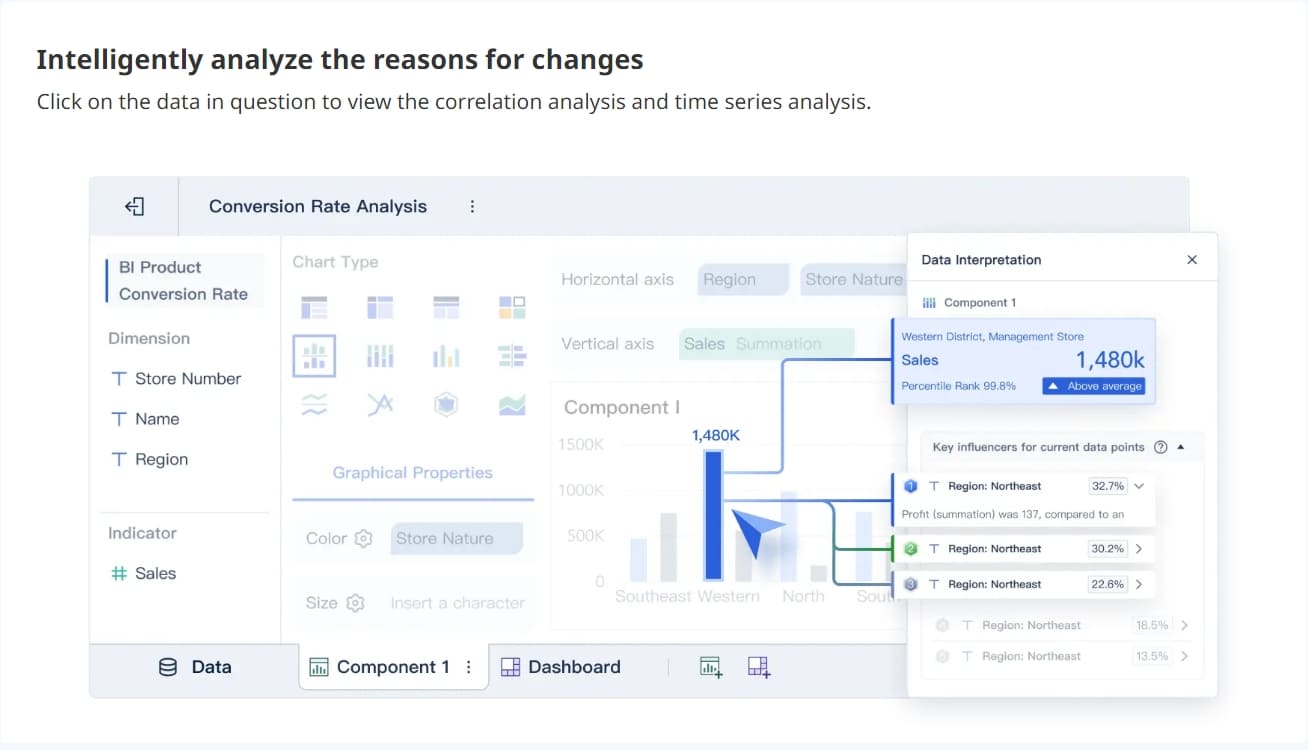
You conduct a survey to understand customer preferences. You collect responses and want to present the results clearly. You use bar graphs to compare answers across different groups. Pie charts show how many people chose each option. Line graphs highlight changes in opinions over time. These visual representations of data help you reveal insights that raw numbers cannot show. FineBI guides you to select the best chart type for your survey data. You visualize trends, compare results, and share findings with your team.
| Chart Type | Effectiveness in Presenting Survey Results |
|---|---|
| Bar Graph | Best for comparisons and showing relationships between data sets. |
| Pie Chart | Best for showing parts of a whole in specific cases. |
| Line Graph | Ideal for highlighting trends over time. |
| Venn Diagram | Useful for showing relationships and overlaps. |
Charts and graphs are great at presenting insights, comparing data, or highlighting trends. They use visuals to help you see patterns, relationships, and key insights at a glance.
FineBI streamlines your workflow for every scenario. You connect to your data sources, prepare your data, and create visualisation dashboards with ease. You use interactive visualizations to enhance meeting efficiency. Advanced data preparation tools let you focus on insights, not data management. Integrated collaboration features help your team share knowledge and improve decision-making. FineBI supports both charts and graphs, so you always choose the best data representation for your needs. You see the difference between charts and graphs in action, making your business analysis faster and more effective.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Interactive Visualizations | Real-time analytics for meetings and decisions. |
| Advanced Data Preparation | Simplifies complex data handling. |
| Integrated Collaboration Tools | Improves teamwork and knowledge sharing. |
The main difference between charts and graphs is that charts help you organize and compare categories, while graphs show relationships and trends over time. To choose the right visual for your data, follow these steps:
FineBI makes it easy for you to create clear visuals and share insights. Try FineBI today and discover how simple data analysis can be.

Bar Chart Race: A Complete Guide
16 Types of Chart for Effective Data Visualization
22 Different Types of Graphs in Data Visualization: A Practical Guide

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles

Top 8 Data Visualization softwares You Should Try in 2025
Compare the top 8 data visualization software for 2025, including FineReport, Tableau, Power BI, and more to find the best fit for your business needs.
Lewis
Dec 19, 2025
10 Must-Have Data Visualization Tools for Modern Businesses
Compare the top 10 data visualization tools for 2025 to boost business insights, streamline analytics, and empower smarter decision-making.
Lewis
Dec 17, 2025

7 Leading Big Data Visualization Tools for the Year Ahead
Compare the top big data visualization tools for 2025 to find advanced analytics, scalability, and interactive dashboards for your business.
Lewis
Dec 17, 2025