Good data visualization examples show you how to turn raw numbers into clear, engaging visuals that help people understand information quickly during a presentation. If you want to spark creativity and improve your own work, you need to see what makes these examples stand out. FineVis and FineReport give you the tools to create impactful visualizations for business and beyond. You can create good data visualization examples by focusing on clarity and making your visuals easy to understand. Check out these key characteristics:
Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Clarity | Helps viewers grasp the message quickly |
| Accuracy | Shows data truthfully |
| Appropriate Chart | Chooses the right chart for the story |
Start by identifying your data, cleaning it, and picking the best chart type. FineBI makes visualization simple for beginners.
Creating good data visualization examples starts with a clear purpose and a step-by-step approach. You want your visuals to highlight important information, focus on one message, and make complex data easy to understand. Let’s walk through each step so you can build effective data visualizations that truly stand out.
Every visualization needs a clear purpose. Ask yourself: What do you want your audience to learn or do after seeing your data visualization? When you set a goal, you give direction to your work and make sure your visuals communicate the right message. Here are some common goals for good data visualization examples:
Defining your goal shapes every choice you make, from chart type to layout. A clear purpose helps you focus on one message and avoid unnecessary details. Clarity is key—your audience should grasp the main point without confusion.
Tip: Write down your goal before you start. This keeps your visualization focused and ensures you highlight key insights.
You need to tailor your data visualizations to your audience. Think about who will view your visuals and what they need. Use the table below to guide your approach:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Domain Knowledge | Assess how familiar your audience is with the topic. Adjust complexity as needed. |
| Purpose and Context | Adapt your visualization for reports, presentations, or educational settings. |
| Accessibility | Make sure everyone can use your visuals, including those with disabilities. |
| Engagement | Use interactive elements or storytelling to keep interest high. |
| Device and Medium | Consider where your audience will see your visuals—desktop, mobile, or print. |
| Age and Demographics | Match your style to the age group and preferences of your viewers. |
| Key Message | Focus on one message and avoid clutter that distracts from the main point. |
Knowing your audience helps you choose the right level of detail and design. If you’re presenting to executives, keep visuals simple and direct. For students, visuals simplify complex ideas and make learning easier.
Selecting the right chart type is essential for effective data visualizations. Beginners often use these popular chart types:
Use the table below to help you pick the best chart for your data visualization examples:
| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Types of metrics | What variables or features are you plotting? |
| Audience | Who will view the data and what is their understanding level? |
| Visualization goals | What conclusions do you want viewers to draw? |
| Primary purpose | What is the main reason for your visualization? |
| Type of data | Is your data categorical, numeric, or time-based? |
| Number of variables | How many variables are you showing? |
| Volume of data points | Do you have a few data points or thousands? |
| Question to answer | What question does your visualization answer? |
The right chart type makes your data visualization clear and helps viewers highlight important information. Always match your chart to your goal and audience.
Simplicity is your best friend in data visualization. When you keep visuals simple, you make it easier for viewers to understand the story behind the data. Avoid clutter, unnecessary colors, and complex layouts. Focus on one message and use clear labels, legends, and titles.
Note: Simplicity helps you highlight key insights and makes your data visualization examples more effective.
Remember, clarity is key. Visuals simplify complex ideas and allow your audience to see patterns and trends without distraction.
Good data visualization examples always add context and interpretation. Without context, viewers may struggle to understand what the data means. Include titles, labels, legends, and annotations so your audience knows what they’re looking at. Use descriptive statistics, visual cues, and storytelling to make your message clear.
| Mistake | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Failing to include necessary context | Viewers get confused without labels, legends, or annotations. |
| Incomplete storytelling | Lack of context can mislead viewers and cause incorrect assumptions. |
Context improves interpretability. Descriptive statistics show averages and distributions. Visual cues help spot outliers and trends. When you add context and interpretation, you guide your audience to the right conclusions and help them identify trends and gaps.
Tip: Always check that your data visualizations include enough context. This makes your visuals more trustworthy and easier to understand.
You should always review and improve your data visualizations. Regular practice helps you create better visuals over time. Ask for feedback from peers or mentors. Collaborate with others to get new ideas and immediate feedback. Test your visuals before sharing them to make sure they communicate your message clearly.
Consistency in design and engaging dashboards help users draw conclusions efficiently. Reviewing your work ensures your data visualization examples stay effective and relevant.
Tip: Use a checklist to make sure your visuals meet your goal, highlight important information, and keep visuals simple.
Now that you know the steps for creating good data visualization examples, you can use tools like FineBI to make the process even easier. FineBI guides you through data integration, processing, visual exploration, and publishing. You can prepare your data, select the right chart, customize your visuals, and create dashboards that highlight key insights. FineBI’s workflow helps you focus on one message and achieve clarity in every visualization.

You want your data visualization to show the signal, not the noise. Noise includes anything that distracts from the main message. Common sources of clutter in data visualizations are excessive colors, too much detail, and complex chart types. Frames, axes, labels, and overlay objects can also add unnecessary elements. To create effective data visualizations, focus on maximizing the signal-to-noise ratio. Remove extra labels, legends, gridlines, and backgrounds. Use whitespace to separate sections and improve readability. Minimalism helps viewers spot patterns and trends faster.
Apply Edward Tufte’s 'data-ink ratio' by removing anything that doesn’t help with interpretation.
Consistency makes your data visualizations easier to read and understand. Use the same styles, colors, and fonts throughout your visualization. Align margins and spacing to create a clear visual hierarchy. Choose chart types that match your data and message. Make sure your color choices support accessibility and understanding.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Chart Types | Pick charts that fit your data and message. |
| Color Usage | Use colors to highlight important data and support accessibility. |
| Text Elements | Select readable fonts and sizes for labels and titles. |
| Accessibility | Design visualizations for all users, including those with disabilities. |
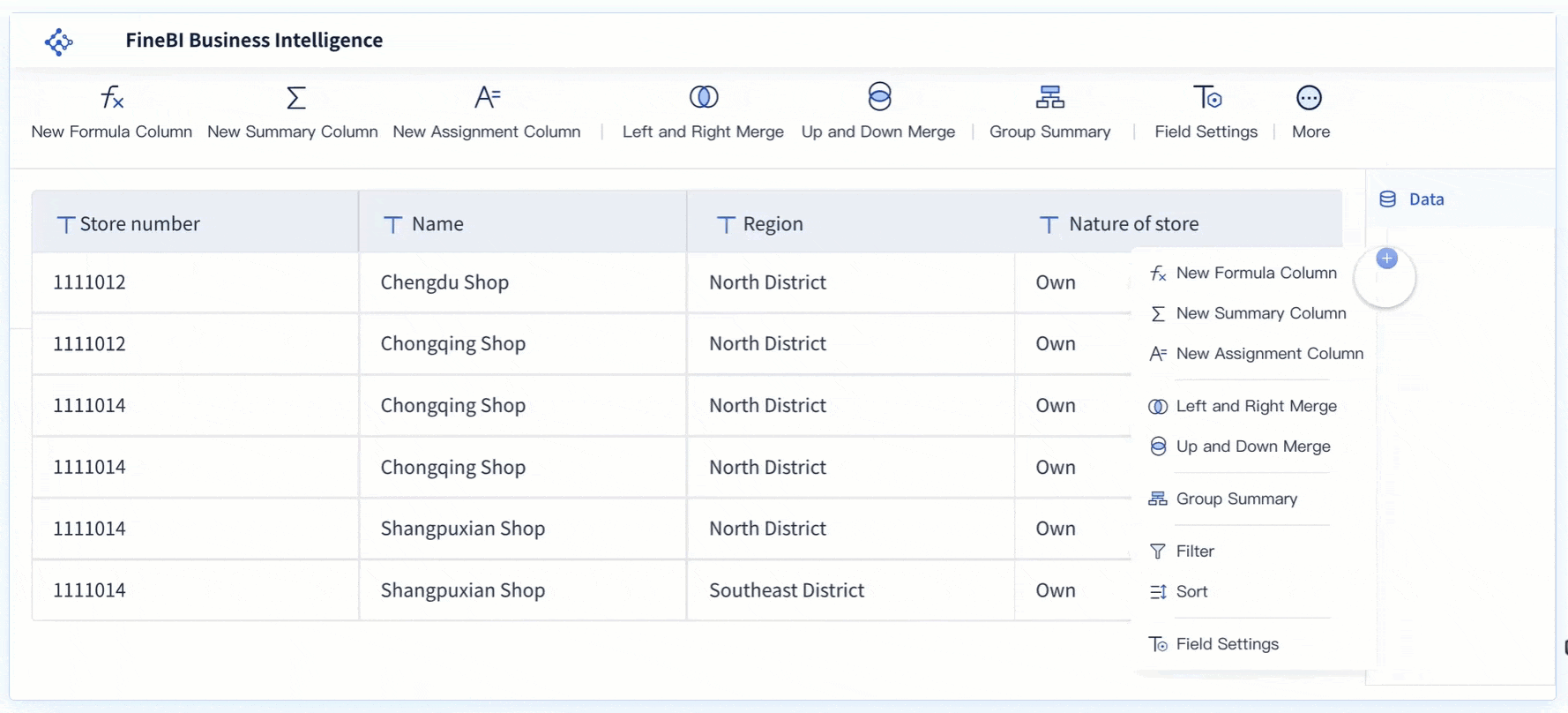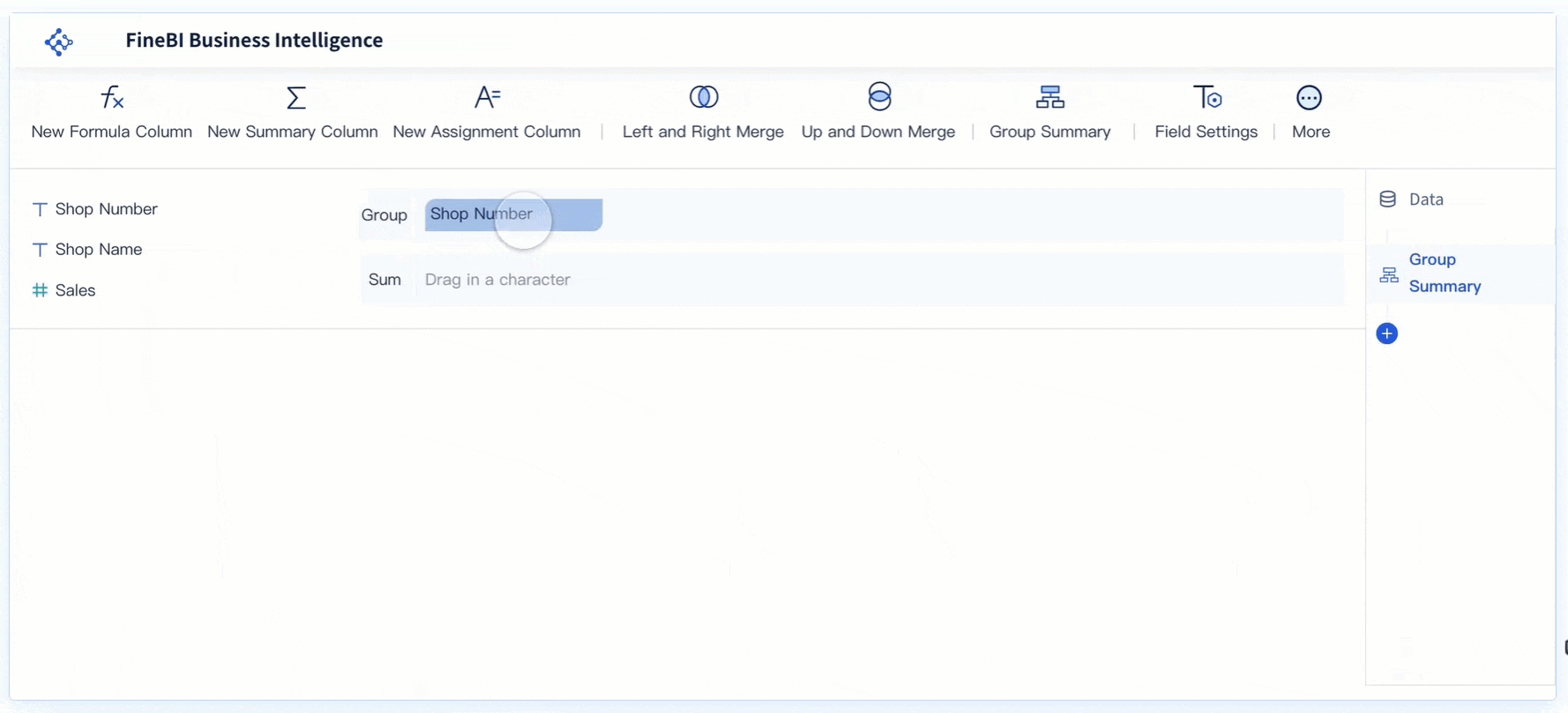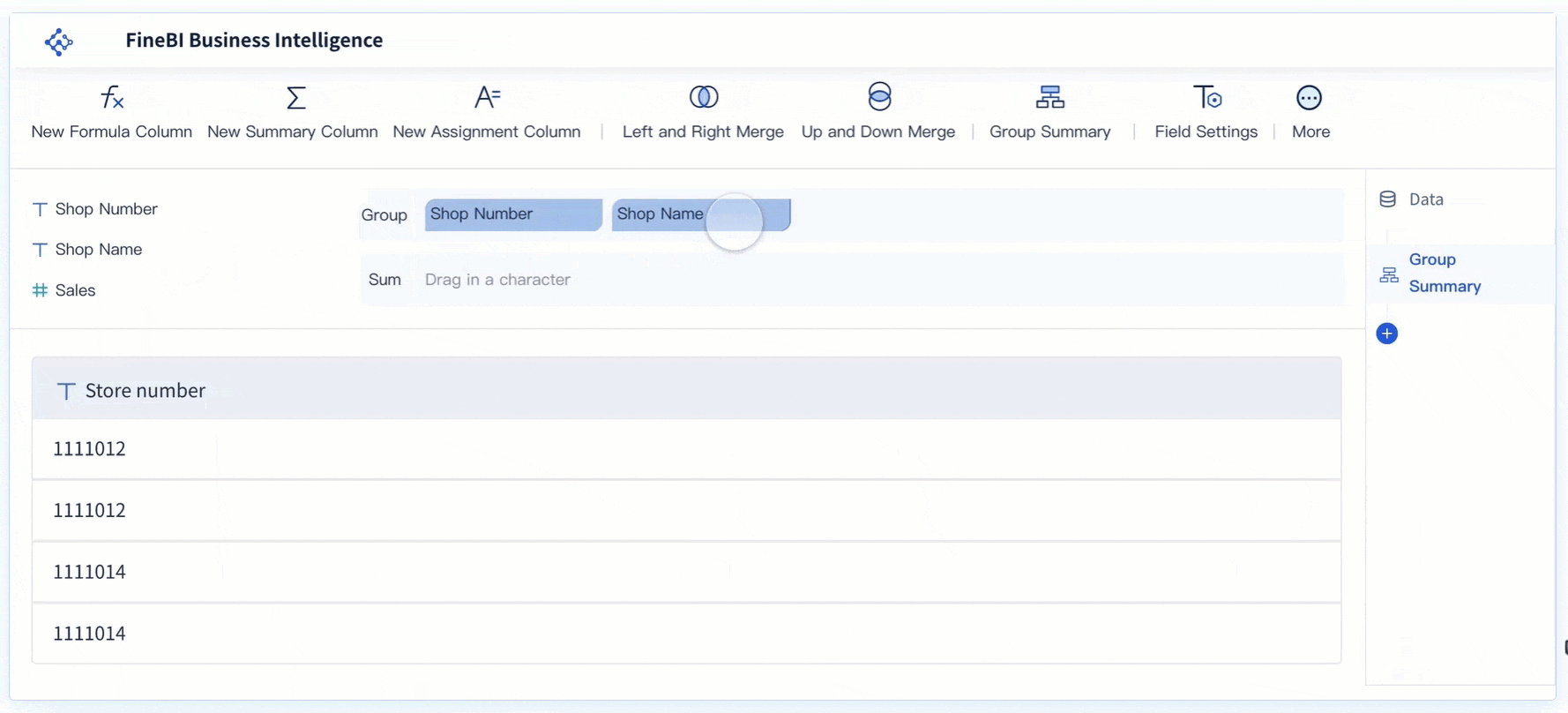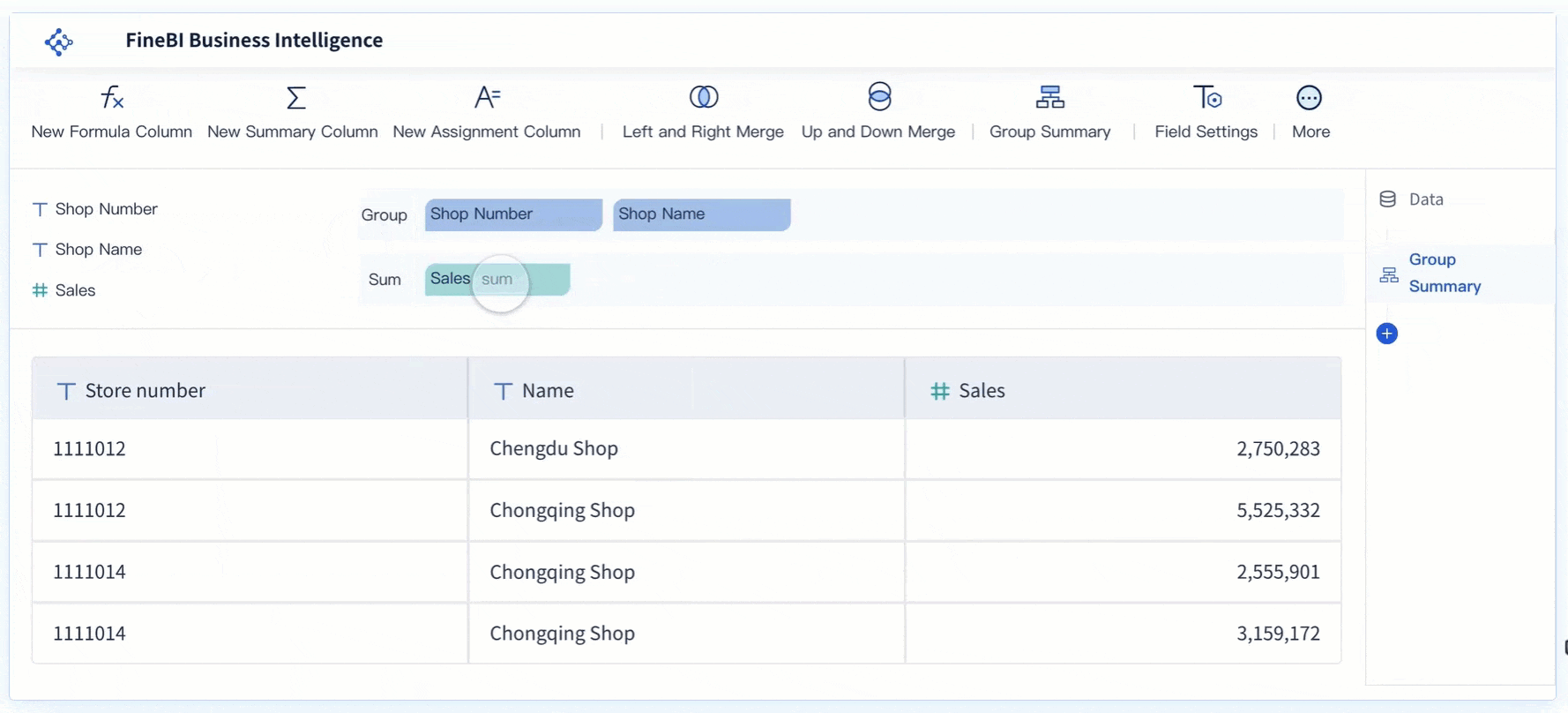
FineBI makes creating data visualizations simple for business users and teams. The drag-and-drop interface lets you build reports without technical skills. Real-time filtering ensures your analysis uses the latest data. You can engage directly with your data, streamline the visualization process, and make faster decisions.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Drag-and-Drop Interface | Create actionable reports quickly, no coding needed. |
| Real-Time Filtering | Analyze up-to-date data for timely decisions. |
FineBI empowers teams to innovate independently, optimize staff structure, and improve data asset utilization. You get more value from your data visualizations and foster a culture of innovation.
Use this data visualization checklist to avoid misleading visualizations and create effective data visualizations:
| Checklist Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Ensure sufficient color contrast | Improves readability. |
| Don’t rely on color alone | Use patterns or textures for clarity. |
| Make charts readable when resized | Maintain clarity at any size. |
| Use alt text for simple charts | Communicate data for basic visualizations. |
Follow these data visualization best practices to create clear, accessible, and effective data visualizations. Always review your visualization and iterate based on feedback. Good interpretation and a strong checklist help you avoid misleading visualizations and improve your results.
You can create strong data visualizations by considering your audience, keeping visuals simple, and using clear labels. FineBI’s intuitive design helps you build skills quickly. When you practice, you make complex data accessible, boost engagement, and uncover valuable insight. Try FineBI for hands-on message creation and see your skills grow.

Effective data visualization examples make information clear, engaging, and memorable. You can achieve this by focusing on clarity, storytelling, interactivity, and visual appeal. FineVis and FineReport support these qualities with powerful features and easy-to-use design tools.
You need clarity and simplicity to help your audience understand data quickly. When you prioritize the message, you make it easier for viewers to see patterns and take action. FineVis and FineReport let you choose the best chart types and layouts, so your visuals stay focused and easy to read.
| Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Visualization | Transforms data into graphical representations, aiding in pattern recognition and improving memory retention. |
| Clarity in Presentation | Clear and concise visualization empowers informed decision-making, allowing stakeholders to quickly grasp situations. |
| Engagement with Visual Data | Well-designed visualizations are easier to remember and capture attention, effectively telling a story without excessive text. |
You should always select geometries that match your data and use a high data-ink ratio for maximum clarity.
Storytelling turns raw data into a narrative that connects with your audience. You can use storytelling to guide viewers through complex information and make insights more persuasive. FineVis and FineReport offer drag-and-drop tools and annotation features that help you build a strong narrative.
Would you like to know more about the functions of FineReport? Click the button below to make your workflow more efficient!
By combining data with a compelling narrative, you help business leaders understand the significance of the data in a real-world context. Storytelling can evoke empathy, create urgency, and inspire action.
Interactivity lets users explore data on their own. You can add interactive maps, drill-down charts, and dynamic dashboards with FineVis and FineReport. These features encourage deeper engagement and longer exploration.
| Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Session Duration | Interactivity leads to longer session durations as users engage more deeply with content. |
| Bounce Rate | Engaging elements reduce bounce rates by encouraging users to stay on the site longer. |
| Return Visits | Users are more likely to return when they have had an interactive experience that they found enjoyable. |
Interactive techniques help you uncover trends and make decisions faster.
Visual appeal draws attention and helps people remember information. You can use colors, shapes, and design elements to make your data stand out. FineVis and FineReport transform raw data into attractive charts and dashboards that support quick pattern recognition.
You should use techniques that combine clarity, storytelling, interactivity, and visual appeal to create effective data visualizations.
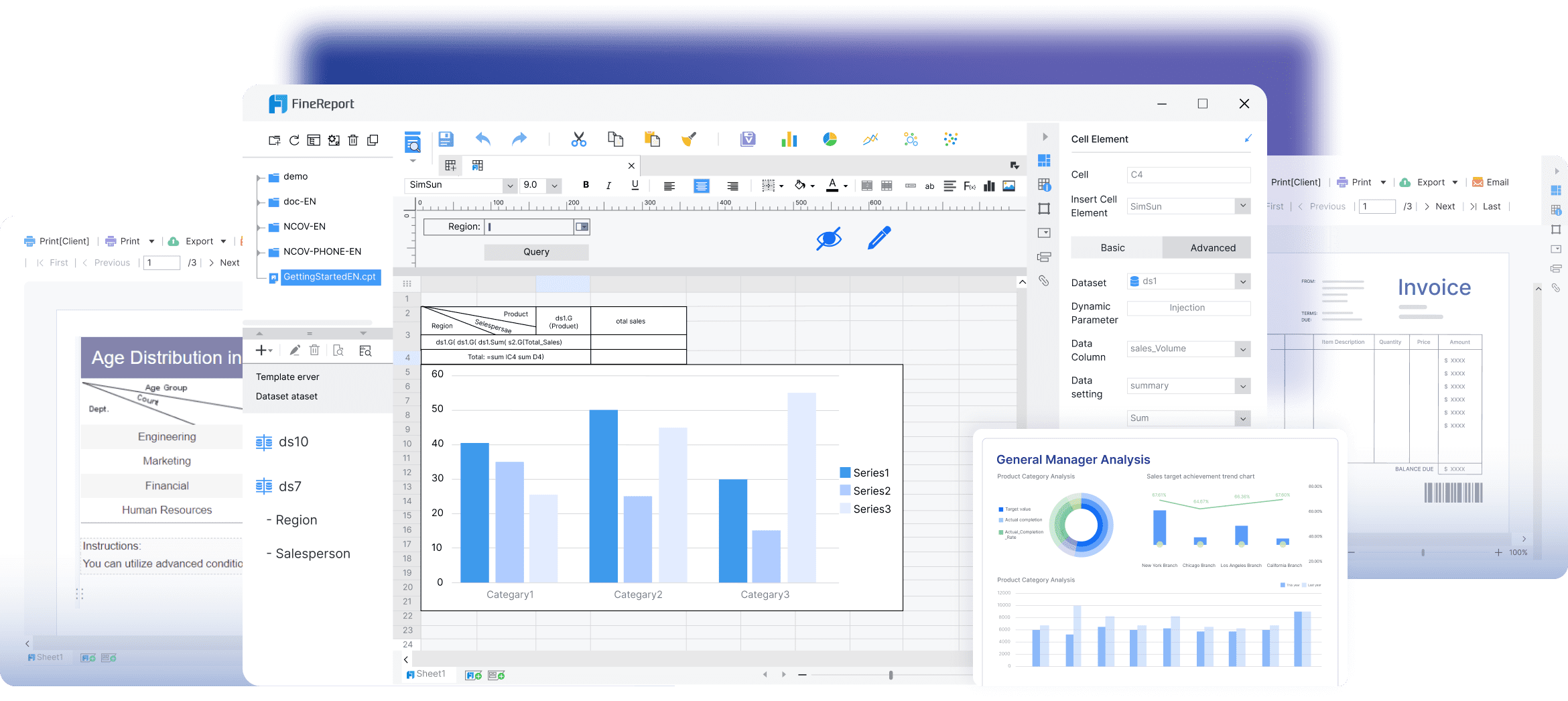
You can apply data visualization examples to your projects by adapting proven techniques, choosing the right chart types, and using creative design strategies with modern visualization tools.
When you start a new data project, you should focus on making your message clear and memorable. Use storytelling to help your audience connect with the data. Simplify complex information so everyone can understand it. FineVis and FineReport let you customize dashboards and add real-time analytics, making your visualizations more effective.

These steps help you turn data visualization for business intelligence into a powerful tool for communication.
You can boost creativity in your data visualization for business intelligence by exploring new formats and features. Try using infographics, interactive dashboards, or even immersive storytelling on your interactive website. FineVis and FineReport support these methods, helping you make your projects stand out.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Infographics | Summarize large data sets in a visual, easy-to-read format. |
| Interactive Dashboards | Let users explore data and find their own insights. |
| Poetic Representations | Add narrative elements for deeper meaning. |
| Immersive Storytelling | Guide users through data with visuals and stories. |
| Augmented Reality | Show historical data changes in a dynamic way. |
By using these strategies and the right visualization tools, you can create engaging and effective data projects.
Exploring diverse data visualization examples helps you grow as a professional. You gain skills to simplify complex data, highlight key insights, and create engaging data stories. When you use FineVis and FineReport, you can experiment with interactive dashboards and industry solutions. Start your next project today and discover new ways to communicate with data.
For more learning, visit FineVis or FineReport.
Bar Chart Race: A Complete Guide
16 Types of Chart for Effective Data Visualization
22 Different Types of Graphs in Data Visualization: A Practical Guide

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles

Top 8 Data Visualization softwares You Should Try in 2025
Compare the top 8 data visualization software for 2025, including FineReport, Tableau, Power BI, and more to find the best fit for your business needs.
Lewis
Dec 19, 2025
10 Must-Have Data Visualization Tools for Modern Businesses
Compare the top 10 data visualization tools for 2025 to boost business insights, streamline analytics, and empower smarter decision-making.
Lewis
Dec 17, 2025

7 Leading Big Data Visualization Tools for the Year Ahead
Compare the top big data visualization tools for 2025 to find advanced analytics, scalability, and interactive dashboards for your business.
Lewis
Dec 17, 2025