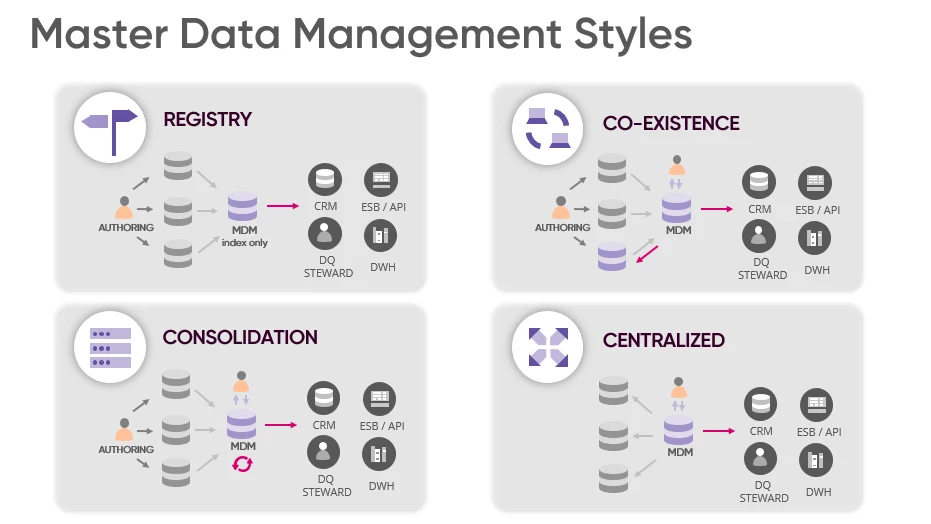
You face four main MDM implementation styles: Registry, Consolidation, Coexistence, and Centralized. Each style manages master data differently, affecting how you integrate systems and control data. Registry links records across sources, while Consolidation gathers master data into a single view. Coexistence lets systems share and update master data, and Centralized stores all master data in one hub. Selecting the right style for your master data management helps you overcome integration complexities, governance issues, and scalability concerns. FineDataLink gives you flexible support for any MDM implementation, helping you match solutions to your organization’s data landscape.

Understanding the main MDM implementation styles and their key differences helps you choose the best approach for your organization. Each style offers a unique way to manage master data and integrate systems. You can see the formal definitions and distinguishing characteristics in the table below:
| Implementation Style | Definition | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Registry | Acts as a central reference point for master data definitions without storing actual data. | Low risk, Scalability | One way updates, Limited control, Decentralized governance |
| Consolidation | MDM platform acts as a hub for data from multiple sources, creating a golden record. | High data quality, Improved reporting, Reduced redundancy | Mostly used for analysis, Potential disruption, Limited flexibility |
| Coexistence | Central MDM hub alongside existing source applications with bi-directional synchronization. | Phased implementation, Flexibility, Improved data quality | Increased complexity, Potential data inconsistencies, Higher costs |
| Centralized | MDM hub is the single source of truth for all master data, with all updates occurring within it. | Maximum control, Improved data governance, Streamlined reporting | Significant disruption, High implementation costs, Reduced flexibility |
You use registry style mdm when you want a central reference for master data without moving or storing the actual data. This style links records across different systems using unique identifiers. You keep data in its original source, which lowers risk and increases scalability. You get limited control over updates, and governance remains decentralized. Registry style mdm works well for organizations with many systems that need to connect data but do not want to disrupt existing processes.
Consolidation style mdm gathers master data from multiple sources into a central hub. You create a golden record for analysis and reporting. This style improves data quality and reduces redundancy. You mostly use it for reporting and analytics, not for operational updates. You may face some disruption during implementation, and flexibility can be limited. Consolidation style mdm suits organizations that want better insights from their master data but do not need real-time updates.
Coexistence style mdm lets you synchronize master data between a central hub and existing source systems. You get bi-directional updates, so changes in one system reflect in others. This style offers flexibility and phased implementation. You improve data quality while keeping legacy systems active. You may encounter increased complexity and higher costs. Coexistence style mdm fits organizations that want to modernize master data management without replacing all systems at once.
Centralised style mdm stores all master data in a single hub. You make all updates in this central system, which becomes the only source of truth. You gain maximum control, strong governance, and streamlined reporting. You may face significant disruption and higher costs during implementation. Centralised style mdm works best for organizations that need strict control and unified management of master data.
FineDataLink supports integration needs for all these mdm implementation styles. You can use its real-time synchronization, ETL/ELT capabilities, and low-code interface to build efficient master data management solutions that match your chosen implementation style.
You often choose the Registry style when you want to connect master data across many systems without moving the actual data. This implementation style uses indexing and cataloging to link records, which means you keep data in its original source. You benefit from lower disruption and faster implementation, especially if your organization needs quick wins or operates in sensitive environments like healthcare or finance. You maintain decentralized control, which works well if you want each department to own its data.
Here is a summary of the Registry style’s features and use cases:
| Key Features | Advantages | Challenges | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indexing records | Lower disruption to existing systems | Less control over data quality | Organizations needing quick wins without overhauling IT |
| Decentralized model | Faster implementation compared to centralized | Integration complexity can grow over time | Sensitive data environments (e.g., healthcare, finance) |
| Catalogue approach | Good for decentralized data ownership scenarios | Reporting relies on multiple sources |
You see Registry style used in industries such as food service manufacturing, business services, healthcare, and financial services. For example, a food service manufacturer gained visibility weeks after an acquisition, while a healthcare provider reduced onboarding time by streamlining credentialing. Financial institutions use Registry style to automate compliance and minimize errors.
FineDataLink helps you implement Registry style by providing real-time data synchronization and flexible ETL/ELT capabilities. You can link records across systems quickly, even when you need to maintain data in its original location.
You select the Consolidation style when you want to create a single source of truth for master data without changing your source systems. This implementation style gathers data from multiple sources into a central hub, cleanses and matches it, and produces high-quality data for analytics and reporting. You benefit from cost-effective and quick setup, since you do not need to modify existing systems.
Key features and benefits of Consolidation style include:
| Feature/Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Consolidation | Multiple data sources are integrated into the MDM hub. |
| Data Stewardship | Human oversight ensures data accuracy through cleansing. |
| Cost-Effective | No changes required on source systems, quick to implement. |
| High-Quality Data | Reliable data warehouse for analytics and reporting. |
Organizations like Red Wing Shoes and IBM have adopted Consolidation style to improve operational efficiency, data accuracy, and customer experiences. You see this style in companies that want better reporting and compliance without disrupting their IT landscape.
FineDataLink supports Consolidation style by enabling you to integrate data from over 100 sources, automate ETL/ELT processes, and build a reliable master data management system for analytics.
You use the Coexistence style when you want to synchronize master data between a central hub and existing systems. This implementation style blends features of both Registry and Consolidation, allowing you to keep legacy systems active while sharing and updating master data across platforms. You gain flexibility and can phase your implementation, which helps you adapt to changing business needs.
The Coexistence style supports both centralized and decentralized master data management. You benefit from data consistency, synchronization, and distribution. This style fits organizations that want to modernize their master data management system gradually, without replacing all systems at once.
FineDataLink's real-time synchronization and low-code integration make it easy for you to implement Coexistence style. You can keep your existing systems running while ensuring master data stays consistent and up to date.
You choose the Centralized style when you need maximum control and consistency for master data. This implementation style creates a central repository that acts as the single source for all master data attributes. You ensure accurate data across all applications and processes, which simplifies governance and compliance.
| Feature/Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Centralized Repository | Central source for all master data attributes. |
| Maximum Control and Consistency | Ensures accurate master data across all applications. |
| Improved Data Governance | Simplifies governance and compliance practices. |
| Streamlined Reporting | Single source for comprehensive analytics and reporting. |
| Complete and Accurate Data | Maintains data integrity and supports advanced security policies. |
| High Implementation Costs | Requires significant investment and integration. |
| Significant Disruption | Major changes to IT infrastructure and business processes. |
Highly regulated industries, companies merging incompatible systems, and businesses with simple, stable data models benefit most from Centralized style. You see this style in organizations that need golden records for compliance or want strict standardization.
FineDataLink helps you build a Centralized master data management system by offering robust ETL/ELT tools, real-time data pipelines, and easy integration with existing applications. You can achieve strong governance and unified control over master data.
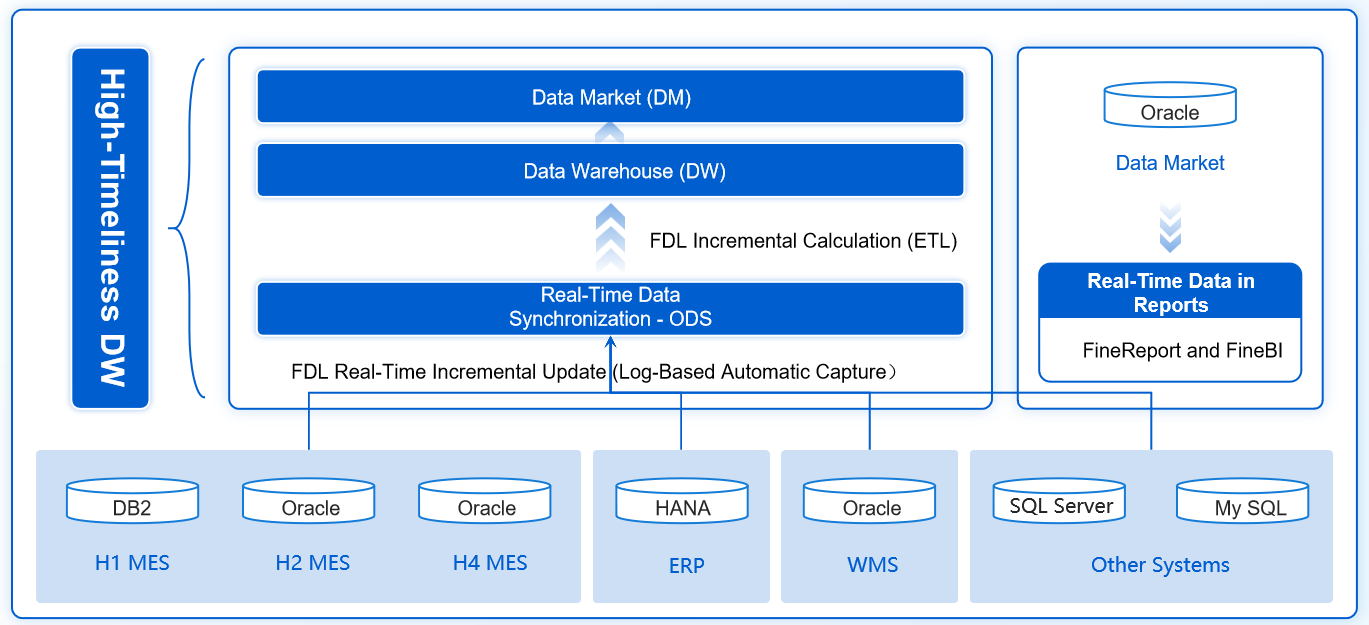

You need to understand how each mdm implementation style manages data storage and synchronization. The differences affect how you access and update master data across your organization. The table below shows how the four styles handle these tasks:
| MDM Style | Data Storage Mechanism | Synchronization Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Consolidation | Central hub for clean, matched data | Does not update original source records |
| Registry | Indexes multiple unstructured source systems | Provides a read-only view of records |
| Centralized | Authors master data and disseminates it | Requires new data management system adoption |
| Coexistence | Creates a consolidated hub and feeds updates | Allows data creation on multiple systems |
You see that consolidation and centralized styles store master data in a hub, while registry style only indexes records. Coexistence style supports updates in both the hub and source systems. FineDataLink helps you synchronize data in real time, no matter which style you choose.
Integration complexity varies across mdm implementation styles. You must consider how much effort is needed to connect systems and maintain data flows. The chart below compares the complexity of each style:
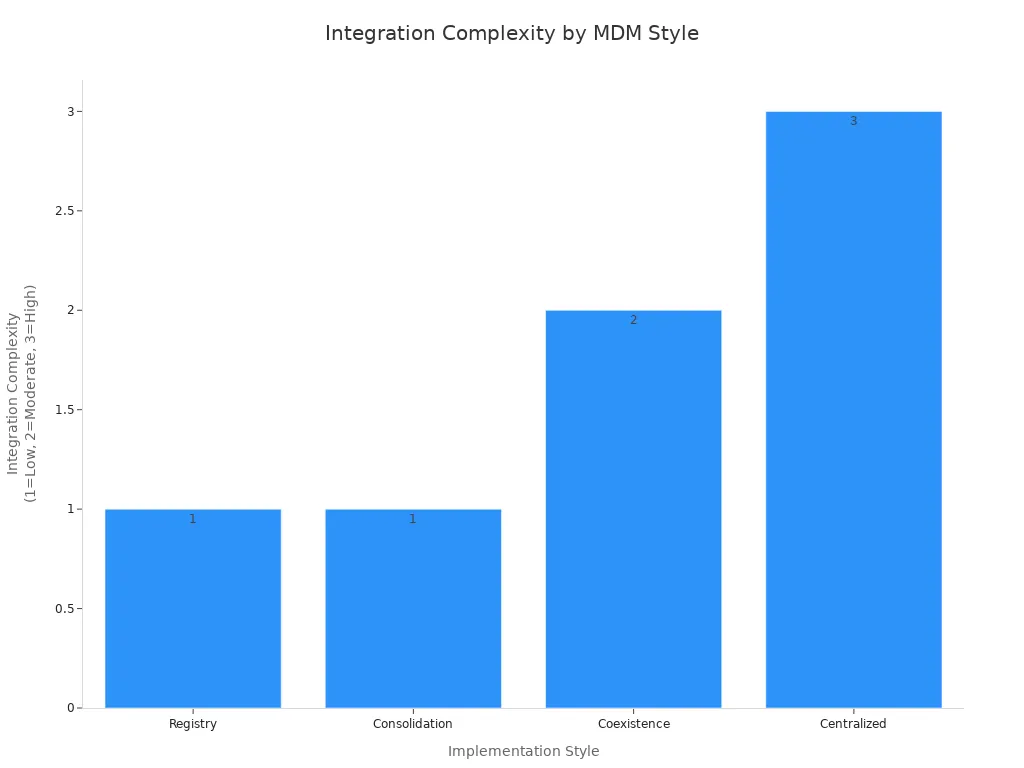
Registry and consolidation styles offer low complexity, making them easier to implement. Coexistence style introduces moderate complexity because you synchronize data between multiple systems. Centralized style requires high complexity due to major changes in infrastructure. FineDataLink’s low-code platform reduces integration challenges, letting you build data pipelines and connect sources quickly.
Governance and control play a key role in master data management system success. You need strong policies to ensure data quality and consistency. Here are best practices for each style:
FineDataLink supports governance by providing tools for data stewardship, monitoring, and automated workflows.
Scalability and organizational fit determine which mdm implementation style works best for you. The table below summarizes how each style matches different business sizes:
| MDM Style | Scalability | Suitability for Organizational Size |
|---|---|---|
| Registry | Limited | Small businesses |
| Consolidation | Moderate | Mid-sized organizations |
| Coexistence | High | Organizations using Consolidation |
| Centralized | Very High | Large enterprises |
Registry style is cost-effective for small businesses. Consolidation style fits mid-sized organizations that need accurate master data. Coexistence style suits those already using consolidation and seeking more flexibility. Centralized style works best for large enterprises with advanced requirements. FineDataLink scales with your needs, supporting real-time synchronization and integration for any style.
You should start by evaluating your organization’s unique requirements before selecting an mdm approach. Consider factors such as pricing, the number of data sources, and the level of data scrutiny needed. The table below summarizes these important considerations:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Pricing | Cost structures vary by mdm style; simpler models like registry are more cost-efficient. |
| Source | The number of data sources influences the choice; more sources may favor the registry model. |
| Data Scrutiny | Ensuring the accuracy of the golden record is crucial for selecting the appropriate mdm style. |
You need to match your business priorities with the right style to achieve the best results.
Your existing data landscape and integration architecture play a major role in determining the best mdm style. If you have complex data or require real-time updates, you may need a more advanced solution. Some organizations need a single source of truth for master data, while others prefer linking data across multiple systems. You should also consider compliance requirements and how data is synchronized. Centralized management works well for strict control, while decentralized approaches offer flexibility.
Strong governance ensures data quality and consistency across your organization. You must also plan for budget needs, as costs can vary widely. The table below outlines typical cost considerations for different mdm styles:
| Cost Factor | Description | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Software Licensing and Subscription | Costs depend on user count and data domains. | $50,000 to $500,000+ |
| Hardware and Infrastructure Costs | Servers, storage, or cloud hosting fees. | $20,000 to $200,000+ |
| Implementation and Integration | Professional services for setup and integration. | $100,000 to $1,000,000 |
| Data Migration and Cleansing | Moving and cleaning legacy data. | $50,000 to $250,000 |
| Training and Change Management | Training staff and managing change. | $20,000 to $100,000 |
| Ongoing Maintenance and Support | Support and updates after launch. | $30,000 to $150,000/year |
| Customization and Scalability | Tailoring and scaling the mdm system. | $50,000 to $300,000 |
You should balance your governance needs with available resources to select the most suitable style.
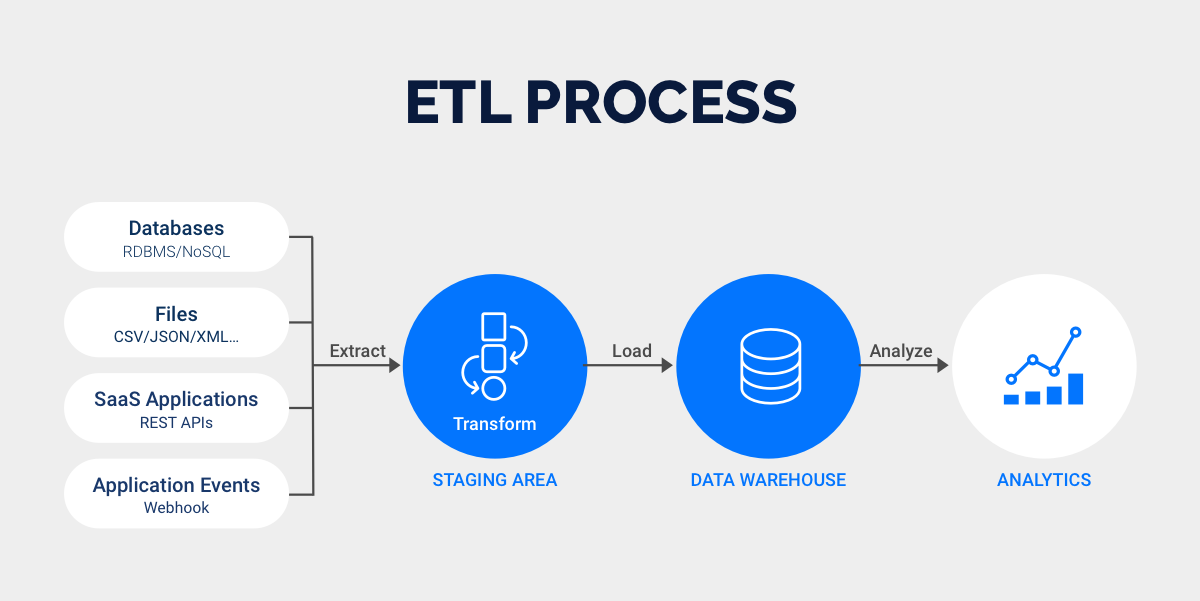
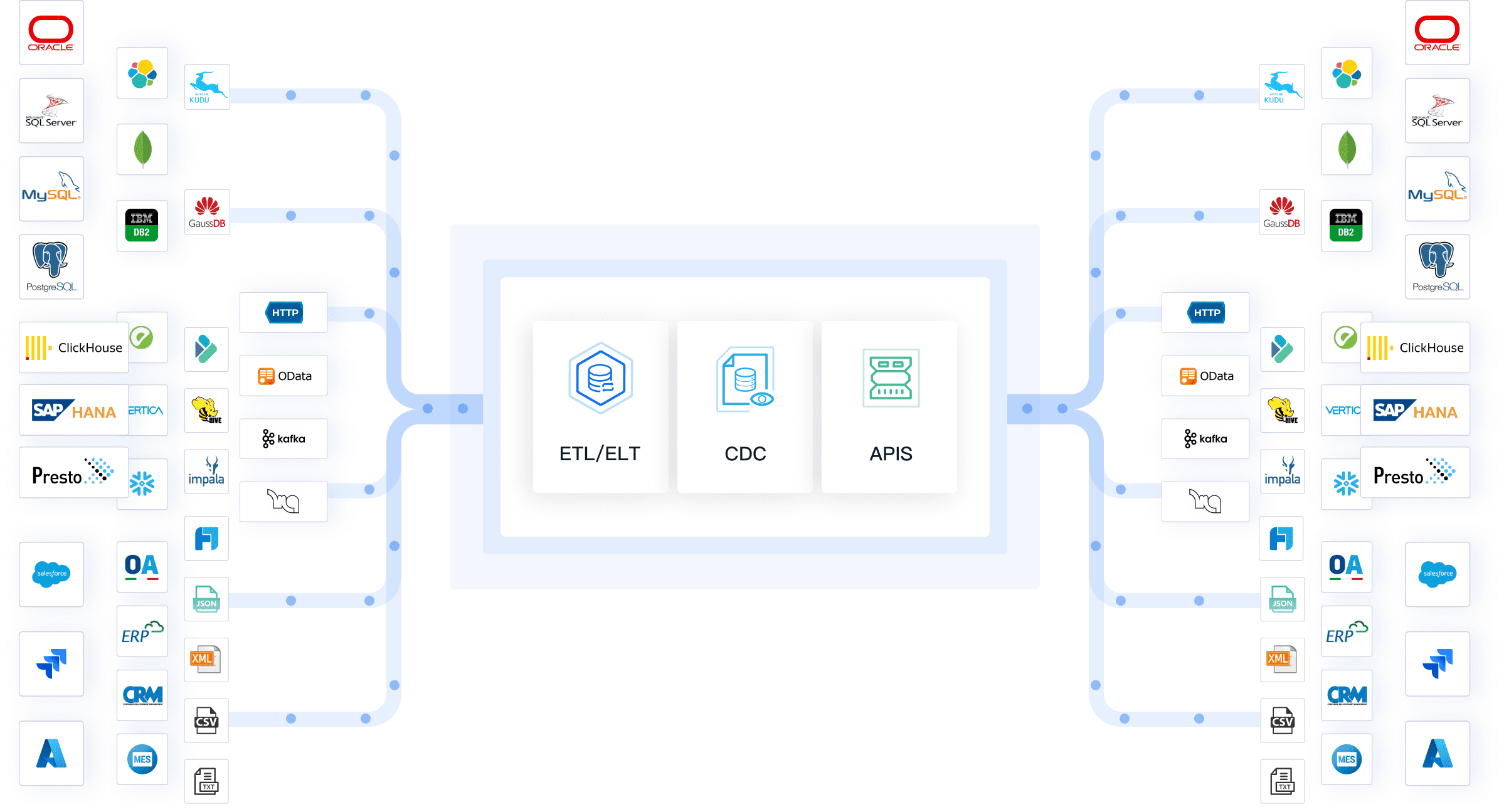
FineDataLink offers a flexible and scalable solution for all mdm styles. You can collect data from many sources, including relational and non-relational databases. FineDataLink supports non-intrusive real-time synchronization, which helps you keep master data up to date. The platform allows you to build low-cost data services using APIs and provides efficient operation and maintenance tools. You can schedule tasks, monitor data in real time, and use built-in Spark SQL for advanced customization. FineDataLink's dual-core engine supports both ETL and ELT processes, giving you the freedom to design solutions that fit your organization’s needs. With five data synchronization methods, you can handle any integration challenge and ensure your master data remains accurate and reliable.
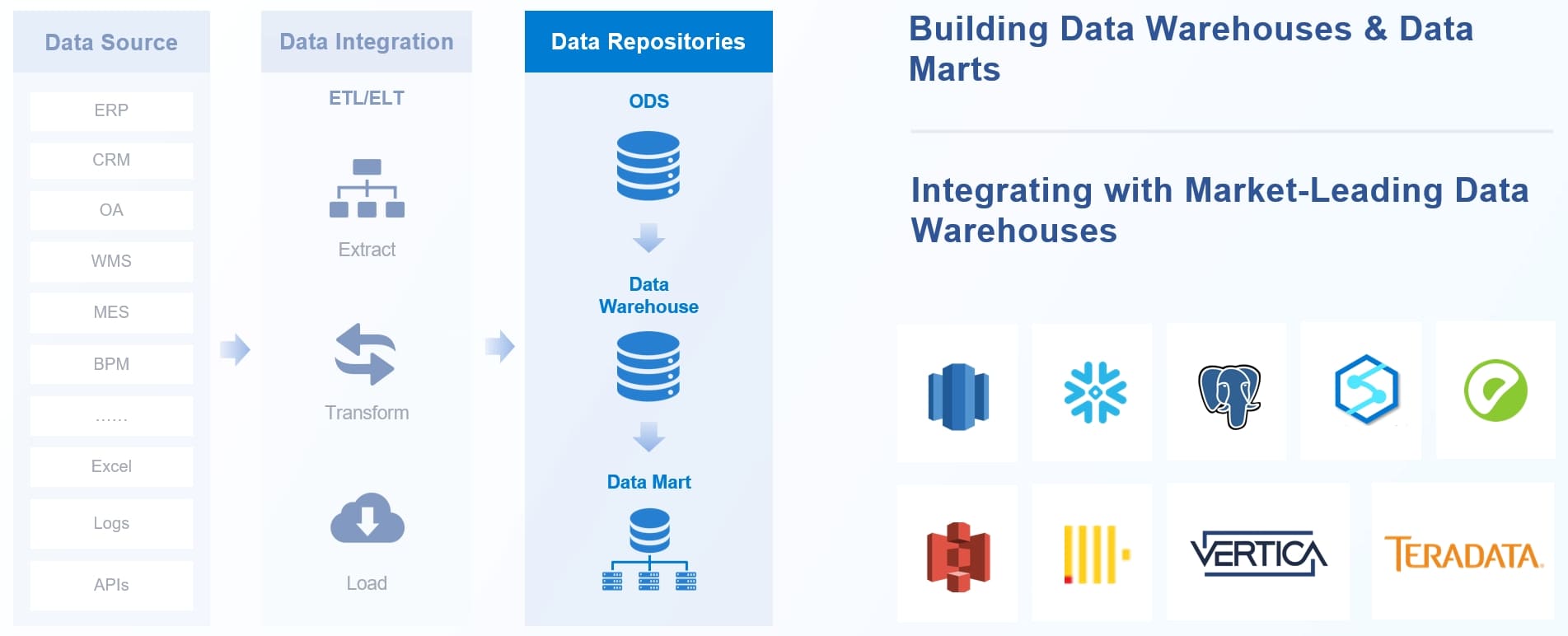
You see clear differences among the four mdm implementation styles. The table below highlights their key characteristics and typical use cases:
| Style | Key Characteristics | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Registry | Non-intrusive, links source system IDs, cleanses data | Regulatory compliance |
| Consolidation | Copies and consolidates master data in a hub | Product data management |
| Coexistence | Integrates golden data back to source applications | Customer data integration |
| Centralized | Migrates and cleanses all master data in a single hub | Financial data workflows |
You should align your chosen style with your business goals and data environment. To ensure successful implementation, follow these steps:
Consider evaluating your data integration capabilities and explore solutions like FineDataLink for flexible support.
Enterprise Data Integration: A Comprehensive Guide
What is enterprise data and why does it matter for organizations
Understanding Enterprise Data Centers in 2025
Enterprise Data Analytics Explained for Modern Businesses

The Author
Howard
Data Management Engineer & Data Research Expert at FanRuan
Related Articles
What is a data management platform in 2025
A data management platform in 2025 centralizes, organizes, and activates business data, enabling smarter decisions and real-time insights across industries.
Howard
Dec 22, 2025

Top 10 Database Management Tools for 2025
See the top 10 database management tools for 2025, comparing features, security, and scalability to help you choose the right solution for your business.
Howard
Dec 17, 2025

Best Data Lake Vendors For Enterprise Needs
Compare top data lake vendors for enterprise needs. See which platforms offer the best scalability, integration, and security for your business.
Howard
Dec 07, 2025