Cost analysis gives you a clear view of where your money goes and why. By examining cost drivers and using structured methods, you improve budgeting accuracy and make smarter decisions about resource allocation. This process helps you spot inefficiencies and ensures you invest in what matters most. When you use cost analysis, you support business profitability by identifying areas to reduce expenses and maximize value. Transparent, data-driven budgeting becomes possible, letting you prioritize investments that deliver the highest returns.

Cost analysis is the review and evaluation of the separate cost elements and profit or fee in an offeror’s or contractor’s proposal to determine a fair and reasonable price or to determine cost realism. Cost analysis includes the application of judgment to determine how well the proposed costs represent what the cost of the contract should be, assuming reasonable economy and efficiency.
You use cost analysis to understand how your business spends money and what you gain in return. This process gives you a structured way to compare the costs and benefits of any decision, project, or investment. Leading business and financial authorities define cost analysis, especially cost-benefit analysis, as a systematic process. You compare projected costs and benefits, both tangible and intangible, and assign monetary values where possible. You also consider opportunity costs and potential risks.
When you perform cost analysis, you start by defining the scope of your project or decision. You identify all possible costs and benefits. You then calculate values such as net present value and discount cash flows. This helps you decide if the benefits outweigh the costs. You use cost analysis as a decision-making tool to judge if a project is worth pursuing. The accuracy of your analysis depends on the quality of your forecasts and assumptions.
Many people think cost analysis is a one-time task or just about cutting expenses. In reality, you need to treat it as an ongoing process. You must review and update your analysis as your business changes. Cost analysis is not just about reducing costs. You use it to make strategic decisions, improve efficiency, and support long-term growth.
In today's volatile markets, cost analysis is no longer just a financial task—it's a strategic advantage. Businesses that understand the full picture behind their cost structure are able to react faster, price smarter, and invest more wisely.
But raw cost data alone doesn’t tell you what actions to take.
That's why data interpretation and storytelling are now essential skills for finance teams, analysts, and decision-makers alike. Knowing the difference between gross profit, margin, and gross profit margin ratio isn't just about formulas—it's about communicating what those numbers actually mean for your business.
Tip: Cost analysis works best when you involve different teams and update your data regularly. This helps you spot new trends and make better decisions.
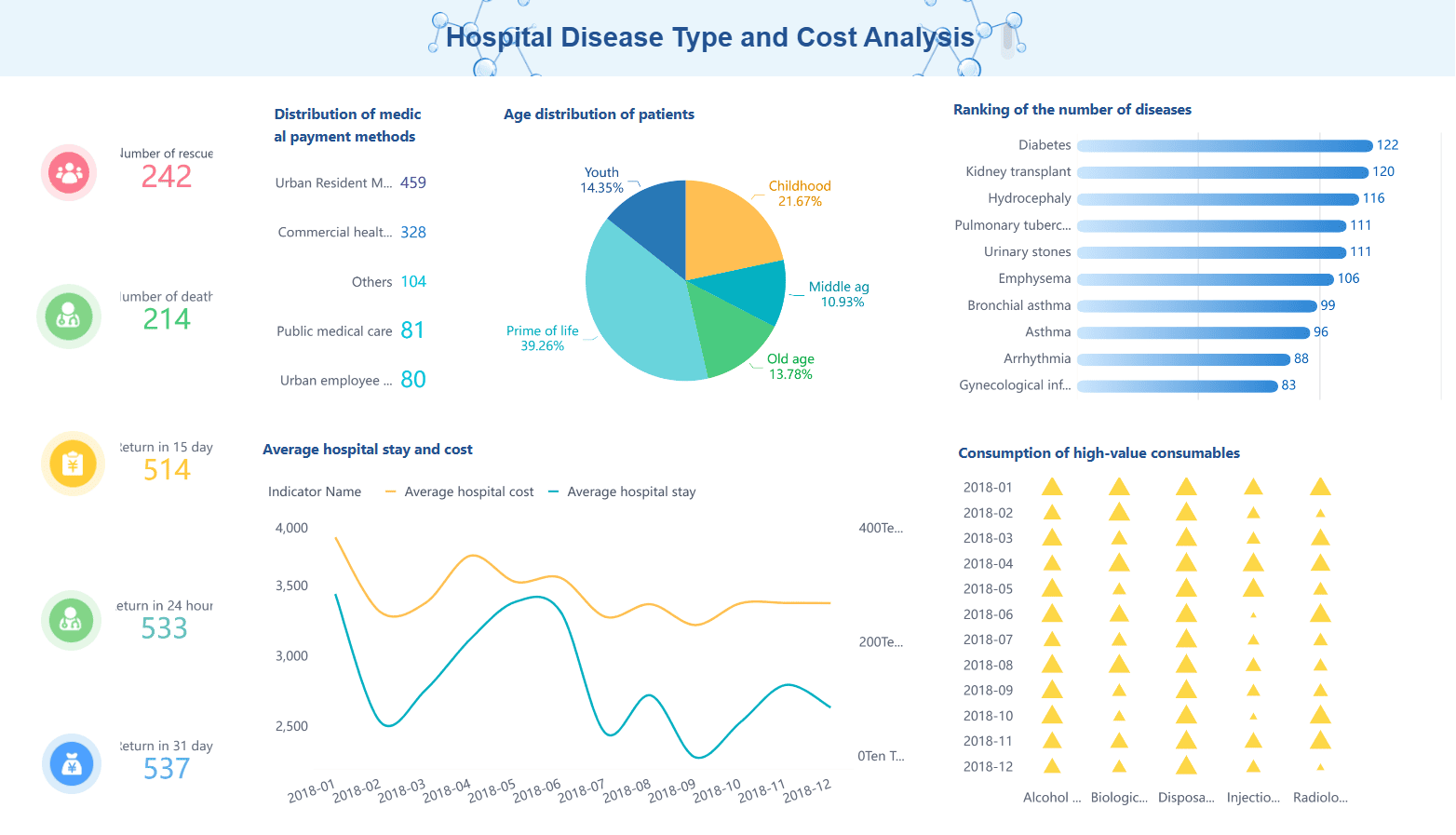
You need to understand the main components of cost analysis to get accurate results. Businesses often break down costs in several ways. Here are the most common cost components you will encounter:
You can see how different types of costs affect your financial statements in the table below:
| Cost Type | Characteristics | Impact on Financial Statements |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed Costs | Remain constant regardless of production or sales. Examples: rent, insurance, salaried labor. | Recorded as overhead expenses on the income statement; may require a larger asset base on the balance sheet. |
| Variable Costs | Fluctuate directly with production or sales volume. Examples: raw materials, hourly labor, commissions. | Included in Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) on the income statement; directly affect gross profit and profitability. |
Semi-variable (Mixed) Costs:
These costs have both fixed and variable parts. Utilities, for example, often have a base charge plus a usage fee. You might also see rent with a sales percentage or commissions with a base salary. Machinery maintenance can include fixed maintenance and variable repair costs. You need to account for these costs carefully to forecast and manage your business accurately.
Understanding how each cost behaves helps you with budgeting, pricing, and break-even analysis. You can make better decisions when you know which costs stay the same and which change with your business activity. Proper classification and reporting of costs in your financial statements support better management and higher profitability.
Note: Many business professionals believe cost reduction only targets variable costs or that it is a simple, one-time fix. In reality, you must look at both fixed and variable costs and treat cost analysis as a continuous, detailed process.
You use cost analysis to guide your business toward smarter spending and higher returns. When you understand each cost component, you can set better budgets, control expenses, and improve your bottom line. Cost accounting methods help you assign and manage costs, making your analysis more precise and actionable.
You use cost-benefit analysis to decide if a project or investment is worth your time and money. This method helps you compare the total cost of an action with the expected benefits. You start by building a framework. Define your question and set the scope, including the timeframe and types of cost and benefits you want to consider. Next, identify all possible cost and benefits, both tangible and intangible. Assign monetary values or key performance indicators (KPIs) to each item. Then, analyze the total cost versus the total benefits. Use financial metrics like net present value or internal rate of return to measure roi. Finally, make a recommendation based on your findings.
Cost-benefit analysis gives you a structured way to weigh options. You can use it for new projects, process changes, or investments. This method helps you see if the benefits outweigh the cost and if the roi meets your goals. You can also use cost benefit analysis to compare different alternatives and choose the most cost-effective one.
Tip: Cost-benefit analysis works best when you include both direct and indirect cost, as well as intangible benefits like customer satisfaction or brand value.
However, cost-benefit analysis has some limits. It can be hard to assign a dollar value to things like employee morale or environmental impact. Sometimes, you may focus too much on monetary values and miss important qualitative factors. Assumptions about future cost and benefits can also affect your results. Always review your analysis for hidden assumptions and optimistic bias.
| Limitation | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Difficulty in quantifying intangibles | Intangible factors like brand reputation are hard to value. |
| Overemphasis on monetary values | May ignore important non-financial factors. |
| Uncertainty and assumptions | Future cost and benefits may change. |
| Ignores distributional impacts | May not show how cost and benefits affect different groups. |
| Oversimplification | Can miss indirect effects or opportunity costs. |
Understanding direct and indirect cost is key for accurate cost-benefit analysis. Direct cost link straight to a product, project, or service. These include raw materials, labor, and supplies used only for that project. Indirect cost support many activities and cannot be traced to one item. Examples include rent, utilities, and administrative salaries.
| Aspect | Direct Costs | Indirect Costs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Costs directly traceable to a specific product, project, or department | Overhead or operating expenses supporting multiple activities, not easily assigned to one cost object |
| Examples | Raw materials, labor directly involved in production | Rent, utilities, administrative wages, depreciation, insurance |
| Allocation Method | Directly assigned to the cost object | Allocated using cost allocation methods, often with accounting software or ERP systems |
| Importance in Accounting | Helps in pricing, tax filing, financial planning | Crucial for distributing overhead, compliance, and funding requirements |
| Impact on Business | Directly affects product cost and profit margins | Affects overall overhead cost estimation and profit margin calculations |
You need to classify cost correctly to improve your cost benefit analysis and roi calculations. Proper tracking helps you set prices, manage cash flow, and meet compliance rules. When you understand the difference between direct and indirect cost, you can allocate expenses more accurately and make better business decisions.
You rely on cost analysis to make informed choices that shape your company's future. This process gives you a clear picture of how each dollar is spent and what you gain in return. When you understand the significance of cost analysis, you can weigh the pros and cons of every option. You see not only the direct expenses but also the hidden costs that might affect your bottom line.
Cost analysis supports financial decision-making by helping you compare alternatives and choose the best path forward. You use frameworks like Cost-Effectiveness Analysis (CEA), Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA), and Programme Budgeting and Marginal Analysis (PBMA) to guide your decisions. The table below shows how these frameworks contribute to better outcomes:
| Framework | Description | Contribution to Better Decision-Making Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Cost-Effectiveness Analysis (CEA) | Jointly considers costs and outcomes (e.g., QALYs) to evaluate programs | Helps you weigh costs against relevant outcomes, guiding resource allocation efficiently |
| Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) | Incorporates multiple criteria beyond cost-effectiveness, including affordability and stakeholder values | Enables you to balance diverse factors relevant to your business context |
| Programme Budgeting and Marginal Analysis (PBMA) | Focuses on reallocating budgets by identifying disinvestments to fund new programs | Provides evidence on opportunity costs and budget constraints, supporting practical decision-making |
You use data from cost analysis to spot inefficiencies and bottlenecks. For example, in manufacturing, you might find ways to optimize your supply chain and reduce waste. In service businesses, you can improve customer experience by analyzing spending patterns. The best results come when you combine data insights with your own judgment. You interpret the numbers, consider the context, and adjust for any limitations. This approach leads to more effective and timely decisions. However, you should not rely on data alone. Qualitative insights and ethical considerations matter just as much as the numbers.
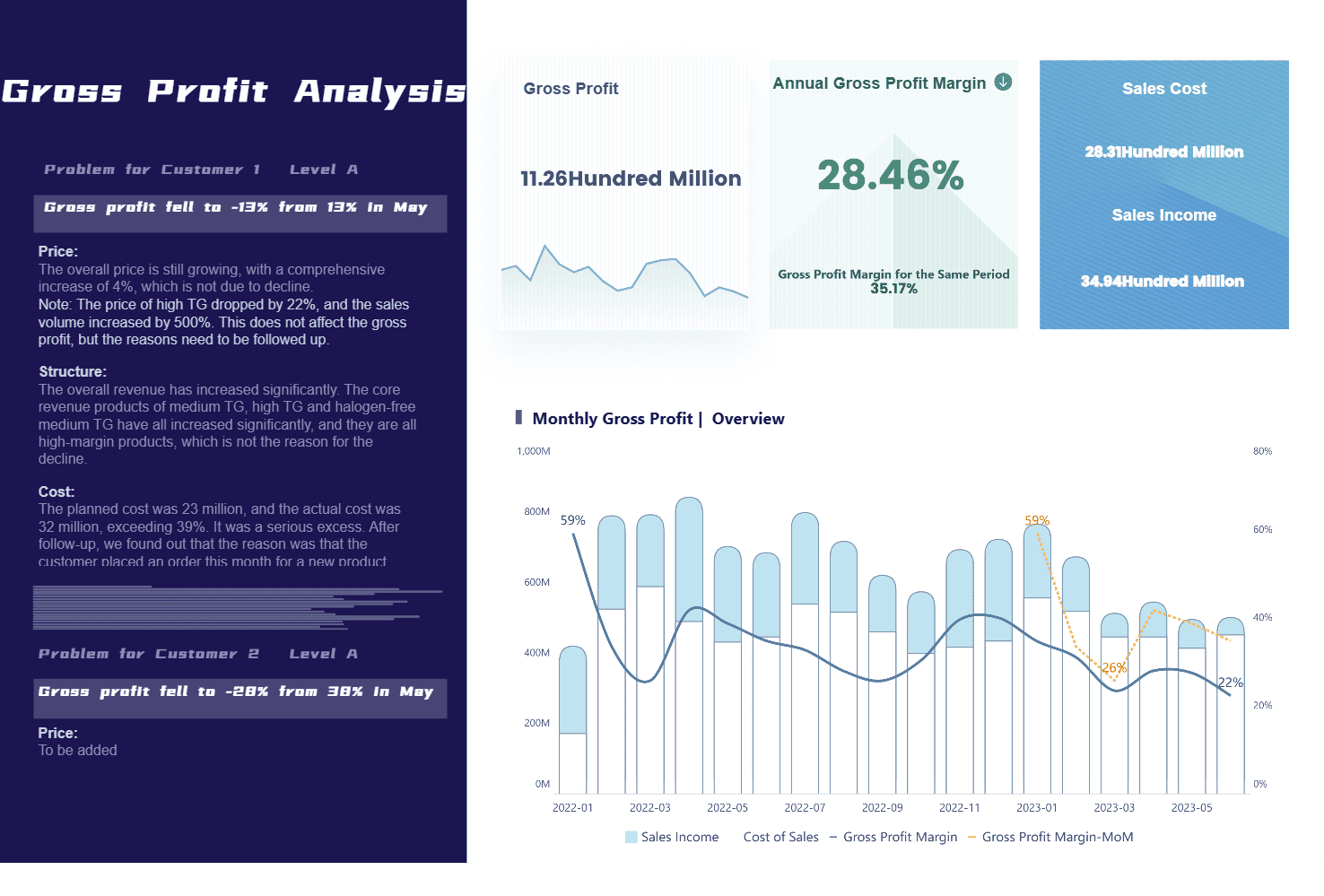
Cost analysis also plays a key role in strategic planning. You gain detailed insights into the costs of products, services, and investments. This helps you identify areas for cost reduction and efficiency improvement. You use tools like cost-benefit analysis, break-even analysis, and net present value (NPV) to evaluate new projects. These methods ensure your investments align with your business goals and financial objectives. By understanding both direct and indirect costs, you get a complete view of your spending. This knowledge helps you control costs and improve efficiency across your organization.
Tip: Use cost analysis to link your business strategy with real-world actions. This connection helps you prioritize projects, allocate resources wisely, and achieve your long-term goals.
You need accurate budgets to keep your business on track. Cost analysis gives you the information you need to estimate expenses, set realistic goals, and manage resources effectively. When you understand the significance of cost analysis, you can build budgets that reflect actual business needs and market conditions.
You should avoid static budgets that do not change with market or internal conditions. Static budgets often miss key cost drivers and can lead to discrepancies between planned and actual expenses. Effective budgeting requires a dynamic process. You need to evaluate costs continuously and integrate your findings with financial statements. This approach helps you optimize resource allocation and support sustainable growth.
Cost analysis also helps you optimize resources in large enterprises. You gain visibility into how you use labor, materials, and infrastructure. For example, labor cost analysis aligns your workforce planning with business objectives. You can use advanced methods like Activity-Based Costing to identify high-overhead areas and optimize processes. By monitoring spending patterns and detecting anomalies, you manage unexpected cost spikes and inefficiencies. Rightsizing your infrastructure based on usage data prevents waste and ensures you scale resources appropriately.
When you break down silos and encourage cross-functional collaboration, you reveal inefficiencies that might otherwise go unnoticed. For instance, a company might discover that errors in one department cause costly issues in others. By analyzing costs across the organization, you can justify investments that improve processes and generate savings. This integrated approach to cost analysis maximizes resource efficiency and supports long-term business success.
Note: Cost analysis is not just about cutting expenses. It is about understanding where your money goes, making informed choices, and driving your business toward higher roi and sustainable growth.
You often face challenges when you try to bring together data for cost analysis. You might deal with large data volumes, different data sources, and the need to keep data quality high. Common issues include:
FanRuan and FineBI help you solve these problems. FineBI connects to many data sources and lets you process and clean your data before analysis. You can use drag-and-drop tools to join tables, filter records, and create custom calculations. This makes it easier for you to prepare accurate data for cost analysis.
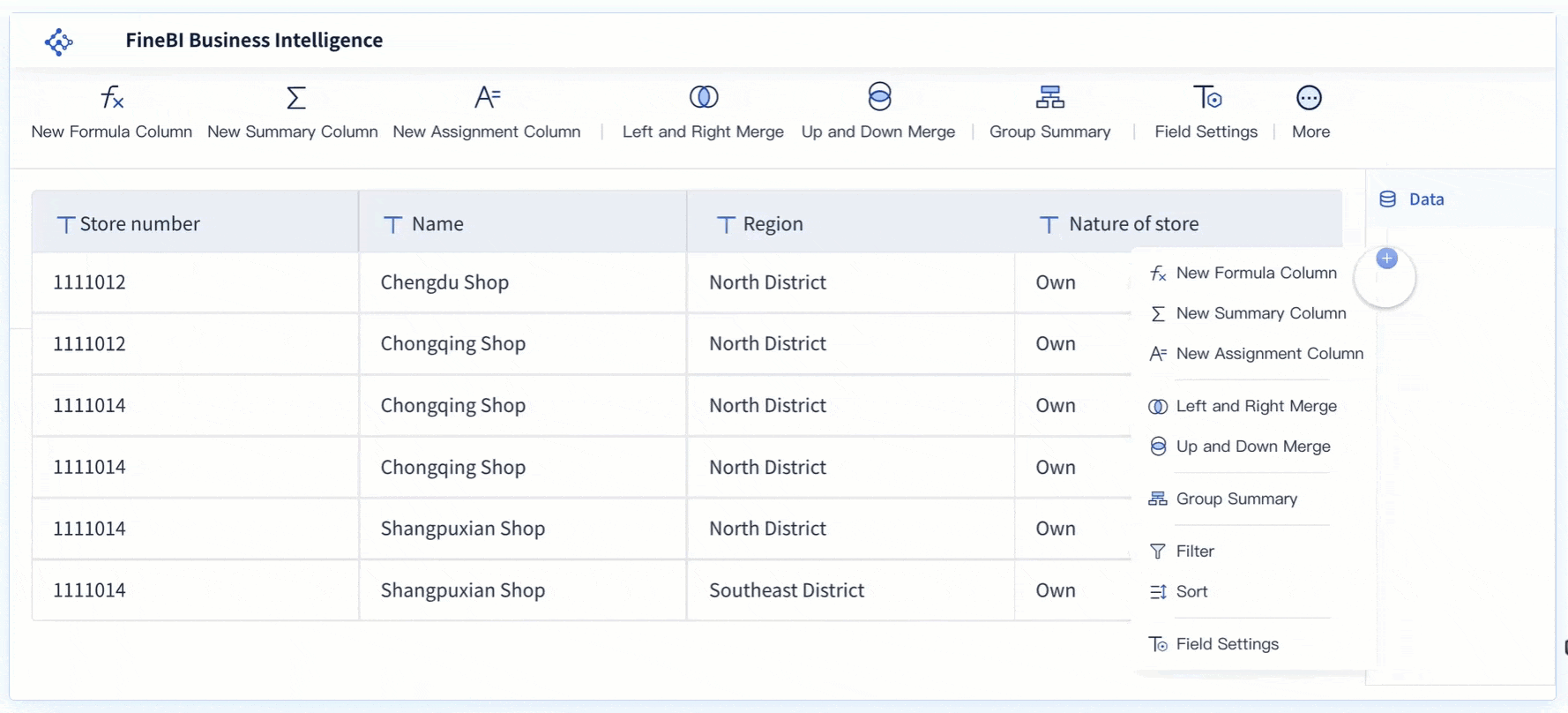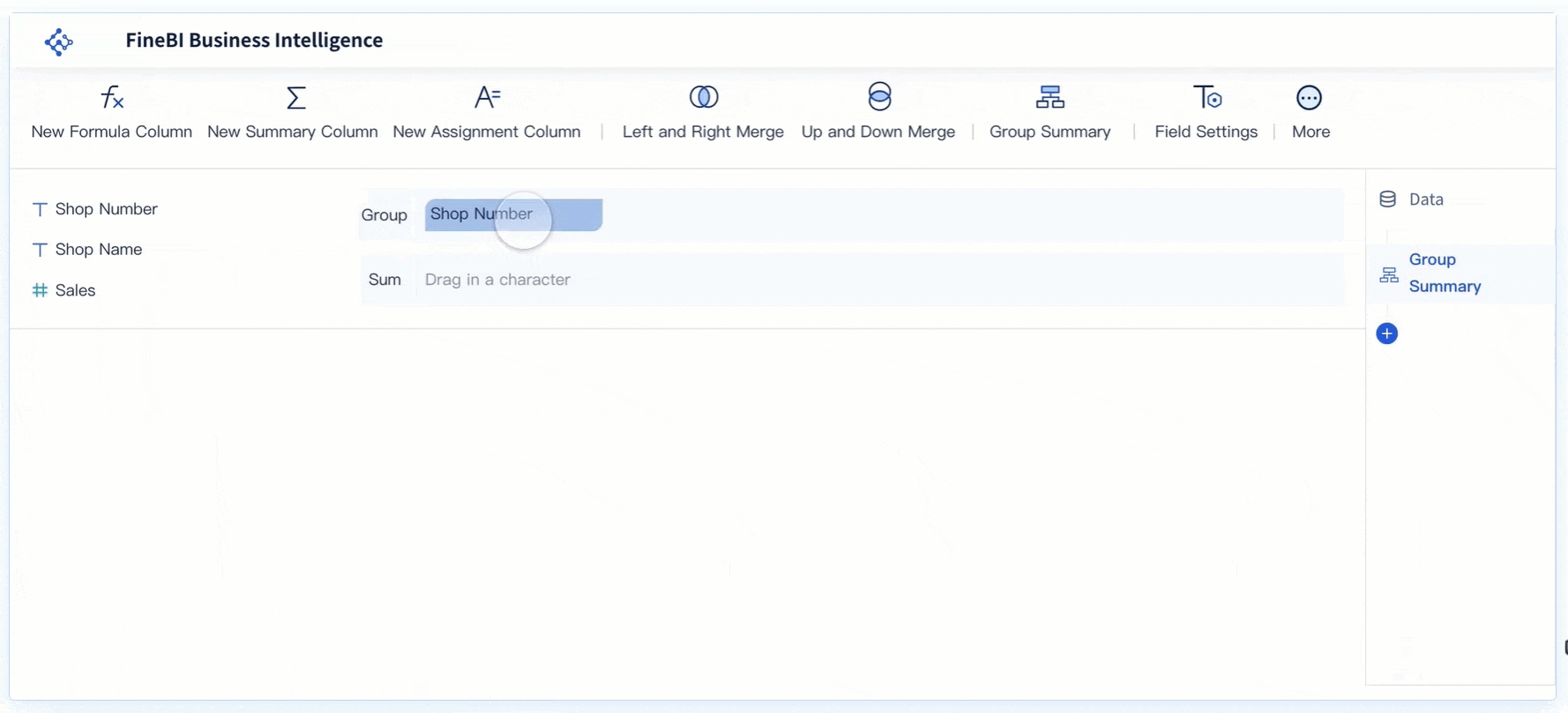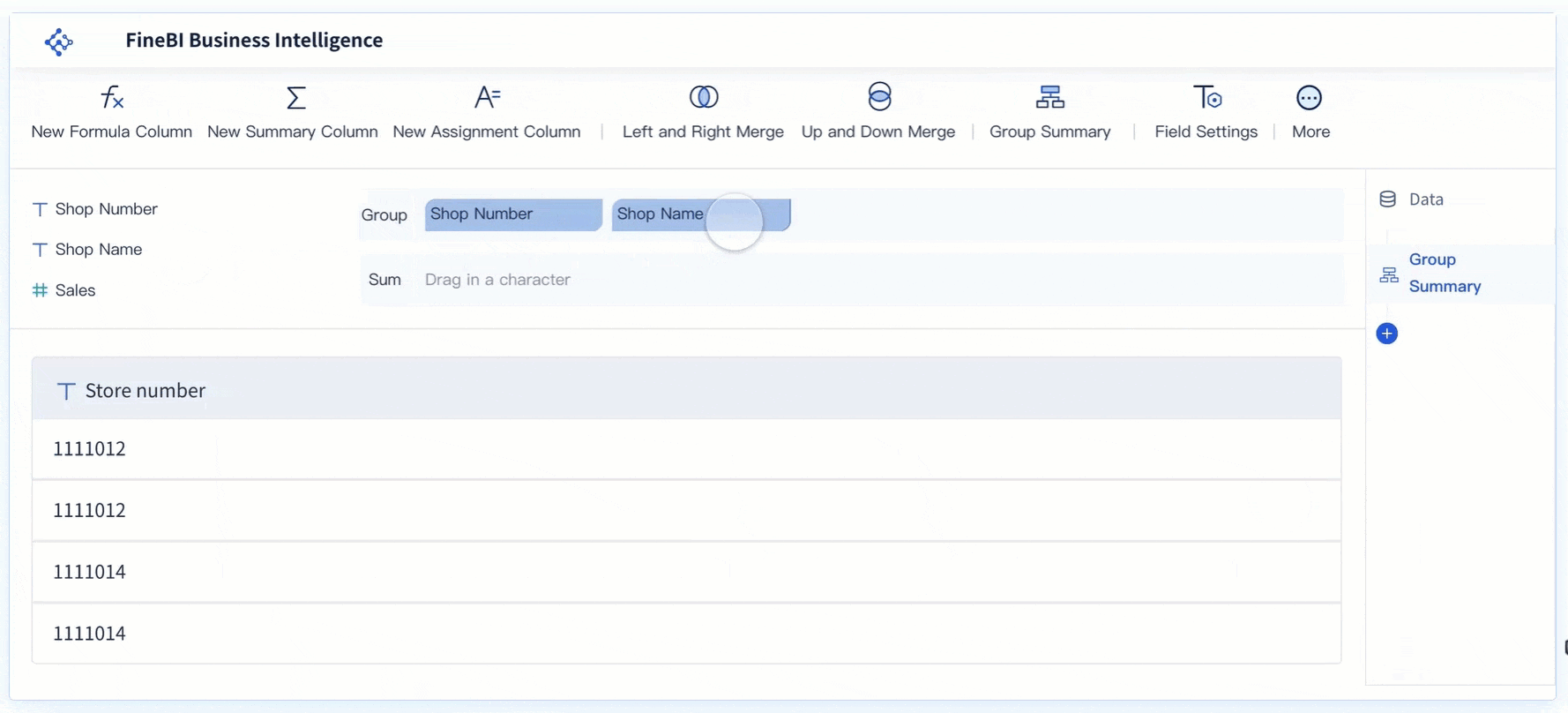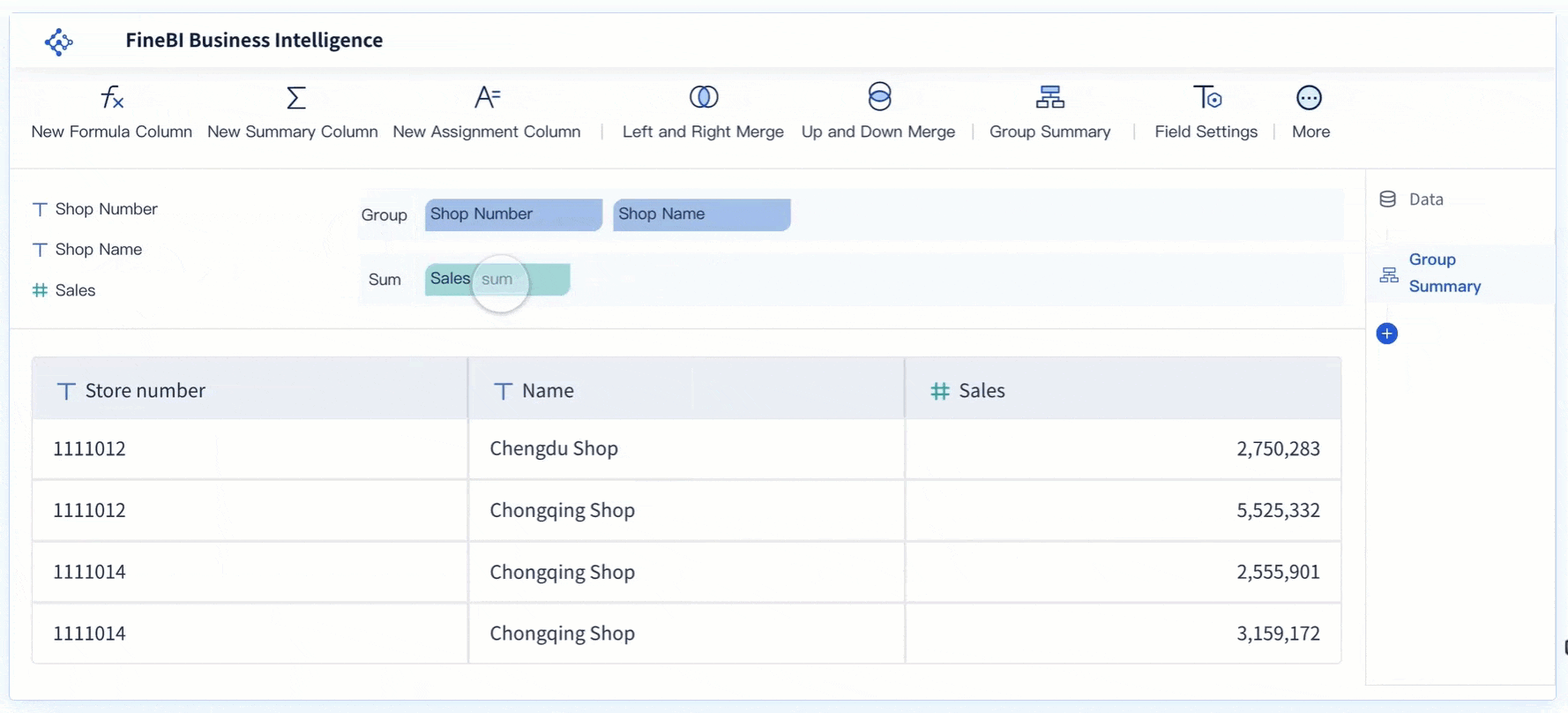
FineBI gives you real-time insights that traditional BI tools cannot match. The table below shows how FineBI compares to older tools:
| Feature Aspect | FineBI | Traditional BI Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Data Engine | Flexible real-time and extracted data access | Fixed data retrieval methods |
| Data Processing Capability | Handles billions of records efficiently | Batch processing, less optimized for large data |
| Analysis and Visualization | Self-service OLAP, interactive dashboards | Fixed-format, less interactive |
| Decision-Making Support | Real-time filtering and analysis for quick decisions | Formal reporting, slower updates |
| Mobile Responsiveness | Full mobile support for analysis and sharing | Limited real-time interaction |
You can explore data, create dashboards, and monitor key metrics instantly. This helps you make timely decisions and improve your roi. FineBI’s mobile features let you access and share insights wherever you are.
You can apply cost analysis in many industries using FanRuan and FineBI. In manufacturing, you analyze direct materials, labor, and overhead to find cost drivers and negotiate better with suppliers. You use methods like activity-based costing and process costing to understand your expenses. In finance, you focus on accurate financial reporting and use cost-benefit analysis to guide investments. Procurement management requires you to track spend, supplier performance, and contract compliance. You monitor KPIs such as cost savings, spend visibility, and procurement cycle time to optimize your processes.
FineBI’s self-service analytics empower you to perform these analyses without waiting for IT support. You can model data, create custom indicators, and visualize results with simple tools. This independence helps you spot trends, drill down into details, and share findings with your team. You gain a clear view of your costs and can act quickly to improve efficiency and profitability.
Also, You can join our upcoming FanRuan webinar series on Data Storytelling, where we’ll go beyond metrics and dashboards to explore how to:
Conduct meaningful cost analysis with context
Interpret gross profit and cost metrics correctly
Visualize and present your findings using real-world BI tools
Use data storytelling to justify strategic decisions
Prepare your data for AI-driven insights
Whether you're an analyst looking to improve your cost reporting or a business leader driving budget decisions, this session will give you the tools and mindset to turn cost data into a clear, actionable narrative.
And of course, you'll see how FineBI helps bring your cost analysis to life through smart dashboards, dynamic charts, and story-ready visuals.
You can conduct cost analysis by following a clear, structured process. This approach helps you understand where your money goes and how to improve your business decisions. Here is a simple step-by-step guide:
Many small and medium-sized businesses use Excel-based templates for this process. These templates let you customize categories, automate calculations, and visualize results with charts. You can also use scenario planning to test how changes in costs or sales affect your bottom line.
Tip: Regularly update your cost analysis to reflect changes in market prices, supplier rates, or business operations. This keeps your data accurate and your decisions relevant.
To get the most from your cost analysis, you should follow industry best practices:
Remember: Cost analysis works best as a continuous process. Keep refining your approach to stay competitive and make smarter decisions.
You gain real business value when you make cost analysis a regular part of your strategy. Companies report these benefits:
| Business Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Better Decision-Making | Data helps you choose the best path and use resources wisely. |
| Improved Budget Management | You find and fix waste, so you stay on budget. |
| Greater Operational Efficiency | You see where to automate or improve workflows. |
| Transparency for Stakeholders | Clear data builds trust with investors and partners. |
FineBI from FanRuan makes this process faster and easier. You turn raw data into clear visuals, track key metrics, and get real-time answers. Automation and self-service tools save you time and help you make smarter choices. Explore FanRuan solutions to manage costs and grow your business with confidence.
Click the banner below to try FineBI for free and empower your enterprise to transform data into productivity!
Unlocking Business Success with the AARRR Metrics Framework
What is Pareto Chart and How Does it Work
Essential Tips for Successful Customer Behavior Analysis
Making Metric Conversion Chart Easy for Everyday Life
What Is Actual Cost in Accounting and Finance
What Is Sales Revenue and Why Is It Important for Businesses

The Author
Lewis
Senior Data Analyst at FanRuan
Related Articles

Self-Service Analytics Defined and Why You Need It
Self-service analytics lets you analyze data without IT help, empowering faster, data-driven decisions and boosting agility for your business.
Lewis
Jan 04, 2026

Best Self-Service Tools for Analytics You Should Know
See which self-service tools for analytics let business users access data, build dashboards, and make decisions faster—no IT help needed.
Lewis
Dec 29, 2025

Understanding Predictive Analytics Services in 2026
Predictive analytics services use data and AI to forecast trends, helping businesses make informed decisions, reduce risks, and improve efficiency in 2026.
Lewis
Dec 30, 2025